Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Why we need nitrogen and sources of nitrates in nature and their effects
Transféré par
Rizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Why we need nitrogen and sources of nitrates in nature and their effects
Transféré par
Rizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
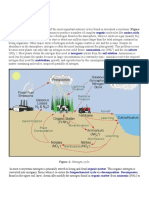
Why do we need nitrogen?
What are the sources
of Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is essential for all living things: animals and plants. Nitrogen forms a part of
the proteins and DNA that are found in cells. Animals get nitrogen by eating plants
and other animals.
Just like animals, plants require nitrogen to grow and survive. But they do not get
nitrogen by consuming proteins like animals do. Plants get nitrogen from water and
from the soil. They get nitrogen by absorbing it in the form of nitrates and
ammonium. Nitrates are the major source of nitrogen for aquatic plants.
Nitrates are not utilized by aquatic organisms such as fish and aquatic insects, but
nitrates are used by aquatic plants.
Eutrophication The process by
which a body of water acquires a high
concentration of nutrients, especially
phosphates and nitrates. These
promote excessive growth of algae. As
the algae die and decompose, high
levels of organic matter and the
decomposing organisms deplete the
water of available oxygen, causing the
death of other organisms, such as fish.
Where do Nitrates come from?
All aquatic organisms excrete wastes and aquatic plants and organisms
eventually die. These activities create ammonia. Some bacteria in the water change
this ammonia to produce nitrite which is then converted by other bacteria to
nitrate. Nitrates (NO3-) are an oxidized form of nitrogen and are formed by combining
oxygen and nitrogen.
Nitrates also come from the earth. Soil contains organic matter, which contains
nitrogen compounds. Just like the ammonia in water, these nitrogen compounds in
the soil are converted by bacteria into nitrates.
Although nitrates occur naturally in soil and water, an excess levels of nitrates
can be considered to be a contaminant of ground and surface waters. Most sources of
excess nitrates come from human activity. The source of excess nitrates can usually
be traced to agricultural activities, human wastes, or industrial pollution.
Nitrogen fertilizers have been applied to yards, fields, golf courses to promote
the growth of plants. Rainwater can wash nitrates in the fertilizer into streams and
rivers or the nitrates can seep into ground water. This can also occur with animal
waste and manure.
In addition to animal waste, untreated human sewage can contribute to nitrate
levels in surface and ground water. Leaking or poorly functioning septic systems are a
source of such nitrates. City sewage treatment plants treat sewage to make it non-
hazardous, but treatment plants still release nitrates into waterways. In addition,
industrial plants and agricultural processing operations are potential sources of nitrate
pollution.
How do nitrates affect human health?
Nitrate concentrations are monitored in municipal water supplies and foods to
prevent exposing people to the potential harmful effects of high levels of nitrates.
Nitrates are highly soluble, meaning that they easily dissolve in water. For many
people in rural areas, the primary source of drinking water is well water, which may be
contaminated with nitrates. Nitrates are colorless and odorless, so their presence
cannot be determined without the use of special testing equipment.
Nitrates can interfere with the ability of our red blood cells to carry oxygen.
Infants are more at risk of nitrate poisoning than older children or adults. Babies can
turn blue when there is not enough oxygen being transported by their blood. This
blue baby syndrome (technically known as methemoglobinemia) is a serious
condition that can cause brain damage or death.
How do nitrates affect the health of aquatic
animals?
Fish and aquatic insects can be affected indirectly by increased nitrate concentrations
in the water.
Basically, any excess nitrate in the water is a source of fertilizer for aquatic
plants and algae. In many cases, the amount of nitrate in the water is what limits how
much plants and algae can grow. If there is an excess level of nitrates, plants and
algae will grow excessively.
Excess plants in a body of water can create many problems. An excess in the
growth of plants and algae create an unstable amount of dissolved oxygen. During
the day, there will be usually be high levels of dissolved oxygen, and at night the
levels of oxygen can decrease dramatically.
o This will create stressful conditions for fish. If they are stressed for a significant
part of the day, they will not behave normally or reproduce. If the conditions
persist for a long period of time, the stressed fish species may choose to leave
that area or die off.
o Excess algae or plant growth is also unsightly. If youve ever been to a beach
where mats of rotting algae wash up on shore or the bottom of the lake is
teaming with weeds, its probably because excess nitrates are available for plant
growth.
