Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Note Chapter 2 - Student
Transféré par
Mandy VoonTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Note Chapter 2 - Student
Transféré par
Mandy VoonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER TWO:
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1 Transport System in Humans
2.2 Human Blood
2.3 Transport System in Plants
Mandy Voon
Science PT3
2015/2016
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1 Transport System in Humans
-Human transport system is called circulatory system.
-It consists of heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries)
Figure 2.1 The human blood circulatory system
Figure 2.2 The capillary
2.1.1 Structure and function of the human heart
-Characteristic of heart:
a) Heart is situated inside the
b)
-shaped and
organ.
c) Made up of cardiac muscle. These cells required food and oxygen to carry out
activities
-Function of heart:
a) To
b) Transport
c) Transport
to all parts of the body
to body cell
from the body cell
1
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
Figure2.3 The Structure of human heart
-Heart is made up of four chambers.
a) two chamber at the top are the
b) two chamber at the below the
- Right atrium and right ventricle carry
-Left atrium and left carry the
blood
blood
- The left and right chambers are separated by the muscular known as
to avoid the deoxygenated blood combine with oxygenated blood.
- Characteristic of the atrium and ventricle:
a) Ventricle has
b) Ventricle has
space and volume
wall
2
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
c) Left ventricle is thicker and more muscular than right ventricle because this
chamber
-Each chamber linked to big blood vessels:
a) Right atrium link to
b) Right ventricle link to
c) Left atrium link to
d) Left ventricle is link
-Three type of valves inside the heart:
a)
valve between right atrium and right ventricle
b)
valve between left atrium and left ventricle
c)
valve- beginning of aorta and pulmonary artery
-The valves are to ensure the blood flow in one direction to prevent flow back of
blood
-Pumping action of heart:
a) Deoxygenated blood flow from body to right atrium through ____________
b) ______________ blood from the lungs flow into the left atrium through pulmonary
vein
c) Both atria (singular: atrium) contract and push the blood through the valves into
the _____________
d) Both ventricles ___________ and force the deoxygenated blood in to pulmonary
artery and oxygenated blood to aorta. The semilunar valves close to prevent the
blood from flowing back into the atria
e) The ________________________ carry deoxygenated blood to lungs and
_____________carries the oxygenated blood to whole body.
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1.2 Blood vessels and their functions
- Three types of blood vessels: __________, ____________ and __________.
-human circulation system is a closed system because blood flow in blood vessels
that are connected
Figure 2.4 Type of Blood vessels
Vein
Artery
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
_______________lumen
Small Lumen
Small L
_________ wall
Thick Wall to withstand high pressure
Very th
exchan
nutrien
With valve
_______________
Withou
Carry ____________ blood except
__________________
Carry ____________ blood except
_______________________
Carry _
deoxyg
Blood flows from ____________________
_________________________________
Blood flow away from ______________
_________________________________
Blood f
______
betwee
_________ and__________ pressure
_________ and__________ pressure
______
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.1.3 Path of blood flow in circulatory system
-Human circulatory system is _____________________ system because he blood in
the body is pumped twice through heart.
- The human circulatory system is divided into two parts:
a) ________________circulation- Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood
from heart to lungs while pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs back
to the heart.
b) _______________circulation- Aorta carries oxygenated blood from heart to others
bodys cell while vena cave carries the deoxygenated blood from the bodys cell back
to the heart.
- RS: Deoxygenated blood flow from body parts to the heart then up to the lung
Figure 2.5 Flow of human circulatory system
- Important to maintain a healthy heart to prevent heart diseases and maintain the
continuous supply of _____________ to the body cells.
- Exercise keeps the heart healthy by
a) _______________the heart muscles
b) Control the ____________________.
- A narrow blood vessel will cause ________________, __________ and _________
- The healthy blood vessels can pump a __________amount of blood at faster rate
while arrowed blood vessel can pump less amount of blood at slower rate.
