Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Questions
Transféré par
Innoj Maco0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
89 vues12 pagesAppendices-Skeletal System, Medical, Anatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAppendices-Skeletal System, Medical, Anatomy
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
89 vues12 pagesSample Questions
Transféré par
Innoj MacoAppendices-Skeletal System, Medical, Anatomy
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
1. Which of them are true in marker placement rule?
a. In chest and abdomen place marker side up, away from IR
b. In limb projection, 2 projection in 1 IR only one projection is marked
c. Lateral projection of head and trunk always mark closest to IR typically
placed posterior to anatomy
i. 4 & 3
ii. 3 & 2
iii. 1 & 3
iv. 1 & 2
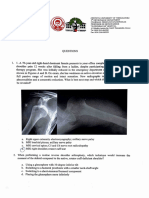
2. For instance the radiographer must position the px in left lateral recumbent
the x-ray beam is directed 10 degrees cephalad towards the sternoclavicular
joint. What is the projection used?
a. AP
b. AP axial
c. PA
d. PA Axial
3. What is true in achieving true lateral of forearm?
a. Flexed elbow 45 degree, thumb side down and forearm epicondyle
parallel to IR
b. Flexed elbow 45 degree, thumb side up and epicondyle perpendicular
to IR
c. Flexed elbow 90 degree thumb side down and epicondyle parallel to IR
d. Flexed elbow 90 degree thumb side up and epicondyle perpendicular
to IR
4. Which specific projection demonstrate?
a. Left lateral decub
b. Left lateral recum
c. Right lateral dec
d. Right lateral recum
5. Px rotated 45 degree, left side elevated, right side attached to table/vertical
grid. Ventral surface facing the cassette and beam entering the back of the
px. What specific projection.
a. AP
b. AP oblique
c. PA
d. PA oblique
6.
7. In general position what is similar to above mentioned?
a. Fowler
b. Lithotomy
c. Sims
d. Trendelenburg
8. Paul George has tibia and fibula injury, he is on the emergency room lying on
the stretcher and cannot sit, the radiographer notice on his CXR that he has
short length of lung and horizontally positioned heart. What affects his organ
location?
a. His fracture
b. Body habitus
c. Radiographers instructions
d. Px position on bed
9. What is the best projection to show zygomatic arches nasal bones and
patella?
a. AP
b. Axial
c. Decubitus
d. Tangential
10.Level of T1.
a. ASIS
b. Five centimeter above jugular notch
c. Inferior angle of scapula
d. Sternal angle
11.What is the CR for lateral hand projection?
a. Perpendicular to 3rd MCP joint
b. Parallel to 2nd DIP joint
c. Perpendicular to 2nd MCP joint
d. Parallel to 2nd PIP joint
12. What is best demonstrated in AP of the hand?
1. Carpal interspace
2. MCP joints
3. Metacarpal
4. Phalanges
13.For instances a px has a metacarpal injury is unable to extend the hand what
is the best projection in this condition
a. AP
b. AP oblique
c. PA
d. PA Oblique
14.
15.
16.What is the best technique in determining the exact location of the wrist joint
when the affected wrist has a wet cast?
a. Compare the affected wrist to the unaffected wrist
17.Which is correct in the evaluation criteria of the PA hand?
a. IP and MCP joints are separated
b. Minimal overlap between second to third and third to fourth
metacarpal shafts
c. Separate second and third metacarpal
d. Slight overlap metacarpal base and head
i. b and c
ii. a, c and d - for oblique
iii. b, c and d
iv. a, b, and d
18.In a general hand survey if the MCP and IP are open it means ____?
a. The hand was in true oblique position
b. The hand was places flat on the IR
c. The px has rheumatoid arthritis
d. There was a beam divergence
19.Which position of the wrist will allow the carpal navicular free from distortion?
a. Radial extension
b. Radial flexion
c. Ulnar extension
d. Ulnar flexion
20.Which position of the wrist that will include the carpal bone on the lateral
side?
a. Stetcher
b. Radial deviation
c. PA oblique
d. Gaynorr-hart
21.
