Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Super Charging
Transféré par
Arjun Reghu0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues2 pagessc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentsc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues2 pagesSuper Charging
Transféré par
Arjun Reghusc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
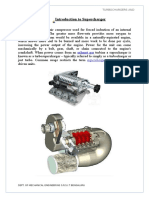
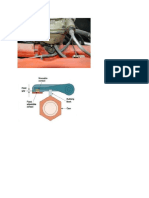
SUPERCHARGING Positive displacement
Both turbochargers and superchargers are Positive-displacement pumps deliver a nearly
called forced induction systems. They fixed volume of air per revolution at all speeds
compress the air flowing into the engine (minus leakage, which is almost constant at all
speeds for a given pressure, thus its
The advantage of compressing the air is that it
importance decreases at higher speeds). The
lets the engine squeeze more air into a
device divides the air mechanically into
cylinder, and more air means that more fuel
parcels for delivery to the engine,
can be added. Therefore, you get more power
mechanically moving the air into the engine
from each explosion in each cylinder. A
bit by bit.
turbocharged engine produces more power
overall than the same engine without the Major types of positive-displacement pumps
charging. This can significantly improve the include:
power-to-weight ratio for the engine
Roots
The key difference between a turbocharger
and a supercharger is its power supply.
Lysholm twin-screw
Something has to supply the power to run the
air compressor. In a supercharger, there is a
Sliding vane
belt that connects directly to the engine. It gets
its power the same way that the water pump or Scroll-type supercharger, also known
alternator does. A turbocharger, on the other as the G-Lader
hand, gets its power from the exhaust stream.
The exhaust runs through a turbine, which in Compression type:
turn spins the compressor. Positive-displacement pumps are further
divided into internal compression and external
In theory, a turbocharger is more compression types.
efficient because it is using the "wasted"
energy in the exhaust stream for its power Roots superchargers are typically external
source. On the other hand, a turbocharger compression only (although high-helix roots
blowers attempt to emulate the internal
causes some amount of back pressure in the
compression of the Lysholm screw).
exhaust system and tends to provide less boost
until the engine is running at higher RPMs. External compression refers to pumps
Superchargers are easier to install but tend to that transfer air at ambient pressure
be more expensive. into the engine. If the engine is
running under boost conditions, the
Types of supercharger pressure in the intake manifold is
There are two main types of superchargers higher than that coming from the
defined according to the method of supercharger. That causes a backflow
compression: positive displacement and from the engine into the supercharger
until the two reach equilibrium. It is
dynamic compressors. The former deliver a
the backflow that actually compresses
fairly constant level of pressure increase at all the incoming gas. This is a highly
engine speeds (RPM), whereas the latter inefficient process, and the main factor
deliver increasing pressure with increasing in the lack of efficiency of Roots
engine speed.[5 superchargers when used at high boost
levels. The lower the boost level the
smaller is this loss, and Roots blowers
are very efficient at moving air at low
pressure differentials, which is what
they were first invented for (hence the
original term "blower").
All the other types have some degree of
internal compression.
Internal compression refers to the
compression of air within the
supercharger itself, which, already at Major types of dynamic compressor are:
or close to boost level, can be
delivered smoothly to the engine with Centrifugal
little or no back flow. This is more
effective than back flow compression Multi-stage axial-flow
and allows higher efficiency to be
achieved. Internal compression
Pressure wave supercharger
devices usually use a fixed internal
compression ratio. When the boost
pressure is equal to the compression Supercharger drive types
pressure of the supercharger, the back
flow is zero. If the boost pressure Superchargers are further defined according to
exceeds that compression pressure, their method of drive (mechanicalor
back flow can still occur as in a roots turbine).
blower. Internal compression blowers
must be matched to the expected boost Mechanical
pressure in order to achieve the higher
efficiency they are capable of, Belt (V-belt, Synchronous belt, Flat
otherwise they will suffer the same belt)
problems and low efficiency of the
roots blowers. Direct drive
Dynamic Gear drive
Dynamic compressors rely on accelerating the Chain drive
air to high speed and then exchanging that
velocity for pressure by diffusing or slowing it Exhaust gas turbines
down.
