Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Childhood Tumors
Transféré par
Chege AmbroseDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Childhood Tumors
Transféré par
Chege AmbroseDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name Characteristics Cancerous Special
Hemangioma Most common tumor of infancy; Benign Usually red boils on face and scalp,
spontansous regression, capillary types RARELY familial. Blood vessels pile up
Lymphangioma Malformations in lymphatic system; Skin or Benign Doughy mass that is slow growing and
deeper regions of neck, axilla, and never progresses to malignancy. Increased
mediastinum size may compress airway
Sacrococcygeal teratomas Most common germ-cell tumor of childhood. Majority Histologically mature = bening immature
Located at base of coccyx benign = may be cancerous
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pre-B cell leukemia is most common; Peaks Malignant Cancer of white blood cells by excess
at age 4, seen in bone marrow and lymphoblast. Malignant imature
peripheral blood. Bone pain, anemia, lymphoblast are overproduced.TdT
petichiae, fever, hepatomegaly and antigens present on pre-B cells.
spenomegaly, and nerve palsies. Hyperdiploidy = more than 50 chrom.
Embryonal Tumors: Small round blue cells Malignant Primitive microscopic appearance
Neuroblastoma (1-2% are Tumors of adrenal medulla and sympathetic Malignant 50% malignancies in infancy. Protuberant
familial autosomal dominant in ganglia. Derived from primordial neural abdomen, hepatomegaly, ascitis, bone
ALK gene) crest cells. Elevated blood catecholamines pain, metastasis to lungs and liver.
and urin VMA and HVA. Random progression Neonates = blueberry muffins deep blue
or progression discloloration.
Stage 1 Localized, resectable, ipsilateral Malignant Good prognosis
Stage 2 Incompletely resected, localized w/lymph Malignant N/A
Stage 3 incompletely resected, spread to body Malignant N/A
stage 4 Spread to distant lymph nodes Malignant Poor prognosis
Stage 4S (<1 year of age) Localized, resectable, spread to liver,BM Malignant Decent prognosis
Retinoblastoma Most common intraocular tumor of children. Malignant Somatic mutations in Rb1 makes up 60%
Germline mutation of Rb1 gene. 40% is and is UNILATERAL. Spread to optic nerve,
familial (bilater or unilateral) CNS, distal bones, lymph
Wilms tumor Nephroblastoma = most common primary Malignant Large well circumscribed mass, tan to
(Nephroblastoma) tumor of the kidney (between 2-5 years old) grey in color, with soft homogenous mass.
Presents as huge abdominal mass with 10% bilateral. 5% resistant to
fever, blood in urine, and intestinal chemotherapy.
obstruction.
WAGR (1/3 get wilms) Genital abnormalities, mental retardation Deletion of WT1 on 11p13
Denys-Drash (90% get wilms) Gonadal disgenesis and renal abnormality dominant negative incativation of WT1
Beckwith-Wiedemann At risk for many other tumors (hepatoblaastoma ect) Loss of imprinting of IGF2 - wilms
Ewing Tumor Painful enlarging mass in long tubular bone Malignant Imaging shows destructive lytic tumor
or pelvic flat bones. Resembles infection. with extension into soft tissue. EWS gene
Chemo, surgery, radiation. and ETS family. 75% 5-year survival.
Rhabdomyosarcoma Most common soft tissue sarcoma of highly Curable in 2/3 of children and seen with
childhood. Head, neck, and genitourinary malignant PAX3 gene on chromosomes 2 and FKHR
tract. gene on chromosome 13.
