Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
165 6 2
Transféré par
Carlos A. Carpio CárdenasTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
165 6 2
Transféré par
Carlos A. Carpio CárdenasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CURRENT IN AMPERES
10000
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
.5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1000 1000
900 900
140K
200K
800 800
700 700
600 600
6K, 10K, 15K, 25K, 40K, 65K,
500 100K, 140K, AND 200K ARE 500
PREFERRED RATINGS; 8K,
100K
10K
12K
15K
20K
25K
40K
50K
65K
80K
400 400
30K
12K, 20K, 30K, 50K, AND
6K
8K
80K ARE INTERMEDIATE
300 300
RATINGS.
200 200
100 100
90 90
80 80
70 70
60 60
50 50
40 40
30 30
20 20
10 10
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
TIME IN SECONDS
TIME IN SECONDS
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
.9 .9
.8 .8
.7 .7
.6 .6
.5 .5
.4 .4
.3 .3
.2 .2
.1 .1
.09 .09
.08 .08
.07 .07
.06 .06
.05 .05
.04 .04
.03 .03
.02 .02
.01 .01
.5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
CURRENT IN AMPERES
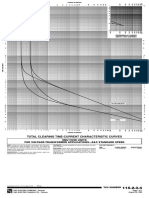
TOTAL CLEARING TIME-CURRENT CHARACTERISTIC CURVES
POSITROL FUSE LINKSS&C K SPEED
BASISThese fuse links are tested in accordance with the proce- COORDINATIONThese curves represent the total time required for 4. Coordination to higher levels of fault current with respect to
dures described in ANSI Standard C37.41-1981, to comply with a fuse link to melt and interrupt a fault current, and should be fol- sequence operation of fuse links.
ANSI Standard C37.42-1981. As required by these standards, the lowed in coordination problems where fuse links are applied as
The breadth of coordination described above can be obtained
minimum melting current is not less than 200% of fuse-link ampere protecting devices.
only by the use of S&C Positrol Fuse Links. No fuse link of low-tem-
rating, and the minimum melting and total clearing curves are
Any preloading reduces melting time. With respect to the pro- perature element construction (tin, lap-joint) can provide similar per-
based on tests starting with the fuse link at an ambient temperature
tected fuse, the effect of preloading must be determined and adjust- formance.
of 25C and no initial load.
ments made to its minimum melting curve:
NOTEA coordination scheme designed to take full advantage of
CONSTRUCTIONFusible elements for fuse links rated 6K through 1. When close coordination is required;
the nondamageability and the superior coordination capabilities of
100K amperes are silver, helically coiled; fusible elements for fuse 2. When automatic circuit reclosers or three-shot cutouts are
S&C Positrol Fuse Links may not function satisfactorily if fuse links
links rated 140K and 200K amperes are silver-tin. All are of solder- involved;
of the same speed but of other makes are substituted. However,
less construction. 3. When, regardless of the preciseness of coordination, the pro-
S&C K Speed Positrol Fuse Links can replace, on a one-for-one
tected fuse is subjected to temporary overloads.
TOLERANCESCurves are plotted to maximum test points. All varia- basis, other manufacturers K speed fuse links in existing coordi-
tions are minus. If close coordination is to be achieved, overloading must be nation schemes. Such replacements, unlike tin-element fuse links,
avoided since it causes a significant shift in time-current character- are not subject to nuisance fuse operations (sneakouts) due to
APPLICATIONLike all high-voltage fuses, these fuse links are
istics. damage from surge currents, load cycling, vibration, and aging.
intended to accommodate overloads, not to interrupt them. Accord-
ingly, they feature fusible elements which are designed with a min- The exclusive use of S&C Positrol Fuse Linksbecause of their FUSE LINKS AVAILABLE
imum melting current of 200% of the fuse-link ampere rating (for inherently narrower tolerance band and because of their nondam-
Style Ampere Ratings
fuse links rated 100K amperes or less) or 220% of the fuse-link ageabilitywill expand the scope of coordination as follows:
Universal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6K through 200K
ampere rating (for fuse links rated over 100K amperes). As a result,
1. Coordination of preferred with adjacent intermediate ratings, Extra-Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6K through 200K
these fuse links have considerable peak-load capabilities; however,
giving twice as many sectionalizing points. This is true for the
they should never be exposed to loading in excess of the peak-load
sequence operation of fuse links alone, or for the sequence
capabilities listed in S&C Data Bulletin 350-190.
operation of fuse links coordinated with automatic circuit
Since fuse links having silver element construction are not sub- reclosers.
ject to damage by aging or transient overcurrents, it is unnecessary 2. Coordination of a larger number of fuse-link ratings with a
to replace unblown fuse links of such construction in single-phase or given automatic circuit recloser between the fast and retarded
three-phase installations when one or more fuse links have blown. curves.
