Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Steady State Stability of A Power System
Transféré par
Kiran KumarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Steady State Stability of A Power System
Transféré par
Kiran KumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
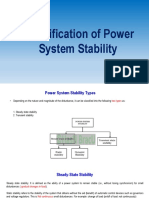
Steady State Stability of a Power System
The steady state stability of a power system is defined as the ability of the system to
bring itself back to its stable configuration following a small disturbance in the
network (like normal load fluctuation or action of automatic voltage regulator). It
can only be considered only during a very gradual and infinitesimally small power
change.
In case the power flow through the circuit exceeds the maximum power permissible,
then there are chances that a particular machine or a group of machines will cease
to operate in synchronism, and result in yet more disturbances. In such a situation,
the steady state limit of the system is said to have reached or in other words the
steady state stability limit of a system refers to the maximum amount of power that
is permissible through the system without loss of its steady state stability.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Power System StabilityDocument3 pagesPower System StabilitySabaMannan123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-3 PsocDocument23 pagesUnit-3 PsocDESI BRAHMNPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Signal Stability AnalysisDocument71 pagesSmall Signal Stability AnalysisRick Leon VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- PS Stability ConceptDocument1 pagePS Stability ConceptdypthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture5 PME403 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS IIDocument25 pagesLecture5 PME403 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS IIMony JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- EEU801 Power System Stability: Dr. Kawita D. Thakur Government College of Engineering, AmravatiDocument20 pagesEEU801 Power System Stability: Dr. Kawita D. Thakur Government College of Engineering, AmravatiSominath HarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1Clemen TeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter ThreeDocument31 pagesChapter Threehabte gebreial shrashrPas encore d'évaluation
- Anderson ADocument11 pagesAnderson Acrisis_zPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Stability OverviewDocument14 pagesPower System Stability Overviewمحمود السيسىPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability Terms+Defs DraftDocument10 pagesStability Terms+Defs DraftKhy-khy PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset-V1 BuX+EEE321+2021 Summer+Type@Asset+Block@Classification of Power System StabilityDocument4 pagesAsset-V1 BuX+EEE321+2021 Summer+Type@Asset+Block@Classification of Power System StabilityAbrar ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijret - Voltage Collapse Mitigation by Reactive Power Compensation at The Load SideDocument7 pagesIjret - Voltage Collapse Mitigation by Reactive Power Compensation at The Load SideInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.6 Voltage Stability: V-Q Sensitivity Is Negative For at Least One Bus, The System Is Voltage UnstableDocument5 pages6.6 Voltage Stability: V-Q Sensitivity Is Negative For at Least One Bus, The System Is Voltage Unstableveeru_puppalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-II: Different Stability LimitsDocument9 pagesUnit-II: Different Stability LimitsManohar PotnuruPas encore d'évaluation
- MATLAB-Based Transient Stability Analysis of A Power SystemDocument34 pagesMATLAB-Based Transient Stability Analysis of A Power Systemsamarahmad2008479875% (4)
- Power System Voltage Stability PDFDocument318 pagesPower System Voltage Stability PDFCarib100% (2)
- Chapter 12Document23 pagesChapter 12sachin235Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted byDocument36 pagesBhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted bytarnedo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- J6 - TPWRD 00370 2003Document16 pagesJ6 - TPWRD 00370 2003ali ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Facts?Document36 pagesWhat Is Facts?TahirAbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage StabilityDocument27 pagesVoltage StabilityDevendra SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machines AssignmentDocument1 pageElectrical Machines AssignmentkahurlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Intelligent Load Shedding 9.0Document43 pagesIntelligent Load Shedding 9.0Sitlesh Ananda PanchalePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1Document28 pagesLec 1ahmedibrahim4260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Question 1Document15 pagesQuestion 1Prasun SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System StabilityDocument1 pagePower System StabilitySatyam SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Stability Course Notes PART-1: Dr. A.Professor Mohammed Tawfeeq Al-ZuhairiDocument8 pagesPower System Stability Course Notes PART-1: Dr. A.Professor Mohammed Tawfeeq Al-Zuhairidishore312100% (1)