22.Which two carpals bones are located most anteriorly in lateral wrist?
a. Capitate and lunate
b. Hamate and pisiform
c. Scaphoid and trapezium
d. Trapezium and trapezoid
23.Which carpal bone is mostly fractured
a. Capitate
b. Scaphoid
c. Trapezium
d. triquetrium
24.In pa wrist which structure is in slightly oblique position?
a. Metacarpals
b. Radius
c. Thumb
d. ulna
25.
26.A method that will best demonstrate scaphoid?
a. Clements nakayama
b. Gaynorr-hart
c. Lawrence
d. stetcher
27.Lateral palmar flexion is used to demonstrate?
1. Carpal boss
2. Distal radial and ulnar fracture
3. Metacarpal displacement
4. Wrist dislocation
28.Method that will best demonstrate trapezium?
a. PA axial oblique
b. PA oblique
c. Radial deviation
d. Tangential inferosuperior
29.What is being demonstrated in carpal bridge tangential position?
a. Calcification and foreign bodies of the dorsum part of the wirst
b. Demonstrate anterior aspect carpal/wrist
c. Scaphoid fracture
d. Lunate dislocation
30.Radial deviation of the wrist will demonstrate carpal interspaces on the?
a. Anterior part
b. Lateral part
c. Posterior part
d. Medial side
31.Reason of not pronating the hand in AP of the forearm
a. To prevent superimposition of the radius of ulna
32.These are the ff routine of the ulna
a. AP and lateral
b. AP and oblique
c. PA and lateral
d. PA and oblique
33.What is the purpose of instructing the px to lean laterally at the end of the
table?
a. Achieve true AP of part
b. Avoid beam divergence
c. Provide px comfort
d. Provide tech convenient
34.Which of the ff, is true about the gaynorr-hart method?
a. Uses inferosuperior and superoinferior beam direction
b. It demonstrate carpal canal
c. Uses tangential projection
d. Demonstrate hamular process
i. A, b, c
ii. A, b ,c, d
iii. B,c,d
iv.
35.Which is not found in the ulna?
a. capitulum
36.elbow medial oblique best demonstrate ___?
a. Coracoid process
b. Coronoid process
c. Epicondyles
d. Olecranon process
37.Which is the importance in flexing the elbow 90 degrees according to
Griswood
a. Coronoid is seen in profile
b. CR is directed to elbow joint
c. Elbow fat pads are in there most relax position
d. Px is comfortable
i. A and b
ii. B and c
iii. C
iv. B
38.What is/are requires in px positioning to obtain a true lateral elbow
a. Hand must be adjusted in lateral
b. Hand must be adjusted in prone
c. Humeral epicondyle must be parallel to IR
d. Humeral epicondyle must be perpendicular to IR
i. A nd b
ii. A and c
iii. And d A and D
iv. B and d
39.
40.Which of the ff, varying hand position used to demonstrate the entire
circumference of ulnar head?
a. Hand supinated
b. Hand lateral
c. Hand pronated none of the above
d. Hand internally rotated
41.What best position will demonstrate the radial head free of superimposition?
a. Acute flexion
b. Axial position
c. Lateral oblique
d. Lateromedial rotation
42.What structure is demonstrated in an AP elbow projection?
a. Capitulum
b. Trochlea
c. Radial head a,b,c
d. none
43.to do a medial oblique projection of the elbow
a. Bend arm 45 degrees
b. Hand is in neutral position
c. Pronate the hand
d. Supinate the hand
44.Method in axiolateral of the hip that can be used to px with bilateral hip
fracture
a. Danelius-Miller
b. Friedman
c. Clements-Nakayama
d. Leonard-George
45.What method in axiolateral of hip places unaffected limb in vertical position?
a. Danellius-Miller
b. Lauenstein
c. Clements-Nakayama
d. Leonard-George
46.Which method of the axiolateral hip that utilizes a curved cassette?
a. Danellius-Miller
b. Friedman
c. Hickey
d. Leonard-George
e. Hughston
47.Which method in the aciolateral of hip can be used for px that can only
tolerate lateral recumbent on the affected side with CR 35 degrees cephalad
to femoral head?
a. Danellius-Miller
b. Friedman
c. Hickey
d. Leonard-George
48.Which method in the lateral hip the utilizes CR direction 20 to 25 degrees
cepahalad to hip joint?
