Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Thermal Resistance of Composite Wall
Transféré par
KTINE08Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Thermal Resistance of Composite Wall
Transféré par
KTINE08Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES: HEAT TRANSFER
SOLVED PROBLEMS
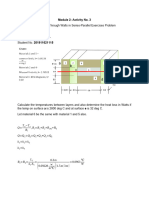
Consider a composite wall that includes an 8-mm thick hardwood siding (k= 0.094 W/mK), 40-
mm by 130-mm hardwood studs (k= 0.16 W/mK) on 0.65-m centers with glass fiber
insulations (paper-faced, 28 kg/m3) (k= 0.038 W/mK), and a 12-mm layer of gypsum
(vermiculite) (k= 0.17 W/mK) wall board. What is the thermal resistance associated with a
wall that is 2.5 m high by 6.5 m wide (having 10 studs, each 2.5 m high)?
Source: Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 6 th edition, by Incropera, et al
SOLUTION:
Mode of Heat Transfer: conduction with resistances in series and parallel
1 RT
Rwall= =
10
10
( R1 )
T
RT =R A + R + R D
1
RT =R A + + RD
1 1
+
R B RC
xA 0.008 m K
RA= = =0.0524
kA AA W W
( 0. 094
mK )( 0.65 m x 2.5 m )
xB 0.130 m K
RB = = =8.125
kB AB W
(0. 16 mW K )( 0. 04 m x 2.5 m )
ENGR. RONNIE V. FLORES Page 1
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES: HEAT TRANSFER
SOLVED PROBLEMS
xC 0.130 m K
RC = = =2.2433
k C AC W W
( 0.038
m K )
( 0.6 1 m x 2.5 m )
xD 0.0 12 m K
R D= = =0.0434
kD AD W
(0. 17 mW K )( 0.65 m x 2.5 m )
K 1 m K
RT =0.0524 + + 0.0434
W 1 1 W
+
K K
8.125 2.2433
W W
K
RT =1.8537
W
K
1.8537
W
Rwall=
10
K
Rwall=0.18537
W
ENGR. RONNIE V. FLORES Page 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NSCP 2010 Deadload and Live Load Specifications for Steel StructuresDocument7 pagesNSCP 2010 Deadload and Live Load Specifications for Steel StructuresIan Dave AdvinculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems in Heat TransferDocument51 pagesSolved Problems in Heat Transfermersad100% (3)
- 5 Examples Shear WallDocument15 pages5 Examples Shear WallRacharla Narasimha Raju Varma100% (2)
- Loadings - NSCP 2015 - 2 Storey Residential Concrete StructureDocument48 pagesLoadings - NSCP 2015 - 2 Storey Residential Concrete StructureRyan MacutoPas encore d'évaluation
- PurlinDocument12 pagesPurlinKhandaker Khairul Alam0% (1)
- Ampacity CalculationDocument6 pagesAmpacity CalculationMohamad HishamPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Absorption Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesGas Absorption Lecture NotesMark Guevarra0% (1)
- CIT-U Heat Transfer GuideDocument113 pagesCIT-U Heat Transfer GuideRoy Christian OroPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Grade Waste Heat Recovery For Optimized Energy Efficiencies and Enhanced Sustainability in Process Industries A Comprehensive ReviewDocument12 pagesLow Grade Waste Heat Recovery For Optimized Energy Efficiencies and Enhanced Sustainability in Process Industries A Comprehensive ReviewEhab Sabry100% (1)
- RESIDENTIAL BUILDING DESIGN USING STAAD & CONCRETE DESIGNERDocument46 pagesRESIDENTIAL BUILDING DESIGN USING STAAD & CONCRETE DESIGNERKenneth LauronPas encore d'évaluation
- InsulationDocument6 pagesInsulationmkha87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat loss calculation for a steel tankDocument3 pagesHeat loss calculation for a steel tankpamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystallizer SelectionDocument8 pagesCrystallizer SelectionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 4M3 Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocument74 pages2013 4M3 Liquid Liquid ExtractionAndré Mendes PiolPas encore d'évaluation
- 15-JWM-Module 15 Mechanical Plumbing and El PDFDocument83 pages15-JWM-Module 15 Mechanical Plumbing and El PDFP V Kolekar0% (1)
- CRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONDocument42 pagesCRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONKTINE0894% (16)
- Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 SolutionsAnonymous GjWVoVAnWYPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrieration Unit Lab ReportDocument29 pagesRefrieration Unit Lab ReportNor Elina Ahmad100% (9)
- Strap Footing Working 1Document3 pagesStrap Footing Working 1Mainali IshuPas encore d'évaluation
- SelectionDocument1 pageSelectionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer Through a Refrigerator WallDocument66 pagesHeat Transfer Through a Refrigerator WallLove StrikePas encore d'évaluation
