Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Edma262 - Assignment Two
Transféré par
api-358330682Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Edma262 - Assignment Two
Transféré par
api-358330682Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
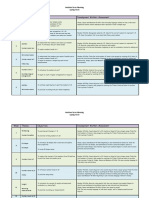
Student A:
Year Level: 3
Growth points reached:
Domain Growth Growth point (in words)
point
(number)
Counting Growth Counting from x (where x>0) by 2s,
Point. 5 5s and 10s
Given a non-zero starting point,
can count by 2s, 5s and 10s to a
given target.
Place Value Growth Reading, writing, interpreting and
Point. 3 ordering three-digit numbers
Can read, write, interpret and order
three-digit numbers
Addition & subtraction Growth Derived strategies (near doubles,
strategies Point. 5 adding 9, build to next ten, fact
families, intuitive strategies)
Given an addition or subtraction
problem, strategies such as near
doubles, adding 9, build to next
ten, fact families and intuitive
strategies are evident.
Multiplication & division Growth Abstracting multiplication and
strategies Point. 4 division (no objects perceived)
Mentally solves multiplication and
division problems (no objects
perceived) using multiplicative
structure of the situation.
Report:
Within this interview, David was able to count forwards and backwards by ones. He is also
able to skip count from zero, as well as a non-zero starting point by 2s, 5s and 10s to a given
target. He was able to identify the number that is more or less than the known number. He was
able to recognise that five more than thirty-five is forty and ten less than seventy is sixty.
David is able to read, write, interpret and order three-digit numbers. He was able to use
concrete materials such as pop-sticks to represent a number. By using the bundles of ten and
loose pop-sticks, David was able to make the number thirty six, but firstly grabbing three
bundles and six loose ones. Additionally, David can interpret two and three-digit number lines
and locate the missing value of the given point. He able was to interpret the number line and
understand that halfway between zero and a hundred was fifty.
David was able to use derived strategies such as near doubles, fact families and build to the
next ten when solving a single-digit addition or subtraction problem. To illustrate this, he was
able to understand that twelve is made up of double six and that three and seven is a fact
family of ten.
When solving multiplication and division problems, David was able to use the strategy of skip
counting by 2s, 3s and 5s to determine the whole of a partial model. He was able to recognize
that four packets with three tennis balls in each, is equivalent to twelve tennis balls altogether.
Within this, he was able to skip count by 4s from zero to twelve. In regards to abstract thinking,
he was able to listen to a story and mentally solve the problem using multiplication and division
strategies of skip counting, to a given point.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mai Report Student BDocument1 pageMai Report Student Bapi-250895737Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mai Growth Points ReportDocument2 pagesMai Growth Points Reportapi-380350226Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Interview Assessment Report and Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesMathematics Interview Assessment Report and Lesson Planapi-459495093Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 Mathematics Supp AssessmentDocument14 pagesEdma262 Mathematics Supp Assessmentapi-357915760Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 MathematicsDocument2 pagesEdma262 Mathematicsapi-235505936Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Edma Nutshell StatementsDocument2 pages5 - Edma Nutshell Statementsapi-254271909Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 2012 Assessment Task 2 Template - Nutshell StatementsDocument3 pagesEdma262 2012 Assessment Task 2 Template - Nutshell Statementsapi-221736773Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lachlans Report - 2015Document2 pagesLachlans Report - 2015api-358964177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Task 2Document6 pagesTask 2api-336072959Pas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 4 Mathematics SyllabusDocument11 pagesICSE Class 4 Mathematics SyllabusAnanya RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Ubd MapDocument12 pagesUbd Mapapi-497961190Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 Sophie Growth Point ProfileDocument2 pagesEdma262 Sophie Growth Point Profileapi-357056328Pas encore d'évaluation
- SF Parish School 1st Quarter Math ScopeDocument8 pagesSF Parish School 1st Quarter Math ScopeLeonardPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Grade 5 (PDFDrive)Document318 pagesMath Grade 5 (PDFDrive)OLIVEEN WILKS-SCOTTPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 3 Maths Part 1 OverviewDocument12 pagesYear 3 Maths Part 1 OverviewMariana MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 4 EvidenceDocument6 pages5 4 Evidenceapi-359353378Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 - Assignment 1Document16 pagesEdma262 - Assignment 1api-319280742Pas encore d'évaluation