6
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
-Patient with narrow blood vessel are advised to
a) Avoid taking _____________ (lead to high blood cholesterol level and heart
diseases)
b) Eat plenty________ and __________
c) Take a balanced diet
d) Lunch menu: rice, steamed fish / chicken, vegetable, salad / fruit and water
2.2 Human Blood
- Composition of blood:
a) Plasma- ____% of volume of blood
- a pale of yellowish liquid made up of 90% ________and 10 % soluble
substances such as glucose , amino acids and mineral
b) Cellular components
i) Red blood cells- produce in ______________
-___________ shape
- No _________
- Each red blood cell contain a pigment call _______________
i) White blood cells- produce in _____________ and ______________
- _________ shape and can change
- Protect against diseases and infection
- Lymphocytes produce ___________ to kill germs
-Phagocytes carry out _______________ by surrounding the
bacteria,
swallow and digest it thus kill it
iii) Platelets- small fragment of cells from larger cell in the bone marrow.
- Help in _______________ to stop the bleeding
2.2.1 Functions of blood
- Functions of blood:
a) As transport medium- carries dissolved gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, food
substances, hormones and waste from one part of body to another. Red blood cell
carries oxygen and plasma carries other substances.
b) White blood cells ___________________________________.
c) Plasma distribute heat from liver to other parts of body to maintain body
temperature at 370C
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.2.2 Blood group and compatibility
- Human blood is divided into four main groups _____, ___, _____, and ____
- ______________ group O
- ___________________ - group AB
- Blood _________________- transfer blood from donor to recipient
- Not compatible blood transfusion causing agglutination or coagulation in blood
vessels
2.3 Transport System in Plants
- Plants like human being need a transport system to transport _______and_______.
- Transport system of plants made up of _________ and___________ tissues.
- There are found in the roots, stems and leaves.
2.3.1 Transport tissues in plant
-___________ transport food (glucose) produced through photosynthesis from
leaves to other parts of the plant
-____________ transport water and dissolved mineral from root up to the stem and
leave during transpiration. Xylem also gives support to the plant.
- The _____________ separates the xylem and the phloem. It also builds new xylem
and phloem cells.
Figure 2.6 Distribution of tissues in the root, stem and leaf of a plant
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
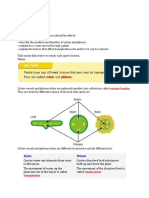
Figure 2.7 Investigate transports of synthesised food substances via the phloem
Plant B function as a control experiment.
Hypothesis: Phloem transports ____________
Variables
Manipulated : ringed or unringed
Constant : _________________
Responding: ______________________.
Conclusion : Phloem transport food from the leaves down to the roots.
Inferences:
i. The ______________ is due to the accumulation of food substances that is unable
to be transported downwards as the phloem has been removed.
ii. The ringed area is wiped with ____________to prevent the area from being dried
up.
iii. After two weeks, the lower part of the plant dies/ shrinks first because the lower
part of the plant does not receive food substances.
2.3.2 Transpiration and function of stoma
-Transpiration defines as loss of water in the form of ____________.
-Water vapour is evaporates through _____________, tiny pore on surface of leaf
- Stoma is tiny pore in between two bean shaped cells called ______________
-Guard contain chloroplast to carry out ___________________ and control the close
and opening of stoma.
- Stoma is open during the day to allow exchange of ___________and
_____________during photosynthesis and allow evaporation of water vapour.
- A plant _________ when it loses more water to surrounding than it absorbs from
soil.
9
CHAPTER TWO
Blood Circulation and Transport
2.3.3 Factors affect the rate of transpiration
-Rate of transpiration influence by:
a) __________
b) Temperature
c) Humidity
d) Air movement / Windy condition
Rate of transpiration can be measured using ________________ and
____________
2.3.4 Role of transpiration in transport system
-Transpiration is import because
a) Help to transport water and dissolved minerals from ___________ to leaves.
b) Help root to absorb water .Keep cell __________ to support the plant
c) Evaporation of water vapour from leaves keep the plant _________ in hot
weather.