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument65 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure Fluidssyayaj dhiniPas encore d'évaluation
- K Value DepriesterDocument4 pagesK Value DepriesterHede HödöPas encore d'évaluation
- HT-027 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT-027 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Unit 2) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)Document7 pages(Unit 2) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)somenewguyonthewebPas encore d'évaluation
- Δt R (T − T) +: T I O Ln (R2 R1) 2Πkl 1 Ho AoDocument3 pagesΔt R (T − T) +: T I O Ln (R2 R1) 2Πkl 1 Ho AoLj SalomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - TutorialDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - TutorialDavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Question 11Document4 pagesQuestion 11maniPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2serizawa91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Online WK 2 Session 2 - Sample 2 Problem Conduction On Plane Wall InstructorDocument1 pageOnline WK 2 Session 2 - Sample 2 Problem Conduction On Plane Wall InstructorGr MacopiaPas encore d'évaluation
- All 10Document11 pagesAll 10YacelinPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Soal Radiasi Dan KonveksiDocument5 pagesContoh Soal Radiasi Dan Konveksi038 - ahmad sidikPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch2 PDFDocument8 pagesCh2 PDFAlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems in Heat TransferDocument51 pagesSolved Problems in Heat TransferAbenliciousPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectroDocument9 pagesElectromoin19usmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Loads Dead Load: Floor Load Floors RoofDocument22 pagesLoads Dead Load: Floor Load Floors RoofJoshua De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Algoritmo Labo Fenomenos P4 TCDocument1 pageAlgoritmo Labo Fenomenos P4 TCJosue David Valerio MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat and Mass Transfer: Unit IDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: Unit ISajad AsemPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-01-20 Thesis Structural DesignDocument3 pages01-01-20 Thesis Structural DesignGui EshPas encore d'évaluation
- InsulationDocument1 pageInsulationCesar Ricardo Lopez ValerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Retaining Wall Design Excel Sheet As Per ACI CodeDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Design Excel Sheet As Per ACI CodeP BalajiPas encore d'évaluation
- HeatDocument2 pagesHeatFarrahxviiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capítulo 03 (PDF - Io)Document1 pageCapítulo 03 (PDF - Io)MATEUSPPPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE 306 - Solved Problems-2Document1 pageCHE 306 - Solved Problems-2Garcia Raph100% (2)
- Jawaban KFDocument3 pagesJawaban KFvianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Exercises Problem 3-1Document3 pagesLesson 2 Exercises Problem 3-1esclitoarhonPas encore d'évaluation
- LOW VOLTAGE CABLE FORMULAS AND RESISTANCE TABLEDocument4 pagesLOW VOLTAGE CABLE FORMULAS AND RESISTANCE TABLEamir amirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5: Electrical Analogy For Conduction ProblemsDocument6 pagesLesson 5: Electrical Analogy For Conduction Problemsmehaksinghgill098Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Mechanics 1Document3 pagesPhysics Mechanics 1Dian Ratri CPas encore d'évaluation
- Saturated Steam Metal Wall 1 Outer Asbestos 3Document4 pagesSaturated Steam Metal Wall 1 Outer Asbestos 3raras atiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving for Moment Values and Reinforcements in a Two-Way SlabDocument904 pagesSolving for Moment Values and Reinforcements in a Two-Way SlabRussell RaferPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem No.2 Conduction Through Cylindrical PipeDocument3 pagesProblem No.2 Conduction Through Cylindrical Pipeariel darisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV and V Solved ProplemsDocument30 pagesUnit IV and V Solved ProplemsRajasekar KaruppusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Examples - Heat Transfer - 1ET1010501 - CompressedDocument69 pagesSolved Examples - Heat Transfer - 1ET1010501 - CompressedPatel SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Exercises Problem 2Document3 pagesLesson 2 Exercises Problem 2esclitoarhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Solución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2Document7 pagesSolución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2SpanishRacingPas encore d'évaluation