However, it is advisable to replace unblown silver-tin element fuse 3. Coordination through a greater range, and to higher levels of
links under the same conditions, sincewhile not subject to aging fault current, with respect to automatic circuit reclosers.
they may be damaged by transient overcurrents.
Supersedes TCC No. 165-6-2 dated 12-17-84 c1986
TCC NUMBER 165-6-2
s S&C ELECTRIC COMPANY Chicago
S&C ELECTRIC CANADA LTD. Toronto
Page 1 of 1
January 20, 1986
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 165 6 PDFDocument1 page165 6 PDFGonzalo Peñafiel CondoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Fault Tamer Fuse LimitersDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Fault Tamer Fuse LimitersStoner WddPas encore d'évaluation
- TCC Number 450 8 PDFDocument1 pageTCC Number 450 8 PDFjavier jimenez rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Smu Fuse Units For Voltage-Transformer Applications-S&C Standard SpeedDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: Smu Fuse Units For Voltage-Transformer Applications-S&C Standard SpeedObed GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minimum Melting Time-Current Characteristic CurvesDocument1 pageMinimum Melting Time-Current Characteristic CurvesObed GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Available Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Document1 pageAvailable Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)jurica_2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Available Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Document1 pageAvailable Three-Phase Symmetrical Short-Circuit Current (Kiloamps)Amr AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiples of Ground Fault Pickup SettingDocument1 pageMultiples of Ground Fault Pickup SettingjosehenriquezsotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shift index curve for long-time overcurrent protectionDocument1 pageShift index curve for long-time overcurrent protectionPrathap KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive guide to circuit breaker ground trip element settingsDocument2 pagesComprehensive guide to circuit breaker ground trip element settingsjurica_2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- DES-101B: Multiple of Trip Rating PlugDocument1 pageDES-101B: Multiple of Trip Rating Plugjurica_2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Curvas FusiblesDocument2 pagesCurvas FusibleswilmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Des-095b - Long TimeDocument1 pageDes-095b - Long Timeshrikanth5singhPas encore d'évaluation
- TCC Number 115 4Document1 pageTCC Number 115 4Dennis RimandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Current in Amperes - An Illustrated ChartDocument1 pageCurrent in Amperes - An Illustrated ChartRafaelo09Pas encore d'évaluation
- DES-095B: Approximately (0.784-Actual Pickup)Document1 pageDES-095B: Approximately (0.784-Actual Pickup)shrikanth5singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerja-Kerja Menaiktaraf Sistem Takungan Air Mentah Di Mukasauk Loji Rawatan Air (Lra) Kina Benuwa, Wilayah Persekutuan LabuanDocument1 pageKerja-Kerja Menaiktaraf Sistem Takungan Air Mentah Di Mukasauk Loji Rawatan Air (Lra) Kina Benuwa, Wilayah Persekutuan LabuanFarith AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- GES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingDocument1 pageGES-6121C: Multiples of Current RatingAdolfo Sotomayor BurgosPas encore d'évaluation
- GES-6122C: Multiples of Current RatingDocument1 pageGES-6122C: Multiples of Current RatingAdolfo Sotomayor BurgosPas encore d'évaluation
- Long-time delay curve shift index for high ambient temperaturesDocument1 pageLong-time delay curve shift index for high ambient temperaturesBolivar MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Shift Index Temperature ChartDocument1 pageShift Index Temperature ChartBolivar MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Rating Multiples ChartDocument1 pageCurrent Rating Multiples ChartAmr AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 9F54Dfc Series: Current in AmperesDocument1 pageModel 9F54Dfc Series: Current in AmperesPaulo H TavaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Long-time delay shift index chartDocument1 pageLong-time delay shift index chartMUSIC ELECPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit Breakers Q LineDocument1 pageMultiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit Breakers Q LineMUSIC ELECPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit BreakersDocument1 pageMultiples of Current Rating: Molded Case Circuit BreakersAmr AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily COVID-19 UpdateDocument3 pagesDaily COVID-19 UpdateFikri MaulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- TCC Number 153 2 PDFDocument1 pageTCC Number 153 2 PDFOmar VazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.5 5.0 Ton at 600mm Load Center: SH1F4-1 / 13 Apr. '10Document30 pages3.5 5.0 Ton at 600mm Load Center: SH1F4-1 / 13 Apr. '10JulianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground Floor PlanDocument1 pageGround Floor Plansydney augustPas encore d'évaluation
