Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fluids and Electrolytes IV Fluids
Transféré par
nursing concept maps0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues1 pageThis document discusses body fluids and electrolytes. It describes intracellular and extracellular fluids, and how their osmolality tends to equalize due to water shifting. It also discusses intravenous therapy solutions and their uses, as well as fluid imbalances, electrolyte imbalances, and age-related changes affecting fluid balance. Diagnostic tests for evaluating fluids and electrolytes are also mentioned.
Description originale:
concept map
Titre original
fluids and electrolytes IV fluids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses body fluids and electrolytes. It describes intracellular and extracellular fluids, and how their osmolality tends to equalize due to water shifting. It also discusses intravenous therapy solutions and their uses, as well as fluid imbalances, electrolyte imbalances, and age-related changes affecting fluid balance. Diagnostic tests for evaluating fluids and electrolytes are also mentioned.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues1 pageFluids and Electrolytes IV Fluids
Transféré par
nursing concept mapsThis document discusses body fluids and electrolytes. It describes intracellular and extracellular fluids, and how their osmolality tends to equalize due to water shifting. It also discusses intravenous therapy solutions and their uses, as well as fluid imbalances, electrolyte imbalances, and age-related changes affecting fluid balance. Diagnostic tests for evaluating fluids and electrolytes are also mentioned.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
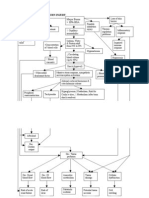
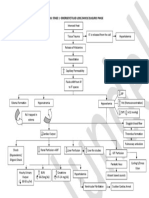
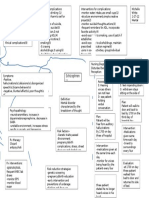
Body fluid with n cell osmolality of intracellular fluid and
Intracellular extracellular fluid tends to equalize
Fluid with in cell because of the constant shifting of
Intravenous therapy
Extracellular water Isotonic
Found in blood vessels NS (0.9% saline)
DW5
Interstitial fluid 25% (the
LR
third space)
Hypotonic
surrounding cells,
NS
including lymph
Hypertonic
Transcellular fluids
3% NS
Lymph, digestive tract,
D10W
sweat, cerebrospinal Fluids and Electrolytes 5% D in LR
Colloids
Ch. 14 Dextran
& Albumin
Hetastarch
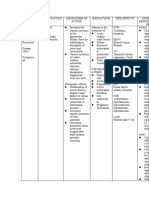
Intravenous therapy
Ch. 18
Electrolytes and imbalances
Infiltration
Sodium (Na) Major cation of extracellular fluid
Hyponatremia Caused by leakage
orthostatic hypotension S/S: pain or burning
Hypernatremia Paleness and puffiness or feel
flushed skin, dry mucous membranes hard and cool
Potassium (K) Excess Fluid Volume
Hypokalemia S/S: BP, bounding pulse,
Muscle cramps BP oliguria edema
Hyperkalemia Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Patients at risk: decreased renal function, Risks of emboli from blood
in metabolic acidosis, taking potassium clots, air, broken catheters
supplements Air can enter the bloodstream if
Chloride (Cl) the infusion system is opened
Hyperchloremia Catheters
Usually associated with metabolic
Respiratory Acidosis pH<7.35 &PaCO2>45 catheter threaded through the
acidosis
Hypoventilation Hypoxia tunnel and into the subclavian
Hypochloremia
Shallow breathing, K+, vein
Usually occurs when sodium is lost
Respiratory Alkalosis pH>7.45 &PaCO2<32 cannulas and the tubing are
because chloride most frequently bound
Deep breathing, hyperve usually changed every 48-72
with sodium ntilation, tachycardia, lethargy & confusion. hours
Metabolic Acidosis pH<7.35 & HCO3<20
Kussmaul respiration, severe diarreah, N,V,D,
muscle twitching
Metabolic Alkalosis pH>7.45 & HCO3>26
Calcium (Ca) Severe vomiting, tremors, muscle cramps
Hypocalcemia
intake of vit D
Hypercalcemia
intake of vitamin D
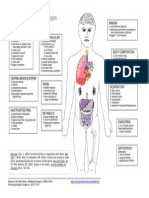
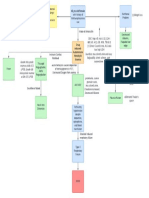
Magnesium (Mg2+) Age-Related Changes Affecting Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Important in heart, nerve, and Fluid Balance
Hematocrit
muscle function Total body water declines with age;
Creatnine
Hypomagnesemia greatest loss from the intracellular fluid BUN
usually from vomiting compartment Albumin
and diarrhea Antihypertensive, diuretics, and antacids
Serum electrolytes
Hypermagnesemia can also contribute to imbalances
excessive use of
magnesium