Medulloblastoma Common in midline cerebellum of children. Malignant Mutations in WNT signaling pathway =
Homer wright rosettes. MYC amplification = more favorable outcomes. 5 year survival
poor outcomes. of 75%.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Childhood TumorsDocument1 pageChildhood TumorsNamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasms of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument25 pagesNeoplasms of Infancy and ChildhoodPakeezaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument23 pages8 Diseases of Infancy and ChildhoodBalaji DPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasms of Infancy and ChildhoodDocument29 pagesNeoplasms of Infancy and ChildhoodtheintrovPas encore d'évaluation
- Radial N. Innervates The BEST!!!! Brachioradialis Extensors Supinator TricepsDocument57 pagesRadial N. Innervates The BEST!!!! Brachioradialis Extensors Supinator TricepsdrsilkPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Neoplasms: Kelompok 3 Dr. Reza Maulana Dr. Intan E. Napitupulu Drg. Andi Arfandi ArifuddinDocument41 pagesThyroid Neoplasms: Kelompok 3 Dr. Reza Maulana Dr. Intan E. Napitupulu Drg. Andi Arfandi ArifuddinIntan Eklesiana NapitupuluPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.4 Malignant Conditions of ChildhoodDocument9 pages7.4 Malignant Conditions of ChildhoodΜατθαίος ΠαππάςPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia 2Document57 pagesNeoplasia 2Dyvanal ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Week8 NeoplasiaDocument13 pagesPathology Week8 NeoplasiaSalifyanji SimpambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervicofacial Vascular Anomalies. I. Hemangiomas and Other Benign Vascular TumorsDocument9 pagesCervicofacial Vascular Anomalies. I. Hemangiomas and Other Benign Vascular TumorsBikash ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Ped Abd Masses PresentationDocument76 pages10 - Ped Abd Masses PresentationansarimgPas encore d'évaluation
- Leukemia: Defintion: Leukemias Are Diseases in Which Localised or Generalised Proliferation orDocument12 pagesLeukemia: Defintion: Leukemias Are Diseases in Which Localised or Generalised Proliferation orsharon victoria mendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasms of The KidneyDocument2 pagesNeoplasms of The KidneyAlyanah AloveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Neoplasia: Philip R. Faught, M.DDocument48 pagesPediatric Neoplasia: Philip R. Faught, M.DEverest87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Childhood Malignancies Radiology Rev CourseDocument35 pagesCommon Childhood Malignancies Radiology Rev CourseIdris Balasa IdrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia (II) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocument138 pagesNeoplasia (II) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityleyreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia Summer 2020Document38 pagesNeoplasia Summer 2020Sharif HossainPas encore d'évaluation
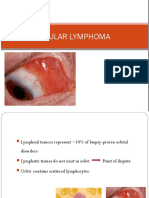
- Ocular LymphomaDocument67 pagesOcular LymphomaFera Yunita RodhiatyPas encore d'évaluation
- Testicular Tumor - Dr. FaizDocument54 pagesTesticular Tumor - Dr. FaizFemale calmPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumors of Melanocytes Benign: (Mole) Acquired Congenital MalignantDocument73 pagesTumors of Melanocytes Benign: (Mole) Acquired Congenital Malignantlovelyc95Pas encore d'évaluation
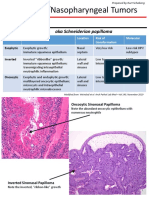
- Sinonasal/Nasopharyngeal Tumors: BenignDocument9 pagesSinonasal/Nasopharyngeal Tumors: BenignIsa EnachePas encore d'évaluation
- Ped Solid TumorDocument52 pagesPed Solid TumorIndranil GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Path Adrenal TumorDocument4 pagesPath Adrenal TumorRama HijaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphoma: 2011-2012 Prof - Dr.Rejin Kebudi, M.DDocument57 pagesLymphoma: 2011-2012 Prof - Dr.Rejin Kebudi, M.Dmia rachmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch7 NeoplasmDocument96 pagesCh7 Neoplasmmormor80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Endometrial TumorsDocument10 pagesEndometrial TumorsleartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: ReviewDocument4 pagesUpdate On Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: ReviewPhn StanleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroblastoma My Lecture 2011Document153 pagesNeuroblastoma My Lecture 2011Wael ElsawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation: DR Tariq Masood TMO Radiology Department, HMCDocument82 pagesCase Presentation: DR Tariq Masood TMO Radiology Department, HMCg1381821Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment and Diagnosis of Abdominal Masses in Children: Resident Education Lecture SeriesDocument45 pagesAssessment and Diagnosis of Abdominal Masses in Children: Resident Education Lecture SeriesboubiyouPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes DermaDocument17 pagesNotes DermaCiullaePas encore d'évaluation