a. Danellius-Miller
b. Friedman
c. Hickey
d. Leonard-George
49.Modified cleaves for the demonstration of femoral neck is also called?
a. Axiolateral
b. Frog leg
c. Gull-Wing
d. Bilateral AP
50.Position that will best demonstrate acetabulum in PA axial?
a. Teufel
b. Judet
c. Hickey
d. Lauenstein
51.Positions in Judet method that demonstrates left & right posterior acetabular
rim and anterior iliopubic columa
a. RPO downside(right hip)
b. LPO upside (right hip)
c. RPO upside(left hip)
d. LPO downside(left hip)
i. And d
ii. B and c
iii. A and c
iv. B and d
52.w/c of the ff. projections produces tangential projection of bicipital grooves
a. Fisk method
b. Grashey method
c. Lawrence method
d. Mechant method
53.How much is the CR angled for inferosuperior axial projections(clements
modification) if the px cannot fully abduct the arms 90 degrees
a. 5 to 15 degrees
b.
c. 25 to 30 degrees
d. 20 degrees
54.Position of the shoulder and proximal humerus demonstrating the lesser
tubercle medially
a. External rotation
b. Neutral rotation
c. Internal rotation
d. Exaggerated rotation
55.What is the major advantage of supine, tangential version of intertubecular
groove projection over the erect version?
a. Less radiation exposure
b. Reduce OID
c. Less risk od motion
d. Ability to use AEC
56.Neer method
a. Subscpularis insertion
b. Supraspinatus outlet
c. Teres minor insertion
d. rhomboideus
57.What is the inferosuperior axial position of the shoulder joint that uses a CR
direction of 25 degrees anteriorly to the horizontal and 25 degrees medially
approximate 12 to 14 cm inferior and 3 to 4 cm to the acromial edge.
a. Clements method
b. Hobbs method
c. Lawrence modified method
d. West point modified
58.It is used to demonstrate px shoulder when the affected arm cannot be
abducted
a. Fisk
b. Hobbs
c. Clements
d. Transthoracic lateral projection (Lawrence method)
59.Which supplementary axial position for shoulder joint that can be used in px
with trauma and arm cannot be abducted?
a. AP axial
b. Axial- arm near in right
c. Cleaves- Rolled film
d. Lawrence- transthoracic lateral
60.Which special projection of shoulder places the glenoid cavity in profile for an
OPEN glenohumeral joint?
a. Garth
b. Grashey
c. Fisk
d. Hobbs
61.What is demonstrated in Pearson method?
a. Coracoid process
b. AC joints
c. Glenonid Fossa
d. Acromion
62.Px supine, shoulder lateral at the midline of the cassette, CR at the
posterosuperior region of the shoulder 45 degrees caudad what method was
made?
a. Fisk
b. Laquerriere-Pierquin
c. Tarrant
d. Lorenz and Lilienfeld
63.Which of the ff. is true about scapular Y?
i. Px is in PA position
ii. Visualizes anterior dislocation
iii. Visualizes posterior dislocation
iv. The scapula is in lateral position
a. I, ii, iii
b. I, iv
c. Ii, iii, iv
d. All of the above
64.What is the projection when px is in lordotic position for clavicle x-ray?
a. AP axial
b. PA
c. PA axial
d. tangential
65.performed to place the lateral border of the scapula free of superimposition
and projected laterally?
a. AP
b. Lateral
c. AP oblique
d. PA oblique
66.
67.Where are the sesamoid bones of the foot most commonly located
a. Plantar surface near head of first metatarsal
b. Plantar surface of first tarsometatarsal joint
c. Dorsal area at base of first metatarsal
d. Plantar surface near cuboid bone
68.What is the name the tarsal bone located medially between the talus and
three cuneiforms?
a. Calcaneus
b. Intermediate cuneiform
c. Cuboid
d. Navicular
69.What is another term for talocalcaneal joint?
a. Tarsometatarsal joint
b. Subtalar joint
c. Mortise joint
d. tibiocalcaneal joint
70.how much is the rotation for the oblique medial of the foot?
a. 3 to 5 degrees
b. 45 degrees
c. 30 degrees
d. 15 to 20 degrees
71.What is demonstrated well in the lateral oblique of foot?
a. Cuboid and lateral cuneiform
b. Navicular, mediolateral and intermediate cuneiform
c. Sinus tarsi
d. Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal and calcaneus
72.
