Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cold War Vocabs
Transféré par
R2589770 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
61 vues4 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
61 vues4 pagesCold War Vocabs
Transféré par
R258977Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Word Definition
Cold War A state of political tension military rivalry
between nations that doesn’t take form of full-
scale war. After world war II, USA and Soviet
Union were in cold war.
Superpower This word was used to describe each of the
rivals that came to dominate global politics
after World War II such as USA and Soviet
Union.
United Nation An international organization whose aims are
to promote peace, international security,
economic development etc. It replaced
ineffective League of Nation.
Satellite Nation Countries that were under the Soviets control
during the Cold War.
Non-aligned nations A term used during the cold war to classify
those nations that were neither of the US.
Policy of containment It is a policy using military, economic, and
diplomatic strategies to temper the spread of
communism.
Domino theory It is a foreign policy theory that stated that if
one land in a region came under the influence
of communism, then the surrounding countries
would follow in a domino effect.
Destalinization It is process of eliminating the cult of
personality and Stalinist political system
created by Joseph Stalin.
Brinkmanship the practice, especially in international
relations, of taking a dispute to the verge of
conflict in the hope of forcing the opposition to
make concessions.
Détente Easing of tension between nations.
Truman Doctrine It’s president’s Harry Truman’s speech
outlining a new strategy on how the United
States would seek to deal with Soviet Union.
Marshall plan It was a massive economic aid package
designed to strengthen democratic
governments and lessen the appeal of
communism.
NATO/WARSAW PACT Western European countries formed a military
alliance that stated if any member countries is
attacked, the other member countries would
help.
The Soviet Union formed the Warsaw Pact that
included the soviet union and seven satellite in
eastern Europe. This was also a defensive
alliance, promising mutual military
cooperation.
Iron Curtain Europe was divided by an imaginary line
known as the iron curtain. In the east were the
Soviet-dominated communist countries. In the
west were the western democracies, led by US.
Zones of occupation The Allied powers who defeated Nazi
Germany divided Germany into four zones.
Each allied country occupied each zone.
Berlin wall Berlin wall was a concrete barrier built by the
German Democratic Republic that completely
enclosed the city of west berlin.
Reunification It is the process in which the German
Democratic Republic(East) joined the Federal
Republic of Germany(west) and berlin was
united into a single city state.
Solidarity It is a polish trade union federation. It was the
first non-communist controlled trade union in a
Warsaw Pact Country.
Sputnik one of a series of ten artificial Earth-orbiting
satellites launched by the former Soviet Union
starting in 1957.
Arms Race A competition between two or more parties for
military supremacy.
H-bomb an explosive weapon of mass destruction in
which huge amounts of energy are released by
the fusion of hydrogen nuclei.
Vietcong of the Communist-led armed forces of the
National Liberation Front of South Vietnam
that fought to unite the country with North
Vietnam between 1954 and 1976.
Khmer Rogue It was the name given to the followers of
Communist in Cambodia.
The killing fields The Killing Fields were a number of sites in
Cambodia where large numbers of people were
killed and buried by the Khmer Rouge.
Vietnam War a conflict in which the Communist forces of
North Vietnam and guerrillas in South Vietnam
fought against the non-Communist forces of
South Vietnam and the United States. It began
in 1954 and ended in 1975 in a Communist
victory.
Pacification Leading to or promoting peace and an end to
conflict.
Korean War a war that lasted from 1950 to 1953 between
North Korea, and its ally China, and South
Korea, supported by United Nations troops,
especially from the United States.
38th Parallel The 38th parallel was first suggested as a
dividing line of Korea in 1986.
Sandinistas a member of a socialist movement in
Nicaragua that successfully overthrew the
government of President Anastasio Somoza in
1979 and fought a U.S.-backed insurgent force
in the 1980s.
ICBM ICBM, also known as Intercontinental Ballistic
Missile, is a long-range missile typically
designed for nuclear weapon delivery.
Germany was the first to develop missile to
attack US. This type of weapons was also
developed by Soviet Union during Cold War.
U-2 U-2 is a single-engine aircraft operated by Air
Force.
Space Race Space race was a heated competition between
the US and Soviet Union, as each side tried to
match or better the other’s accomplishments in
exploring outer space.
Glasnost A policy that commits a government or
organization to greater accountability,
openness, discussion, and freer disclosure of
information than previously, especially that of
Mikhail Gorbachev in the former Soviet Union.
Perestroika A political and economic restructuring in the
former soviet union that stated the
decentralized control of industry and
agriculture and some private ownership.
Cuban Missile Crisis It’s a confrontation between US, Soviet Union
and Cuba during Cold War. The Cuban and
Soviet governments placed nuclear missiles in
Cuba. When United States military intelligence
discovered the weapons, the U.S. government
did all it could to ensure the removal of the
missiles.
