Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Budgets
Transféré par
bim269Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Budgets
Transféré par
bim269Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Budgets
My former boss used to say if you fail to plan, then you have planned to fail
(Benjamin Franklin). He used to advise us to make a list of things we want to
achieve the next day so that at the end of the day we can know how far we have
performed for the day by comparing what we have actually done against what we
have written down on the list.
Budget to my understanding is making a list of items or things which will make it
possible for you to achieve a set target or aim with the monetary value estimated to
drive the listed items to achievement. From this we can actually say that budget is
like a plan one makes to ensure that a business goes in the right direction, it acts as
the driving force for a business.
Budget Process
So what are the things we need to consider when drawing up our budgets? Those
things that we put into consideration when drawing up the budget to ensure that
the budget even though is an estimate of what we hope to achieve is as near reality
as possible makes up the budget process.
What business you are involved in or the strategic plans you hope to achieve drives
the type of budget drawn up. For a large retail Internet Service provider, the
processes involved in drawing up a budget are as listed below.
1. Setting up business goals and achievement
The internet service provider needs to consider how far its business has gone
and how far they want the business to go. What achievement do they want
from the business in the next few years to come and what customers base
are they targeting.
a. How far do I want my reach to go?
b. How many customers can do I want to afford my service?
c. What price is affordable to customers and profitable to me?
d. How many retailers and resellers do I want to push my service up?
e. What are the services that I want to provide to my customers that will
ensure customer satisfaction and drive up sales; is it off the shelf or
customized to their needs?
2. Gather data from previous and current year
There is need to gather data to aid in the proper preparation and planning of
the budget which acts as a guide (Anon, 2009) on how a business makes its
income, what it expects to expend on its expenses and what and how to drive
revenue.
Information and data gathered can include but not limited to
a. How much sales was made on services provided
b. The demographics of the past and current customer
c. What product sold more and what product has a tendency for sales
if pushed more
d. What expenses did we incur and so on
e. Who are my customers and which of my services do they patronize
the most
3. Project the future needs of the business and customers
Project the future needs of the business based on the data gathered and
goals of the business as already stated. Here you need to answer questions
(Wood & Sangster, 2005). such as
a. How many more customers are coming on board
b. How much to spend on expenses
c. If the business is expanding, how much to be spent on equipment,
labor and employees
d. From previous data gathered do we need to customized services or
continue with off the shelf service we are currently providing and
how much can we expect from their sales
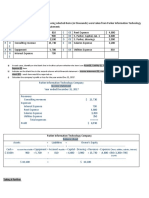
4. Prepare the budget
After going through steps one to three, we now prepare the budget based on
the business strategic goals, the data gathered and the business projections
of the near future. We prepare the budgets based on sales we expect to
generate (sales budget), if there is need for expansion, what equipment are
needed (purchase budget), what are the expenses we incur along the way
(expenses budget) and what cash is coming into and going out of the
business (cash budget) (Atrill & McLaney, 2013). Also when preparing
budgets, it is good that we make provisions for alternatives, that is what will
happen in case we need a new employee mid year? Or if sales does not go as
forecasted what to do?
5. Budget implementation
After the budget has been prepared, implementing the budget is the next
step. Ensuring that the budgeted sales and revenue are achieved, the
overhead cost do not unnecessarily increase more than budgeted, and also
ensuring that capital project cost such as purchase of equipment necessary
for expansion do not unnecessarily increased more than budgeted or if it
increases, it has a valid reason for it to go off budget are ways the Internet
service provider can implement his budget.
6. Controlling the budget of the business
What happens when a budgeted item goes beyond its budget? Ensuring that
items budgeted for do not unnecessarily increased is part of budget control
(Wood & Sangster, 2005). It is important to note that the budget was
prepared with the hope of achieving some business goals and as such the
budget needs to be properly monitored and controlled to ensure that those
goals are met.
7. Evaluating business performance based on budget
As said earlier, a budget is a guide and as such it is important to ensure that
the business evaluates its actual performance against the budgeted items.
Were we able to bring in the sales budgeted, did we keep to the monetary
value budgeted for expenses, how much did the actual cost of equipment
overlap the budgeted cost? All these are done by comparing actual with
budgeted. Evaluating your budgets enables you to cut cost where necessary.
Have we been able to save from implementing the budget or not. (Concordia,
n.d.)
References
Atrill, P. and McLaney, E. (2013) Accounting and Finance for Non - Specialists 8th Ed.
Harlow, Essex: Pearson Education Limited.
