Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas 1 Petrologi Filzha
Transféré par
Filzha Leemin0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues3 pagesThis table provides useful criteria for distinguishing igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks by comparing their typical examples, characteristic minerals, textures observable in hand specimens, common structures observable in the field, other features, and geographic and geologic positions of outcrops in 3 sentences or less. It outlines that igneous rocks form from cooling magma and have interlocking crystals, sedimentary rocks form from compressed particles and have layers and fossils, and metamorphic rocks were once igneous or sedimentary but were changed by heat and pressure and retain traces of their original structures.
Description originale:
petro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis table provides useful criteria for distinguishing igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks by comparing their typical examples, characteristic minerals, textures observable in hand specimens, common structures observable in the field, other features, and geographic and geologic positions of outcrops in 3 sentences or less. It outlines that igneous rocks form from cooling magma and have interlocking crystals, sedimentary rocks form from compressed particles and have layers and fossils, and metamorphic rocks were once igneous or sedimentary but were changed by heat and pressure and retain traces of their original structures.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues3 pagesTugas 1 Petrologi Filzha
Transféré par
Filzha LeeminThis table provides useful criteria for distinguishing igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks by comparing their typical examples, characteristic minerals, textures observable in hand specimens, common structures observable in the field, other features, and geographic and geologic positions of outcrops in 3 sentences or less. It outlines that igneous rocks form from cooling magma and have interlocking crystals, sedimentary rocks form from compressed particles and have layers and fossils, and metamorphic rocks were once igneous or sedimentary but were changed by heat and pressure and retain traces of their original structures.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
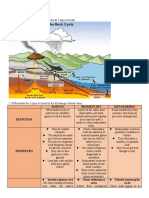
TABLE
Useful Criteria for Distinguishing Igneous , Sedimentary , And ,
Metamorphic Rocks
Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic
Typical Examples
Granite Shale Gneiss
Gabbro Sandstone Schist
Peridotite Limestone Marble
Basalt Conglomerate Quartzite
Rhyolite, etc Tillitle , etc Slate , etc
Characteristic minerals
Orthoclase Mostly quartz , calcite , or Staurolite
mostly clay minerals
Perthite Mineral of chemical and Kyanite
organic precipitates
Microcline Halite Andalusite
Plagioclas Sylvite Sillimanite
Quartz Gypsum Cordierite
Nepheline Anhydrite Garnet
Leucite Glauconite Zeosite
Hornblende Chert Wollastonite
Augite Carbonat, etc , Tremolite
Biotite Cholorite
Muscovite Graphite
Olivine Talc , etc
Typical texterus observable in hand specimen
Glassy , vesicular , Textural changes in bands Cristaloblastic , brecciated ,
amygdaloidal , granitoid , laterally and vertically granulated , augen , mortar ,
gabbroic , diabasic , Fragmental , oolitice , flaser , hornfelsic
graphic , porphyritic , pisolitic , porous , angular ,
miarolitic , etc subangular , rounded , and
sorted grains
Common structures observable is the field
Coloumnar joints , Well sratified , Parallelism of mineral grains ,
spheroidal weathering , crossbedding , mud banding , foliation , lineation
occasionally , banded , cracks , ripple marks , schistosity , Seconadary
folition , flow , etc footprints , concretions , cleavage independent of
septaria , bedding , bedding , interlocking grains ,
lamination , lenses , distorted pebbles , crystals ,
fassility etc Bent cleavage , minor
folds , and faults
Other Features
Tightly interlocking grains Disseminated minerals , Retain traces or relics of
Unsossiliferous. loose ,friable boulders , original of structures of
pebbles , cements. sedimentary or igneous rocks
Fossiliferous : well- from which the metamorphic
preserved or fragmentary. rocjs wer formed .
