Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Appendix 3. Uk Brain Bank Criteria PDF
Transféré par
drrselvaraj0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
152 vues1 pageThe document outlines the UK Parkinson's Disease Society Brain Bank clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease in 3 steps. Step 1 defines the diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome. Step 2 lists exclusion criteria that rule out Parkinson's disease. Step 3 provides supportive positive criteria that require 3 or more for a definite diagnosis of Parkinson's disease along with meeting the criteria in step 1.
Description originale:
Titre original
Appendix 3. Uk brain bank criteria.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document outlines the UK Parkinson's Disease Society Brain Bank clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease in 3 steps. Step 1 defines the diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome. Step 2 lists exclusion criteria that rule out Parkinson's disease. Step 3 provides supportive positive criteria that require 3 or more for a definite diagnosis of Parkinson's disease along with meeting the criteria in step 1.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
152 vues1 pageAppendix 3. Uk Brain Bank Criteria PDF
Transféré par
drrselvarajThe document outlines the UK Parkinson's Disease Society Brain Bank clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease in 3 steps. Step 1 defines the diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome. Step 2 lists exclusion criteria that rule out Parkinson's disease. Step 3 provides supportive positive criteria that require 3 or more for a definite diagnosis of Parkinson's disease along with meeting the criteria in step 1.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
UK PARKINSONS DISEASE SOCIETY BRAIN BANK CLINICAL DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA*
Step 1. Diagnosis of Parkinsonian Syndrome
Bradykinesia
At least one of the following
o Muscular rigidity
o 4-6 Hz rest tremor
o postural instability not caused by primary visual, vestibular, cerebellar, or proprioceptive
dysfunction
Step 2 Exclusion criteria for Parkinsons disease
history of repeated strokes with stepwise progression of parkinsonian features
history of repeated head injury
history of definite encephalitis
oculogyric crises
neuroleptic treatment at onset of symptoms
more than one affected relative
sustained remission
strictly unilateral features after 3 years
supranuclear gaze palsy
cerebellar signs
early severe autonomic involvement
early severe dementia with disturbances of memory, language, and praxis
Babinski sign
presence of cerebral tumor or communication hydrocephalus on imaging study
negative response to large doses of levodopa in absence of malabsorption
MPTP exposure
Step 3 supportive prospective positive criteria for Parkinsons disease
Three or more required for diagnosis of definite Parkinsons disease in combination with step one
Unilateral onset
Rest tremor present
Progressive disorder
Persistent asymmetry affecting side of onset most
Excellent response (70-100%) to levodopa
Severe levodopa-induced chorea
Levodopa response for 5 years or more
Clinical course of ten years or more
*From: Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic
Parkinsons disease. A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. JNNP 1992;55:181-184.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GetPdf PDFDocument1 pageGetPdf PDFprabhat0% (1)
- GetPdf PDFDocument1 pageGetPdf PDFFozia HayatPas encore d'évaluation
- UKPDS Brain Bank PD CriteriaDocument1 pageUKPDS Brain Bank PD CriteriaBush HsiehPas encore d'évaluation
- Get PDFDocument1 pageGet PDFAlfiatur RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Uk Parkinson's Disease Society Brain Bank Clinical Diagnostic CriteriaDocument1 pageUk Parkinson's Disease Society Brain Bank Clinical Diagnostic CriteriaAdelina OpreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders: Eugene C. Lai, M.D., PH.DDocument39 pagesAtypical Parkinsonian Disorders: Eugene C. Lai, M.D., PH.DAssolaSaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To ParkinsonismDocument113 pagesApproach To ParkinsonismDr Ganeshgouda MajigoudraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaines K Adjunctive Therapy in PD The Role of Rasagiline Neuropsych Dis and Treat 2012 V2Document10 pagesGaines K Adjunctive Therapy in PD The Role of Rasagiline Neuropsych Dis and Treat 2012 V2Dany RockPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological Disorders of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument45 pagesNeurological Disorders of Infancy and ChildhoodsamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Parkinson's Disease.: Dr. Sanjiv Chandratre. Consultant in Med. For Elderly 2010Document107 pagesManagement of Parkinson's Disease.: Dr. Sanjiv Chandratre. Consultant in Med. For Elderly 2010Prince TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice: Parkinson's Disease: Summary of Updated NICE GuidanceDocument7 pagesPractice: Parkinson's Disease: Summary of Updated NICE GuidanceLouisePas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson DiseaseDocument56 pagesParkinson Diseasen&t3000100% (1)
