Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
QMT280
Transféré par
mrr85350 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues1 pageQMT280
Transféré par
mrr8535Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
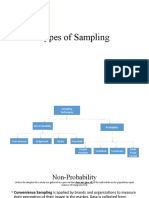
Sampling
Monday, July 12, 2010
7:11 AM
sampling-process of selecting a sample from a population.
In order to obtain accuracy
Expensive
Allows Ensure
interview to interviewer are
clarify terms competent
Sampling technique is used Is done by
Face to face interviews
Sampling technique • Yield high response rates
Limit to people
with telephone
Response are
Non pr0bability probability
lower
• Convenience sampling Other methods Less expensive
○ Recommended for pre-research • e-mail Telephone
○ Respondent chosen because it was at the right time • Srs(simple random sampling • Internet surveys interviews
and right place. ○ Each item in frame list has • sms • asks question from
• Judgemental a same chance of selected aprepared questionaire
○ Selected based on researcger judgement to be a sample, • Interviews are in short
○ Be based on experiences ○ Technique duration
Data collection
• Snowball/chain The frame is method
○ First respondents based on randomly obtained
○ 1st respondent will be asked whether he . she knows Computer generated
others from same targeted population or table of random
• Quota sampling numbers
Direct questionaire
○ same as convenience,differ because, rsearchersmay • Systematic sampling
Direct observation • Researcher will
look for different characteristic ○ k=N/n
• Used in work, studies and great the
○ Limited by a fixed number k=range
organisation respondent ang
N=population size
• Enable researchers to record explain his
n=sample size
what actually happens, not intention b4 giving
○ The first sample element is
to influenced by people say questionaire.
chosen by the range by SRS
○ Then the next element is or think
selected by formula
(r+ak),a=2,3,,,(n-1) Mail questionaire
• Stratified sampling technique • A questionaire will be
○ Divide the population into mailed, and need to
several mutual grup(strata) return it with a Cheaper
○ Elements are usually certain period of Coverage is wider
n probability strentgh weak selected randomly by SRS time No interview influence
sampling ○ The purpose is to divide Has more time think
Convenience Less into more homogenous
sampling Selection bias, not recommended
expensive,time, for descriptive or casual research subgroup
Judgemental convenient • Cluster sampling technique
sampling Does not allow generalization, Rate of respond is
subjective ○ Divide ninto lower
subpopulation(cluster) May a particular type
Quota sampling ○ The subpopulation/cluster
Selection bias, no assurance of people will reply
is selected randomly Only very simple
○ All the elements in the question can be
snowbal/chain Sample can be cluster is to be icluded in
Time consumed asked
controlled by the sample or/ May be a team effort
several chrctr ○ drawn by a probability
Can estimate rare manner
characteristic • Multi-stage
○ Divide population from
Sample random Easy applied,reults Difficult to obtain respondents, cluster to cluster,
sampling can be projected to sometimes no assurance of Should be short and simple>> less time to answer
population representative
Begin with simple and less
Systematic Easuer to implment Can decrease reprsentativeness controversional question
sampoling
techniques
The question must NOT biased towards
Stratified Easy to implemented Difficult to select different 1. Groups
sampling stratas, not feasible for 2. Etnic
techniques stratify many variable 3. Race
4. religion
A questionaire checlist
Cluster sampling Easy to implement,cost Imprecise diffficult to compute can be made by
effective work is reduced and interpret result facilitate
1. Objectives of study
2. Answers sought from
the study
3. Variable used in the
study
4. Methods of data
analysis
QMT280 Page 1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sampling and Data Gathering Techniques: Institute of Computing and Engineering Mathematics DepartmentDocument6 pagesSampling and Data Gathering Techniques: Institute of Computing and Engineering Mathematics DepartmentDanilo Oppus JacobePas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Auditing of Laboratory Quality Management SystemsDocument66 pagesInternal Auditing of Laboratory Quality Management Systemsmarwa100% (4)
- The Master Key System: Unlocking Your Unlimited PotentialDocument164 pagesThe Master Key System: Unlocking Your Unlimited PotentialLuis Oropeza100% (1)
- Laboratory RubricDocument1 pageLaboratory RubricsyedmuhammadtariquePas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling TechniquesDocument17 pagesSampling TechniquesArminda CostunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership and Decision-Making A StudyDocument13 pagesLeadership and Decision-Making A Studyjhoms8100% (1)
- Discipline in Social Sciences: Hermeneutical PhenomenologyDocument12 pagesDiscipline in Social Sciences: Hermeneutical PhenomenologyFrancheska Venize Barola RevillosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blake Topic Bank Working BackwardsDocument15 pagesBlake Topic Bank Working BackwardsDaneil PaulinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Values Education Let ReviewerDocument15 pagesValues Education Let ReviewerDhanz90% (30)