73.Projection that will best demonstrate mortise of the ankle?
a. AP
b. AP oblique(15 to 20 degrees medial rotation)
c. AP (15 to 20 degrees lateral rotation)
d. Mediolateral
74.What is the angulation of the sole of the foot in PA (plantodorsal) oblique
position
a. 45 deg
b. 30 deg
c. 10 deg
d. 25 deg
75.A true lateral of the foot is achieved in ___ position?
a. Bilateral
b. Lateromedial
c. Mediolateral
d. Weight bearing
76.Grashey method oblique method of the foot
a. 30 deg lateral and 20 deg medial rotation
b. 20 deg lateral and 30 deg medial rotation
c. 30 deg medial and 20 deg oblique rotation
d. 20 deg lateral and 30 deg oblique rotation
77.A congenital club foot is otherwise known as?
a. Talipes equinovarus
78.What is being investigated on the lateral of the weight bearing of the foot?
a. Equinus
b. Longitudinal arch
c. Ligament tear
d. Osteoarthritis
79.What is the method that uses dorsoplantar axial projection in the examination
of club feet?
a. Kandel
b. Kite
c. Grashey
d. Davis
80.Which is not true about the composite dorsoplantar position of the foot?
a. It is an axial image of the entire foot
b. It uses simultaneously posterior and anterior angulation
c. Structures shown with feet free of shadow of leg
d. It is perform in px in weight bearing
i. A c d
ii. B, c, d
iii. A, b, c, d
iv. nota
81.the axial image of the calcaneus can be demonstrated in both plantodorsal
and dorsoplantar position?
a. True
b. False
c. True, only in lateral
d. False only in plantodorsal
82.Which is correct about the deviations of congenital club feet? Incomplete
data
a. Supination
b. Equinos
c. Adduction
i. A,b,c
ii. B, c
iii. A,c
iv. b
83.weight bearing coalition position for calcaneotalar coalition was described
by ___?
a. Lorenz
b. Lilienfeld
c. Kite
d. Broden
84.
85.Anterior articulation of the subtalar forms the ___?
a. Talocalcaneal joint
b. Talocalcaneocuboidal joint
c. Talocalneonavicular joint
d. Calcaneonaviculotalar joint
86.CR for ankle AP?
a. Between lateral and medial malleolus
87.A procedure used to verify the presence of ligamentous tear in the affected
ankle
a. AP 45 deg medial rotation
b. AP stress studies
c. AP weight bearing
d. AP dorsiflexion
88.Which is true about the AP radiograph of leg?
a. Patella is superimposed
b. Follow up projections should include both ankle and knee joints
c. Proximal and distal articulations of tibia and fibula have no overlapping
d. CR directed perpendicular to the center of leg
89.What is the CR direction in the AP of knee
a. cm inferior to the patellar base at an angle of 5-7deg cephalad
b. inch inferior to the patellar apex at an angle of 5-7deg cephalad
c. cm inferior to the patellar apex at an angle of 5-7deg cephalad
d. inch inferior to the patellar base at an angle of 5-7deg cephalad
90.What is the degree of flexion in lateral of the knee?
a. 10-15deg
b. 20-30deg
c. 15-30deg
d. 30-45deg
91.To demonstrateFemoropatellar joint, px is in supine with knees flexed 40 deg,
and angulated 30 deg caudad from horizontal, the cassette is in below the
legs supported by a special device. What is the method used?
a. Camp Coventry
b. Settegast
c. Hughston
d. Bilateral merchant
92.A projection is performed in knees flexed, cassette is below the thigh, used to
detect fracture vertically in the said bone. What method is this?
a. Beclere
b. Camp coventry
c. Settegast
d. holmblad
93.A method where the intercondylar fossa is in PA axial position and could be
done in standing upright with knees on foot stool or kneeling on the table.
a. Camp Coventry
b. Settegast
c. Holmblad
d. hughston
94.intercondylar fossa that is investigated in AP axial position with image
improved by using curved cassette
a. Camp Coventry
b. Beclere
c. Tunnel view
d. hughston
95.why is that toes are internally rotated 15deg in AP femur?