Extremely poorly sorted Fossils only rarely present ,
( tillite and till ) distorted
Geographic and geologic positin of outcrop
1. Precambrian teranes 1. Widespread and 1. In Precamrian terranes
2. Orogenic belts characterized by made up peg essentially of
3. Sporadic outcrops stratification and granite gneiss , migmatit
4. Occupy dikes , siils ,
sorting , wide lateral ( mixed rock) , and
laccoliths , lopoliths ,
extent , intercalations pegmatitic injection
phacholiths , stocks , 2. In inner , originally deep-
with known sediments
batholiths , etc., seated zones of eroded
and gradations to them
breaking across other fold mountain chains ;
both laterally and
rocks. Massive , rocks mayshow gradual
vertically
irregular shape , chilled 2. Formation shows change in degree or grade
borders marked and regular of metamorphism
5. Volcanoes , lava flows 3. Aureoles araound
difeferences in
lithologic composition sporadic igneous
3. Bodies of sedimentary intrusions ; rocks may
rocks may be display zonal arrangement
described as afan , 4. Along narrow zone of
delta , sheet , blankets, intense deformation such
lens, wedge, as the sole of thrust
shoestring, and prism
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tugas Petrologi Filsa FixDocument7 pagesTugas Petrologi Filsa FixFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Sedimentary Rocks2Document254 pagesSedimentary Rocks2yoviePas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and MineralsDocument38 pagesRocks and MineralsJuliah PeñalosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alunan, Jorbelle Dane A.Document3 pagesAlunan, Jorbelle Dane A.JORBELLE DANE ALUNANPas encore d'évaluation
- CIV234: GUIDE TO BUILDING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENTDocument50 pagesCIV234: GUIDE TO BUILDING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENTGanesh.RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- ES-Lesson 4 Rocks PDFDocument4 pagesES-Lesson 4 Rocks PDFTinetine Dizon MalqueridoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and MineralsDocument48 pagesRocks and Mineralsianespecial0830Pas encore d'évaluation
- Act 2Document4 pagesAct 2Mark Anthony FelicianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and minerals guideDocument21 pagesRocks and minerals guideRockers ArulPas encore d'évaluation
- Index Mineral of Metamorphic Rock: By:Florence Guzon and Jovan SenaresDocument29 pagesIndex Mineral of Metamorphic Rock: By:Florence Guzon and Jovan SenaresStalk Pa MorePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Manual Geology For Civil Engineers (2.0 Units) III Petrology PDFDocument7 pagesLecture Manual Geology For Civil Engineers (2.0 Units) III Petrology PDFAd PlusPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of RocksDocument29 pagesTypes of RocksHickory DickoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Geology. Identifications of Rocks and Minerals in The FieldDocument62 pagesSurface Geology. Identifications of Rocks and Minerals in The FieldAlvaro MadridPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Aggregates in ConcreteDocument14 pagesAggregates in ConcreterajasekharPas encore d'évaluation
- Batuan MetamorfDocument20 pagesBatuan MetamorfSurvey ParapatanPas encore d'évaluation
- VISAYAS STATE UNIVERSITY Soil Science Lab on Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesVISAYAS STATE UNIVERSITY Soil Science Lab on Rocks and MineralsAleah TyPas encore d'évaluation
- You Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Document12 pagesYou Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Lance AmoresPas encore d'évaluation
- SR ColumnDocument9 pagesSR ColumnAdnan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphic RockDocument18 pagesMetamorphic RockPrianda Kea SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrology Lec FinalsDocument2 pagesPetrology Lec FinalsMcAndrew GaveriaPas encore d'évaluation
- National University of Moquegua: Professional School of Mining EngineeringDocument7 pagesNational University of Moquegua: Professional School of Mining EngineeringJeff Seid :3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geology and Drilling TheoryDocument20 pagesGeology and Drilling TheoryJose Antonio Sanchez SegoviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - StoneDocument52 pagesLecture 5 - Stonenasir khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab: Sedimentary Rock Identification: Composition. Examples Are Shales, Sandstones, andDocument8 pagesLab: Sedimentary Rock Identification: Composition. Examples Are Shales, Sandstones, andSig BahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Mineral IntroDocument27 pagesRock Mineral IntroCharles BualePas encore d'évaluation
- CHORRILLOSDocument7 pagesCHORRILLOSDaniel Vega VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Origins of Soils Lab ReportDocument6 pagesOrigins of Soils Lab ReportCrystaline Ann B. BorilePas encore d'évaluation