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cholecystitis Concept MapDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Pathophys BURNDocument2 pagesPathophys BURNpaupaulala83% (6)
- Physiological ChangesDocument1 pagePhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganPas encore d'évaluation
- Infertility Concept MapDocument1 pageInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocument1 pageNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- AIC - AirROCT35 - Spare Parts ManualDocument153 pagesAIC - AirROCT35 - Spare Parts ManualMuhammad Arqam Al Ajam67% (3)
- Prayer and Bible Band Topics Fall Quarter 2021 (Sep-Nov): Fall Quarter 2021 (Sep-Nov)D'EverandPrayer and Bible Band Topics Fall Quarter 2021 (Sep-Nov): Fall Quarter 2021 (Sep-Nov)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Guide Pagan ChristianityDocument5 pagesDiscussion Guide Pagan ChristianityFrank Viola100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramJessica Peñamora100% (1)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocument1 pagePituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument1 pageCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Bomber JacketDocument3 pagesBomber JacketLaura Carrascosa FusterPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity - Alien DNA - CompleteDocument36 pagesActivity - Alien DNA - CompleteJennifer ShawkiPas encore d'évaluation
- HPE 3PAR StoreServ 20000 Storage Service and Upgrade Guide Service EditionDocument282 pagesHPE 3PAR StoreServ 20000 Storage Service and Upgrade Guide Service Editionben boltPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and Electrolytes Study GuideDocument13 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Study GuideElizabeth McKeePas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Hormone Pill, Patch, Ring Progestin Only Mini Pill, Depo-Provera, IUDDocument1 pageCombined Hormone Pill, Patch, Ring Progestin Only Mini Pill, Depo-Provera, IUDnkuligowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Smith WigglesworthDocument5 pagesNotes For Smith WigglesworthFernandoGonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- Divine Healing 33Document84 pagesDivine Healing 33Matija NovakPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypogonadism JunDocument2 pagesHypogonadism JunoimoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 11 - The Double-Portion Anoiting IDocument3 pagesLesson 11 - The Double-Portion Anoiting Iapi-3826922Pas encore d'évaluation
- Significance of BloodDocument8 pagesSignificance of BloodJoaniBaileyRossPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Eternal Judgment PDFDocument70 pages07 Eternal Judgment PDFGoodReadsPas encore d'évaluation
- Last Giant Before PromiseDocument12 pagesLast Giant Before PromiseJeremy PolingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hand of God: Ancient Prophesies - Modern Miracles of IsraelDocument114 pagesThe Hand of God: Ancient Prophesies - Modern Miracles of IsraelBill HeinrichPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of God Resource Guide 2021Document3 pagesName of God Resource Guide 2021Rebelle JacobsPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Tribus PerdidasDocument5 pages10 Tribus PerdidasGil CorpusPas encore d'évaluation
- The Book of JonahDocument21 pagesThe Book of JonahCharlyn Arlante DuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Cognitive and Degenerative DisordersDocument73 pages2.1 Cognitive and Degenerative DisordersAbanoub AwadallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Encouragement from the Psalms: A 40-Day Devotional JourneyD'EverandEncouragement from the Psalms: A 40-Day Devotional JourneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Water-Salt Metabolism: Prof. Oleksandr AtamanDocument35 pagesDisorders of Water-Salt Metabolism: Prof. Oleksandr AtamanZAKIA KHALID ALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Esophageal VaricesDocument1 pageEsophageal VaricesDanielle DiorioPas encore d'évaluation
- W2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Document6 pagesW2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Syximsh FPPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 29-Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesChapter 29-Fluids and ElectrolytesCharlena LittlePas encore d'évaluation
