Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current Circuits
Transféré par
Chris LauCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current Circuits
Transféré par
Chris LauDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
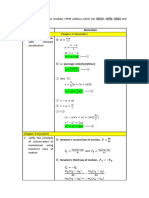
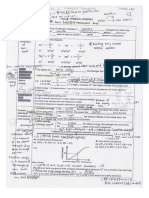
SMK SACRED HEART, SIBU STPM PHYSICS CHAPTER 18 ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS
1. Circuit with alternating current:
Characteristics Purely resistive circuit (R-circuit) Purely inductive circuit (L-circuit) Purely capacitive circuit (C-circuit)
a) Circuit
b) Voltage V = Vo sin , Vo = peak voltage V = Vo sin , Vo = peak voltage V = Vo sin , Vo = peak voltage
c) Current To maintain I in inductor, V across inductor For a.c. circuit, rate of charges are
I= = is V = -E conserved. Q=CV
I = Io sin Vsupply = Vinductor = I = C
Vo sin = -E , E= I = C
= L
= CVo cos
=
= Io cos
= = Io sin (
I =
I = Io cos
= Io sin (
d) Peak current, Io = Io = = Io = CVo =
Io
e) Resistance / XR = R XL = =2 = Xc = = ==
Reactance
f) Ir.m.s. From I = Io sin , Mean square From XL = From Xc = ,
(Same as Vrms) I2 = sin2 value of
sin2 = Irms = = Irms = = Vrms
=
Ir.m.s. =
g) Phase = 0o = 90o = 90o
difference
h) Instantaneous P = IV P = IV P = IV
power = (Io sin ) (Vo sin ) = (Io cos ) (Vo sin ) = (Io cos ) (Vo sin )
= Io Vo sin2 = Io Vo sin = Io Vo sin
i) Maximum P = I2R Io = P o = I o Vo P o = I o Vo
power = (Io sin )2 R
Po = R Po = R Po = R
= R sin
P o = I o Vo
P = Po sin Po = Po =
Po =
j) Mean power From P = R sin , P=0 P=0
P= P = Vrms Irms (No heat dissipated) (no heat dissipated)
=( )( ) Energy stored, U = LI2 Energy stored, U = CV2
= = 2
= L (Io sin ) = C (Vo sin )2
= Mean energy = 0 Mean energy = 0
Mean square value of sin 2
= Peak energy, Uo = L Peak energy, Uo = C
k) Leading Both are in the same phase Voltage Current
quantity From CIVIL, Capacitor = I leading V ; V leading I = Inductor (L)
l) Phasor
diagram
(let direction of I
lies on X-axis)
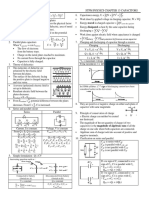
SMK SACRED HEART, SIBU STPM PHYSICS CHAPTER 18 ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS
2. Circuit with alternating current:
Characteristics R-C circuit in series R-L circuit in series R-L-C circuit in series
a) Circuit
b) Phasor
diagram
(let direction of I
lies on X-axis)
c) Voltage V = Vo sin , Vo = peak voltage V = Vo sin , Vo = peak V = Vo sin , Vo = peak voltage
voltage
VR = IR VR = IR VR = IR
Vc =IXc VL =IXL VL =IXL Vc = IXc
Vz = IZ Vz = IZ Vz = IZ
d) Impedance, Z Vz = Vz = Vz =
IZ = IZ = IZ =
Z= Z= Z=
= = =
= = =
e) Current I = Io sin ( I = Io sin ( I = Io sin (
f) Phase = tan-1 ( ) = tan-1 ( ) = tan-1 ( ) = tan-1 ( ) = tan-1 ( ) = tan-1 ( )
difference -1 -1
= tan ( ) = tan ( ) = tan-1 ( )
g) Leading Current Voltage Nil
quantity by
h) Resonance Nil Nil Impedance Z is minimum when f = fr
frequency or when XL = Xc
3. Alternating current 6. Root-mean-square value of an a.c. 8. Reactance
- Current in which the direction of - The value of a constanct direct - Opposition to the current by an inductor or
the current changes or reverses current which can produce the a capacitor in an a.c. circuit
periodically. same heating power as the 9. Impedance
4. Direct current alternating current in a given - The vector sum of the resistance and the
- Current in which the direction of resistor. reactance in an a.c. circuit
the current is always the same 7. Phasor 10. Mean power
5. Peak value - A phasor is a vector of constant - Rate of heat dissipation
- Maximum value or amplitude of magnitude and rotating in an 11. Instantaneous power
the alternating current anticlockwise direction with a - Power at a particular moment of time
constant angular velocity
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumChris Lau100% (7)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsDocument22 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsChris Lau100% (12)
- Effects of Ac Ripple Current On Vrla Battery LifeDocument8 pagesEffects of Ac Ripple Current On Vrla Battery Lifebomberl3k4Pas encore d'évaluation
- There Are Fifty Questions in This Paper. Answer All Questions. Marks Will Not Be Deducted For Wrong AnswersDocument16 pagesThere Are Fifty Questions in This Paper. Answer All Questions. Marks Will Not Be Deducted For Wrong AnswersSean100% (1)
- List of Physics Derivation STPM Term 1Document4 pagesList of Physics Derivation STPM Term 1Wong Chai YenPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 2 FormulaeDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 FormulaeBen50% (8)
- Physics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document0 pagePhysics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Choe Kok HuanPas encore d'évaluation
- LHB Eog Power CarDocument41 pagesLHB Eog Power Carvishak MkPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMDocument13 pagesPhysics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMShi JiePas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics 2008Document26 pagesSTPM Physics 2008Tang Siew Eng100% (2)