- CIVIL BuildingDocument1 pageCIVIL BuildingChandra manandharPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo ConductosDocument8 pagesCatalogo ConductosCarlos ManriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Minimum Tripping Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyDocument1 pageMinimum Tripping Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyEddy UberguagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyDocument1 pageTotal Clearing Time-Current Characteristic Curves: S&C Electric CompanyEddy UberguagaPas encore d'évaluation
- All TCSDocument9 pagesAll TCSPurshottam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nifty Technical AnalysisDocument136 pagesNifty Technical Analysisapi-3728932Pas encore d'évaluation
- Current in Amperes ChartDocument1 pageCurrent in Amperes ChartEddy UberguagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Plan 2022 - Koordinat - Papadino-ModelDocument1 pageMaster Plan 2022 - Koordinat - Papadino-ModelASPas encore d'évaluation
- P2 PlanDocument1 pageP2 PlanFrancis Lloyd MalganaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rop Sinaw Cable & Water Line RouteDocument1 pageRop Sinaw Cable & Water Line RouteAkbar DahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Floor Power Layout: Scale 1:100MDocument1 pageSecond Floor Power Layout: Scale 1:100MJane JimesPas encore d'évaluation
- Kolkata 700 001 7, Hare StreetDocument1 pageKolkata 700 001 7, Hare Streetkoushik42000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Office A1 PDFDocument1 pageOffice A1 PDFalfredo agsunodPas encore d'évaluation
- Forklift NISSAN Model W1F4A40UDocument12 pagesForklift NISSAN Model W1F4A40UfitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Schedule of Door and WindowsDocument1 pageSchedule of Door and Windowsalezandro del rossiPas encore d'évaluation
- ADA Index and Sample Output PDFDocument8 pagesADA Index and Sample Output PDFKavita GohelPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 - Commissary ELEC Rev 00-E-3Document1 page00 - Commissary ELEC Rev 00-E-3edmar jay conchadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Butterfly Valve Head LossDocument1 pageButterfly Valve Head LosskuchaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Floor Plan Roof Plan: Roof Eaves Line Roof Eaves LineDocument1 pageFloor Plan Roof Plan: Roof Eaves Line Roof Eaves LineJifty Parojinog Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- PARAN3E ExerciseNo2 Layout1Document1 pagePARAN3E ExerciseNo2 Layout1Mickaela Kassandra ParanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nivafer Layout PDFDocument1 pageNivafer Layout PDFOdubiyi AdewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Wadd ChartDocument39 pagesWadd ChartIlhamPas encore d'évaluation
- FSXA Quick Selection Chart TitleDocument2 pagesFSXA Quick Selection Chart TitleEmmanuel Ber SPas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminary 12.03.2019: Client Global HydroDocument2 pagesPreliminary 12.03.2019: Client Global HydroJoseph NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Site Plan + Luas - 230426 - 223115Document1 pageSite Plan + Luas - 230426 - 223115J.T HalohoPas encore d'évaluation
- A B C D E: Roof Deck PlanDocument1 pageA B C D E: Roof Deck PlanChocoSparklesPas encore d'évaluation
- Denah LT - Dasar Kitchen CikarangDocument1 pageDenah LT - Dasar Kitchen Cikarangbss kateringPas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum Interrupters Technology (07 - 04)Document24 pagesVacuum Interrupters Technology (07 - 04)Carlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal-Clad or Metal-Enclosed Switchgear: What's the DifferenceDocument1 pageMetal-Clad or Metal-Enclosed Switchgear: What's the DifferenceCarlos A. Carpio Cárdenas100% (1)
- Eng MvfusesDocument8 pagesEng MvfusesCarlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- 165 6 2Document1 page165 6 2Carlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- HHBDocument14 pagesHHBCarlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng MvfusesDocument8 pagesEng MvfusesCarlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB High Voltage Fuses CatalogueDocument64 pagesABB High Voltage Fuses CataloguerocketvtPas encore d'évaluation