- Midterm Ucsp FinalDocument7 pagesMidterm Ucsp FinalJoe Jayson CaletenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuzzy Logic Control Systems ExplainedDocument7 pagesFuzzy Logic Control Systems ExplainedmeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Looking-Glass: Sociological Perspective: The Self As A Product of SocietyDocument18 pagesThe Looking-Glass: Sociological Perspective: The Self As A Product of SocietyJEMABEL SIDAYEN100% (1)
- Perdev Melc Based Module PDFDocument100 pagesPerdev Melc Based Module PDFShane Favia Lasconia-Maceren70% (10)
- Lecture 11Document2 pagesLecture 11adjsauntiePas encore d'évaluation
- 00d Qualitative - Research - Validity - Mapch7Document1 page00d Qualitative - Research - Validity - Mapch7ika mayasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Research Methods (Session 3 - Sampling Techniques)Document6 pagesBusiness Research Methods (Session 3 - Sampling Techniques)Scorpions StingPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling-MethodsDocument2 pagesSampling-Methodsxellee shethPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-10: Survey Research: Communicating With RespondentsDocument28 pagesChapter-10: Survey Research: Communicating With RespondentsshubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyzing Population, Samples, and Testing for Normality in DataDocument8 pagesAnalyzing Population, Samples, and Testing for Normality in Datamuhammad andrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 4: Population, Sample, and Testing For Normalitas DataDocument8 pagesSection 4: Population, Sample, and Testing For Normalitas Datamuhammad andrianPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Research PDFDocument1 page2 Research PDFLynssey DaniellePas encore d'évaluation
- 271 33 Powerpoint Slides Chapter 6 Types Sources DataDocument59 pages271 33 Powerpoint Slides Chapter 6 Types Sources DataShashank Shekhar100% (1)
- CHAPTER 12: Selecting A SampleDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 12: Selecting A Samplealia.delareinePas encore d'évaluation
- Research Methodology OverviewDocument29 pagesResearch Methodology OverviewMaiden GeePas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Techniques and MethodsDocument43 pagesSampling Techniques and Methodsvinnu kalyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling TechniquesDocument23 pagesSampling TechniquesKanwal KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling: Design and Procedures: Chapter ElevenDocument24 pagesSampling: Design and Procedures: Chapter Elevenrajaraghuramvarma1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quota SamplingDocument15 pagesQuota SamplingVenusya DharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quant METHODSDocument18 pagesQuant METHODSGracePas encore d'évaluation
- CPS211 Guide to Sampling TechniquesDocument31 pagesCPS211 Guide to Sampling TechniquesADREANA FARHANIM MOHD YUSOFPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 7Document20 pagesSession 7Shubham RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Methods ExplainedDocument1 pageSampling Methods ExplainedPamela laquindanumPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Sampling Design and ProceduresDocument21 pages11 Sampling Design and ProceduresAhanafPas encore d'évaluation
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Mapangelica.amandy.gPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Expressions Education Presentation in Orange Green Red Nostalgic Handdrawn StyleDocument19 pagesNumerical Expressions Education Presentation in Orange Green Red Nostalgic Handdrawn StyleZarah Jane SinayPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.Data CollectionDocument1 page1.Data Collectionannabel.turner1412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling DistributionDocument22 pagesSampling DistributionMaria Fe DomondonPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling KKKKDocument21 pagesSampling KKKKShimul HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Tosca and Brown Minimalist Illustrated Job Search Strategy PresentationDocument12 pagesTosca and Brown Minimalist Illustrated Job Search Strategy PresentationRuaa JabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Techniques Education PresentationDocument39 pagesSampling Techniques Education PresentationsanguanmaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Research Session 04Document36 pagesMarketing Research Session 04Harshael SawantPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Ready ReckonerDocument4 pagesReview Ready ReckonerGarima SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Sampling and Data Collection MethodsDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Sampling and Data Collection MethodsJohn SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6 SamplingDocument18 pagesCH 6 Samplingraghvendra2309Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of Research: Understanding Sampling TechniquesDocument18 pagesMethods of Research: Understanding Sampling TechniquesRenj LoisePas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Sampling: Methods, Process and Factors Impacting Sample SizeDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Sampling: Methods, Process and Factors Impacting Sample SizeNawal MuneebPas encore d'évaluation
