Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ZAPOTE - SLOPE STABILITY - LTP
Transféré par
Antoniette Samantha NacionDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ZAPOTE - SLOPE STABILITY - LTP
Transféré par
Antoniette Samantha NacionDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review and Detailed Engineering Design of Comprehensive
River Management of Zapote River
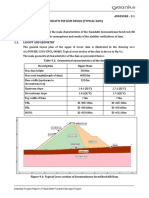
SLOPE STABILITY ANALYSES OF GUADALUPE RIVER CROSS SECTIONS
1. INTRODUCTION
Slope stability refers to the resistance of the soil from sliding or collapsing when subjected to
external loads during excavation and embankment works. Normally, factors such as pore
water pressure, surcharge and weight of the soil contributes to the stresses applied to the
ground which can exceed the soil strength and capacity resulting to instability. The idea of
slope stability is to investigate the adequacy of soil strength and parameters considering
probable failure mechanisms.
Soil shear strength is the primary parameter considered for slope stability since it relates
either total or effective normal stress on the failure plane. Shear strength is obtained through
the cohesion and angle of internal friction as determined from the laboratory shear test.
The analysis method used by Soil Works software is the Limit Equilibrium Method. It
examines slope stability using slice method (lines and arcs) projected along the assumed
slope failure. The concept of this method satisfies the forces and moment equilibrium
condition by assuming a linearly proportional relationship between the horizontal force and
the normal force of the slice. The approach determinesthe minimal factor of safety for arc
failure surface and critical failure surface.
Performance of slope based on its design life can be evaluated using an acceptable factor of
safety. Minimum factor of safety used in the design is based on the provided factor of safety
guidance by the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE).
Table 1.0-1
Minimum Required Factors of Safety (USACE, 2003)
Required Minimum
Analysis Condition Slope
Factor of Safety
Upstream &
End of construction (including stage construction) 1.3
Downstream
Long term (Steady seepage, maximum storage
1.5 Downstream
pool, spillway crest or top of gates)
Maximum surcharge pool 1.4 Downstream
Rapid drawdown 1.1 1.34.5 Upstream
Soil Stability Analysis
March 2017
Review and Detailed Engineering Design of Comprehensive
River Management of Zapote River
2. RESULTS OF SELECTED CROSS SECTIONS
The slope stability model was analyzed using SoilWorks software with modified soil
parameters. The surcharge load used in the model is equal to 12kN/m 2, and the weight of
the coping beam is also applied which is equal to 25kN, safety factor should not be less than
1.5.
2.1. Station 0+000 (LEFT BANK)
2.1.1. Soil Properties
Table 2.1.1-A
Soil Properties for Station 0+000
Internal
Wet unit Saturated Modulus of
Cohesion friction Poisson's
Section weight unit weight elasticity
(kN/m) angle ratio
(kN/m) (kN/m) (kN/m)
([deg])
SILTY SAND 18.00 18.00 5.0 29.00 - -
WELL 21.00 21.00 - 38.50 - -
GRADED
GRAVEL
RIGID LEM 24.00 24.00 365.0 35.00 - -
2.1.2. Analysis and Result
Table 2.1.2-A
Result for Station 0+050
LEM
Standard safety factor 1.500 Evaluation
Analysis safety factor OK
2.621
(Arc failure surface) Determined to be safe.