- Targets Math Year2Document8 pagesTargets Math Year2Marc WalshPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9D'EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5: Numbers To 100 (30 Periods) : Competencies Learning Strategies AssessmentDocument2 pagesUnit 5: Numbers To 100 (30 Periods) : Competencies Learning Strategies AssessmentyitagesPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 6 Mathematics SyllabusDocument15 pagesICSE Class 6 Mathematics SyllabusTania BhaumikPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 3 Long Term Curriculum Plans Essentials Curriculum®Document4 pagesYear 3 Long Term Curriculum Plans Essentials Curriculum®api-357252563Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Progression Map Multiplication and Division Reasoning F v2Document7 pages3 Progression Map Multiplication and Division Reasoning F v2Ummi LiyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Maths Syl NumberDocument39 pages03 Maths Syl NumberMerich Jane BarlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mme Elias 2/3B 2020-2021 Long Range PlansDocument5 pagesMme Elias 2/3B 2020-2021 Long Range PlansAngela YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths ProgressionsDocument15 pagesMaths Progressionsapi-3509019030% (1)
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 4v1Document60 pagesScheme of Work Maths Stage 4v1Keren Hapkh50% (2)
- Math CentersDocument18 pagesMath Centersapi-5290956020% (1)
- ICSEClass 2 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesICSEClass 2 Maths Syllabussailasree potayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cip Maths Grade3Document5 pagesCip Maths Grade3Sadaf RasheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 2 Maths SyllabusDocument7 pagesClass 2 Maths Syllabuskids duniyaPas encore d'évaluation
- No 2Document3 pagesNo 2api-3723109Pas encore d'évaluation
- (GR) Part 01 Overview MathsDocument12 pages(GR) Part 01 Overview MathskarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths in Year 1Document29 pagesMaths in Year 1Mar AttardPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 3 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesClass 3 Maths SyllabusKamal VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 1-8 - Part16Document2 pagesMathematics 1-8 - Part16yitagesPas encore d'évaluation
- Y1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Multiplication & DivisionDocument3 pagesY1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Multiplication & DivisionAndy BrookePas encore d'évaluation
- Year 2 Mathematics CurriculumDocument46 pagesYear 2 Mathematics Curriculumwaldorfknoll101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Number: Early Learning Progression: Key Concept Importance of Concept Teaching and Learning Points Pre-CountingDocument2 pagesNumber: Early Learning Progression: Key Concept Importance of Concept Teaching and Learning Points Pre-CountingNicole DyerPas encore d'évaluation
- MTED 3109 Place Value - NumerationDocument20 pagesMTED 3109 Place Value - NumerationKristin HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- Math MWDocument20 pagesMath MWHarvey GallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Primary Mathematics Scheme of WorkDocument42 pagesCambridge Primary Mathematics Scheme of WorkKatongole Atwib100% (1)
- TERM 1 MATHS TOPICSDocument2 pagesTERM 1 MATHS TOPICSHeidi JayPas encore d'évaluation
- Number Talks Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNumber Talks Lesson Planapi-505836597100% (1)
- Ilp FinalDocument20 pagesIlp Finalapi-299133932Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths 2TDocument3 pagesMaths 2TMaría GoicoecheaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Grade 3 Lesson GuideDocument5 pagesMath Grade 3 Lesson GuideDyames TVPas encore d'évaluation
- Kindergarten Unit 3 Outline Overview 2017Document26 pagesKindergarten Unit 3 Outline Overview 2017api-401628488Pas encore d'évaluation
- COMPETENCY BASED ASSESSMENT - MATHEMATICS CLASS- VI CH 8 DECIMALSDocument6 pagesCOMPETENCY BASED ASSESSMENT - MATHEMATICS CLASS- VI CH 8 DECIMALSArnav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Plan Week 6Document3 pagesMaths Plan Week 6woodward_jodie_jPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 7Document14 pagesScheme of Work Maths Stage 7Arumugam PalaniapanPas encore d'évaluation
- 7609 Resource 5b954169b3b6d632722185Document2 pages7609 Resource 5b954169b3b6d632722185Ramy RedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Counting Guide 508 PDFDocument95 pagesCounting Guide 508 PDFSyauqi AnugrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 3 Maths Part 2 OverviewDocument12 pagesYear 3 Maths Part 2 OverviewMariana MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 5 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum ObjectivesDocument16 pagesYear 5 Week 2 Lesson 1 Main Focus Prior Knowledge Key Vocabulary Curriculum Objectiveslenson kinyuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work - Mathematics Stage 2: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3Document46 pagesScheme of Work - Mathematics Stage 2: Term 1 Term 2 Term 3Tumwesigye robertPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 2.v1Document46 pagesScheme of Work Maths Stage 2.v1Tu Minh100% (10)