- Correccion Del Factor de PotenciaDocument28 pagesCorreccion Del Factor de PotenciaTaras MykytyukPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Protection Application HandbookDocument356 pagesABB Protection Application HandbookSyed Muhammad Munavvar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Correccion Del Factor de PotenciaDocument28 pagesCorreccion Del Factor de PotenciaTaras MykytyukPas encore d'évaluation
- TeckCatalogue NEXANS PDFDocument42 pagesTeckCatalogue NEXANS PDFCarlos A. Carpio CárdenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Requirements - Online Casino and Betting v2.1 PDFDocument36 pagesTechnical Requirements - Online Casino and Betting v2.1 PDFDiana IonitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Brushless Motor Pre-Drivers For Paper FeedDocument25 pagesThree-Phase Brushless Motor Pre-Drivers For Paper FeedBruce MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- BB TNS Up 4Document10 pagesBB TNS Up 4Haphaell ResplandesPas encore d'évaluation
- P87.0634-030.317-En V5e Appl PDFDocument61 pagesP87.0634-030.317-En V5e Appl PDFAldo J Briones DorantesPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2Document12 pagesModule 2Earl averzosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sva PDP TV Service ManualDocument30 pagesSva PDP TV Service Manualcapt2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator SimulationDocument20 pagesEvaporator SimulationRaihan HaidarPas encore d'évaluation
- Volvo Penta D6-370Document2 pagesVolvo Penta D6-370Anonymous alQXB11EgQ100% (3)
- Attachment-2, Water Transfer Pump (Movitec)Document5 pagesAttachment-2, Water Transfer Pump (Movitec)Hanugroho AjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Masonry tools guideDocument9 pagesMasonry tools guideAbby MclidPas encore d'évaluation
- Beacons of Discovery: The Worldwide Science of Particle PhysicsDocument28 pagesBeacons of Discovery: The Worldwide Science of Particle PhysicsGagan DhughaPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE484 Note BookDocument104 pagesEEE484 Note BookNazır DoganPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Calculate Your Exterior Square FootageDocument3 pagesHow To Calculate Your Exterior Square FootageSuryaadeviKhatriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Gauss 8Document4 pages2017 Gauss 8xmetal123dev100% (1)
- Rainer Wenty, Plasser & TheurerDocument40 pagesRainer Wenty, Plasser & TheurerLpstokio100% (2)
- Unilateral Tonsil EnlargementDocument5 pagesUnilateral Tonsil EnlargementBryan Albert LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice - Exercise - 2 - Chap 4Document13 pagesPractice - Exercise - 2 - Chap 4drashtipatel6888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Itrainonline MMTK Access Point Configuration HandoutDocument11 pagesItrainonline MMTK Access Point Configuration HandoutSantosh KhadkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Formwork DesignDocument17 pagesConcrete Formwork DesignRsjBugtongPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Vibrating Feeders & ConveyorsDocument8 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Vibrating Feeders & ConveyorsKarin AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- LON Builder ManualDocument26 pagesLON Builder ManualMardo MaddisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits of Sap Hana On Vmware Vsan: Solution BriefDocument4 pagesBenefits of Sap Hana On Vmware Vsan: Solution Briefjalvarez82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methods For Causality Assessment of Adverse Drug.3Document17 pagesMethods For Causality Assessment of Adverse Drug.3Adnan NazirPas encore d'évaluation
- Diploma, Anna University-UG, PG., HSC & SSLC: Ps5006 Design of SubstationsDocument2 pagesDiploma, Anna University-UG, PG., HSC & SSLC: Ps5006 Design of Substationsanon_8292835620% (1)
- Grade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Document15 pagesGrade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Shalini KulshresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- WebAssembly Literacy PDFDocument98 pagesWebAssembly Literacy PDFpayevePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Optical Waveguides: Dr. Lukas ChrostowskiDocument66 pagesIntroduction To Optical Waveguides: Dr. Lukas ChrostowskiTiewsoh LikyntiPas encore d'évaluation
- S7-1200 Programmable Controller - Example - Modbus RTU Master ProgramDocument3 pagesS7-1200 Programmable Controller - Example - Modbus RTU Master ProgramChhoan Nhun100% (1)
- VNLP-an Open Source Framework For Vietnamese Natural Language Processing PDFDocument7 pagesVNLP-an Open Source Framework For Vietnamese Natural Language Processing PDFpbtaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Al KarajiDocument4 pagesAl KarajiAnonymous hcACjq8Pas encore d'évaluation