- Borile Crystaline Bsam2b Soil100 Output1Document6 pagesBorile Crystaline Bsam2b Soil100 Output1Crystaline Ann B. BorilePas encore d'évaluation
- NS4 Activity 2.2 Guide and Rubrics-RocksDocument8 pagesNS4 Activity 2.2 Guide and Rubrics-Rockshera chanelsPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Exercise 5: Metamorphic Rock IdentificationDocument8 pagesLaboratory Exercise 5: Metamorphic Rock IdentificationAmir Nazri Juljani KaibingPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Metamorphic ClassificationDocument22 pages2 Metamorphic ClassificationVinay Pratap Singh ShekhawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Metamorphic PetrologyDocument71 pagesPractical Metamorphic PetrologyZekariyas Ze AmharaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 StonesDocument43 pages1 StonestonydisojaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gneiss Rock (Metamorphic Rock) Shale Rock (Sedimentary Rock)Document2 pagesGneiss Rock (Metamorphic Rock) Shale Rock (Sedimentary Rock)Cabunoc Andre LouisPas encore d'évaluation
- 0004 Glge2a2 RocksDocument51 pages0004 Glge2a2 RocksAndile MavusoPas encore d'évaluation
- Praktikum Singkapan Batuan: Kompetensi TujuanDocument2 pagesPraktikum Singkapan Batuan: Kompetensi Tujuanoctavira auliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Igneous Sedimentary MetamorphicDocument3 pagesIgneous Sedimentary MetamorphicKezel AtangenPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringDocument55 pagesMetamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringAvinash Upadhyay100% (1)
- Geology Mid-Year Assessment Study GuideDocument1 pageGeology Mid-Year Assessment Study GuideanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining Minerals and Rocks: Their Properties and ClassificationDocument22 pagesExamining Minerals and Rocks: Their Properties and ClassificationAbegail DimaanoPas encore d'évaluation
- MetamorfDocument19 pagesMetamorfrandom personPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining Minerals and RocksDocument27 pagesExamining Minerals and RocksminingnovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formation and Types of Metamorphic RocksDocument42 pagesFormation and Types of Metamorphic Rockssalwa aa100% (1)
- Earth Scie. Module 3Document9 pagesEarth Scie. Module 3Jasmin BelarminoPas encore d'évaluation
- Porosity PETE - 312: Many Slides Contain More Detailed Notes That May Be Shown Using The "Notes Page View"Document74 pagesPorosity PETE - 312: Many Slides Contain More Detailed Notes That May Be Shown Using The "Notes Page View"JosueGuayuscaSoriaGalvarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mining Geology Part 2Document21 pagesMining Geology Part 2Parth TilakPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphic Rocks-2Document42 pagesMetamorphic Rocks-2Adnan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mineral Deposit Classification GuideDocument2 pagesMineral Deposit Classification GuideKareemAmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrology PPTDocument27 pagesPetrology PPTbreighamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect - No.3 Rocks and Texture Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesLect - No.3 Rocks and Texture Microsoft Word Documentbinod2500Pas encore d'évaluation
- EESC 1101 - Lab 4 - Brooklyn College Building Stone PDFDocument13 pagesEESC 1101 - Lab 4 - Brooklyn College Building Stone PDFLorenzo YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Endapan SkarnDocument40 pagesEndapan SkarnFrans AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and MineralsDocument50 pagesRocks and MineralsCzarina Bea SaberonPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 Rocks and MineralsDocument48 pages1.3 Rocks and MineralsriePas encore d'évaluation
- Rock FlashcardsDocument7 pagesRock FlashcardsbudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of ISO 900-2008 QMS, Total Quality ManajemenDocument6 pagesEffect of ISO 900-2008 QMS, Total Quality Manajemenfery73Pas encore d'évaluation
- KRS Filzha PDFDocument1 pageKRS Filzha PDFFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Album Mineral OptikDocument27 pagesAlbum Mineral OptikEndarto YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Big BossDocument1 pageBig BossFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Convergen Boundary: Pertemuan 3-4Document35 pagesConvergen Boundary: Pertemuan 3-4Filzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Introduction MetamorficDocument10 pages10 Introduction MetamorficFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipi256821 PDFDocument15 pagesIpi256821 PDFAmrizal D's PatriPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework English LeagueDocument1 pageHomework English LeagueFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework English LeagueDocument1 pageHomework English LeagueFilzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Croseas Tabrani Putra 121.101.056 ( ..)Document1 pageCroseas Tabrani Putra 121.101.056 ( ..)Filzha LeeminPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock and Minerals - Eyewitness HandbooksDocument129 pagesRock and Minerals - Eyewitness Handbookspramu cahyadi100% (2)