Soil Stability Analysis
March 2017
Review and Detailed Engineering Design of Comprehensive
River Management of Zapote River
Soil Stability Analysis
March 2017
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Slope Stability Analysis Veladero MineDocument93 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Veladero MineAlcides PanezPas encore d'évaluation
- Caol Clay Core Reassessment - ISSUEDocument13 pagesCaol Clay Core Reassessment - ISSUEDavid Thomson100% (1)
- Volume III (Design Annexures)Document103 pagesVolume III (Design Annexures)Gangeyula samyakPas encore d'évaluation
- SSI Analysis of LILW Silo - SMiRT 26Document10 pagesSSI Analysis of LILW Silo - SMiRT 26YoungSun JangPas encore d'évaluation
- Offshore Seismic Analysis Using SACSDocument24 pagesOffshore Seismic Analysis Using SACSLinda Cendekia Suprobo100% (1)
- LRFD Abut & Ret Wall DesignDocument35 pagesLRFD Abut & Ret Wall DesignVictor De los ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- EMBANKMENT ANALYSISDocument7 pagesEMBANKMENT ANALYSISP Allen Samuel IgnatiusPas encore d'évaluation
- PDA Test - Result AnalysisDocument13 pagesPDA Test - Result AnalysisNazmul100% (1)
- Dhankuta - Multi Purpose Building - Structural DesignDocument13 pagesDhankuta - Multi Purpose Building - Structural DesignAbhay SuwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Slope stability analysis worked exampleDocument4 pagesSlope stability analysis worked exampleEric ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seepage-Stress Semi Coupled Tutorial 1492124883Document97 pagesSeepage-Stress Semi Coupled Tutorial 1492124883Jan BakosPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Soil Stability AssessmentDocument5 pagesGlobal Soil Stability AssessmentJulian TumielewiczPas encore d'évaluation
- Instar Vibration Testing of Small Satellites Part 1Document11 pagesInstar Vibration Testing of Small Satellites Part 1Youssef wagdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Des Using Eurocode 7Document12 pagesPile Des Using Eurocode 7H AnimePas encore d'évaluation
- I-7. Probabilistic Stability Analysis (Reliability Analysis)Document14 pagesI-7. Probabilistic Stability Analysis (Reliability Analysis)Dio Alif HutamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Demands On Structure Components: S D C - J 2006 - V 1.4Document8 pagesDemands On Structure Components: S D C - J 2006 - V 1.4Jason ToraldePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Summary: 1.1 Overview Per Stage and TestDocument4 pages1 Summary: 1.1 Overview Per Stage and Testcandice2811Pas encore d'évaluation
- AASHTO Flexible Pavement Design MethodDocument24 pagesAASHTO Flexible Pavement Design MethodTorhile Kenneth MO AggnPas encore d'évaluation
- PLAXIS 2D 2018-Tutorial-Lesson05Document18 pagesPLAXIS 2D 2018-Tutorial-Lesson05amka pasar cimahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Pit Design Assignment - 2021Document9 pagesOpen Pit Design Assignment - 2021pauloreceado07Pas encore d'évaluation
- AWC STD342 1 WFCM2015 WindLoads 160922Document55 pagesAWC STD342 1 WFCM2015 WindLoads 1609226Bisnaga100% (1)
- Analysis of Underground Road Tunnel Subjected To Seismic ForceDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Underground Road Tunnel Subjected To Seismic Forcesourabh mahanaPas encore d'évaluation
- FOUNDATION DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION GUIDEDocument8 pagesFOUNDATION DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION GUIDEManoj SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102Document9 pagesStructural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102MinhddPas encore d'évaluation
- REVISION A: ANODE SLED BOLTING ANALYSISDocument4 pagesREVISION A: ANODE SLED BOLTING ANALYSISejim2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Saundatti Volume III Designs 28072022Document157 pagesSaundatti Volume III Designs 28072022Gangeyula samyakPas encore d'évaluation
- Group ProjectDocument2 pagesGroup Projectmai-badePas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Design For 66kV Steel Poles Bo-Kenema-SOIL CLASS 2A-08-11-21Document22 pagesFoundation Design For 66kV Steel Poles Bo-Kenema-SOIL CLASS 2A-08-11-21BAWA ALEXPas encore d'évaluation
- P650 658Document9 pagesP650 658Anonymous USbc7XzsA6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Creep SettlementDocument16 pagesCreep Settlementalien kilPas encore d'évaluation
- Verification Without Test Pile FactorsDocument27 pagesVerification Without Test Pile FactorsDavid NewbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Structural AnalysisDocument66 pagesSample Structural AnalysisJohn Vincent L. Ambrocio50% (2)
- Cast in Place Pipe Anchor Pole FoundationDocument2 pagesCast in Place Pipe Anchor Pole FoundationBAWA ALEXPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 General 1.1 ScopeDocument9 pages1.0 General 1.1 ScopeSmit Patel100% (1)
