Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RSP Session Plan-1
Transféré par
Mohan Raj0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues2 pageskljljl
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentkljljl
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues2 pagesRSP Session Plan-1
Transféré par
Mohan Rajkljljl
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
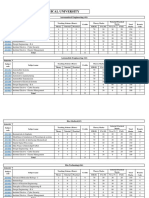
Sl.
Topics in JNTU Lecture
Modules and Sub modules Suggested Books Remarks
No. syllabus No.
UNIT I
1. Introduction: Introduction to Radar T2-Ch1,
systems L1
Radar Signal Processing
Applications,
2 Radar Block Block diagram of Pulsed T2-Ch1,
L2
Diagram, Radar
3 Radar Equation, Derivation of Radar Range T2-Ch1,
L3
equation
2. Information Extraction of available T2-Ch2,
L4
Available from information from radar
Radar Echo echo
3. Review of Radar Performance of Range T2-Ch2,
L5
Range equation in the presence
Performance of Noise
General Radar Modified range in terms of T2-Ch2,
L6
Range Equation, single pulse, and n-
pulses
4. Radar Detection Radar detection with T2-Ch2,
L7
with Noise noise, range equation for
Jamming, jamming
Beacon and Beacon and Repeater
Repeater Equations,
L8
Equations, Bistatic Radar.
Bistatic Radar.
5. Matched Filter Importance of Matched
Receiver filter, L9
Impulse Response, Impulse response of
Matched filter response
6. Frequency Frequency Response
Response Characteristic and its L10
Characteristic and Derivation,
its Derivation,
7 Matched Filter and Matched Filter and
Correlation Correlation Function, L11
Function, Correlation Detection and &
GATE,
Correlation Cross-Correlation L12
IES
Detection and Receiver,
Cross-Correlation
Receiver,
8. Efficiency of Non- Efficiency of Non-Matched L19
Matched Filters, Filters, Matched Filter for & GATE,
Matched Filter for Non-White Noise L20 IES
Non-White Noise
UNIT -II: Detection of Radar Signals in Noise
9. Detection Criteria Detection Criteria
Neyman-Pearson Neyman-Pearson
Observer, Observer, Likelihood-Ratio L21
Likelihood-Ratio
Receiver, Inverse & GATE,
Receiver, Inverse
Probability Receiver, L22 IES
Probability
Receiver, Sequential Observer,
Sequential
Observer,
Detectors Types of detectors
Envelope Detector, Envelope, Logarithmic L24
GATE,
Logarithmic and I/Q detectors &
IES
Detector, I/Q L25
Detector.
10 Automatic Automatic Detection
Detection - CFAR
****
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFDocument136 pages021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFmekidmu tadesse100% (1)
- Hollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFDocument20 pagesHollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFMichael Wiese Productions0% (1)
- NRSPDocument27 pagesNRSPMuhammad Farhan67% (3)
- CONNECTIFYDocument3 pagesCONNECTIFYAbhishek KulshresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- tsb16 0008 PDFDocument1 pagetsb16 0008 PDFCandy QuailPas encore d'évaluation
- Describing An Object - PPTDocument17 pagesDescribing An Object - PPThanzqanif azqaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution BrochureDocument4 pagesEvolution Brochurelucas28031978Pas encore d'évaluation
- (V) 2020-Using Extensive Reading in Improving Reading Speed and Level of Reading Comprehension of StudentsDocument7 pages(V) 2020-Using Extensive Reading in Improving Reading Speed and Level of Reading Comprehension of StudentsMEYTA RAHMATUL AZKIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Cats - CopioniDocument64 pagesCats - CopioniINES ALIPRANDIPas encore d'évaluation
- List of DEA SoftwareDocument12 pagesList of DEA SoftwareRohit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CM Template For Flora and FaunaDocument3 pagesCM Template For Flora and FaunaJonathan Renier Verzosa0% (1)
- AIIMS Mental Health Nursing Exam ReviewDocument28 pagesAIIMS Mental Health Nursing Exam ReviewImraan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Indra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043Document28 pagesIndra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043AnhTuấnPhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Membrane in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument13 pagesAmniotic Membrane in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgerySooraj SPas encore d'évaluation
- Principal Component Analysis of Protein DynamicsDocument5 pagesPrincipal Component Analysis of Protein DynamicsmnstnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs On RH IncompatibilityDocument17 pagesCs On RH IncompatibilityRupali Arora100% (2)
- 2020 - Audcap1 - 2.3 RCCM - BunagDocument1 page2020 - Audcap1 - 2.3 RCCM - BunagSherilyn BunagPas encore d'évaluation
- Lending Tree PDFDocument14 pagesLending Tree PDFAlex OanonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Handbook MSC Marketing Sept2022Document58 pagesCourse Handbook MSC Marketing Sept2022Tauseef JamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduDocument34 pagesProgramming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduNaruto DragneelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Nor-man KusainPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo de Investigación FormativaDocument75 pagesTrabajo de Investigación Formativalucio RPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Acron PharmaDocument23 pagesCase Acron PharmanishanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Purp Com Lesson 1.2Document2 pagesPurp Com Lesson 1.2bualjuldeeangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Manual TempoLink 551986 enDocument12 pagesOperation Manual TempoLink 551986 enBryan AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringDocument16 pagesGujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringumodiPas encore d'évaluation
- PSAII Final EXAMDocument15 pagesPSAII Final EXAMdaveadePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One: Business Studies Class XI Anmol Ratna TuladharDocument39 pagesChapter One: Business Studies Class XI Anmol Ratna TuladharAahana AahanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPDocument10 pages50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPsivananda11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 5Document22 pagesLec 5Abcdefgh EfghabcdPas encore d'évaluation