- Uts Opmp - Ramadhan - 1800020148 - Kelas CDocument6 pagesUts Opmp - Ramadhan - 1800020148 - Kelas CAnnanda AdhiPutra MPas encore d'évaluation
- O B F 1/ 2 F o C, F oDocument2 pagesO B F 1/ 2 F o C, F oAbhinash KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- HT Solved NumericalsDocument56 pagesHT Solved NumericalsKiran AkkoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Capítulo 2 - IncroperaDocument33 pagesCapítulo 2 - IncroperaCaio MunizPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Problems ConductionDocument9 pagesExample Problems ConductionAJ100% (1)
- Parallel ResonanceDocument4 pagesParallel ResonancesreekanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Valid of Turbulent Flow: The Chemical Engineers' Resource PageDocument8 pagesValid of Turbulent Flow: The Chemical Engineers' Resource PagebunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Purlins 2aDocument1 pagePurlins 2aKrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicio MutoDocument39 pagesEjercicio MutoJhostinMundacaDejoPas encore d'évaluation
- STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS TITLEDocument9 pagesSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS TITLEjohnnycollidePas encore d'évaluation
- SEISMIC SHEAR WALL STIFFNESSDocument15 pagesSEISMIC SHEAR WALL STIFFNESSVenkat Deepak SarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Point Voltage CalculationDocument1 pageKnee Point Voltage CalculationredwariorPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set - Settling and SedimentationDocument1 pageProblem Set - Settling and SedimentationKTINE08100% (1)
- HT 033 SolutionDocument6 pagesHT 033 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Q A H T TDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Q A H T TKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT-029 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT-029 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT 034 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT 034 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT 036 SolutionDocument1 pageHT 036 SolutionKTINE08100% (2)
- Chemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: T t T t WC Mc K K θDocument1 pageChemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: T t T t WC Mc K K θKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT 032 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT 032 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT 030 SolutionDocument3 pagesHT 030 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- HT-026 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT-026 SolutionKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lenses Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageLenses Practice ProblemsKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacture of Sulfuric AcidDocument9 pagesManufacture of Sulfuric AcidDiajeng M.100% (1)
- Evaluation Form Pnri SeminarDocument2 pagesEvaluation Form Pnri SeminarKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - Process Dynamic Models PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 2 - Process Dynamic Models PDFnoteasytobebooPas encore d'évaluation
- IEC Written ReportDocument9 pagesIEC Written ReportKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Process 3 For Soda AshDocument2 pagesProcess 3 For Soda AshKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Floor Plan (Testimonial Dinner)Document1 pageFloor Plan (Testimonial Dinner)KTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudiesDocument46 pagesCase StudiesKTINE080% (1)