- Tunnel Series - 1D Tunnel LiningDocument18 pagesTunnel Series - 1D Tunnel Lininggowtham reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Stability of EPS EmbankmentsDocument30 pagesSeismic Stability of EPS EmbankmentsSteven BartlettPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.0m - Tier 3 (16m)Document11 pages6.0m - Tier 3 (16m)dongngosutPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable On-Bottom Stability Analysis for Zakum Oil Lines Replacement ProjectDocument12 pagesCable On-Bottom Stability Analysis for Zakum Oil Lines Replacement ProjectSourabhPas encore d'évaluation
- Construct Road Embankment on Soft SoilDocument16 pagesConstruct Road Embankment on Soft SoilBiao DengPas encore d'évaluation
- San Roque Dam Static Slope Stability Analysis ReportDocument5 pagesSan Roque Dam Static Slope Stability Analysis ReportIndrian Cyril MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridge-Ch-5-Box-Girder DesignDocument7 pagesBridge-Ch-5-Box-Girder DesignAbera Mamo JaletaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impedance ComplanceDocument30 pagesImpedance ComplancebiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Paperpdf 1432 GhoDocument8 pagesPaperpdf 1432 Gho_Asylum_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slope Stability Analysis Under Earthquake - Formatted Paper PDFDocument8 pagesSlope Stability Analysis Under Earthquake - Formatted Paper PDFAkun DownloadPas encore d'évaluation
- MANUAL CALCULATION AND VERIFICATION FOR SUBSTRUCTURE FOUNDATION DESIGN OF GLS TANK (35M DIADocument21 pagesMANUAL CALCULATION AND VERIFICATION FOR SUBSTRUCTURE FOUNDATION DESIGN OF GLS TANK (35M DIAMohammed FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- San Roque Dam Static Stability Analysis ReportDocument5 pagesSan Roque Dam Static Stability Analysis ReportIndrian Cyril MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calc Sheet CIRCULAR - MH (HT 6000mm)Document23 pagesCalc Sheet CIRCULAR - MH (HT 6000mm)Civil EngineerPas encore d'évaluation
- Underground Circular Water TankDocument16 pagesUnderground Circular Water TankHAMZA SAEEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathcad - Appendix - Operation-10W+1C-SW, S, SE, S DIRECTIONDocument16 pagesMathcad - Appendix - Operation-10W+1C-SW, S, SE, S DIRECTIONPetrus SanctusPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural TipsDocument18 pagesStructural TipsGaurav MalyaPas encore d'évaluation
- As-1170.4-2007 - Worked ExamplesDocument10 pagesAs-1170.4-2007 - Worked ExamplesMihnea CostachePas encore d'évaluation
- Op-015. Procedure For Obtaining Shear Strengths Parameters From Back-Analyses of Identified Slip SurfaceDocument6 pagesOp-015. Procedure For Obtaining Shear Strengths Parameters From Back-Analyses of Identified Slip Surfacejinwook75Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6.0m - Tier 2 (16m)Document12 pages6.0m - Tier 2 (16m)dongngosutPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Latbsdc Criteria Final 06-08-17Document52 pages2017 Latbsdc Criteria Final 06-08-17Rannie IsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Measurement: By Square-Edged Orifice Plate Using Corner TappingsD'EverandFlow Measurement: By Square-Edged Orifice Plate Using Corner TappingsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationD'EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerothermodynamics of Turbomachinery: Analysis and DesignD'EverandAerothermodynamics of Turbomachinery: Analysis and DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Fault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureD'EverandFault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureMarion Y. ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Practice in Servo Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringD'EverandModern Practice in Servo Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Cutoff ChannelDocument4 pagesCutoff ChannelAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of ThumbDocument14 pagesRules of ThumbAntoniette Samantha Nacion100% (1)
- 9 800Document18 pages9 800Antoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 700Document18 pages9 700Antoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- TableofContents DocumentTitlesDocument12 pagesTableofContents DocumentTitlesAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical ForcesDocument8 pagesCritical ForcesAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Cro TicalDocument15 pagesCro TicalAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Pressures: EH, ES, LS, DDDocument3 pagesEarth Pressures: EH, ES, LS, DDAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Project Killers and How to Avoid ThemDocument20 pages6 Project Killers and How to Avoid Themsanjai_rahulPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 VTQKcoj UGDocument2 pages4 VTQKcoj UGhalloarnabPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Project Killers and How to Avoid ThemDocument20 pages6 Project Killers and How to Avoid Themsanjai_rahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Cover SheetDocument1 pageCover SheetAntoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel 2007 VBADocument103 pagesExcel 2007 VBAAtul SartapePas encore d'évaluation