SALT Strategic Arms Limitation Talk refers to series
of bilateral talks and international treaties
involving US and Soviet Union on limiting
their nation’s stock of nuclear weapons.
Détente Easing tension between two nations.
Eastern Bloc/ Western Bloc Eastern Block referred to countries under
Soviet Control under the Warsaw Pact.
Western Bloc refers to countries under
democratic influences under NATO.
Hungarian Revolt It was revolt overthrow soviet influenced
government.
Prague Spring It was a period of liberalization in
Czechoslovakia during the era of its
domination by the Soviet Union after World
War II.
Star Wars Star wars referred to Strategic Defense
Initiative created under Ronald Regan to use
groud and space based systems to protect the
US from the attack by strategic nuclear ballistic
missiles.
Coup Seizure of political power.
Military junta It’s a government led by a committee of
military leaders.
Leonid Brezhnev He was leader of soviet union during the colder
war. He was responsible for putting missiles in
Cuba.
Lech Walesa Polish politician and trade union and human
rights activist. He contributed to collapse of
communism in Poland.
Fidel Castro A Cuban politician, one of the primary leaders
of the Cuban Revolution. He is a communist
dictator in Cuba
Pol pot Saloth sar, also known as pol pot, was the
leader of Cambodian communist movement as
the Khmer Rouge.
Ho chi Minh He was a Vietnamese communist revolutionary
and statesman who was prime minister and
president of the Democratic Republic of
Vietnam.
Daniel Ortega He was the president of Nicaragua. He was the
leader of Liberation Front.
Richard Nixon He was the president of US during cold war.
Kim Jung II He was the supreme leader of Democratic
People’s Republic of Korea.
Mikhail Gorbachev Seventh and last General Secretary of the
communist party of Soviet Union.
Boris Yeltsin He was the first President of Russian
Federation after the dissolution of Soviet
Union.
Vladimir Putin He was the second president of Russian
Federation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Violent Video GamesDocument1 pageViolent Video GamesR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Descriptive Study MethodolgyDocument2 pagesDescriptive Study MethodolgyR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- First Declension Nouns CasesDocument2 pagesFirst Declension Nouns CasesR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Latin Common PhraseDocument2 pagesLatin Common PhraseR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pilot Survey Descriptive StudyDocument2 pagesPilot Survey Descriptive StudyR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Violent Video Games-Students Assisting Teacher Survey (Raw Data)Document2 pagesViolent Video Games-Students Assisting Teacher Survey (Raw Data)R258977Pas encore d'évaluation
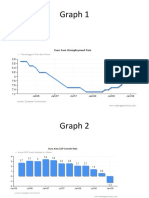
- Graph 1 Descriptive StudyDocument2 pagesGraph 1 Descriptive StudyR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Descriptive Study-Final ReportDocument8 pagesDescriptive Study-Final ReportR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Graph 2 Descriptive StudyDocument3 pagesGraph 2 Descriptive StudyR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Popcorn Experiment ProcedureDocument2 pagesPopcorn Experiment ProcedureR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
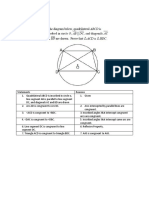
- Proof 4Document1 pageProof 4R258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ozone and Biological EffectsDocument5 pagesOzone and Biological EffectsR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Popcorn ExperimentDocument2 pagesPopcorn ExperimentR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Proof 2Document1 pageProof 2R258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Proof 1Document1 pageProof 1R258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consent Form-Descriptive StudyDocument1 pageConsent Form-Descriptive StudyR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Proof 3Document1 pageProof 3R258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lorenzo's Oil-Why Research Is Important?Document4 pagesLorenzo's Oil-Why Research Is Important?R2589770% (1)
- Russian Revolution, WWII, Rise of Fascism, Cold War & Collapse of Soviet UnionDocument3 pagesRussian Revolution, WWII, Rise of Fascism, Cold War & Collapse of Soviet UnionR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Russian Revolution, WWII, Rise of Fascism, Cold War & Collapse of Soviet UnionDocument3 pagesRussian Revolution, WWII, Rise of Fascism, Cold War & Collapse of Soviet UnionR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Explanation Behind CasesDocument2 pagesExplanation Behind CasesR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
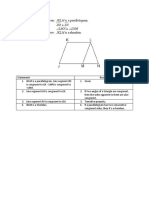