Excess plants and algae will also create conditions where organic matter
accumulates. High densities of algae will create a condition where sunlight cannot
reach very far into the water. Since plants and algae require some sunlight, plants
and algae not receiving sunlight will die off. These dead plant materials will settle to
the bottom of the water and bacteria that feed on decaying organic material will
greatly increase in numbers. These bacteria will consume oxygen and, therefore, the
level of dissolved oxygen in this water will fall to levels that are too low for many
aquatic insects and fish to survive. Also, this can cause extreme changes in habitat.
Fish that need gravel or sand for spawning may find nothing but mats of vegetation
and muck so will be unable to produce offspring.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Year 8 Sample Paper BSCDocument5 pagesYear 8 Sample Paper BSCUmayal SivanandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stormwater: A Resource for Scientists, Engineers, and Policy MakersD'EverandStormwater: A Resource for Scientists, Engineers, and Policy MakersPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument14 pagesWater PollutionJojo Chan100% (1)
- Protocol K: Topical CDS ApplicationDocument3 pagesProtocol K: Topical CDS ApplicationKhiemPas encore d'évaluation
- Yummy Jelly Business PlanDocument19 pagesYummy Jelly Business PlanGlesie Zarate100% (3)
- Unit Ii WWSTDocument15 pagesUnit Ii WWSTSameerPas encore d'évaluation
- River Centric Urban Planning GuidelinesDocument36 pagesRiver Centric Urban Planning GuidelinesRaghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Saehan Industries Inc. KoreaDocument13 pagesSaehan Industries Inc. Koreadalton2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- LS20-100 Sullair Manual PDFDocument114 pagesLS20-100 Sullair Manual PDFRich_78100% (1)
- EASEC-11 Paper418 BucklingDocument8 pagesEASEC-11 Paper418 Bucklinginge ocPas encore d'évaluation
- D3370 Sampling Water From Closed ConduitsDocument11 pagesD3370 Sampling Water From Closed ConduitsBalas43100% (1)
- Phil Iri ReadingsDocument17 pagesPhil Iri ReadingsResian Garalde Bisco71% (7)
- Nitrogen and PhosphorusDocument3 pagesNitrogen and PhosphorusAchmadAgustianFarezaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nitrogen Cycle: Element Living Things Plants Animals AtomsDocument1 pageThe Nitrogen Cycle: Element Living Things Plants Animals AtomsjeffsorcePas encore d'évaluation
- The Nitrogen CycleDocument19 pagesThe Nitrogen CycleLiam Nathaniel V. SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument3 pagesWater PollutionbedahrockPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution Presentation Chemistry: Tasheika RichardsDocument4 pagesWater Pollution Presentation Chemistry: Tasheika Richardstashy richardsPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes and Types of Water Pollution ExplainedDocument4 pagesCauses and Types of Water Pollution ExplainedkevineasawPas encore d'évaluation
- 2000 Project Oceanography Pollution and Water QualityDocument14 pages2000 Project Oceanography Pollution and Water QualityMartha Letchinger100% (1)
- What Is Water Pollution?Document3 pagesWhat Is Water Pollution?Ch. Muhammad UsamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Traveling Nitrogen Game AnswersDocument6 pagesTraveling Nitrogen Game Answersapi-356036396Pas encore d'évaluation
- What is water pollution and how can we prevent itDocument60 pagesWhat is water pollution and how can we prevent itMd Hamid RezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution An OverviewDocument10 pagesWater Pollution An OverviewShashi Kiran PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument2 pagesWater PollutionareenaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cycle of Nitrogen Sulphur & Carbon - Analysis by FahmidDocument5 pagesThe Cycle of Nitrogen Sulphur & Carbon - Analysis by FahmidFahmid Tousif KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument11 pagesWater Pollutionhamza sheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Eutrophic at I OnDocument16 pagesEutrophic at I OnAlba, Janell D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument3 pagesWater PollutionsahilmaknojiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution: Presented By-Jagannath Kumar 13 PGDM11Document15 pagesWater Pollution: Presented By-Jagannath Kumar 13 PGDM11Galatanu DenisaPas encore d'évaluation
- DinosaurStatePark NitrogenDocument1 pageDinosaurStatePark NitrogenHartford CourantPas encore d'évaluation
