Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin K
Transféré par
You know who0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2K vues7 pagesDrug Study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDrug Study
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2K vues7 pagesVitamin K
Transféré par
You know whoDrug Study
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
Picture
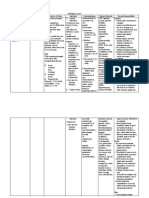
Generic Name Vitamin K (Phytonadione)
Brand Name Mephyton
Classification Blood coagulation modifier, fat soluble vitamin
Action It works by helping the liver to produce blood clotting factors.
Dosage 0.1 ml at Right Vastus Lateralis
Vitamin K is used to treat and prevent low levels of certain
Indication substances (blood clotting factors) that your body naturally produces.
These substances help your blood to thicken and stop bleeding
normally.
Contraindication Hypersensitivity.
Side Effects Pain, swelling, or soreness at the injection site may occur. flushing,
taste changes, dizziness, rapid heartbeat
Adverse Sweating, shortness of breath, or bluish lips/skin/nails.
Reactions
Drug Aspirin, NSAIDs and Warfarin
Interactions
Nursing 1. Educate the patient about the indication and contraindication of
Responsibilities vitamin K.
2. Inform the patient about the side and adverse effects.
3. Instruct patient if side effects persist immediately notify the
physician.
4. Stop administration of vitamin K if severe side effects occur.
5. Assist patient when ambulating, dizziness may occur.
6. Educate patient about the drug interaction of vitamin k
7. Instruct patient not to take any medication without doctors
prescription.
8. Do not give aspirin for pain medication.
9. Encourage patient to eat green leafy vegetables especially
broccoli, lettuce and spinach.
10. Continue to administer medication as prescribed by the doctor.
Source Gilliam, S.T. Springhouse Nurses Drug Guide 2006 (9 th ed.).
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 323, Norristown Road, Suite 200,
Ambler.
Picture
Generic Name Dexamethasone
Brand Name Dexasone
Dosage 0.08 0.3 mg/kg/day PO divided q6-12h
Therapeutic: Anti asthmatics, corticosteroids
Classification Pharmacologic: Corticosteroids (systemic)
Suppress inflammation and the normal immune response.
Suppress adrenal function.
Action Have negligible mineralocorticoid activity.
Therapeutic Effects: Suppression of inflammation and modification of
the normal immune response. Replacement therapy in adrenal
insufficiency.
Used systemically and locally in a wide variety of chronic diseases
Indication including inflammatory, allergic, hematologic, neoplastic and
autoimmune disorders.
Management of cerebral edema
Active untreated infections (may be used in patients being treated for
Contraindication some forms of meningitis)
Known alcohol, bisulfite or tartrazine hypersensitivity or intolerance
Administration of live virus vaccines
Depression, euphoria, headache, intracranial pressure (children only),
personality changes, psychoses, restlessness, cataracts, intraocular
pressure hypertension, peptic ulceration, anorexia, nausea, vomiting,
Side Effects and acne, wound healing, ecchymoses, fragility, hirsutism, petechiae,
Adverse Effects adrenal suppression, hyperglycemia, fluid retention (long-term high
doses), hypokalemia, hypokalemic alkalosis, thromboembolism,
thrombophlebitis, weight gain, muscle wasting, osteoporosis, avascular
necrosis of joints, muscle pain.
Increase risk of hypokalemia with thiazide and loop diuretics, or
amphotericin B.
Hypokalemia may increase risk of digoxin toxicity.
Drug Interaction May increase requirement for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
Phenytoin, phenobarbital, and rifampin increase metabolism; may
decrease effectiveness.
Hormonal contraceptives may increase metabolism.
Increase risk of adverse GI effects with NSAIDs (including aspirin).
Monitor and report S&S of Cushing's syndrome (see Appendix F) or
other systemic adverse effects.
Nursing
Responsibilities
Monitor neonates born to a mother who has been receiving a
corticosteroid during pregnancy for symptoms of hypoadrenocorticism.