Wood, F. & Sangster, A. (2005). Business Accounting, 10 th Ed. Harlow, Essex:
Pearson Education Limited
Anon (2009). Essential five steps on budgeting process. [Online] Available From:
http://accounting-financial-tax.com/2009/02/essential-five-steps-on-budgeting-
process/ (Accessed: 26 August 2016)
Concordia (n.d.). Basic steps to making a budget. [Online] Available From:
http://www.concordia.ca/students/financial-support/budgeting/basic-steps-to-
makingabudget.html (Accessed: 26 August 2016)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Internet of Things (IoT)Document7 pagesInternet of Things (IoT)bim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Managing Change in Is: CKIT521 - Managing The Software EnterpriseDocument6 pagesManaging Change in Is: CKIT521 - Managing The Software Enterprisebim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Week 7-8 Group C Project FinalDocument26 pagesWeek 7-8 Group C Project Finalbim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- M4-WK2-HIA - SubmissionDocument7 pagesM4-WK2-HIA - Submissionbim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Week 7-8 Group C Project FinalDocument26 pagesWeek 7-8 Group C Project Finalbim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Need, Want and DemandDocument5 pagesNeed, Want and Demandbim269100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesFinancial Statementsbim269Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Chapter 5 Test BankDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Test Bankmyngoc181233% (3)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Public Education Finances: 2015 Economic Reimbursable Surveys Division Reports Issued June 2017Document65 pagesPublic Education Finances: 2015 Economic Reimbursable Surveys Division Reports Issued June 2017FOX45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Team 4: Storytelling - MORRIS V FC of T 2002 ATC 4404: PrecedenceDocument3 pagesTeam 4: Storytelling - MORRIS V FC of T 2002 ATC 4404: PrecedenceTiancheng HuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Far Quick Notes and Test Bank PDFDocument72 pagesFar Quick Notes and Test Bank PDFFujikoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Principles and Concept 2Document21 pagesPrinciples and Concept 2JeffreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- 1.1 Background of The EnterpriseDocument25 pages1.1 Background of The EnterpriseBARBO, KIMBERLY T.Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Chapter 3 - Double EntriesDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - Double Entries33. Nguyễn Huyền ThanhPas encore d'évaluation
- Percentages Part 1Document4 pagesPercentages Part 1Sushrut DalviPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- IND AS 103 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldDocument26 pagesIND AS 103 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldSoham Upadhyay100% (1)
- Operating CostingDocument45 pagesOperating CostingVivek Tiwari100% (1)
- AFAR2 - Dayag - Solman PDFDocument411 pagesAFAR2 - Dayag - Solman PDFHazel Mae LasayPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Construction Contracts: Connolly - International Financial Accounting and Reporting - 4 EditionDocument47 pagesConstruction Contracts: Connolly - International Financial Accounting and Reporting - 4 EditionJosette Mae AtanacioPas encore d'évaluation
- (Aa35) Corporate and Personal Taxation: Association of Accounting Technicians of Sri LankaDocument8 pages(Aa35) Corporate and Personal Taxation: Association of Accounting Technicians of Sri LankaSujan SanjayPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- ACCT 2211 Assignment 1Document12 pagesACCT 2211 Assignment 1Tannaz SPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study On Indian Bicycle Industry With Special Reference To Atlas CycleDocument11 pagesA Case Study On Indian Bicycle Industry With Special Reference To Atlas CycleHimanshuWadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Pengantar Akuntansi-1Document23 pagesTugas Pengantar Akuntansi-1Wiedya fitrianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Mr. Lindbergh Lendl S. Soriano Practice Set MerchandisingDocument5 pagesProblem Mr. Lindbergh Lendl S. Soriano Practice Set MerchandisingRayna AbrenicaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Gabrielle's BudgetDocument3 pagesGabrielle's BudgetRH - 10PS 790469 Streetsville SSPas encore d'évaluation
- Havi ExpressDocument24 pagesHavi Expressghulam hussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Factory ProfileDocument8 pagesBrand Factory Profilesuresh jain100% (2)
- 823 Cost Accounting SQPDocument5 pages823 Cost Accounting SQPSayandip DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Analysis and Effects of Government ExpenDocument67 pagesAnalysis and Effects of Government ExpenGetachew HussenPas encore d'évaluation
- DRDDDDocument12 pagesDRDDDWaqar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Examination CfasDocument5 pagesFinal Examination CfasBSA 1BRICHELL ASHLEY M. PAGADUANPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment AMA PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment AMA PDFPritesh Ranjan Sahoo100% (1)
- SPPRA Rules Amended 2010 (Amended Uptodate)Document52 pagesSPPRA Rules Amended 2010 (Amended Uptodate)Hammad ShamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Business Administration Group Assignment On Fundamental of Accounting IDocument5 pagesDepartment of Business Administration Group Assignment On Fundamental of Accounting IMohammed HassenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Review Questions and ProblemsDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Review Questions and ProblemsLars FriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions. F6. CLC.2020. PIT and CIT. 12 Feb 2020Document19 pagesMultiple Choice Questions. F6. CLC.2020. PIT and CIT. 12 Feb 2020MinhDuong100% (1)
- Conclusion AccDocument1 pageConclusion AccRohan KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)