- Subtype Incidence Courde and Prognosis: 1. Risk Factors For NHLDocument5 pagesSubtype Incidence Courde and Prognosis: 1. Risk Factors For NHLKeepItSecretPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyps AdvancedDocument5 pagesPolyps AdvancedblablalbablablablaPas encore d'évaluation
- Testicular TumorsDocument14 pagesTesticular TumorsJose SirittPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenal TumorsDocument6 pagesAdrenal TumorsJose SirittPas encore d'évaluation
- Cáncer Precoz, MastologíaDocument31 pagesCáncer Precoz, MastologíaDr. Pablo Maria Peralta LorcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DiseasesDocument31 pagesGenetic DiseasesAlon GoldfainerPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia and Cancer: Week 1Document8 pagesNeoplasia and Cancer: Week 1rise wiiinPas encore d'évaluation
- Epk FDocument73 pagesEpk FBryan FjbPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Neoplasms: Muhammad Haris Aslam Janjua Resident, Surgical Unit I SIMS/Services Hospital, LahoreDocument116 pagesThyroid Neoplasms: Muhammad Haris Aslam Janjua Resident, Surgical Unit I SIMS/Services Hospital, LahoreHajra IsrarPas encore d'évaluation
- Melanoma 2Document13 pagesMelanoma 2Rajarshi KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain TumorsDocument78 pagesBrain Tumorsnarswiponshistoryan100% (3)
- Childhood Solid Tumors: For C-1 StudentsDocument72 pagesChildhood Solid Tumors: For C-1 StudentsYemata HailuPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Doc PaclibarDocument6 pagesAdditional Doc PaclibarJoherPas encore d'évaluation
- Round Cell Tumors FinalDocument86 pagesRound Cell Tumors FinalKush Pathak100% (2)
- Most Common PathoDocument4 pagesMost Common PathoTrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Evaluation of The Child With A Suspected MalignancyDocument21 pagesInitial Evaluation of The Child With A Suspected MalignancywiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumors of Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesTumors of Nervous SystemNininghrPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Head and Neck Tumors: Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCH FRCR Stanford RadiologyDocument78 pagesPediatric Head and Neck Tumors: Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCH FRCR Stanford RadiologykathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aparato Genital MasculinoDocument22 pagesAparato Genital MasculinoletttttPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of Neoplasia Cancer Malignant Benign Carcinoma Lecture PDFDocument8 pagesPathology of Neoplasia Cancer Malignant Benign Carcinoma Lecture PDFjax111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Diseases: Mendelian Inheritance Multifactorial Inheritance Chromosome Inheritance Mitochondria InheritanceDocument74 pagesGenetic Diseases: Mendelian Inheritance Multifactorial Inheritance Chromosome Inheritance Mitochondria InheritanceinakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasms of Testis NishDocument54 pagesNeoplasms of Testis NishRamesh ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari, M.B.B.S.,D.C.P., Tutor in Pathology, MapimsIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- Vascular Skin LesionsDocument39 pagesVascular Skin LesionsApril Mae Magos LabradorPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Most CommonDocument3 pagesUSMLE Most Commonibrahim 12100% (1)
- NE0PLASIADocument28 pagesNE0PLASIADaniel SutantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Intraoral Benign TumorsDocument4 pagesIntraoral Benign TumorsSaman SadeghiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Facts: Myelofibrosis: Reviewed by Professor Ruben A. MesaD'EverandFast Facts: Myelofibrosis: Reviewed by Professor Ruben A. MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- You Are Born To Blossom A P J Abdul Kalam 2015 Annas ArchiveDocument94 pagesYou Are Born To Blossom A P J Abdul Kalam 2015 Annas ArchiveChege Ambrose100% (1)
- Rand RB9408 PDFDocument3 pagesRand RB9408 PDFChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Army Contracting Commands Contract PDFDocument110 pagesAssessment of Army Contracting Commands Contract PDFChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Ebola Research ProposalDocument10 pagesEbola Research ProposalChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Information Overload Final - EditedDocument15 pagesInformation Overload Final - EditedChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Bias and EquivalenceDocument19 pagesBias and EquivalenceChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- 3 How To Build Your Real Estate BusinessDocument11 pages3 How To Build Your Real Estate BusinessChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Pricing Is Chapter 10 of The Text Book Name:: Marketing. Real People. Real Choices. 