a. To prevent anterversion of the femoral head
b. To prevent anterversion of the femoral neck
c. To prevent anterversion of the trochanter
d. To prevent anterversion of the femoral shaft
96.In PA axial for intercondylar fossa for px in prone position w/ knee
flexed/elevated 40 deg and CR directed 40 deg caudally. What method?
a. Camp-coventry
b. Beclere
c. Tunnel view
d. Hughston
97.This position utilizes to view the patella
a. Huhgston
b. Merchant
c. Kuchendorf
d. settegast
98.this position demonstrates the patella in prone position with Cr angulated 45
deg cephalad and directed to the patellofemoral joint.
a. Hughston
b. Settegast
c. Camp Coventry
d. kuchendorg
99.a method that recommends right angle oblique position for the determination
of posterior articular facets of os calcis to determine joint involvement in
comminuted fracture.
a. Isherwood
b. Lilienfeld
c. Kite
d. Broden
100. Which is true about Blackett-Healy method
a. Radiograph of teres minor insertion in patient in prone
b. Radiograph of subscapular insertion px in supine
c. Radiograph of teres minor insertion in px supine
d. Radiographos subscapular insertion in px prone
i. B and c
ii. A and b
iii. A and d
iv. C and d
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- EV EXAM 2 Answer KeyDocument10 pagesEV EXAM 2 Answer KeyRachelle Danya Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof. ChingDocument9 pagesProf. ChingJanelle Ann CasuyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiographic Positioning and Special Procedure1Document38 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Special Procedure1renred1225Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quizzess PosiDocument10 pagesQuizzess PosikylaabelendePas encore d'évaluation
- GROSS HSB A Prelim 2018Document18 pagesGROSS HSB A Prelim 2018nge257Pas encore d'évaluation
- EXAM B SolDocument10 pagesEXAM B SolNuhad Bou MoslehPas encore d'évaluation
- VC ExamDocument16 pagesVC ExamJo Hn VengzPas encore d'évaluation
- Cluster 3 Pre Board 2022Document19 pagesCluster 3 Pre Board 2022Princess Joy CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Thoracic Spine Quiz TestDocument16 pagesThoracic Spine Quiz TestAnuj AryanPas encore d'évaluation
- MRD400Document14 pagesMRD400AKID MARHA ARMIZIPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition by LampignanoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition by Lampignanopellucidutter.uka6lr100% (43)
- Mentoring Class MidtermDocument9 pagesMentoring Class MidtermJanelle Ann CasuyonPas encore d'évaluation
- General Sciences Q A From WellsDocument1 921 pagesGeneral Sciences Q A From Wellscanaduh2023Pas encore d'évaluation
- AAOS Hand and Wrist (49 Soal)Document14 pagesAAOS Hand and Wrist (49 Soal)Fasa RoshadaPas encore d'évaluation
- DDM 2-A5: General Anatomy Sas 1: The Upper LimbDocument7 pagesDDM 2-A5: General Anatomy Sas 1: The Upper LimbKathleen Abegail Bacay NalzaroPas encore d'évaluation
- D. Cardiac EnlargementDocument10 pagesD. Cardiac EnlargementNuhad Bou Mosleh100% (1)
- C. Suspension of BreathingDocument18 pagesC. Suspension of BreathingChar RachterPas encore d'évaluation
- C. Kyphosis: Measures An Angle or Allows An Object To Be Rotated To A Precise Angular MotionDocument4 pagesC. Kyphosis: Measures An Angle or Allows An Object To Be Rotated To A Precise Angular MotionJojo JustoPas encore d'évaluation
- SoalDocument8 pagesSoalNunis Nur AzizahPas encore d'évaluation
- Sas 3Document8 pagesSas 3Kathleen Abegail Bacay NalzaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Le Ga 1Document15 pagesLe Ga 1Carlos NiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Workbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test BankDocument9 pagesWorkbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test Bankedselladonna6c2d76100% (28)
- Exam C SolDocument10 pagesExam C SolNuhad Bou MoslehPas encore d'évaluation
- Rivera - LABORATORY EXERCISE No. 1 - ANAPHYDocument3 pagesRivera - LABORATORY EXERCISE No. 1 - ANAPHYRivera, Trishia PilonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test BankDocument16 pagesBontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test BankMrsKellyHammonddqnya100% (9)
- Test Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 4th Edition by KelleyDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 4th Edition by KelleyDavid Perry100% (31)
- Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test BankDocument13 pagesBontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test Bankloganwalkertcaenpjsid100% (33)
- PRP RationaleDocument12 pagesPRP Rationalemarquezjayson548Pas encore d'évaluation
- Floyd17 TB Ch12Document5 pagesFloyd17 TB Ch12sdjuknicPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Prelim Answer KeyDocument8 pagesAnatomy Prelim Answer KeyDominic DinioPas encore d'évaluation
- Mes 3Document4 pagesMes 3Johnpeter EsporlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Prometric Ortho 2014Document10 pagesPrometric Ortho 2014moutaz702100% (1)
- Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8Th Edition Bontrager Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8Th Edition Bontrager Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdecagrambarrymfh100% (6)
- Apk 1997Document9 pagesApk 1997Pau CMedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compiled MSPC 235 Past Questions Volume IIIDocument15 pagesCompiled MSPC 235 Past Questions Volume IIIPaapaErnestPas encore d'évaluation
- IBO QuestionsDocument3 pagesIBO QuestionsMariyamPas encore d'évaluation
- MIS109Document13 pagesMIS109AKID MARHA ARMIZIPas encore d'évaluation
- Apk Mock Boards Practice Questions Set A No AnswerDocument26 pagesApk Mock Boards Practice Questions Set A No AnswerYuvienco DrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Bontragers Handbook of Radiographic Positioning and Techniques 9th Edition by Lampignano DownloadDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Bontragers Handbook of Radiographic Positioning and Techniques 9th Edition by Lampignano Downloadstevenstevensjgzaryxbdp100% (25)
- Chapter 11 - The Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 11 - The Appendicular Skeletal Systemmedianoche191% (11)
- Basic Biomechanics 6th Edition Hall Test BankDocument33 pagesBasic Biomechanics 6th Edition Hall Test Bankterrysmithnoejaxfwbz100% (17)
- Ebook Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy 6Th Edition Lippert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesEbook Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy 6Th Edition Lippert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJeffreyLawsonmkbof100% (12)
- FC Cebu 2015 Bort Radiographic Positioning Solicitation ExamDocument43 pagesFC Cebu 2015 Bort Radiographic Positioning Solicitation ExamRadTech ReviewerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ortho Exams 31.1.23Document14 pagesOrtho Exams 31.1.23samg4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Anatomy Preliminary Exams SamplexDocument12 pagesGross Anatomy Preliminary Exams SamplexCarlos NiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Test Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 4th Edition by Kelley PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Sectional Anatomy For Imaging Professionals 4th Edition by Kelley PDF Full Chapterflotageepigee.bp50100% (21)
- 1665578086932-Q Bank A Physio Officer 5Document23 pages1665578086932-Q Bank A Physio Officer 5mosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Biomechanics 6Th Edition Hall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesBasic Biomechanics 6Th Edition Hall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtrancuongvaxx8r100% (13)
- Test Bank For Anatomy Physiology and Disease 2nd Edition ColbertDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Anatomy Physiology and Disease 2nd Edition ColbertJoseph Benson100% (35)
- Anp ch1 Quiz 2Document3 pagesAnp ch1 Quiz 2api-421863070Pas encore d'évaluation
- D. Cavitation A. Halo OrthosisDocument10 pagesD. Cavitation A. Halo OrthosisHakim Alhaady100% (1)
- MPT Question PaperDocument4 pagesMPT Question Paperjuveriya mubeen100% (1)
- In All The Slides Questions From 1 To 20 Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument22 pagesIn All The Slides Questions From 1 To 20 Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerABUBAKER ZANBOUZIPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Anatomy Physiology and Disease 2nd Edition ColbertDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Anatomy Physiology and Disease 2nd Edition ColbertgwynethmyrqtxPas encore d'évaluation
- جذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما A) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-A)Document9 pagesجذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما A) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-A)Nuhad Bou MoslehPas encore d'évaluation