Monitor for S&S of a hypersensitivity reaction (see Appendix F). The
acetate and sodium phosphate formulations may contain bisulfites,
parabens, or both; these inactive ingredients are allergenic to some
individuals.
Source Hopfer, J. D., Vallerand, A. H., & Sanoski, C. A. (2011). Davis's Drug Guide
for Nurses (12th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company.
Ateneo de Davao University
Jacinto St., Davao City
School of Nursing
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of Intensive Nursing Practicum
At SPMC Delivery Room
Drug Study (Dexamethasone)
Nursing Care Plan
Reading
Submitted to:
Anabel T. Bauzon, RN MN
Clinical Instructor
Submitted by:
Patricia Anne P. Hipol
Bachelor of Science in Nursing 4A
January 27, 2017
Ateneo de Davao University
Jacinto St., Davao City
School of Nursing
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of Intensive Nursing Practicum
At SPMC Delivery Room
Drug Study (Vitamin K)
Nursing Care Plan
Submitted to:
Anabel T. Bauzon, RN MN
Clinical Instructor
Submitted by:
Patricia Anne P. Hipol
Bachelor of Science in Nursing 4A
January 27, 2017
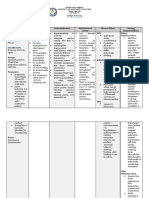
Date Cues Need Diagnosis Objectives Interventions
Jan. 17, Subjective N Ineffective After 8 Establish rapport. To
2017 The client U infant feeding hours of an
3-11 Shift verbalized, T pattern related nursing Assess vital signs. Pr
Sige rag R to muscle intervention for
tulog akong I weakness , the infant ev
baby, lisod T secondary to will initiate int
siya I prematurity. or sustain Assess for factors that So
patotoyon, O an effective pr
interfere with neonate
gamay baya N Rationale suck. in
establishing effective
siyag A Ineffective ne
feeding pattern.
timbang. L infant feeding a
Mao ra na pattern is a fee
among M state in which
Assess parents Mi
ginadugayan E an infant (birth
knowledge of feeding alt
diria sa T to 9 months)
techniques to help identify fee
hospital. A demonstrates
and clear up
Unsa may B an impaired
misconceptions.
buhaton O ability to suck or
Evaluate mothers ability Co
nako ani uy? L coordinate the
to position, give cues, and go
I suck-swallow
help infant latch on. co
Objective C response,
br
Infant is not resulting in
P inadequate oral Evaluate infants ability to Pr
suckling
A nutrition for properly grasp areola with ac
mothers
T metabolic lips, tongue and jaw. br
breast
Mother tries T needs.
E Encourage the mother to En
her best to
R Source stroke the neonates re
breastfeed
N Moyet, cheek with fingers or eff
baby
Lynda Juall nipple. sw
Baby is small
Carpenito-, all
and presently nu
weighs 1.6 Handbook
of Nursing Di
kg
Diagnosis, Promote comfort and wi
Mother gave
Edition 13, relaxation to reduce pain ca
birth to infant dis
page 305 (in breast) and anxiety.
at 34 weeks br
Kelly, M. M.
G2P2 (2002) pr
(2006,
V/S taken as September- Provide support by Pr
follows: October). actively helping mother to br
Temperature: Primary correctly position infant
36.5 C care issues and encouraging her to
Blood for the continue trying.