- Roa Non Probability SamplingDocument12 pagesRoa Non Probability SamplingRuaa JabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling TechniquesDocument8 pagesSampling TechniquesMARIA ABIGAIL PAMAHOYPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Key Sampling TechniquesDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Key Sampling TechniquesSAIRA QAMARPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Research Design From Respondents PerspectiveDocument1 page1 Research Design From Respondents PerspectiveArpana GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniqueDocument11 pagesGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniquepriyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Six Sigma Black Belt Measure ChapterDocument196 pagesSix Sigma Black Belt Measure ChapterMedia Team100% (1)
- Rural Marketing Research - Session 3Document46 pagesRural Marketing Research - Session 3Sankalpa KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Target Population: Rely On Probability and Non ProbabilityDocument15 pagesTarget Population: Rely On Probability and Non ProbabilityNoufal Asif0% (1)
- (I) (Ii) (Iii)Document1 page(I) (Ii) (Iii)Sai PrasannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Include a brief description for each designDocument23 pagesInclude a brief description for each designWazzupPas encore d'évaluation
- AI and Expert SystemDocument23 pagesAI and Expert SystemCharles TomyPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of SamplingDocument13 pagesTypes of SamplingCAELUM ONLINEPas encore d'évaluation
- The Influence of Values On Technology Adoption: Using A Mixed-Method DesignDocument11 pagesThe Influence of Values On Technology Adoption: Using A Mixed-Method DesignSonal GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement & Data Collection ConceptsDocument30 pagesMeasurement & Data Collection ConceptsRakshith gowda H DPas encore d'évaluation
- Laoag City, Ilocos Norte: Mat 101: Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument46 pagesLaoag City, Ilocos Norte: Mat 101: Mathematics in The Modern WorldShannaiah Kim BaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation1 Sampling TheoryDocument21 pagesPresentation1 Sampling TheoryshouryaPas encore d'évaluation
- A/B Testing, Theory, Practice and Pitfalls: SrimugunthanDocument33 pagesA/B Testing, Theory, Practice and Pitfalls: SrimugunthanPratyush KharePas encore d'évaluation
- Non Probability Sampling TechniquesDocument11 pagesNon Probability Sampling Techniquesrani hadassa pacisPas encore d'évaluation
- Module0 IntroductionDocument27 pagesModule0 Introductionrohan kalidindiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Pre - Workshop - Week - 6Document46 pages2018 Pre - Workshop - Week - 6Rafi RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Selecting The Reserarch Question 2016Document26 pagesSelecting The Reserarch Question 2016ChristoPher TorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes SamplingDocument26 pagesLecture Notes SamplingSrikumar Revanur100% (1)
- 01 Obtaining Data Part 01Document37 pages01 Obtaining Data Part 01Princess Diane SuyatPas encore d'évaluation
- Curmadev FixxDocument24 pagesCurmadev FixxCahaya Qur'aniPas encore d'évaluation
- OLS estimation questionsDocument26 pagesOLS estimation questionsgleniaPas encore d'évaluation
- ForeignDocument13 pagesForeignJovelyn AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 1 Information: Your TaskDocument3 pagesAssessment 1 Information: Your TaskPooja Nikunj AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- OB c2 Personality, Learning, Attitudes and PerceptionDocument35 pagesOB c2 Personality, Learning, Attitudes and Perceptionkuyu2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- BSED-SCIENCE3B GROUP VI ppt.7Document11 pagesBSED-SCIENCE3B GROUP VI ppt.7Novy SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Technology and Culture, Identifying Fragmentary and Holistic Perspectives of Culture - Michael GallivanDocument44 pagesInformation Technology and Culture, Identifying Fragmentary and Holistic Perspectives of Culture - Michael Gallivanb7826509Pas encore d'évaluation
- Personality Psychology As Science: Research Methods: Sixth EditionDocument44 pagesPersonality Psychology As Science: Research Methods: Sixth EditionorsibogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Allen - Factual AmbiguityDocument38 pagesAllen - Factual Ambiguitybeltran-pinillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Korean Wave: It's Impact To The Senior High School Students' LifestyleDocument7 pagesKorean Wave: It's Impact To The Senior High School Students' LifestyleGlaizeCharm SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Leading Teams - Intro To HackmanDocument7 pagesLeading Teams - Intro To HackmanBoon LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuzzy Numbers & Fuzzy EquationDocument51 pagesFuzzy Numbers & Fuzzy Equationvpkvikas100% (1)
- Science Notebook - Methods of ScienceDocument6 pagesScience Notebook - Methods of ScienceJean Carlos Tejada SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Social Work Theories in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesMajor Social Work Theories in 40 CharactersAnnbonavie BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research On AppleDocument2 pagesResearch On Applesrishti bhatejaPas encore d'évaluation
- StatisticsDocument4 pagesStatisticsPakistani ReactionPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 15 Validity of Measurement and Reliability PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 15 Validity of Measurement and Reliability PDFMarkChristianRobleAlmazanPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Social PsychologyDocument21 pagesHistory of Social PsychologyHafsa KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- EthicsDocument23 pagesEthicsSining PanaghoyPas encore d'évaluation