- A. Steady State StabilityDocument2 pagesA. Steady State StabilitygteklayPas encore d'évaluation
- 17th International Conference On Electrical, Electronics and Systems Engineering December 21 - 22, 2015 Istanbul, TurkeyDocument47 pages17th International Conference On Electrical, Electronics and Systems Engineering December 21 - 22, 2015 Istanbul, TurkeyPraveen Nayak BhukyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Collapse: M. H. SadeghiDocument31 pagesVoltage Collapse: M. H. Sadeghiken84hnPas encore d'évaluation
- HVDC - Pat 2 - AnswwersDocument27 pagesHVDC - Pat 2 - AnswwersFundayyy moviesPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Stability Improvement Using Facts Devices: S.V College of Engineering, Dept. of EEEDocument21 pagesPower System Stability Improvement Using Facts Devices: S.V College of Engineering, Dept. of EEEbhuvanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability and Control - P. Kundur (Part01) PDFDocument600 pagesStability and Control - P. Kundur (Part01) PDFJimena Rafael LeónPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Yogesh KarlekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Power System StabilityDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Power System Stabilitytarnedo1100% (1)
- Stability 2 PDFDocument24 pagesStability 2 PDFPrajwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Stability-Chapter 3Document84 pagesPower System Stability-Chapter 3Du TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Automatic Generation Control (AGC) in Energy Management SystemDocument49 pagesRole of Automatic Generation Control (AGC) in Energy Management Systemhodeegits9526Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study of SMES Technology & Its Integration To AGC: and E, Connected Through Consider The Simple PowerDocument22 pagesStudy of SMES Technology & Its Integration To AGC: and E, Connected Through Consider The Simple PowerzahidPas encore d'évaluation
- PSR Chapter 10Document98 pagesPSR Chapter 10kamal arreazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Study in Power System Analysis: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Shebl Mohamed Dr. Nader Shawky Abd El HakeemDocument16 pagesAdvanced Study in Power System Analysis: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Shebl Mohamed Dr. Nader Shawky Abd El HakeemMohab MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyristor Controlled Series CapacitorDocument9 pagesThyristor Controlled Series CapacitorVamshiKrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-1: 1.2 Motivation of The Project 1.3 Literature SurveyDocument6 pagesChapter-1: 1.2 Motivation of The Project 1.3 Literature Surveysanthosh kanthalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System TransientsDocument11 pagesPower System TransientsKhairul AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Stability of IEEE 30 Bus System Using E TAP SoftwareDocument7 pagesTransient Stability of IEEE 30 Bus System Using E TAP SoftwareAzie Tantowi100% (2)
- Power System StabilityDocument2 pagesPower System StabilityNishant SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW Ijltemas inDocument4 pagesWWW Ijltemas insiva kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Application of FACTS Devices in Power System Stability ImprovementDocument5 pagesA Review On Application of FACTS Devices in Power System Stability ImprovementIJSTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability Analysis Unit 5Document20 pagesStability Analysis Unit 5dineshpeterPas encore d'évaluation
- VOLUME 1 - General Notes On Transient Stability & Control - FinalDocument253 pagesVOLUME 1 - General Notes On Transient Stability & Control - FinalOoi Ban JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- P Matlab y Estab TransitDocument4 pagesP Matlab y Estab TransitrdelgranadoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1611942Document15 pages1611942kifle godanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit VDocument29 pagesUnit Vv.saigeetha lakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Load Shedding Strategy On Interconnected Power Systems Stability When A Blackout OccursDocument6 pagesEffect of Load Shedding Strategy On Interconnected Power Systems Stability When A Blackout OccursMoon3pellPas encore d'évaluation