- Parkinson Disease An Update AAFP 2013Document7 pagesParkinson Disease An Update AAFP 2013Anna ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Presented byDocument31 pagesGuillain-Barré Syndrome: Presented bySanjay SilwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson S DiseaseDocument91 pagesParkinson S DiseaseTrisha Tolentino100% (1)
- Parkinson's Disease-Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument9 pagesParkinson's Disease-Diagnosis & Treatmentvivek_win95100% (1)
- Demyelinating DiseaseDocument42 pagesDemyelinating Diseasemirabel IvanaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome:: A Consensus Approach On Diagnosis, Assessment, Management and Trial MetodologyDocument16 pagesLennox-Gastaut Syndrome:: A Consensus Approach On Diagnosis, Assessment, Management and Trial MetodologyVania Elvira SingkaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On The Diagnosis and Management of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument6 pagesUpdate On The Diagnosis and Management of Parkinson's DiseaseAsniar RPas encore d'évaluation
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Southern Philippines Medical CenterDocument44 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Southern Philippines Medical CenterMaureen JadePas encore d'évaluation
- Samii 2004Document11 pagesSamii 2004Anna Beatriz Silva EspindolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Andradi Suryamiharja, SPS (K)Document39 pagesDr. Andradi Suryamiharja, SPS (K)Ricky SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Status EpilepticusDocument43 pagesStatus EpilepticusPatsuda DreematurakulPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On Management of Parkinson's Disease: Dr. Alim Akhtar Bhuiyan Consultant & Co-OrdinatorDocument42 pagesUpdate On Management of Parkinson's Disease: Dr. Alim Akhtar Bhuiyan Consultant & Co-Ordinatoridno1008Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Management of Parkinson's Disease:: Which Treatments To Start and When?Document14 pagesThe Management of Parkinson's Disease:: Which Treatments To Start and When?Andreas StathatosPas encore d'évaluation
- Criteria For Diagnosing Disease: Parlunson'sDocument3 pagesCriteria For Diagnosing Disease: Parlunson'sapi-3806049Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson y ParkinsonismoDocument5 pagesParkinson y ParkinsonismoGiovannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pilate Week 12 ParkinsonsDocument86 pagesPilate Week 12 ParkinsonsFiona Balfour PilatePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 23Document82 pagesChapter 23mohadese bideshkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nigro 25 - 05 - 2020Document60 pagesNigro 25 - 05 - 2020Ioana CoseruPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurologic DiseasesDocument13 pagesNeurologic DiseasesCzarinah BacuadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson'S Disease : Idiopathic Parkinsonism or Paralysis AgitansDocument30 pagesParkinson'S Disease : Idiopathic Parkinsonism or Paralysis AgitansJeoffrey DuranPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurofibromatosis in OrthoDocument18 pagesNeurofibromatosis in OrthocorneliusPas encore d'évaluation
- Epi LepsiDocument41 pagesEpi LepsiElvon DailyPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Progress: Review ArticlesDocument10 pagesMedical Progress: Review ArticlesDiana Patricia Molano PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial (ONTT) : R.R.Battu Narayana Nethralaya BangaloreDocument36 pagesThe Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial (ONTT) : R.R.Battu Narayana Nethralaya BangaloreMaha lakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinitis Pigmentosa: Main Moderator - Prof. S. N. Askari Assistant Moderator - Dr. Abdul WarisDocument79 pagesRetinitis Pigmentosa: Main Moderator - Prof. S. N. Askari Assistant Moderator - Dr. Abdul WarisRSPas encore d'évaluation
- Neur4305 PD Marx PDFDocument14 pagesNeur4305 PD Marx PDFShawn HayleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome and IntroductionsDocument113 pagesWelcome and IntroductionsJames PerianayagamPas encore d'évaluation