- 00 Renal FabsDocument9 pages00 Renal FabsAngelica AlayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Urine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerDocument30 pagesUrine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerSalman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM112 LP1 Transes - RosalesDocument4 pagesNCM112 LP1 Transes - RosalesChristine CalleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Lesson 12. Serous, Duodenal, and Gastric FluidDocument4 pagesLecture Lesson 12. Serous, Duodenal, and Gastric FluidHANA LUNARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Uia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYDocument5 pagesUia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYIbrahim QariPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock EditedDocument56 pagesShock EditedJeevan VelanPas encore d'évaluation
- HD B Braun For CNN TakersDocument6 pagesHD B Braun For CNN TakersWhimsey CipresPas encore d'évaluation
- Burn Stage I - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBurn Stage I - Pathophysiologydecsag06Pas encore d'évaluation
- FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES UpdatedDocument8 pagesFLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES UpdatedSJane FeriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Physio #1 - Fluid and Electrolyte Notes (Dr. Nobleza)Document3 pagesRenal Physio #1 - Fluid and Electrolyte Notes (Dr. Nobleza)Hannah Grace Protasio LumongsodPas encore d'évaluation
- Jenis ShockDocument6 pagesJenis ShockMuhamad Pathu RohmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids & Electrolytes: Thirst Reflex Triggered byDocument7 pagesFluids & Electrolytes: Thirst Reflex Triggered byGummie Akalal SugalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Terapi CairanDocument81 pagesTerapi CairanMarsa ZaidanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5Document2 pages5Ayesha Mae Baniaga DoctoleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Caso 35Document5 pagesCaso 35Laura ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument38 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesJohn Anthony de GùzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 pagesNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial Infarction PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction PathophysiologyPowell TabogocPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study D5LRDocument2 pagesDrug Study D5LRCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- IV Fluids Cheat SheetDocument1 pageIV Fluids Cheat SheetAmanda MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- ShockDocument30 pagesShockLập Trương Minh QuốcPas encore d'évaluation
- Week12 13 RENAL PhysiologyDocument41 pagesWeek12 13 RENAL Physiologyirwan kastellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument12 pagesFluid and Electrolytesjanolo_rc5847Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quizlet (4) MMMMMMDocument30 pagesQuizlet (4) MMMMMMnaimPas encore d'évaluation
- Whatsapp: +1 (402) 235-1397Document312 pagesWhatsapp: +1 (402) 235-1397Khushi RPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and Electrolytes-SeminarDocument119 pagesFluids and Electrolytes-Seminarنديم الباهليPas encore d'évaluation
- CPC CaseDocument1 pageCPC CaseJill ZabalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolytes, Balance and DisturbancesDocument157 pagesFluid and Electrolytes, Balance and DisturbancesDani PhilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Limfatik: M. Rasjad Indra Laboratorium Ilmu Faal Fk. UnibrawDocument24 pagesSistem Limfatik: M. Rasjad Indra Laboratorium Ilmu Faal Fk. UnibrawLuthfi HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystalloids 33333Document8 pagesCrystalloids 33333hebaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypovolemic Shock Pathophysiology: Large Volume Third Spacing Occurs In: Large Volume Third Spacing Occurs inDocument4 pagesHypovolemic Shock Pathophysiology: Large Volume Third Spacing Occurs In: Large Volume Third Spacing Occurs inMardie ArcesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Case 4 Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Case 4 Sickle Cell AnemiaKARL MARLU LUZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared By: Mark Joseph V. Liwanag, RN, MSNDocument136 pagesPrepared By: Mark Joseph V. Liwanag, RN, MSNjosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Icu 4Document7 pagesIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 4 ReviewDocument3 pagesExam 4 