- UL MCQs STAGE Best BestDocument9 pagesUL MCQs STAGE Best BestMuhammad kamran ameerPas encore d'évaluation
- For All of The Questions Upper LimpDocument22 pagesFor All of The Questions Upper LimpKAAB MEDICS ZONEPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Shoulder Region - Hussein 2028Document49 pagesAnatomy of The Shoulder Region - Hussein 2028hcnk yvsnkPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ of UpperDocument17 pagesMCQ of Upperد.مهاجر في أرض اللهPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsD'EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (15)
- Muscle Flash CardsDocument127 pagesMuscle Flash Cardsjoelh9100% (3)
- Blount's Disease (Textbook)Document17 pagesBlount's Disease (Textbook)Fadzhil AmranPas encore d'évaluation
- Trauma Atlas Insertin Transoseous Wires Etc IlizarovDocument47 pagesTrauma Atlas Insertin Transoseous Wires Etc Ilizarovsergiu_inaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Normal Foot and AnkleDocument12 pagesThe Normal Foot and AnkleDRRANGELLUNAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ankle JointDocument33 pagesAnkle JointAtanu Kumar NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.anatomi EXTREMITAS SUPERIORDocument65 pages3.anatomi EXTREMITAS SUPERIORAzhardin Maralaut SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- JUST MEDICAL - Product Catalog - Hip&Knee - Specs - OE - 202206Document41 pagesJUST MEDICAL - Product Catalog - Hip&Knee - Specs - OE - 202206Jack ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteologyDocument96 pagesOsteologyBenita Putri MD100% (2)
- Resume Anatomi Ekstremitas 2Document8 pagesResume Anatomi Ekstremitas 2Adinda Malinda KumalawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Joint Anatomy ManualDocument6 pagesKnee Joint Anatomy ManualDungani AllanPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument65 pagesAppendicular Skeletonnanak00ciaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles of The ScapulaDocument6 pagesMuscles of The ScapulaAndika Anjani AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Limb LowerDocument70 pagesBone Limb LowerGutu Garemewu BiruPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre TestDocument5 pagesPre TestRolly HeridaPas encore d'évaluation
- BP OrthoDocument1 pageBP Orthoyenidwianggra sudarmajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Elbow DislocationsDocument23 pagesElbow DislocationsbonemenderPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendicular Skeleton: Upper Lower Limbs GirdlesDocument37 pagesAppendicular Skeleton: Upper Lower Limbs GirdlesAprilSensengPas encore d'évaluation
- 206 Bones ReviewerDocument2 pages206 Bones ReviewerJofelle Goc-Ong Torres100% (4)
- 16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)Document30 pages16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)kath-kath100% (1)
- Female PelvisDocument41 pagesFemale Pelvissanthiyasandy100% (6)
- Acetabulum Fractures - Classification and Management - Emile LetournelDocument26 pagesAcetabulum Fractures - Classification and Management - Emile LetournelThanat AuwattanamongkolPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Teacher Worksheets Word Search 4Document3 pagesSuper Teacher Worksheets Word Search 4Muhammad TayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Limb AxisDocument18 pagesLimb AxisBadea Mihai LaurentiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteology Lower Limb, by DR IramDocument76 pagesOsteology Lower Limb, by DR IramimmmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Femur, Patella and TibiaDocument10 pages2 Femur, Patella and Tibiaطه طارقPas encore d'évaluation
- Similarity & Difference AnatomyDocument2 pagesSimilarity & Difference AnatomyhoopsPas encore d'évaluation
- Head, Neck, and Trunk: Nama: Jihan Syifa PRAYUDIPTA NPM1806179882 Jurusan: Fisioterapi'18Document26 pagesHead, Neck, and Trunk: Nama: Jihan Syifa PRAYUDIPTA NPM1806179882 Jurusan: Fisioterapi'18Fatiha GustiarniPas encore d'évaluation
- X-Ray Views HipDocument1 pageX-Ray Views Hipjuly mirandillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionDocument15 pagesBones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionChess Nuts100% (1)
- Color Atlas of Surgical Approaches To The Bones and Joints of The Dog and CatDocument245 pagesColor Atlas of Surgical Approaches To The Bones and Joints of The Dog and CatScott Rose100% (8)