Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HTTPS://WWW - scribd.com/doc/207663656/FS 4 Exploring The Curriculum Full Episode
Transféré par
Clydylyn Jane PastorTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HTTPS://WWW - scribd.com/doc/207663656/FS 4 Exploring The Curriculum Full Episode
Transféré par
Clydylyn Jane PastorDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The 12 Principles of High Quality
HIERARCHY OF OBJECTIVES
Assessment of Learning for Teachers
1. CLARITY & APPROPRIATENESS OF (BLOOM) (ANDERSON)
LEARNING TARGETS Evaluation Create
Assessment should be clearly stated and Synthesis Evaluate
specified and centered on what is truly Analysis Apply
important. Application Analyze
"Teaching emphasis should parallel Comprehension Understand
testing emphasis." Knowledge Remember
several
Learning Targets types of
Knowledge Students mastery of the content. validity
Reasoning Students ability to use their that are
knowledge. to be
Skills Students ability to demonstrate what
they have learned.
Products Students ability to create.
Affects Students emotional attainments.
established.
2. APPROPRIATE ASSESSMENT TYPES OF
ASSESSMENT METHODS VALIDITY
LEARNING TARGETS
Objective Supply Knowledge Content Validity
Objective Select Knowledge Face Validity
Essay ReasoningConcurrent Validity
Performance-based Predictive Validity
Skills, products
Oral-question Discriminant
Knowledge, reasoningValidity
Observation Knowledge, skills Validity
Construct
Self-report Affects 5.
METHOD. Assessment should utilize RELIABILITY
assessment methods suitable for a Assessment should show consistent and
particular learning target. stable results. There are methods which
can be used to measure and establish
3. BALANCE reliability.
Assessment
DOMAINS OF methods 6. FAIRNESS
LEARNING: should be Assessment should give
Cognitive able to equal opportunities for every student.
Affective assess all There should be no discrimination of any
Psychomotor domains of kind (racial, age, gender, etc.)
learning and 7. AUTHENTICITY
hierarchy of objectives. Assessment should touch real life
situations and should emphasize
practicability.
8. PRACTICALITY & EFFICIENCY
Assessment should save time, money,
etc. It should be resourceful.
4. VALIDITY 9. ASSESSMENT IS A CONTINUOUS
Assessment should be valid. There are PROCESS.
Because assessment is an integral part of
ASSESSMENT FORMS:
RELIABILITY CAN BE MEASURED PLACEMENT Done before instruction
USING: ASSESSMENT learners to determine th
capabilities.
Test-retake or Giving the same FORMATIVE Done during instruction
Retest Method examination after ASSESSMENT to monitor students pr
several minutes to reinforce learning.
DIAGNOSTIC Done to see the problem
to several years.
SPLIT-HALF This is used to ASSESSMENT learning difficulties of t
SUMMATIVE Done after instruction t
establish internal
ASSESSMENT achievement and to se
consistency
teaching-learning proces
using Pearson r
formula.
Parallel- Giving the same
10. ETHICS IN ASSESSMENT
form/Equivalence examination
test within the day. Assessment should not be used to
Test of Stability Giving the same derogate the students. One example of
examination this is the right to confidentiality.
content but not
in the same 11. CLEAR COMMUNICATION
manner or form
after several Assessment's results should be
minutes to communicated to the learners and the
several years. people involved. Communication should
Measurement of Giving the same also be established between the teacher
stability & examination and the learners by way of pre- and post-
Equivalence content but not test reviews.
in the same
12. POSITIVITY OF CONSEQUENCE
manner or form
within the day. Assessment should have a positive
Kuder-Richardson Establishment of effect. It should motivate students to
reliability using learn and do more and should give way
KR 21 and KR 20 to improve the teacher's instruction.
formulas.