ReviewAlyssa MondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Edema Dan PerdarahanDocument13 pagesEdema Dan PerdarahanKost Vila SakinahPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map TemplateDocument1 pageConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocument1 pageDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology EmphysemaGil AswiguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map BlankDocument2 pagesConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Health Concept MapDocument2 pagesMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip FractureDocument3 pagesHip Fracturenursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Reason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDDocument6 pagesReason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Schizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Bronchitis and EmphesemaDocument2 pagesChronic Bronchitis and Emphesemanursing concept maps100% (2)
- The Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareDocument40 pagesThe Gingerbread Man-1 EnglishareamayalibelulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Book 2 - Koning (COMPLETO)Document100 pagesBook 2 - Koning (COMPLETO)Kevin VianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Practices in Tray DesignDocument7 pagesGood Practices in Tray Designmehul10941100% (2)
- Curso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsDocument12 pagesCurso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsFausto Inzunza100% (1)
- Chapter 5 TEstDocument18 pagesChapter 5 TEstJeanneau StadegaardPas encore d'évaluation
- A Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnDocument14 pagesA Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnPaul SchumannPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics Course FileDocument81 pagesHydraulics Course FileSwarna LathaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyundai Forklift Catalog PTASDocument15 pagesHyundai Forklift Catalog PTASjack comboPas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 6 Unesco Water SanatationDocument5 pagesGoal 6 Unesco Water Sanatationapi-644347009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Camouflage Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCamouflage Lesson Planapi-344569443Pas encore d'évaluation
- Burst Abdomen 3Document12 pagesBurst Abdomen 3Satvik BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ae 2 PerformanceDocument4 pagesAe 2 PerformanceankitPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8Document22 pagesLecture 8Ramil Jr. EntanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeDocument2 pagesApplication of Eye Patch, Eye Shield and Pressure Dressing To The EyeissaiahnicollePas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Lesson 1 Ethics & Moral PhiloDocument13 pagesMid Lesson 1 Ethics & Moral PhiloKate EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- ZW250-7 BROCHURE LowresDocument12 pagesZW250-7 BROCHURE Lowresbjrock123Pas encore d'évaluation
- 65 ActsDocument178 pages65 ActsComprachosPas encore d'évaluation
- SFT PresentationDocument16 pagesSFT Presentationapna indiaPas encore d'évaluation
- مشخصات فنی بیل بکهو فیات کوبلکو b200Document12 pagesمشخصات فنی بیل بکهو فیات کوبلکو b200Maryam0% (1)
- Second Advent Herald (When God Stops Winking (Understanding God's Judgments) )Document32 pagesSecond Advent Herald (When God Stops Winking (Understanding God's Judgments) )Adventist_TruthPas encore d'évaluation
- Library: Astrology and WisdomDocument13 pagesLibrary: Astrology and Wisdomalimuhammedkhan2115Pas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate of No Damages in EarthquakeDocument5 pagesCertificate of No Damages in EarthquakeLemlem BardoquilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes in Pregnancy: Supervisor: DR Rathimalar By: DR Ashwini Arumugam & DR Laily MokhtarDocument21 pagesDiabetes in Pregnancy: Supervisor: DR Rathimalar By: DR Ashwini Arumugam & DR Laily MokhtarHarleyquinn96 DrPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandvik Saf 31803 Tube and Pipe, Seamless: DatasheetDocument9 pagesSandvik Saf 31803 Tube and Pipe, Seamless: DatasheetPaul NeedhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5, Abdominal TraumaDocument41 pagesChapter 5, Abdominal TraumaRandy HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hollow Boy Excerpt PDFDocument52 pagesThe Hollow Boy Excerpt PDFCathy Mars100% (1)