- Compatiblity Reading - Beyonce and Jay-ZDocument14 pagesCompatiblity Reading - Beyonce and Jay-ZNikola Durdevic ArtePas encore d'évaluation
- MetallurgyDocument8 pagesMetallurgyBandita DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ay An Am SH ADocument5 pagesAy An Am SH AShankarananda SherPas encore d'évaluation
- Grapevine Issue5Document20 pagesGrapevine Issue5api-268244952Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forming and Using Superlative AdjectivesDocument3 pagesForming and Using Superlative Adjectivessheneen_abdullaPas encore d'évaluation
- Importancia de Las EnzimasDocument9 pagesImportancia de Las EnzimasGregorio AronePas encore d'évaluation
- Geomagnetism v1 Chapman-GeomagnetismVol1 - TextDocument619 pagesGeomagnetism v1 Chapman-GeomagnetismVol1 - TextAnonymous QlJjisdlLIPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Controls of NE Russia GoldDocument18 pagesStructural Controls of NE Russia GoldAnonymous YSnVjegPas encore d'évaluation
- Simply Supported Beam With Eccentric LoadingDocument6 pagesSimply Supported Beam With Eccentric LoadingBasith AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Influence of Geology on Tunnel Design & ConstructionDocument29 pagesInfluence of Geology on Tunnel Design & ConstructionGEOMAHESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Topographic Map of PettyDocument1 pageTopographic Map of PettyHistoricalMapsPas encore d'évaluation
- TAXONOMYDocument12 pagesTAXONOMYVaishnavi SiewPas encore d'évaluation
- Archimedes Archimedes of Syracuse (Greek: Ἀρχιμήδης; c. 287 BC - c. 212 BC) was a GreekDocument2 pagesArchimedes Archimedes of Syracuse (Greek: Ἀρχιμήδης; c. 287 BC - c. 212 BC) was a GreeksarayooPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Guide Observation of Sedimentary RockDocument1 pageField Guide Observation of Sedimentary Rockmukhammad nurdiansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Pustaka: Billings, Marland P. 1984. Structural Geology. Third Edition. New Delhi:Prenticehall of IndiaDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Billings, Marland P. 1984. Structural Geology. Third Edition. New Delhi:Prenticehall of IndiatyasherjatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Earmark RequestDocument1 pageEarmark RequestdjsunlightPas encore d'évaluation
- DHANA YOGAS-Parijaat, ComDocument2 pagesDHANA YOGAS-Parijaat, ComKrishna Das C100% (1)
- Alien Supercivilizations Absent From 100,000 Nearby Galaxies - Scientific AmericanDocument8 pagesAlien Supercivilizations Absent From 100,000 Nearby Galaxies - Scientific AmericanMarlon FariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Expanding EarthDocument44 pagesExpanding Earth_G_BPas encore d'évaluation
- Attention and PerceptionDocument20 pagesAttention and PerceptionDeepak KripalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Astrology of Local SpaceDocument212 pagesThe Astrology of Local SpaceDaisy100% (6)
- 3rd Rock Vocab 2013Document2 pages3rd Rock Vocab 2013api-277568334Pas encore d'évaluation
- University of Mumbai: Revised Syllabus W.E.F. Academic Year, 2016-18Document5 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: Revised Syllabus W.E.F. Academic Year, 2016-18YashRanePas encore d'évaluation
- A Gallery of Planet HuntersDocument4 pagesA Gallery of Planet Huntersmidi64Pas encore d'évaluation
- For More Info See Pages 7-9Document4 pagesFor More Info See Pages 7-9ecargxnagemPas encore d'évaluation
- The Solid Earth An Introduction To Global GeophysiDocument15 pagesThe Solid Earth An Introduction To Global Geophysiq584403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes For Introduction To CosmologyDocument168 pagesLecture Notes For Introduction To Cosmologytduality100% (1)
- Nucleosynthesis: Elements Are Made in Four Distinct Ways (Plus Another We Didn't Go Into)Document10 pagesNucleosynthesis: Elements Are Made in Four Distinct Ways (Plus Another We Didn't Go Into)Ananyo BhattacharyyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Barrett - Mesquita - Ochsner - Gross - 2007 - The Experience of Emotion PDFDocument39 pagesBarrett - Mesquita - Ochsner - Gross - 2007 - The Experience of Emotion PDFwhitepaladinPas encore d'évaluation
- Crushed Ore Agglomeration and Its Control For Heap Leach OperationsDocument18 pagesCrushed Ore Agglomeration and Its Control For Heap Leach Operationsmehra222100% (3)