- 13 271 147184877610 16Document7 pages13 271 147184877610 16Antoniette Samantha NacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Tune boilers regularlyDocument2 pagesTune boilers regularlyEliecer Romero MunozPas encore d'évaluation
- StompIO-1 User ManualDocument92 pagesStompIO-1 User ManualFederico Maccarone50% (2)
- 02 Judgment On CompromiseDocument49 pages02 Judgment On CompromiseAlbedo SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ausat Final Set 1Document13 pagesAusat Final Set 1Rajiv RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Trash and Recycling Space Allocation GuideDocument24 pagesTrash and Recycling Space Allocation GuideJohan RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S1350630720317192 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S1350630720317192 MainmaximPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy and Memory Efficient Clone Detection in WSN AbstractDocument4 pagesEnergy and Memory Efficient Clone Detection in WSN AbstractBrightworld ProjectsPas encore d'évaluation
- Commercial and EsplanadeDocument2 pagesCommercial and EsplanadeDanica Mae AmicayPas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 Expedition/Navigator 4WD Systems Workshop Manual DiagnosisDocument18 pages2003 Expedition/Navigator 4WD Systems Workshop Manual DiagnosisAngelina IsaacsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nissan service bulletin DTC C1A12 C1A16 sensor cleaningDocument5 pagesNissan service bulletin DTC C1A12 C1A16 sensor cleaningABDULNAZER C P 001Pas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual - User Manual - Original and Genuine Veronica® 1W PLL (1WPLLM)Document39 pagesUser Manual - User Manual - Original and Genuine Veronica® 1W PLL (1WPLLM)Carlos Evangelista SalcedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryDocument4 pagesJameson 2000 The Journal of Prosthetic DentistryKarthikmds ElangovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Action Plan Stratcom PDFDocument5 pagesAction Plan Stratcom PDFDaniel SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sing Pilot CardDocument1 pageSing Pilot CardTushar Gupta100% (1)
- Research Methodology MCQ 400Document190 pagesResearch Methodology MCQ 400dhanusiya balamurugan67% (18)
- Access User GuideDocument49 pagesAccess User GuideShivaji JagdalePas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL REPORT WV Albania Buiding Futures PotentialDocument30 pagesFINAL REPORT WV Albania Buiding Futures PotentialVasilijePas encore d'évaluation
- 17 "Flow" Triggers That Will Increase Productivity - Tapping Into Peak Human Performance in BusinessDocument7 pages17 "Flow" Triggers That Will Increase Productivity - Tapping Into Peak Human Performance in BusinessFilipe RovarottoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Early Transcendentals 10th Edition Anton Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesCalculus Early Transcendentals 10th Edition Anton Solutions Manualcrenate.bakshish.7ca96100% (16)
- 2021.10.06 Boq Facade Civil Works at b10 - 20211129Document24 pages2021.10.06 Boq Facade Civil Works at b10 - 20211129Irul HimawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Deckers v. Comfy - Minute OrderDocument2 pagesDeckers v. Comfy - Minute OrderSarah BursteinPas encore d'évaluation
- Nadig Reporter Newspaper Chicago June 19 2013 EditionDocument20 pagesNadig Reporter Newspaper Chicago June 19 2013 EditionchicagokenjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 70 CCNA Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesTop 70 CCNA Interview QuestionsRekha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Barbara S. Hutchinson, Antoinette Paris-Greider Using The Agricultural, Environmental, and Food Literature Books in Library and Information Science 2002Document491 pagesBarbara S. Hutchinson, Antoinette Paris-Greider Using The Agricultural, Environmental, and Food Literature Books in Library and Information Science 2002Paramitha TikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Value at Risk with F&S Investments PortfolioDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Value at Risk with F&S Investments Portfolio7aadkhan100% (2)
- Trudeau Prorogues Parliament: (HDFFC - 00003S /D.TDocument32 pagesTrudeau Prorogues Parliament: (HDFFC - 00003S /D.TBoki VaskePas encore d'évaluation
- Biju Patnaik University of Technology MCA SyllabusDocument18 pagesBiju Patnaik University of Technology MCA SyllabusAshutosh MahapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines Islands Judiciary Torrens System Title in Rem - BLP FoundationDocument2 pagesPhilippines Islands Judiciary Torrens System Title in Rem - BLP FoundationBLP CooperativePas encore d'évaluation
- Set Up A Mail Server On LinuxDocument56 pagesSet Up A Mail Server On Linuxammurasikan6477Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sreeja.T: SR Hadoop DeveloperDocument7 pagesSreeja.T: SR Hadoop DeveloperAnonymous Kf8Nw5TmzGPas encore d'évaluation