Pressure: healthy Enhance the flow of milk. Br
90/70 premature Teach mother to massage en
Pulse Rate: infant. breast. Switch to other pr
72 bpm Journal of breast when Infants sh
Respiration Pediatric swallowing slows down. bo
Rate: 26 Health Care, fee
20 (5), 293- Discourage bottle Ma
299 feedings. all
co
mi
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Drug Study - Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Vitamin KJustin Ancog100% (1)
- ErythromycinDocument6 pagesErythromycinkitsilcPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Intrapartum DrugsDocument9 pagesDrug Study Intrapartum DrugsAyessah Mapa100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMethergine Drug StudyjoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Vitamin KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Vitamin KFlorence NightingalePas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamin K Drug StudyDocument6 pagesVitamin K Drug Studychristianmark24100% (2)
- Drug Study For VaccinesDocument6 pagesDrug Study For VaccinesMarion RebolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Hepatitis B VaccineJustin AncogPas encore d'évaluation
- ErythromycinDocument6 pagesErythromycinapi-3797941100% (1)
- Vit. KDocument2 pagesVit. KMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- PhytomenadioneDocument3 pagesPhytomenadioneanareads100% (1)
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- ErythromycinDocument2 pagesErythromycinKathleen PalomariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyYaniiee DeFiestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Availability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)Document3 pagesAvailability: Dinoprostone (Pge, Prostaglandin E)steffy sojan100% (1)
- Final Drug Study - PediaDocument2 pagesFinal Drug Study - PediaMae Estillore100% (1)
- VITAMIN K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVITAMIN K Drug StudyMarl DumiligPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug Study - Ambroxol, AmpicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Ambroxol, AmpicillinPaul John RutaquioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study DRDocument6 pagesDrug Study DRBheigh Lomitao AlbueraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisPas encore d'évaluation
- BACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBACILLUS CALMETTE - GUERIN (BCG) Drug StudyCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (2)
- Hep B Vaccine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHep B Vaccine Drug StudyFrian MariñasPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogPas encore d'évaluation
- EpinephrineDocument3 pagesEpinephrinealexjerimiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyJenivic Empig PuedanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyDocument7 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyGabriel Rosales RM RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Vit K Drug Study PDFDocument2 pagesVit K Drug Study PDFA sisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDelivery Room Drug StudyJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RN100% (6)
- Drug Study Form OxyDocument3 pagesDrug Study Form OxyRyan OdioPas encore d'évaluation
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesName of Drugs Indications Contraindications ADVERSE Reactions To Watch Out For Drug Interactions Nursing ConsiderationsAlexis SilvestrePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRenmen Rosito Hortelano100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKrysPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Vitamin KChristian Daayata50% (2)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudycuakialyannaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY-Mam CarulloDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY-Mam CarulloJorelyn Frias83% (6)
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lansoprazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLansoprazole Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- CatapresDocument1 pageCatapres去約翰Pas encore d'évaluation
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Vit. K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit. K Drug StudyJulie May74% (35)
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study in GentamicinDocument2 pagesDrug Study in Gentamicinanthony_alviar100% (1)
- Roxipan (Oxytocin) - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesRoxipan (Oxytocin) - Drug StudyIzza DeloriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxytocics: Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesOxytocics: Adverse EffectsMarielle ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive Drugs Nursing Considerations and RationaleDocument5 pagesReproductive Drugs Nursing Considerations and RationaleKathleen AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Cefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDeva HiyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyPeetah PanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amikacin SulphateDocument3 pagesAmikacin Sulphatemahmoud mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study AngelaDocument8 pagesDrug Study AngelaIrene Grace BalcuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Document1 pageDRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Echanique, James F.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc. College of NursingDocument16 pagesDipolog Medical Center College Foundation Inc. College of NursingTiffany AdriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Plan: MedicationDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan: MedicationJastine Joyce Madlang-awaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in ObstetricsDocument19 pagesDrugs Used in ObstetricsAnuradha Maurya100% (8)