- Transformation RotationDocument1 pageTransformation RotationR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- First Declension Nouns CasesDocument2 pagesFirst Declension Nouns CasesR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Poetry ProjectDocument5 pagesPoetry ProjectR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Latin Common Phrase-2003 FormatDocument2 pagesLatin Common Phrase-2003 FormatR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global Vocabs IndustralizationDocument3 pagesGlobal Vocabs IndustralizationR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ancient CalendarDocument2 pagesAncient CalendarR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Graphs Power PointDocument9 pagesGraphs Power PointR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Bio Study SheetDocument1 pageCell Bio Study SheetR258977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- PSC201 Final Term PapersDocument5 pagesPSC201 Final Term PapersHaMza Afzal67% (3)
- Adapting America S China Strategy in An Age of Competitive InterdependenceDocument224 pagesAdapting America S China Strategy in An Age of Competitive InterdependenceOleksandrRuzevychPas encore d'évaluation
- SAMAAN, J. The RAND Corporation 1989-2009 The Reconfiguration of Strategic Studies in The United States. Springer, 2012.Document199 pagesSAMAAN, J. The RAND Corporation 1989-2009 The Reconfiguration of Strategic Studies in The United States. Springer, 2012.Luan BrumPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cold War - David G. Williamson - Hodder 2013 PDFDocument329 pagesThe Cold War - David G. Williamson - Hodder 2013 PDFMohammed Yousuf0% (1)
- Korean War Chart Amari WoodsonDocument2 pagesKorean War Chart Amari WoodsonAmari WoodsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Peace Movements Are Not Weatherproof - Mient Jan FaberDocument9 pagesPeace Movements Are Not Weatherproof - Mient Jan FaberMartijn DekkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 26 - The Vietnam War PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 26 - The Vietnam War PDFGelePas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of War On EconomyDocument7 pagesEffects of War On Economyapi-3721555100% (1)
- Road To 2040 07 - 2021Document23 pagesRoad To 2040 07 - 2021erioPas encore d'évaluation
- Roger E. Kanet (Eds.) - Russian Foreign Policy in The 21st Century (2011, Palgrave Macmillan UK)Document305 pagesRoger E. Kanet (Eds.) - Russian Foreign Policy in The 21st Century (2011, Palgrave Macmillan UK)rmdclbPas encore d'évaluation
- Buzan, New Patterns of Global Security in The Twenty-First CenturyDocument22 pagesBuzan, New Patterns of Global Security in The Twenty-First CenturymxbelemmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib History Study Guide Johnson Foreign Policy Vietnam WarDocument2 pagesIb History Study Guide Johnson Foreign Policy Vietnam WarFrancesca D'AnnunzioPas encore d'évaluation
- Defence UK 'PRO PATRIA' Journal Volume 4 (Web)Document25 pagesDefence UK 'PRO PATRIA' Journal Volume 4 (Web)Andy SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Korea War Worksheet (CNN Documentary On Korean War) : V Tllvlaw9CpiDocument3 pagesKorea War Worksheet (CNN Documentary On Korean War) : V Tllvlaw9CpiWilliam HaugheyPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel GCE History A World Divided Superpower Relations Unit 3 PDFDocument225 pagesEdexcel GCE History A World Divided Superpower Relations Unit 3 PDFJK67% (3)
- Geography, MilitaryDocument466 pagesGeography, Militarywvwinters100% (1)
- Vietnam Timeline - Vietcong Formed (1955-1963)Document1 pageVietnam Timeline - Vietcong Formed (1955-1963)Andrew Kimo Quirino GallowayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold War Research PaperDocument6 pagesCold War Research PaperJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Dynamics of Russia's Geopolitics Remaking The Global Order by David OualaalouDocument149 pagesThe Dynamics of Russia's Geopolitics Remaking The Global Order by David OualaalouJohn TheBaptistPas encore d'évaluation
- Puño // Volume II, Issue 005Document24 pagesPuño // Volume II, Issue 005BCN MES / Barcelona Para Llevar in Eng, Cas i CatPas encore d'évaluation
- Jssa Vol Vii No1Document230 pagesJssa Vol Vii No1Mashood Ahmed AlviPas encore d'évaluation
- New Alliances of The Twenty-First Century - David MurrinDocument12 pagesNew Alliances of The Twenty-First Century - David MurrinSafdar Hussain0% (1)
- Historical Background of World English's: Presented To: Mam. Sehar Presented by Saira Basharat (9512) Group 7Document15 pagesHistorical Background of World English's: Presented To: Mam. Sehar Presented by Saira Basharat (9512) Group 7sairaPas encore d'évaluation
- 0275983099Document282 pages0275983099Asim Raheel KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 外交部发言整理(六)Document8 pages外交部发言整理(六)RubyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Q1 River North EditionsDocument84 pages2015 Q1 River North EditionsIndependent Publishers GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- AP European History SyllabusDocument32 pagesAP European History SyllabusBrian Walker100% (1)
- Top FiftyDocument11 pagesTop Fiftyapi-400180777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mesmerized by The Bear The Great Soviet Deception (Part II)Document17 pagesMesmerized by The Bear The Great Soviet Deception (Part II)The Fatima CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- LSE 100 Summary NotesDocument16 pagesLSE 100 Summary NotesOKBYENOWPas encore d'évaluation