- FinalDocument48 pagesFinalmanish jatPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument11 pagesWater PollutionKmcpKimyatzPas encore d'évaluation
- MalolosDocument7 pagesMalolosJulia Opeña ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Eutrophic at I OnDocument7 pagesEutrophic at I OnKrizelle Mae BaronganPas encore d'évaluation
- What Causes WPDocument22 pagesWhat Causes WPAnonymous VIZNI30PYPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterpollution 150120063202 Conversion Gate02Document64 pagesWaterpollution 150120063202 Conversion Gate02JM MagayanesPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Water Pollution?: Health Effects of MicrorganismsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Water Pollution?: Health Effects of MicrorganismsVel MuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- BrochureDocument6 pagesBrochureapi-357284204Pas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Studies Project On Water PollutionDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Studies Project On Water PollutionShobhit Goswami86% (7)
- Presentation 4Document11 pagesPresentation 4Hawra SafriPas encore d'évaluation
- Neeeew Water - PollutionDocument14 pagesNeeeew Water - PollutionDl Al-azizPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4 Water PollutionDocument11 pages4.4 Water PollutionBharti JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution ReportingDocument42 pagesWater Pollution ReportingMoreno, Leanne B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Did Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksD'EverandDid Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Pollution of The WaterDocument25 pagesPollution of The WaterJeprox Martinez100% (1)
- Surface Water PollutionDocument18 pagesSurface Water PollutionTotztutz Togodunz TonztunzPas encore d'évaluation
- Domingo - Water Pollution - PPTDocument14 pagesDomingo - Water Pollution - PPTGolden DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Management 2Document6 pagesWaste Management 2tvkeliye9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water Chemistry EcotoxDocument25 pagesWater Chemistry EcotoxElma AlfiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrients Pollution Takes Place Due To Excessive Algae and Plant Growth When Too ManyDocument2 pagesNutrients Pollution Takes Place Due To Excessive Algae and Plant Growth When Too ManyLadyPas encore d'évaluation
- A4 EutrophicationDocument2 pagesA4 EutrophicationRovv icPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrogen CycleDocument3 pagesNitrogen CycleAliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 Environmental Pollution and ControlDocument14 pagesTopic 1 Environmental Pollution and ControlMichael LangatPas encore d'évaluation
- BS Zoology Lecture 2Document12 pagesBS Zoology Lecture 2Syeda SharqaPas encore d'évaluation
- Excess Nutrients Trigger Harmful Eutrophication ProcessesDocument5 pagesExcess Nutrients Trigger Harmful Eutrophication ProcessesPerkresht PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Water PollutionDocument8 pagesChemistry of Water PollutionAbeera Hassan ChohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cala Component CDocument5 pagesCala Component CPeace MutombwaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Nitrogen Cycle and Why Is It Key To Life - Frontiers For Young MindsDocument17 pagesWhat Is The Nitrogen Cycle and Why Is It Key To Life - Frontiers For Young Mindsploki12Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7-Discuss Briefly The Role of Microorganisms in Water Quality ?Document4 pages7-Discuss Briefly The Role of Microorganisms in Water Quality ?Salma AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- WQPBDocument2 pagesWQPBAline1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pollution and It's TypesDocument38 pagesPollution and It's TypesMUHAMMAD AHMED ALI ABBASIPas encore d'évaluation