- Antiemetic Drug Use in Children What The.3Document6 pagesAntiemetic Drug Use in Children What The.3Zafitri AsrulPas encore d'évaluation
- MedicationsDocument23 pagesMedicationsYou know whoPas encore d'évaluation
- AminolebanDocument2 pagesAminolebanYou know who0% (1)
- PonstanDocument5 pagesPonstanYou know whoPas encore d'évaluation
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYou know whoPas encore d'évaluation
- Norepinephrine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNorepinephrine Drug StudyYou know who100% (10)
- Revisiting Structural Family TherapyDocument2 pagesRevisiting Structural Family TherapyKim ScottPas encore d'évaluation
- Working With Addicted PopulationsDocument9 pagesWorking With Addicted PopulationsWhimsical BrunettePas encore d'évaluation
- Iridology and HypoglycemiaDocument15 pagesIridology and Hypoglycemiasohail_mashwnaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation On Parkinson'S Disease: Presented By: T.Avinash Vith Pharm D Y13PHD0721Document21 pagesCase Presentation On Parkinson'S Disease: Presented By: T.Avinash Vith Pharm D Y13PHD0721AVINASH TALAPALA100% (1)
- Barksy - The Paradox of Health PDFDocument5 pagesBarksy - The Paradox of Health PDFdani_g_1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Medicine Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesGeneral Medicine Thesis Topicsxxsfomwff100% (2)
- Bacteriophage Therapy SummitDocument12 pagesBacteriophage Therapy SummitZhibek AbyshevaPas encore d'évaluation
- 209 (8) 6Document1 page209 (8) 6Rajesh DmPas encore d'évaluation
- WHO 2019 nCoV Therapeutics 2022.4 EngDocument142 pagesWHO 2019 nCoV Therapeutics 2022.4 Engelsie versiePas encore d'évaluation
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 pagesARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogPas encore d'évaluation
- OSPE DU MedicineDocument101 pagesOSPE DU MedicinesaifPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Leiomyomas (Fibroids) - Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Natural History - UpToDateDocument48 pagesUterine Leiomyomas (Fibroids) - Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Natural History - UpToDateRuben Orduño RizoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mia SmsDocument8 pagesMia SmsGlasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Egypt Biosimilar Guidline Biologicals RegistrationDocument54 pagesEgypt Biosimilar Guidline Biologicals Registrationshivani hiremathPas encore d'évaluation
- Date/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseDocument2 pagesDate/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseRoland Yuste67% (3)
- INS Standards of Practice 2016 - 0Document169 pagesINS Standards of Practice 2016 - 0Laura López González100% (1)
- SOMATOM Volume Zoom Routine VA40Document136 pagesSOMATOM Volume Zoom Routine VA40gallu797462Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9497Document45 pages9497David axtonPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs On IMMUNOLOGYDocument8 pagesMCQs On IMMUNOLOGYNOORPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Kasus Neurogenic ShockDocument44 pagesLaporan Kasus Neurogenic ShockAkbar TaufikPas encore d'évaluation
- Artículo de Trabeculectomía.Document13 pagesArtículo de Trabeculectomía.Dore OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Plan Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Plan Interventions Rationale EvaluationDuran JustinePas encore d'évaluation
- ME 4 - Acute and Post Acute COVID-19 Neurological Syndrome-How To Manage - Dr. Kartika Maharani, SP.S (K) - 1Document31 pagesME 4 - Acute and Post Acute COVID-19 Neurological Syndrome-How To Manage - Dr. Kartika Maharani, SP.S (K) - 1winnerfromparisPas encore d'évaluation
- Rent AgreementDocument4 pagesRent Agreementkhushbu chitrePas encore d'évaluation
- Common Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - 6Document3 pagesCommon Dermatology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - 6Atul Kumar Mishra100% (1)
- Case Report Two Blue Chromhidrosis Patients in Emergency RoomDocument2 pagesCase Report Two Blue Chromhidrosis Patients in Emergency RoomInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Echinochrome A and Cytokine Storm SyndromeDocument11 pagesEchinochrome A and Cytokine Storm SyndromeNicolas Fernandez RubilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue OutlineDocument6 pagesDengue OutlineLouie George NeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 - The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pagesLesson 3 - The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsEmieleah Lorenzo PauigPas encore d'évaluation
- OB-GYN - MCQ - 2012 - 5th-Year - Mu - TahDocument16 pagesOB-GYN - MCQ - 2012 - 5th-Year - Mu - TahHalah100% (1)