- Operational Objectives: Module 1: Introduction Lecture 3: Operating States ObjectivesDocument5 pagesOperational Objectives: Module 1: Introduction Lecture 3: Operating States ObjectivesMahima ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorD'EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Interpretation - Gr8AmbitionZDocument14 pagesData Interpretation - Gr8AmbitionZKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Arya 2Document1 pageArya 2Kiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vro Sree CommunicationsDocument21 pagesVro Sree CommunicationsGhani CHPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Interpretation - Gr8AmbitionZDocument13 pagesData Interpretation - Gr8AmbitionZamolkhadsePas encore d'évaluation
- The Basic Principle of Dynamic Voltage Restoration Is To Inject ADocument1 pageThe Basic Principle of Dynamic Voltage Restoration Is To Inject AKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Secretariet Abilities 2Document7 pagesSecretariet Abilities 2Kiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Secretariet Abilities 1Document7 pagesSecretariet Abilities 1Kiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagala Premi Kutty Badha Arya 2Document1 pagePagala Premi Kutty Badha Arya 2Kiran Kumar0% (1)
- Katamarayudu Is An Telugu Language Film Directed by Kishore Kumar Pardasani Which FeaturesDocument1 pageKatamarayudu Is An Telugu Language Film Directed by Kishore Kumar Pardasani Which FeaturesKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Duvvada JagannadhamDocument1 pageDuvvada JagannadhamKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mirchi (English: Chilli) Is A 2013: Maanikya BindaasDocument1 pageMirchi (English: Chilli) Is A 2013: Maanikya BindaasKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ninnu KoriDocument1 pageNinnu KoriKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelli ChoopuluDocument1 pagePelli ChoopuluKiran Kumar33% (3)
- Nenu Local Movie StoryDocument1 pageNenu Local Movie StoryKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Voltage StabilityDocument16 pages3 Voltage StabilityKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Between Statcom and SVCDocument1 pageComparison Between Statcom and SVCKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Baahubali 2Document1 pageBaahubali 2Kiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Eshwar Varsham Chatrapathi Chakram Billa Darling Mr. Perfect Mirchi Action Jackson Baahubali: The Beginning Baahubali 2: The ConclusionDocument1 pageEshwar Varsham Chatrapathi Chakram Billa Darling Mr. Perfect Mirchi Action Jackson Baahubali: The Beginning Baahubali 2: The ConclusionKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Eshwar Varsham Chatrapathi Chakram Billa Darling Mr. Perfect Mirchi Action Jackson Baahubali: The Beginning Baahubali 2: The ConclusionDocument1 pageEshwar Varsham Chatrapathi Chakram Billa Darling Mr. Perfect Mirchi Action Jackson Baahubali: The Beginning Baahubali 2: The ConclusionKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence and Neural Network Applications in Power SystemsDocument18 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Neural Network Applications in Power SystemsS Bharadwaj ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- IBPS Bank PO Exams Numerical Aptitude Questions and Answers: Downloaded FromDocument9 pagesIBPS Bank PO Exams Numerical Aptitude Questions and Answers: Downloaded Fromsishir321Pas encore d'évaluation
- XTFlex-Zinc Ribbon AnodeDocument1 pageXTFlex-Zinc Ribbon AnodeKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Differential RelayDocument2 pagesTypes of Differential RelayKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Autonomus Syllabus12/mtechps/rpcmDocument1 pageAutonomus Syllabus12/mtechps/rpcmKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Puzzle Problem Solving Part I Gr8AmbitionZ PDFDocument2 pagesPuzzle Problem Solving Part I Gr8AmbitionZ PDFKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 2353 High Voltage Engineering Faculty Name:A.JAIBUNISHA Faculty Code: EE 58 Designation: LECTURER Department: EEEDocument24 pagesEe 2353 High Voltage Engineering Faculty Name:A.JAIBUNISHA Faculty Code: EE 58 Designation: LECTURER Department: EEEKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- February 2015 Current Affairs Quick ReviewDocument8 pagesFebruary 2015 Current Affairs Quick Reviewmass1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- May 2016 Current Affairs Quick Review PDFDocument19 pagesMay 2016 Current Affairs Quick Review PDFharitha01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of High Voltage and High Currentunit IV Full VersionDocument39 pagesMeasurement of High Voltage and High Currentunit IV Full VersionKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation