Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes in Clinical Chemistry MLT
Transféré par
wailjs0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
169 vues4 pagesThis document summarizes several enzymes that are important in clinical chemistry, including their function, class, source, and clinical significance. Some key enzymes discussed are CK, which is important for diagnosing heart disorders; LD and AST, which can be elevated in cardiac, hepatic, and muscle diseases; ALT and ALP, which are elevated in hepatic disorders; and GGT, which is used to evaluate liver and biliary disorders when increased. The document provides a high-level overview of the clinical importance of these enzymes.
Description originale:
Quick chart of the enzymes commonly tested in the laboratory
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document summarizes several enzymes that are important in clinical chemistry, including their function, class, source, and clinical significance. Some key enzymes discussed are CK, which is important for diagnosing heart disorders; LD and AST, which can be elevated in cardiac, hepatic, and muscle diseases; ALT and ALP, which are elevated in hepatic disorders; and GGT, which is used to evaluate liver and biliary disorders when increased. The document provides a high-level overview of the clinical importance of these enzymes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
169 vues4 pagesEnzymes in Clinical Chemistry MLT
Transféré par
wailjsThis document summarizes several enzymes that are important in clinical chemistry, including their function, class, source, and clinical significance. Some key enzymes discussed are CK, which is important for diagnosing heart disorders; LD and AST, which can be elevated in cardiac, hepatic, and muscle diseases; ALT and ALP, which are elevated in hepatic disorders; and GGT, which is used to evaluate liver and biliary disorders when increased. The document provides a high-level overview of the clinical importance of these enzymes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Enzymes in Clinical Chemistry MLT
Function Class of Source Clinical importance
enzyme
CK ATP generation Transferase Muscle, brain, -CK-MB is sensitive
heart to heart disorders but
not specific
-AMI
-Duchennes
muscular dystrophy
-Polymyositis
-CNS disorders,
hypothyroidism,
hyperpyrexia, Reyes
syndrome
LD Catalyzes conversion of Oxido- Highest amt in - in cardiac,
lactic acid and pyruvic reductase heart, liver, hepatic, skeletal
acid skeletal muscle, renal
muscle, diseases,
kidneys, rbcs hematologic and
neoplastic
disorders
- highest amts in
pernicious
anemia and
hemolytic
disorders
AST Synthesis and degradation Transferase Highest in -can be found in AMI
of amino acids liver, then - in pulmonary
heart, then embolism and
skeletal following CHF
-highest levels in
hepatocellular
disorders (viral
hepatitis up to 100X
UNL, cirrhosis up to
4X UNL)
-high levels seen in
skeletal muscle
problems
-other diseases such
as Niemann Pick,
Gauchers, diabetic
ketoacidosis,
hyperthyroidism,
myelocytic leukemia
ALT Similar to AST Transferase Highest in in hepatic disorders,
liver higher in cellular
disorders than in
obstructive disorders
-if no liver
involvement, would
not elevate in AMI
ALP Release inorganic Hydrolase Highest in - in hepatobiliary
phosphate from organic bone, liver disorders, more so in
phosphate ester and (also intestine, obstructive disorders
produces alcohol upon spleen, than hepatocellular
release placenta, disorders
kidney) - in bone disorders,
highest in Pagets
disease
also in bone
healing, growth in
children, and bone
fractures (key is
pathological is >5X
UNL whereas
growth/heal is <5X
UNL)
- in pregnancy
ACP Prostate related but is now Hydrolase prostate PSA has replaced
replaced by PSA ACP for prostate
analysis
GGT Transfers -glutamyl Highest in -Evaluate liver and
residue from -glutamyl kidneys but biliary disorders
peptides to amino acids, also in liver when increased
water, and small peptides -monitor chronic
alcoholism
AMY/AM Breaks down starch and Hydrolase Acinar cells of -serum and urine
S glycogen to glucose, pancreas and shows acute
maltose, and dextrin salivary glands pancreatitis
- in intra-abdominal
problems such as
acute appendicitis,
peptic ulcers, etc
LIPASE Breaks down fats to Hydrolase pancreas Diagnosis of acute
alcohols and fatty acids pancreatitis, usually
done as a follow-up
for amylase because
it is more specific but
less sensitive
CHOLIN- ACHe hydrolyzes ACHe RBCs, - PCHe seen in liver
ETERASE acetylcholine neural disease, malignancy,
(acetylchol PCHe - degradation of synapses (also starvation, burn
inesterase exogenous choline ester lungs and injuries, poisoning
or ACHe,
drugs spleen) -ACHe on amniotic
pseudochol
PCHe serum, fluid for the detection
inesterase
or PCHe) liver (pancreas, of neural tube defects
heart, white
matter also)
G6PD Involved in the normal Oxido- -Most critical - in RBCs, maintains
processing of reductase is inside RBCs NADPH levels in
carbohydrates. It plays a - also in reduced form (needed
critical role in red blood adrenal cortex, to regenerate proteins
cells, which carry oxygen spleen, from oxidized to
from the lungs to tissues thymus, lymph reduced state)
throughout the body. This nodes, - impt for glutathione,
enzyme helps protect red lactating which protects the
blood cells from damage mammary hgb from oxidation
and premature destruction glands -sex-linked disorder
ALDOLAS Helps muscle turn sugar Diagnose and
E into energy monitor skeletal
muscle diseases
5NUCLE Cell membrane enzyme Liver-specific but not
OTIDE that hydrolyzes at an as sensitive as ALP,
optimum pH 7.5 AST, and ALT
usually used to
determine whether an
in ALP is from liver
or bone disease
AMI Acute Myocardial Infarction
Hgb hemoglobin
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandCLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- ENZYMOLOGYDocument2 pagesENZYMOLOGYCarla Lagar FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry 2 Lecture Notes in Trace ElementsDocument6 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 Lecture Notes in Trace ElementsMoira Pauline LibroraniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hematologic DisordersDocument20 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hematologic Disorderschristine mercado100% (1)
- CHEM 2 CH 29 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesCHEM 2 CH 29 Review QuestionsthrowawyPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideDocument9 pagesCOMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideKaycee Gretz LorescaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Iron Kinetics and Heme MetabolismDocument12 pagesDisorders of Iron Kinetics and Heme MetabolismJoanne JardinPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Reagent Strip TestsDocument8 pagesSummary of Reagent Strip TestsDarla YsavelPas encore d'évaluation
- Alloimmunisation To Blood Group AntigensDocument34 pagesAlloimmunisation To Blood Group AntigensbloodbankPas encore d'évaluation
- HeamatologyDocument45 pagesHeamatologypikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- A. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)Document19 pagesA. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)IcePas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology QuizDocument5 pagesHematology Quizkep1313100% (1)
- Clin Chem CompiledDocument9 pagesClin Chem CompiledReg LagartejaPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneralDocument31 pagesGeneralpikachu100% (1)
- Recall 1Document4 pagesRecall 1pikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- LN Hematology MLT FinalDocument549 pagesLN Hematology MLT FinalMahfuzur Rahman100% (3)
- Board of Directors: Ascp-Ascp Certification & Qualification Comparison ChartDocument1 pageBoard of Directors: Ascp-Ascp Certification & Qualification Comparison ChartMustaffah KabelyyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Correctly: IncorrectlyDocument70 pagesCorrectly: IncorrectlyDjdjjd Siisus100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunohematology & Blood Bank: Alyazeed Hussein, BSCDocument58 pagesImmunohematology & Blood Bank: Alyazeed Hussein, BSCVijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Aubf Lab CSFDocument6 pagesAubf Lab CSFAndrei Tumarong AngoluanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology PDFDocument85 pagesHematology PDFammarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 25 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Immune Causes Final DraftDocument2 pagesChapter 25 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Immune Causes Final DraftNathaniel SimPas encore d'évaluation
- MTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Document9 pagesMTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Nathan DrakePas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno Serology ReviewDocument16 pagesImmuno Serology ReviewM CPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnHenry QuimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 IH Lab L3 ABO Forward Reverse Typing Manual and Gel MethodDocument8 pagesC1 IH Lab L3 ABO Forward Reverse Typing Manual and Gel MethodDIVINA KYLE YGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood BankDocument32 pagesBlood Bankpikachu100% (1)
- ML7111 MCQs Answers March 2020Document15 pagesML7111 MCQs Answers March 2020Cleo SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pass Ascp 2020 LatestDocument6 pagesPass Ascp 2020 LatestLorelie ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- CM Review Notes 2Document22 pagesCM Review Notes 2USMAN JuhaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Banking: RH Blood Group SystemDocument2 pagesBlood Banking: RH Blood Group SystemRomie Solacito100% (1)
- CC Conversion-FactorsDocument1 pageCC Conversion-FactorsAndrei Tumarong AngoluanPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood ComponentDocument17 pagesBlood ComponentJes CmtPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood BankingDocument7 pagesBlood BankingRoiland Atienza BaybayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Exam Topic ChecklistDocument3 pagesBoard Exam Topic ChecklistVianney Angeli LorenzanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case StudyDocument8 pagesImmuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case StudyRomie SolacitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistry IMariel AbatayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Edition by Susan King Strasinger - Test BankDocument45 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Edition by Susan King Strasinger - Test Bankroseyoung0Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASCPi Recalls Sep 23 2017Document3 pagesASCPi Recalls Sep 23 2017Jaine SalongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Detection of AntibodiesDocument7 pagesDetection of AntibodiesJezreeljeanne Largo CaparosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryDocument8 pagesLesson 5: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryJohn Daniel AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry KeyNotes For Board ExaminationDocument12 pagesClinical Chemistry KeyNotes For Board ExaminationPrincess Alen Aguilar100% (2)
- Histopathology Review BookletDocument21 pagesHistopathology Review BookletMarie Llanes100% (1)