Axial turbine
Radial turbine
Other
Electric motor
Auxiliary Power Unit in some large
industrial applications
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SuperchargerDocument27 pagesSuperchargerRamachandran SubburathinamPas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharging of Diesel EnginesDocument6 pagesSupercharging of Diesel EnginesPolavarapu Srinivasa RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharged Induction Systems Are Used To Aid Aircraft OperationsDocument2 pagesSupercharged Induction Systems Are Used To Aid Aircraft OperationsAntonov VodkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbocharger and Supercharger ReportDocument18 pagesTurbocharger and Supercharger ReportMayank Burman100% (3)
- Supercharger: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesSupercharger: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSesan FesobiPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Supercharger: Positive DisplacementDocument10 pagesTypes of Supercharger: Positive DisplacementMamdouhAlhanafyPas encore d'évaluation
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument16 pagesDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerMelvin MhdsPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Document25 pagesTurbocharger Vs Supercharger 1Vibhor JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Supercharging TurbochargingDocument33 pagesChapter 12 Supercharging Turbochargingdesie yalewPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine PresentationDocument231 pagesEngine Presentationjoy todi100% (3)
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerAnand KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharging System Chap 4 Fall 2019 PDFDocument10 pagesSupercharging System Chap 4 Fall 2019 PDFSergen SerinPas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargersDocument2 pagesSuperchargersVenses FranklinPas encore d'évaluation
- Why A SuperchargerDocument16 pagesWhy A SuperchargerMohamad MousaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 2020 10 06!03 05 20 AmDocument10 pages5 2020 10 06!03 05 20 AmHakim ChelghamPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Supercharger: BY Manhar 15AE60R18Document19 pagesSeminar On Supercharger: BY Manhar 15AE60R18Hatinderpal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument65 pagesTurbocharger and Superchargerzia malikPas encore d'évaluation
- Aupercharging Turbocharging and Nitrous Oxide Perfomance - Earl Davis - TextDocument156 pagesAupercharging Turbocharging and Nitrous Oxide Perfomance - Earl Davis - Textblackmailer hackPas encore d'évaluation
- K.D.K College of Engineering, Nagpur: SuperchargerDocument18 pagesK.D.K College of Engineering, Nagpur: SuperchargerPratik KatkePas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument24 pagesSuperchargerpravat dalai100% (1)
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerrishirajtomar100% (8)
- What Is Forced Induction?Document15 pagesWhat Is Forced Induction?Fugaru Paul - AlexandruPas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargersachin yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Superchargers: Figure 1 Working of Supercharges Used in AutomobilesDocument3 pagesSuperchargers: Figure 1 Working of Supercharges Used in Automobilesvj kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbine Engines PrincessDocument70 pagesTurbine Engines Princessmaddiehatway64Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Design of Air Booster PDFDocument7 pages6 Design of Air Booster PDFSalih AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerveer1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerSunil ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Centrifugal CompressorsDocument17 pagesPresentation On Centrifugal CompressorsakshayupadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharger ReportDocument24 pagesSupercharger ReportRohit RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Seminar On: "SuperchargersDocument17 pagesTechnical Seminar On: "SuperchargersSiddarth NPas encore d'évaluation
- CompressorDocument37 pagesCompressorNitish Kumar100% (1)
- 5 - Supercharging and TurbochargingDocument21 pages5 - Supercharging and TurbochargingAshik HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument22 pagesSuperchargerVinod Subramaniam50% (2)
- Chapter III Propulsion Systems Thrust and Performance ParametersDocument29 pagesChapter III Propulsion Systems Thrust and Performance ParametersshmyePas encore d'évaluation
- BY K Surya Kondal RaoDocument15 pagesBY K Surya Kondal Raoans_tejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharger - WikipediaDocument7 pagesSupercharger - Wikipediaexcel beemapallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineDocument10 pagesTurbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineYasewn KALAWANTPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in Pplant 2 - PrelimsDocument5 pagesReviewer in Pplant 2 - Prelimssulitstephanie007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supercharger VS TurbochargerDocument25 pagesSupercharger VS TurbochargerAllen CastorPas encore d'évaluation
- Superchargers: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncDocument8 pagesSuperchargers: © 2016 Scrivener Publishing LLC. Published 2016 by John Wiley & Sons, IncPandu SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pplant Lec 2Document6 pagesPplant Lec 2Alyssa SisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviwer Pplant - Module 1&2Document4 pagesReviwer Pplant - Module 1&2Santos MainePas encore d'évaluation
- SuperchargerDocument14 pagesSuperchargerRangappa swamyPas encore d'évaluation
- TurbochargingDocument18 pagesTurbochargingmhawan104Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Production of Compressed AirDocument4 pages02 Production of Compressed AirNatsuko KayamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance and Power Augmentationupdated PrinoutDocument19 pagesPerformance and Power Augmentationupdated PrinoutSamarth SPas encore d'évaluation
- Fans and BlowersDocument3 pagesFans and BlowersLurking RoguePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CompressorsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To CompressorsSriram SuryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.PrasadDocument10 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gas Turbine Blade: Mr. M.Prasadejzuppelli8036Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract:: Supercharging of I.C. EnginesDocument15 pagesAbstract:: Supercharging of I.C. Enginesjui100% (1)