- STPM Physics QuestionDocument10 pagesSTPM Physics Questionmuhdsabri510% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERDocument31 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERChris Lau75% (4)
- Overexcitation ProtectionDocument13 pagesOverexcitation Protectionalonso100% (1)
- Physic Experiment 6Document2 pagesPhysic Experiment 6JasonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Coursework STPMDocument4 pagesIntroduction Coursework STPMSarath KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 1 DefinitionBen40% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Document28 pagesSTPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Chris Lau60% (10)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (2)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Document2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Chris LauPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListDocument4 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListredrosePas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Term PDFVishalinie RamanPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocument9 pagesChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionBen100% (4)
- STPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesSTPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Project Presentation SlideDocument15 pagesSTPM Physics Project Presentation SlideWengMan Sew0% (1)
- STPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second TermDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Experiment 8 Earth S Magnetic Field Second Termhonghong_LCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Viva f6Document11 pagesAssignment Viva f6Magendren Raman50% (2)
- STPM 2010 Mathematics T 2 AnswerDocument3 pagesSTPM 2010 Mathematics T 2 AnswerSKPas encore d'évaluation
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDocument13 pages962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTPas encore d'évaluation
- Math M Coursework - Doc3Document1 pageMath M Coursework - Doc3Chong Yin Ping100% (1)
- Mathematics (T) Coursework: Title: Mathematical Investigation (Am - GM)Document1 pageMathematics (T) Coursework: Title: Mathematical Investigation (Am - GM)Elil MathhyPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionBen67% (3)
- 1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseDocument9 pages1 3 0 X 2, 2 3 (3 X), 2 X 3, 0, OtherwiseWendy LohPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Chemistry 2002 - Paper 1Document16 pagesSTPM Chemistry 2002 - Paper 1Steve_Sam93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Viva Sem 3Document21 pagesMath Viva Sem 3Xiangjun Woo50% (2)
- STPM Project 2017Document10 pagesSTPM Project 2017LiuJiewChuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Chemistry STPM Practical (2011)Document2 pagesExperiment 1 Chemistry STPM Practical (2011)Fu HongPas encore d'évaluation
- IPTA Cut Off Point For PHYSICS STPM 2011 / 2012 University EntryDocument12 pagesIPTA Cut Off Point For PHYSICS STPM 2011 / 2012 University EntrySKPas encore d'évaluation
- MPM 3 Sample ADocument3 pagesMPM 3 Sample AmakoplPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 2 STPM Trial 2014Document10 pagesPhysics 2 STPM Trial 2014Abdul Shariff100% (1)
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Document10 pagesAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Formulas (Derived)Document3 pagesSTPM Physics Formulas (Derived)Fu HongPas encore d'évaluation
- Endothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsDocument9 pagesEndothermic.: A The Forward Reaction IsSatyrKuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian Sem2 Physics STPM 2017Document9 pagesUjian Sem2 Physics STPM 2017Bestah Joewellster TeoPas encore d'évaluation
- MT Chapter 14Document9 pagesMT Chapter 14ShyweyPas encore d'évaluation
- PPU: 960 Physics Practical Report Format SAMPLEDocument4 pagesPPU: 960 Physics Practical Report Format SAMPLEJosh, LRT50% (2)
- STPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsHannah KaienPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM 2016 Physics 1Document16 pagesSTPM 2016 Physics 1Abdul ShariffPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryDocument9 pagesSem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryVZYFVVZHVMPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 3 FormulaeDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 3 FormulaeBenPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2016Document2 pagesProposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2016Voon Keat Nicholas Thoo100% (1)
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3MarcTnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 STPM 2013 SkemaDocument6 pagesPaper 3 STPM 2013 SkemaSaiful MaslulPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths T CourseworkDocument9 pagesMaths T CourseworkJonathanCharanrajPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Document10 pagesSTPM Maths T Assignment (Semester 1) 2012Nicholas Chong0% (2)
- Sample Formula Sheet FinalDocument3 pagesSample Formula Sheet Finalanmol singhPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE 2.1 Electrical Components Across AC Jotted PDFDocument20 pagesLECTURE 2.1 Electrical Components Across AC Jotted PDFMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No.1 QIT: 1 ProblemsDocument3 pagesAssignment No.1 QIT: 1 ProblemsObaid Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet Final 2013 Power Electronics PDFDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Final 2013 Power Electronics PDFvipulPas encore d'évaluation
- Metc SesiuneDocument10 pagesMetc SesiuneRazvan 888Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4) AC CircuitsDocument40 pages4) AC CircuitsS x DPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 Hoja de FormulasDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Hoja de Formulaslsanc308Pas encore d'évaluation
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionD'EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionPas encore d'évaluation
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64D'EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64Pas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesSTPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumDocument25 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentChris LauPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFDocument14 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFChris Lau100% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumDocument6 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumChris Lau100% (2)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument18 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsChris Lau67% (3)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Document15 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Chris Lau88% (17)
- AISWEI New Energy Technology Three Phase Inverters 3 To 6 KW DatasheetDocument1 pageAISWEI New Energy Technology Three Phase Inverters 3 To 6 KW DatasheetNalika De ZilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 12 Partial Equations: Differential (PDE)Document40 pagesUnit 12 Partial Equations: Differential (PDE)SonuPas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument10 pagesNullapi-25932525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Lab Manual Volume OneDocument60 pagesElectrical Lab Manual Volume OneMahesh M P NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi PS21767-VDocument9 pagesMitsubishi PS21767-VMadai Sanchez TopetePas encore d'évaluation
- Turbomachinery: of TheDocument165 pagesTurbomachinery: of TheAnoopPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter OneDocument28 pagesChapter Oneadisu100% (2)
- Differential EquationDocument6 pagesDifferential Equationমে হে দীPas encore d'évaluation
- Wait To Begin: SectionDocument8 pagesWait To Begin: SectionJoderPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanyo Ds13320 Service ManualDocument26 pagesSanyo Ds13320 Service ManualMauricio SolanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 535 1 NLSC Sample 24 GuideDocument6 pages535 1 NLSC Sample 24 Guidekyeyuneyasin572100% (1)
- Arihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Physics 2022-Motion in A Straight Line-19-28Document10 pagesArihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Physics 2022-Motion in A Straight Line-19-28shakthivinayaka6Pas encore d'évaluation
- I1. S.H.M. Estudy of The Mass-Spring System and Analysis of Oscillation With Cassy-LabDocument14 pagesI1. S.H.M. Estudy of The Mass-Spring System and Analysis of Oscillation With Cassy-LabSergio Lozano MijaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Physics and Measurement: 1.1 Basic and Derived UnitsDocument18 pagesChapter 1: Physics and Measurement: 1.1 Basic and Derived UnitsMin NaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Shin Se Kyung100% (1)
- Mechanics of Machines 15ME32TDocument8 pagesMechanics of Machines 15ME32TRaghuraj DanadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Document7 pagesExam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Jerome RacalPas encore d'évaluation
- Avm 1309S PDFDocument0 pageAvm 1309S PDFcarlosavictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolated Power Supply 30wDocument43 pagesIsolated Power Supply 30wchinnadurai20006034100% (1)
- HA16129FPJ: Single Watchdog TimerDocument24 pagesHA16129FPJ: Single Watchdog TimerMichael PorterPas encore d'évaluation
- BCS TheoryDocument56 pagesBCS TheoryhitupyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemsheets KS3 040 Density 2Document2 pagesChemsheets KS3 040 Density 2PopDV-SquaredPas encore d'évaluation
- Ficha Tecnica SkyAir CODocument1 pageFicha Tecnica SkyAir COErnesto Garza - CN8 ProyectosPas encore d'évaluation
- Standing Wave RatioDocument6 pagesStanding Wave RatioBea Mariz BilbaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 - Q1 - DW5Document3 pagesScience 8 - Q1 - DW5Argyll PaguibitanPas encore d'évaluation
- KKC Model Number System2Document3 pagesKKC Model Number System2zayerirezaPas encore d'évaluation
- SB2011-10 Online EN PDFDocument66 pagesSB2011-10 Online EN PDFAmanda KaizerPas encore d'évaluation