the teaching-learning process, it should
be continuous.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Verbs Worksheet 5th English Grammar NTSEDocument2 pagesVerbs Worksheet 5th English Grammar NTSESuvashreePradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Eyes Open 1.2 A Unit 7 TestDocument4 pagesEyes Open 1.2 A Unit 7 TestDorota SmolinskaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6-Cross Training As A Motivational and ProblemDocument3 pages6-Cross Training As A Motivational and Problemakositabon100% (1)
- HTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/doc/266247979/xxx Apartments Episode 1Document11 pagesHTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/doc/266247979/xxx Apartments Episode 1Clydylyn Jane PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/doc/129517288/exploring The Curriculum FS4Document10 pagesHTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/doc/129517288/exploring The Curriculum FS4Clydylyn Jane PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphic Designer: Page One Designs and Accessories, IncDocument6 pagesGraphic Designer: Page One Designs and Accessories, IncClydylyn Jane PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- I Have Always Maintained That Sociology Is A Science of Liberation and Not of Restraint. L. F. Ward, Pure Sociology (1914)Document2 pagesI Have Always Maintained That Sociology Is A Science of Liberation and Not of Restraint. L. F. Ward, Pure Sociology (1914)Clydylyn Jane PastorPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Ranjith CV PDFDocument4 pagesDR Ranjith CV PDFRanjith ArPas encore d'évaluation
- Level of Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Learning in Facilitating Instruction For Grade One Learners: Basis For A Proposed Teaching ModelDocument11 pagesLevel of Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Learning in Facilitating Instruction For Grade One Learners: Basis For A Proposed Teaching ModelPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Deployment Guide Series IBM Tivoli Configuration Manager Sg246454Document420 pagesDeployment Guide Series IBM Tivoli Configuration Manager Sg246454bupbechanhPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Involvement - How Do I Help My Child Study - ChieSB - FDocument5 pagesFamily Involvement - How Do I Help My Child Study - ChieSB - FChie SBPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtue Ethics FinalDocument19 pagesVirtue Ethics FinalAlna JaePas encore d'évaluation
- ACR-Staff MeetingDocument3 pagesACR-Staff MeetingLynlyn MerniloPas encore d'évaluation
- Variables Predictoras de La Lectura y La Escritura en CastellanoDocument14 pagesVariables Predictoras de La Lectura y La Escritura en CastellanoMontserratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Your Weekly SDR Calendar-Peer Review Assignment-Mohamed AbdelrahmanDocument3 pagesBuilding Your Weekly SDR Calendar-Peer Review Assignment-Mohamed AbdelrahmanrtwthcdjwtPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Solve A Case StudyDocument2 pagesHow To Solve A Case StudySaYam ReHania100% (1)
- Demo K-12 Math Using 4a's Diameter of CircleDocument4 pagesDemo K-12 Math Using 4a's Diameter of CircleMichelle Alejo CortezPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 8 LP 2nd RevisionDocument3 pagesGRADE 8 LP 2nd RevisionFrezlyn ManangbaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Development Plan (Required)Document4 pagesProfessional Development Plan (Required)api-314843306Pas encore d'évaluation
- Risk and Protective Factors in Schizophrenia: Heinz Hafner (Editor)Document322 pagesRisk and Protective Factors in Schizophrenia: Heinz Hafner (Editor)Eva CastanheiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 12 Q1 A1Document2 pagesGrade 12 Q1 A1Ma. Catherine PaternoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fern Smith's Classroom IdeasDocument24 pagesFern Smith's Classroom IdeasSandra Viviana BayonaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Natural Approach To Second Language Acquisition PDFDocument14 pagesA Natural Approach To Second Language Acquisition PDFchaitali choudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- 16th EMPLOYABILITY REVISEDDocument31 pages16th EMPLOYABILITY REVISEDSaharah PundugPas encore d'évaluation
- Hartmann 1931Document12 pagesHartmann 1931Matheus Pereira CostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Olivarez College: Graduate SchoolDocument3 pagesOlivarez College: Graduate SchoolNico PelomianoPas encore d'évaluation
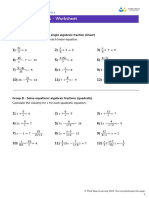
- Algebraic FractionsDocument11 pagesAlgebraic FractionsSafiya Shiraz ImamudeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Is WealthDocument100 pagesKnowledge Is WealthmustaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Krista Pankau Cover LetterDocument3 pagesKrista Pankau Cover Letterapi-514564329Pas encore d'évaluation
- UG Unconditional Offer LetterDocument2 pagesUG Unconditional Offer Letterzwt208961360Pas encore d'évaluation
- Language Analysis - Functional Language: Making A SuggestionDocument2 pagesLanguage Analysis - Functional Language: Making A Suggestionhossein srPas encore d'évaluation
- BBDM1023 BOM Coursework - Specs 202301Document7 pagesBBDM1023 BOM Coursework - Specs 202301SHEVENA A/P VIJIANPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulado InglêsDocument3 pagesSimulado InglêsJkBrPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th BASIC ENGLISH TEST - 10-08-19 PDFDocument3 pages9th BASIC ENGLISH TEST - 10-08-19 PDFJIM GUIMACPas encore d'évaluation