- How students evaluated their math tutorDocument5 pagesHow students evaluated their math tutorKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation Form Pnri SeminarDocument2 pagesEvaluation Form Pnri SeminarKTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Republic Act No. 318Document37 pagesRepublic Act No. 318KTINE08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indra: A - INST/K. Fujita 11-SEP-2018Document13 pagesIndra: A - INST/K. Fujita 11-SEP-2018med chabanePas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamic Properties of R134a (1112-Tetrafluoroethane) PDFDocument11 pagesThermodynamic Properties of R134a (1112-Tetrafluoroethane) PDFJuan Daniel Perez LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- QB Unit 1Document6 pagesQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Problem - Hydro, Steam & Geo PlantDocument4 pagesSample Problem - Hydro, Steam & Geo Plantibong tiririt0% (1)
- BARC Interview Questions Glassdoor Co PDFDocument5 pagesBARC Interview Questions Glassdoor Co PDFRajat kumbharPas encore d'évaluation
- HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER LAB MANUAL COMPOSITE WALL APPARATUSDocument6 pagesHEAT AND MASS TRANSFER LAB MANUAL COMPOSITE WALL APPARATUSVillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chilled Water Flow, Pipe SizeDocument3 pagesChilled Water Flow, Pipe SizeSatya N.GPas encore d'évaluation
- Bimetallic Thermometer PDFDocument3 pagesBimetallic Thermometer PDFHesti Nur AiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Development and Evaluation of A Night Ventilation Precooling AlgorithmDocument26 pagesDevelopment and Evaluation of A Night Ventilation Precooling AlgorithmEx LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Past Present and Future Perspectives of Refrigerants in Air-Conditioning Refrigeration and Heat Pump ApplicationsDocument13 pagesPast Present and Future Perspectives of Refrigerants in Air-Conditioning Refrigeration and Heat Pump ApplicationsviclucPas encore d'évaluation
- MECE2640 Chapter 3Document33 pagesMECE2640 Chapter 3colaarawrPas encore d'évaluation
- Modelling Annealing Lehrs For Flat Glass: Robert GardonDocument8 pagesModelling Annealing Lehrs For Flat Glass: Robert GardonAmer AlkalaifhPas encore d'évaluation
- TT7-2.2KC3-2 (Rev 02)Document5 pagesTT7-2.2KC3-2 (Rev 02)Jacenty FrymusPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry - Experiment 1Document8 pagesPhysical Chemistry - Experiment 1Ronald Deck Yami0% (1)
- SEM-3 and 4 (15 Scheme-CBCS)Document64 pagesSEM-3 and 4 (15 Scheme-CBCS)Charanganesh VaithianathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Chemistry Question Bank Units on Polymer Chemistry, Thermodynamics, Spectroscopy, Phase Rule, and NanochemistryDocument2 pagesEngineering Chemistry Question Bank Units on Polymer Chemistry, Thermodynamics, Spectroscopy, Phase Rule, and NanochemistryMohammed ThawfeeqPas encore d'évaluation
- AHU Guide to Components and OperationDocument44 pagesAHU Guide to Components and OperationreshmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 30RB - RQ - Carrier - ManualzzDocument19 pages30RB - RQ - Carrier - ManualzzmelodyPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 3 y 4Document34 pagesClase 3 y 4EdinberSPPas encore d'évaluation
- R407C R407C: Technical Manual Manual TécnicoDocument80 pagesR407C R407C: Technical Manual Manual TécnicoramonmartinezcatalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 231 All Instructors Whharris 11-9-17SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesME 231 All Instructors Whharris 11-9-17SOLUTIONEstebanGiraldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Exam Questions Focus on Cycles, Processes, and Efficiency CalculationsDocument26 pagesThermodynamics Exam Questions Focus on Cycles, Processes, and Efficiency CalculationsSuhas G MPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of Drying Characteristics of A Solid MaterialDocument5 pagesRate of Drying Characteristics of A Solid MaterialYasir MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- GE T700 Gas Turbine Engine (Updated 7 - 22 - 2014)Document4 pagesGE T700 Gas Turbine Engine (Updated 7 - 22 - 2014)Habib ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- FBHVN-0916-C Air Cooled PackageDocument6 pagesFBHVN-0916-C Air Cooled PackageJeghiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stephen Hawking: Black Holes and Other Contributions From One of The Greatest Scientists of Our TimeDocument5 pagesStephen Hawking: Black Holes and Other Contributions From One of The Greatest Scientists of Our TimeIJAERS JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - PychrometryDocument90 pagesLecture 2 - PychrometryTajul Aiman Tajul AnuarPas encore d'évaluation