- Identifying and Managing Aquatic Vegetation: PurdueDocument19 pagesIdentifying and Managing Aquatic Vegetation: PurdueMuraleetharan BoopathiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is EutrophicationDocument28 pagesWhat Is EutrophicationSoumya ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PollutionDocument36 pagesWater PollutionBenedick Jayson MartiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Versus Organic FertilizersDocument6 pagesChemical Versus Organic FertilizersN.MurugesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution: A Threat to Freshwater ResourcesDocument2 pagesWater Pollution: A Threat to Freshwater Resourcesanandhu anilPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Monitoring & Testing GuideDocument26 pagesWater Monitoring & Testing GuidedileeppatraPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - CHEMISTRY OF SEAWATER 16122022 115400amDocument40 pages11 - CHEMISTRY OF SEAWATER 16122022 115400amHamza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Pollution Proyecto Integrado Social Mafer 1Document4 pagesWater Pollution Proyecto Integrado Social Mafer 1api-252851708Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write A Project ReportDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Project ReportRizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionDocument38 pagesExtensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionRizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Irrigation Design Principles: Southwest Turfgrass Association Recreational Landscape Conference and ExpoDocument39 pagesBasic Irrigation Design Principles: Southwest Turfgrass Association Recreational Landscape Conference and ExpoRizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionDocument38 pagesExtensive Survey Project Fieldwork and Data CollectionRizwan Arshad Abhimanigala BalagaPas encore d'évaluation
- General About ConcreteDocument10 pagesGeneral About Concretekeshav1980Pas encore d'évaluation
- (2020) Carranza Et Al. Socio-Environmental Con Icts An Underestimated Threat To Biodiversity Conservation in ChileDocument14 pages(2020) Carranza Et Al. Socio-Environmental Con Icts An Underestimated Threat To Biodiversity Conservation in ChileVicente Venegas100% (1)
- Description of The ProcessDocument7 pagesDescription of The ProcessMaxPas encore d'évaluation
- 46 07 13 - Packaged Water Treatment Equipment PDFDocument9 pages46 07 13 - Packaged Water Treatment Equipment PDFmasoodaePas encore d'évaluation
- Irrigation Project WorkDocument9 pagesIrrigation Project WorkVedant ThakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Transport and its TypesDocument8 pagesImportance of Transport and its TypesMustajab HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Disasters Flooding Information PowerPointDocument13 pagesNatural Disasters Flooding Information PowerPointAlvie Mae MagparocPas encore d'évaluation
- Invertebrate DiversityDocument9 pagesInvertebrate DiversityAsma AyyadPas encore d'évaluation
- S Giáo D C Và Đào T o Tp. H Chí Minh Ngày Thi: 03/04/2021Document8 pagesS Giáo D C Và Đào T o Tp. H Chí Minh Ngày Thi: 03/04/2021An AnPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Yourself 4: D. Cook D. Town D. Seat D. TR SportDocument4 pagesTest Yourself 4: D. Cook D. Town D. Seat D. TR SportNguyễn Thương ThảoPas encore d'évaluation
- MasterBrace ADH 2200 Part B EngDocument1 pageMasterBrace ADH 2200 Part B EngSayed Salah0% (1)
- Challenges of Implementing World Class Manufacturing Techniques in Zimbabwe Zimwara and MbohwaDocument12 pagesChallenges of Implementing World Class Manufacturing Techniques in Zimbabwe Zimwara and MbohwaFatimah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- SDS Weber Backing RodDocument4 pagesSDS Weber Backing RodAmadou MokshaPas encore d'évaluation
- NBC Form A-06 Sanitary/Plumbing PermitDocument1 pageNBC Form A-06 Sanitary/Plumbing PermitMark Anthony FolleroPas encore d'évaluation
- GURLI Cushion Cover, White, 50x50 CM - IKEADocument11 pagesGURLI Cushion Cover, White, 50x50 CM - IKEAAimi GhazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Flex Separation Systems S Separator 805 815Document4 pagesFlex Separation Systems S Separator 805 815coleiroPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Broșură Lot 43 .SemnatDocument4 pages10 - Broșură Lot 43 .SemnatBố Của DơiPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Body Water Volumes For Adult Males and Females Estimated From Simple Anthropometric Measurements1Document13 pagesTotal Body Water Volumes For Adult Males and Females Estimated From Simple Anthropometric Measurements1Nanda AzaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant Design SchemeDocument1 pageDomestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant Design SchemeReza MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- WatersupplymanagementDocument12 pagesWatersupplymanagementRica Joy Cenera BerosPas encore d'évaluation
- Steripen Users GuideDocument4 pagesSteripen Users GuideJoe SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- IEE Fast Food ProjectDocument26 pagesIEE Fast Food ProjectaviePas encore d'évaluation