- Pre Transfusion TestingDocument57 pagesPre Transfusion TestingDominic Bernardo100% (4)
- Study Questions (Hematology)Document11 pagesStudy Questions (Hematology)tkanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Microscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaDocument30 pagesMicroscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaBrent LagartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1 - Analysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument11 pagesGroup 1 - Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluidsjulo_05100% (3)
- Beginings of MTDocument65 pagesBeginings of MTMel JamitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Component Therapy-Transfusion of TheDocument8 pagesComponent Therapy-Transfusion of TheGennelyn Ross Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Banking Chapter 1Document9 pagesBlood Banking Chapter 1throwawyPas encore d'évaluation
- HAEMOPOIESISDocument6 pagesHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody IdentificationDocument27 pagesAntibody Identificationhamaada100% (1)
- Incorrectly: CorrectlyDocument25 pagesIncorrectly: CorrectlypikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Agglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4D'EverandAgglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions for Haematology and Core Medical TraineesD'EverandMultiple Choice Questions for Haematology and Core Medical TraineesPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandSenior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- IHSCforAll2024Document510 pagesIHSCforAll2024Gvidas MikalauskasPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Form (Pledge Form) For Whole Body DonationDocument1 pageApplication Form (Pledge Form) For Whole Body DonationVasanthakumar BasavaPas encore d'évaluation
- ALP Crestline PDFDocument2 pagesALP Crestline PDFJashmyn JagonapPas encore d'évaluation
- PyodermaDocument19 pagesPyodermaNewton LongjamPas encore d'évaluation
- University Journal of Medicine and Medical SpecialitiesDocument4 pagesUniversity Journal of Medicine and Medical SpecialitiesVivek ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Secrets To Gaining Muscle Mass Fast by Anthony Ellis PDFDocument125 pagesThe Secrets To Gaining Muscle Mass Fast by Anthony Ellis PDFVishal DokaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ownership, Operation, Maintenance, and Inspection of Amusement Rides and DevicesDocument4 pagesOwnership, Operation, Maintenance, and Inspection of Amusement Rides and DevicesMarlon Piarpuito Enriquez0% (1)
- Stem Cell Research PaperDocument3 pagesStem Cell Research Papermyrentistoodamnhigh100% (1)
- Sri Lanka NMRA GazetteDocument9 pagesSri Lanka NMRA GazetteSanjeev JayaratnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumoret e VeshkaveDocument118 pagesTumoret e VeshkavealpePas encore d'évaluation
- Taema Monnal D2 Anaesthesia Machine - Users ManualDocument13 pagesTaema Monnal D2 Anaesthesia Machine - Users ManualJuan carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- ProliaDocument17 pagesProliamktantumPas encore d'évaluation
- The Antimicrobial ActivitiesDocument4 pagesThe Antimicrobial ActivitiesromalfioPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimalarials - Are They Effective and Safe in Rheumatic DiseasesDocument10 pagesAntimalarials - Are They Effective and Safe in Rheumatic DiseasesYahya RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 8 Blood Pressure HighDocument1 pageSanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 8 Blood Pressure HighEduardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Plan About Conjunctivitis: Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument3 pagesTeaching Plan About Conjunctivitis: Haemophilus InfluenzaeJanaica Juan100% (1)
- Basic Safety TrainingDocument1 pageBasic Safety TrainingMade HartawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Obat Apotek MutiaraDocument7 pagesDaftar Obat Apotek Mutiarafany hertinPas encore d'évaluation
- Palpation and Assessment SkillsDocument305 pagesPalpation and Assessment SkillsElin Taopan97% (34)
- What Are Thrombosed External Hemorrhoids?Document3 pagesWhat Are Thrombosed External Hemorrhoids?Hanine HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Toefle UjianDocument19 pagesToefle UjianhistoryPas encore d'évaluation
- PostpartumDocument3 pagesPostpartumMuhammad RifaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eac MsdsDocument2 pagesEac Msdsteguh30Pas encore d'évaluation
- ATARAXIE S7 Cours Par CoursDocument251 pagesATARAXIE S7 Cours Par CoursOussama Hamadi100% (1)
- The Performance Wellness SeminarDocument8 pagesThe Performance Wellness SeminarMirelaAlexandraPas encore d'évaluation
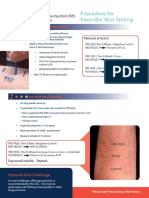
- Procedure For Penicillin Skin TestingDocument4 pagesProcedure For Penicillin Skin TestingHarshan Isuru KumaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathfinder 2nd Edition House Rules Compendium - GM BinderDocument119 pagesPathfinder 2nd Edition House Rules Compendium - GM BinderBrandon PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)Document4 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)mkpnurdinPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength Training & Weight Training 101Document28 pagesStrength Training & Weight Training 101Maru PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Therapeutic Hypothermia Targeted Temperature Manangement (TTM) Quick SheetDocument3 pagesPost-Cardiac Arrest Therapeutic Hypothermia Targeted Temperature Manangement (TTM) Quick SheetkimberlyPas encore d'évaluation