- EpilepsyDocument48 pagesEpilepsyvelsyasukriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument32 pagesParkinson's DiseaseKristina Marie HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo Grupal Del Articulo - S03 - TMDocument5 pagesTrabajo Grupal Del Articulo - S03 - TMClendy Yudith Rimapa GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson Disease - Radiology Reference ArticleDocument8 pagesParkinson Disease - Radiology Reference Articlenurul auliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Sclerosis 2023-2024Document34 pagesMultiple Sclerosis 2023-2024Lamis AlianPas encore d'évaluation
- TG 4 Parkinson (NL)Document20 pagesTG 4 Parkinson (NL)Novi AdriPas encore d'évaluation
- EpilepsyDocument134 pagesEpilepsyVarun B Renukappa100% (1)
- Epilepticencephalopathy 190421115925Document78 pagesEpilepticencephalopathy 190421115925ZakirPas encore d'évaluation
- Medback - Cerebral PalsyDocument47 pagesMedback - Cerebral Palsyyreshgem100% (2)
- Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures (PNES)Document19 pagesPsychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures (PNES)adzhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Dravet SyndromeDocument61 pagesDravet SyndromeSnezana MihajlovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Homocystein and NeuropathyDocument25 pagesHomocystein and NeuropathyhanartoajiPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Infection: Nurcahaya Sinaga Haji Pemprovsu Hospital, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera UtaraDocument34 pagesCNS Infection: Nurcahaya Sinaga Haji Pemprovsu Hospital, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utaramuhammad alqoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Hood Seizuer ManagmantDocument78 pagesChild Hood Seizuer Managmantsentayehu siyumPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson's Disease Information BrochureDocument2 pagesParkinson's Disease Information BrochureE S ShilpaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCase PresentationMuhammad HarisPas encore d'évaluation
- QRP Neurology Part 2Document245 pagesQRP Neurology Part 2lakshminivas PingaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Delirium in Critically IllDocument37 pagesDelirium in Critically IllSanj.etcPas encore d'évaluation
- Epilepsy in Children XDocument61 pagesEpilepsy in Children XSsenyonga DominicPas encore d'évaluation
- Fifty Years of Clinical Holistic Treatment for Parkinson’s: A Unique ApproachD'EverandFifty Years of Clinical Holistic Treatment for Parkinson’s: A Unique ApproachÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- NATUROPATHYDocument2 pagesNATUROPATHYdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- The-Weight-loss-Diet-Chart-1 INDIADocument5 pagesThe-Weight-loss-Diet-Chart-1 INDIAdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Change and Adolescent Development: Issues and ChallengesDocument15 pagesSocial Change and Adolescent Development: Issues and ChallengesdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
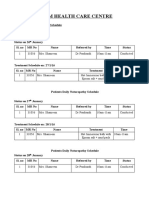
- I-Aim Health Care Centre: Patients Daily Yoga Schedule Date: 1/10/2016 Sl. No MR No Name Referred by TimeDocument1 pageI-Aim Health Care Centre: Patients Daily Yoga Schedule Date: 1/10/2016 Sl. No MR No Name Referred by TimedrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Kasturi Ispat PVT LTDDocument3 pagesKasturi Ispat PVT LTDdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Kasturi Ispat PVT LTDDocument5 pagesKasturi Ispat PVT LTDdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- MDS Research Criteria For Prodromal Parkinson's Disease: ReviewDocument10 pagesMDS Research Criteria For Prodromal Parkinson's Disease: ReviewdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Jan 26th-29th - OdtDocument2 pagesJan 26th-29th - OdtdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix 8 PDQ39 PDFDocument3 pagesAppendix 8 PDQ39 PDFdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Jan 26th 29thDocument1 pageJan 26th 29thdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- I-Aim Health Care CentreDocument2 pagesI-Aim Health Care CentredrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- AssemblingCyawanapraash A&M PDFDocument13 pagesAssemblingCyawanapraash A&M PDFdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- I-AIM Health Care Centre: Institute of Ayurveda & Integrative MedicineDocument2 pagesI-AIM Health Care Centre: Institute of Ayurveda & Integrative MedicinedrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture2 PDFDocument36 pagesLecture2 PDFdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Asana Pranayama Mudra BandhaDocument8 pagesAsana Pranayama Mudra BandhadrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonly Chanted Ashram MantrasDocument3 pagesCommonly Chanted Ashram MantrasdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Om MeditationDocument3 pagesOm MeditationdrrselvarajPas encore d'évaluation