- STEP Standard 3-5Document23 pagesSTEP Standard 3-5Charon HolmesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fact Families and Intro To Adding 3 Numbers 2016Document2 pagesFact Families and Intro To Adding 3 Numbers 2016api-340834297Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hist106 - Assignment TwoDocument2 pagesHist106 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edss468 - Assignment Three1Document7 pagesEdss468 - Assignment Three1api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Task 2Document2 pagesAssessment Task 2api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Task 2Document2 pagesAssessment Task 2api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cybersafety PolicyDocument2 pagesCybersafety Policyapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Area AssessmentDocument1 pageArea Assessmentapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics - Area 2Document1 pageMathematics - Area 2api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edla369 - Assessment Task 33Document2 pagesEdla369 - Assessment Task 33api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edla369 - Assessment Task 3Document6 pagesEdla369 - Assessment Task 3api-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edfd260 - Assignment TwoDocument1 pageEdfd260 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Post ReviewDocument1 pagePost Reviewapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma262 - Assignment TwoDocument9 pagesEdma262 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edfd261 - Assignment OneDocument6 pagesEdfd261 - Assignment Oneapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edma360 - Assignment TwoDocument3 pagesEdma360 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682Pas encore d'évaluation
- BMGT 26-TQM (Revised)Document11 pagesBMGT 26-TQM (Revised)Jay Montegrande LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- OB c2 Personality, Learning, Attitudes and PerceptionDocument35 pagesOB c2 Personality, Learning, Attitudes and Perceptionkuyu2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- David Rapaport - Emotions and MemoryDocument305 pagesDavid Rapaport - Emotions and Memorymanutoutcourt83% (6)
- Assumption of Normality Analysis in SPSSDocument27 pagesAssumption of Normality Analysis in SPSSEmy LilyPas encore d'évaluation
- NIST Handbook PDFDocument426 pagesNIST Handbook PDFFaryalBalochPas encore d'évaluation
- Atthasalini Pe Maung TinDocument10 pagesAtthasalini Pe Maung TinvasubandhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14&15Document42 pagesChapter 14&15Avie Acu50% (2)
- BSED-SCIENCE3B GROUP VI ppt.7Document11 pagesBSED-SCIENCE3B GROUP VI ppt.7Novy SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Theory PDFDocument28 pagesWhat Is Theory PDFTeo FilusPas encore d'évaluation
- GEED10053 FIRST LONG EXAM SOLUTIONSDocument5 pagesGEED10053 FIRST LONG EXAM SOLUTIONSDanicaEsponillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blaisdell Rational Animals Rational Animals Irrational Humans Chapter 9 PDFDocument20 pagesBlaisdell Rational Animals Rational Animals Irrational Humans Chapter 9 PDFDrăgulescu Ionela AndaPas encore d'évaluation
- Referential TheoryDocument24 pagesReferential TheorysehrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Differences between maxims and disciplines - Edu601 topicsDocument14 pagesDifferences between maxims and disciplines - Edu601 topicsRanaFarhan0% (1)
- Minggu 14 Rekabentuk Campuran-20190429030630Document62 pagesMinggu 14 Rekabentuk Campuran-20190429030630aquartojyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Master Key System: Unlocking Your Unlimited PotentialDocument164 pagesThe Master Key System: Unlocking Your Unlimited PotentialLuis Oropeza100% (1)
- Your Values ProfileDocument13 pagesYour Values ProfileJuan De La HozPas encore d'évaluation
- TEXT BOOK - Book - Stangor.complete - OptimizedDocument479 pagesTEXT BOOK - Book - Stangor.complete - OptimizedDaniel GetahunPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Ooad NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 3 Ooad Notesdivyarose50% (2)
- The Doctrine of Acquired Rig TS: PI R E A. LalivDocument29 pagesThe Doctrine of Acquired Rig TS: PI R E A. LalivKen CasanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of Semantics To An IndividualDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Semantics To An IndividualTwilight100% (1)
- Consumer and Business MarketDocument27 pagesConsumer and Business MarketYsah CortezPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Scaffolding - Through - Language - v2Document7 pages3 Scaffolding - Through - Language - v2Elena Gil ZambranaPas encore d'évaluation
- THY 1 Unit Test PDFDocument3 pagesTHY 1 Unit Test PDFmaxinePas encore d'évaluation
- Automating Data Extraction in Systematic Reviews: A Systematic ReviewDocument16 pagesAutomating Data Extraction in Systematic Reviews: A Systematic ReviewJose Inti Matamala PizarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Klein, by EternityDocument31 pagesKlein, by EternityClaudia AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Problem and Its SettingDocument48 pagesThe Problem and Its SettingVyunTae TAEPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Organisational Behaviour and CultureDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Organisational Behaviour and CultureSuhrab Khan JamaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Maykut MorehouseDocument16 pagesMaykut MorehousefarumasPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Auditing of Laboratory Quality Management SystemsDocument66 pagesInternal Auditing of Laboratory Quality Management Systemsmarwa100% (4)
- Par ReportDocument5 pagesPar ReportShyam Kishore TripathiPas encore d'évaluation