- of SuperchargerDocument18 pagesof SuperchargerNEERAJPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo NotesDocument18 pagesTurbo NotescleousPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine DevelopmentsDocument5 pagesEngine DevelopmentsKarim Sowley DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 15 (Gas Turbine Engine)Document31 pagesModule 15 (Gas Turbine Engine)trinadh yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesD'EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedD'EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (7)
- Toolmakersmicroscope 140722144506 Phpapp02Document32 pagesToolmakersmicroscope 140722144506 Phpapp02Arjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- IC Model QPDocument2 pagesIC Model QPArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Orsat ApparatusDocument6 pagesOrsat ApparatusArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Variation of Specific HeatDocument7 pagesVariation of Specific HeatArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Comb ChamberDocument5 pagesComb ChamberArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- VCR EngineDocument8 pagesVCR EngineArjun Reghu100% (1)
- Analysis of Flue GasesDocument21 pagesAnalysis of Flue GasesArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationGbsReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- IC Model QPDocument2 pagesIC Model QPArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- CarburetorDocument1 pageCarburetorArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Wankel or Rotary EngineDocument6 pagesWankel or Rotary EngineAjay Singh ChoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Spark AdvanceDocument2 pagesSpark AdvanceArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- SCR EngineDocument11 pagesSCR EngineArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- FDGDHDFHDocument24 pagesFDGDHDFHKarthi Keyan R KPas encore d'évaluation
- Wankel (Rotary) Engines: By: Hoa ChuDocument8 pagesWankel (Rotary) Engines: By: Hoa ChuArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion in Si EnginesDocument36 pagesCombustion in Si Enginesrgopi_83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wankel or Rotary EngineDocument6 pagesWankel or Rotary EngineAjay Singh ChoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- VCR EngineDocument8 pagesVCR EngineArjun Reghu100% (1)
- Planning and ShedulingDocument14 pagesPlanning and ShedulingArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- TransmissionDocument97 pagesTransmissionArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- C Make ListsDocument5 pagesC Make ListsArjun ReghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Stag / Lynx (Bs Ii) Parts CatalogueDocument345 pagesStag / Lynx (Bs Ii) Parts CatalogueBhawani CopyPas encore d'évaluation
- International - N13.2013 - 2014Document15 pagesInternational - N13.2013 - 2014Eduardo Alvarez100% (1)
- REPORT PETER VICTOR'S SIWES Report WpsDocument31 pagesREPORT PETER VICTOR'S SIWES Report Wpsdidiloved007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Massey Ferguson 263 TRACTORS (GB) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 819774)Document14 pagesMassey Ferguson 263 TRACTORS (GB) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 819774)zhuangfuqian31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wa Engine CatDocument32 pagesWa Engine CatthailanPas encore d'évaluation
- FAR 33 para MotoresDocument32 pagesFAR 33 para MotoresErick Trejo ZuñigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plugin-2004 Evinrude JohnsonDocument172 pagesPlugin-2004 Evinrude Johnsonjohnnyg02275% (4)
- Parts Catalog: Model NB3200AU/A (CE SPEC.) NB3300AU-E (CE SPEC.)Document15 pagesParts Catalog: Model NB3200AU/A (CE SPEC.) NB3300AU-E (CE SPEC.)ManuelSilvaPedrosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbojet Design: ME4935 Aircraft Propulsion October 31, 2013Document27 pagesTurbojet Design: ME4935 Aircraft Propulsion October 31, 2013محمد القدوميPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Y6H1200E1Document57 pages1Y6H1200E1Roberto Vertel RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- 26-918 Diesel Generator 130kva Silent TypeDocument1 page26-918 Diesel Generator 130kva Silent TypeRiski AdilPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Generator Sets: CAT Diesel Engines Engine SpecificationsDocument4 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: CAT Diesel Engines Engine SpecificationsduaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6lya STD 6lya Ste YanmarDocument101 pages6lya STD 6lya Ste YanmarYew LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Fuel EngineDocument14 pagesDual Fuel EngineGUJJARI PREM KUMAR 19981A0344Pas encore d'évaluation
- 0599 PDFDocument2 pages0599 PDFEdinson Ariel Chavarro QuinteroPas encore d'évaluation
- H 010984Document1 pageH 010984Anonymous uKoNmLxkPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo Service Manual Cat 120KDocument41 pagesDemo Service Manual Cat 120KJimmy Jimmy100% (2)
- E0836Document3 pagesE0836criveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Update of NCMDocument3 pagesUpdate of NCMfahadullahPas encore d'évaluation
- 45 sb213025Document2 pages45 sb213025ahmedalgaloPas encore d'évaluation
- GSX-R600L8: Parts CatalogueDocument115 pagesGSX-R600L8: Parts CatalogueTara ChandPas encore d'évaluation
- Tohatsu 2009Document15 pagesTohatsu 2009dedeseven100% (1)
- MEE 312 Lecture Notes - Turning Moment Diagram and FlywheelDocument16 pagesMEE 312 Lecture Notes - Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheeljoseph UyovwisuohwoPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Caterpillar C175Document132 pagesMotor Caterpillar C175Jc Vera100% (7)
- Pantalla Anterior Bienvenido: Cr080vbesDocument3 pagesPantalla Anterior Bienvenido: Cr080vbesJuan Pablo Virreyra TriguerosPas encore d'évaluation
- Overhead Set (003-004) : WarningDocument14 pagesOverhead Set (003-004) : WarningRasoolKhadibiPas encore d'évaluation
- DML Expenses SampleDocument12 pagesDML Expenses SampleSamson MaqwazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jac Carlos PachecoDocument2 pagesJac Carlos PachecoOliver lealPas encore d'évaluation
- TEN100: Test 02 - Study GuideDocument4 pagesTEN100: Test 02 - Study GuidenhstechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Otc 6488Document6 pagesOtc 6488marranPas encore d'évaluation