9Document1 pagePricing Is Chapter 10 of The Text Book Name:: Marketing. Real People. Real Choices. 9Chege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1Document3 pagesTask 1Chege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- The Psychological Needs of Women Prisoners: Implications For Rehabilitation and ManagementDocument11 pagesThe Psychological Needs of Women Prisoners: Implications For Rehabilitation and ManagementChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Task: Report Writing: Title Background Research Question/ Objectives Method Timescale Resources References TotalDocument1 pageTask: Report Writing: Title Background Research Question/ Objectives Method Timescale Resources References TotalChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber CrimesDocument13 pagesCyber CrimesChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentChege Ambrose0% (2)
- Mobile Phone Repairing PDFDocument80 pagesMobile Phone Repairing PDFChege Ambrose100% (5)
- Service Journal 1 Chinese Mutual Aid AssociationDocument4 pagesService Journal 1 Chinese Mutual Aid AssociationChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- Service Journal 1 Chinese Mutual Aid AssociationDocument4 pagesService Journal 1 Chinese Mutual Aid AssociationChege AmbrosePas encore d'évaluation
- E CA 72-4 en 9Document3 pagesE CA 72-4 en 9Hassan GillPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 ItemDocument9 pages2 ItemDaniberg RimenisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Holistic Cancer SolutionDocument10 pagesThe Holistic Cancer SolutionromalfioPas encore d'évaluation
- Append ADocument18 pagesAppend ARizalArisMunandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankDocument5 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankVictoriaWilliamsegtnm100% (84)
- CAFL DatabaseDocument178 pagesCAFL Databasetonym35100% (1)
- Bengali - Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Cancer BackupDocument10 pagesBengali - Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Cancer Backupapi-26176346Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Tumor 1Document30 pagesSkin Tumor 1Vicky Ilda Viantini100% (1)
- Paragangliomas and Paraganglioma SyndromesDocument26 pagesParagangliomas and Paraganglioma SyndromessanasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer and CarcinosinDocument12 pagesCancer and CarcinosinDr. Nur-E-Alam RaselPas encore d'évaluation
- IOTA - Simple - Rules - Susanne - Johnson 2 PDFDocument76 pagesIOTA - Simple - Rules - Susanne - Johnson 2 PDFBenyamin Rakhmatsyah TitaleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Pathology Batch '21 Viva Questions CompilationDocument20 pagesSpecial Pathology Batch '21 Viva Questions Compilationuzair akhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasm 20&20 Metabolic 20 DiseasesDocument30 pagesNeoplasm 20&20 Metabolic 20 DiseasesSaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CancerDocument81 pagesCancerCodered Review100% (1)
- Follicular Thyroid CarcinomaDocument9 pagesFollicular Thyroid CarcinomaRum Afida RasfaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is CancerDocument10 pagesWhat Is CancerDS100% (1)
- Tumor Targeting: Presented by M.Pharm 2 Semester (Pharmaceutics) Reg No. 121725101005Document41 pagesTumor Targeting: Presented by M.Pharm 2 Semester (Pharmaceutics) Reg No. 121725101005TridevPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia PDFDocument182 pagesNeoplasia PDFmarwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia: Basic PathologyDocument12 pagesNeoplasia: Basic Pathologyandroid tricksPas encore d'évaluation
- Icd Code (Diagnosis)Document34 pagesIcd Code (Diagnosis)Zyralyn PanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Intraductal Papillary Mucinous NeoplasmDocument22 pages05 Intraductal Papillary Mucinous NeoplasmGabriela ZahiuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Biochemistry of CancerDocument18 pages1 - Biochemistry of CancerJoo Se HyukPas encore d'évaluation
- Eponyms SyndromesDocument23 pagesEponyms Syndromestekennn021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Cancer TherapyDocument208 pagesCellular Cancer TherapyneuralterapianetPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesothelioma: A Clinical ReviewDocument43 pagesMesothelioma: A Clinical Reviewmynoidanh19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Immaculate Heart of Mary Academy Long Test in Music 7Document6 pagesImmaculate Heart of Mary Academy Long Test in Music 7Cryzel MuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 (Cancer)Document8 pagesAssignment 1 (Cancer)Leo Aurelio MarcelinoPas encore d'évaluation
- NLS DiagnosticsDocument71 pagesNLS DiagnosticsMarkus van der WesthuizenPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 4Document10 pagesExam 4pauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign and Malignant Tumors of Foot and AnkleDocument19 pagesBenign and Malignant Tumors of Foot and AnkleICPas encore d'évaluation