10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Note Chapter 4Document9 pagesNote Chapter 4Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei FusionServer Pro V5Document22 pagesHuawei FusionServer Pro V5Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 2Document11 pagesNote Chapter 2Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 3Document5 pagesNote Chapter 3Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 3Document5 pagesNote Chapter 3Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Machines: Chapter TenDocument4 pagesSimple Machines: Chapter TenMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 1Document18 pagesNote Chapter 1Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 2Document12 pagesNote Chapter 2Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruckus Indoor-AP User-Guide 100.2.0Document193 pagesRuckus Indoor-AP User-Guide 100.2.0Anonymous GPw8phMiKtPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless TestingDocument37 pagesWireless TestingMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Wireless Technology v3Document25 pagesPresentation On Wireless Technology v3Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- WirelessDocument2 pagesWirelessMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Aruba 3D Outdoor PlannerDocument52 pagesAruba 3D Outdoor PlannerMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- ORGANIZING THE MANAGEMENT PROCESSDocument32 pagesORGANIZING THE MANAGEMENT PROCESSMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- ORGANIZING THE MANAGEMENT PROCESSDocument32 pagesORGANIZING THE MANAGEMENT PROCESSMandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Mass Transport in Plants 2024Document14 pagesMass Transport in Plants 2024krrish5906Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Plants IIDocument19 pagesTransport in Plants IIMarko ĆaletaPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE Biology GCSE Transport in Plants NotesDocument3 pagesCIE Biology GCSE Transport in Plants NotesMd A RAZZAK100% (1)
- Bio IADocument4 pagesBio IARohan ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- The Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDocument40 pagesThe Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDeanne Saz100% (1)
- BiotechnologyDocument322 pagesBiotechnologyimtiazali2008100% (1)
- Calculate Crop Water NeedsDocument326 pagesCalculate Crop Water NeedsDoni HidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- It's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Document36 pagesIt's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Fathmath JameelPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Induced Plant Plasticity Lab Using: Raphanus Sativus RadishDocument10 pagesLight Induced Plant Plasticity Lab Using: Raphanus Sativus RadishBrycePas encore d'évaluation
- AQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B15Document9 pagesAQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B15josephPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 11 Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 11 Earth and Life Sciencemedsdelfrancis.cenizaPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF EGGPLANT TO SALT STRESSDocument26 pagesPHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF EGGPLANT TO SALT STRESSMuhammad Ibnu NazariPas encore d'évaluation
- LET REVIEW QUESTIONSDocument12 pagesLET REVIEW QUESTIONSMarvin V. Rubia50% (2)
- Biology Module 2 PRELIM 2019Document5 pagesBiology Module 2 PRELIM 2019ChamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Plants and Animals.Document126 pagesTransport in Plants and Animals.Kiama GitahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Arihant BioDocument16 pagesArihant BioMridhu MadaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare Plant and Animal Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesCompare Plant and Animal Organ SystemsJENNY MAY SUDAYPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Photosynthesis M1Document22 pagesUnit 3 Photosynthesis M1Kanittarin SukumpantanasarnPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 1 MARK SCHEME Cell Biology Homework BookletDocument20 pages4 1 MARK SCHEME Cell Biology Homework BookletsaadPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Boardworks PhotosynthesisDocument48 pagesBoardworks Photosynthesiskian shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes-Transport in PlantsDocument15 pagesNotes-Transport in PlantsKisna guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Notes Biology UpdatedDocument8 pagesIgcse Notes Biology UpdatedAlfy YulePas encore d'évaluation
- Transport System in OrganismsDocument19 pagesTransport System in OrganismsJue Hazea GoldshopPas encore d'évaluation
- Relationship Analysis Between Leaf-Stomata CharactDocument12 pagesRelationship Analysis Between Leaf-Stomata CharactTia AfridaPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Document3 pagesGCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Fasih AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis - Class 9th Grade Biology Science Project Free PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis - Class 9th Grade Biology Science Project Free PDF Downloado díasPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Adaptation-ContentDocument25 pagesPlant Adaptation-ContentSRIDHAR R MPas encore d'évaluation
- BOT 121 TranspirationDocument7 pagesBOT 121 TranspirationSakshi SargarPas encore d'évaluation