Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Review On Fast Dissolving Buccal Film An Emergency Treatment
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review On Fast Dissolving Buccal Film An Emergency Treatment
Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No: - 2456 2165
Review on Fast Dissolving Buccal Film: An
Emergency Treatment
Savita V. Pol*, Mr. Jagtap R.S.1, Dr. Doijad R.C.2, Mr. Desai J.R.3,Mr. Pawar J.D.4, , Ms. Jadhav V.V.5 Mrs. Jagtap S.R.6
* Department of Pharmaceutics, Ideal College of Pharmacy, Kalyan, Thane, India
1 Department of Pharmaceutics , Annasaheb Dande college of B.Pharmacy Ashta
2,3,4,5 Department of Pharmaceutics, Shree Santkrupa College of pharmacy, Ghogoan
6 Department of Pharmaceutics , Annasaheb Dande college of D.Pharmacy Ashta
Abstract:- Orally fast dissolving films (OFDFs) have such as strip-forming polymers, plasticizers, active
been introduced in the market recently as they provide pharmaceutical ingredient, sweetening agents, saliva
convenience and ease of use over other dosage forms stimulating agent, flavoring agents, coloring agents,
such as orally disintegrating tablets. Fast-dissolving stabilizing and thickening agents. From the regulatory
drug-delivery systems is an alternative to tablets, perspectives, all excipients used in the formulation of oral
capsules, and syrups for paediatric and geriatric patients drug strips should be approved for use in oral
which rapidly disintegrate and dissolve in saliva and pharmaceutical dosage forms. be approved for use in oral
then easily swallowed without need of water.Mouth pharmaceutical dosage forms.
dissolving buccal films are advantageous particularly for
pediatric, geriatric and mentally ill patients who have A. Need of Fast Dissolving Film
difficulty in swallowing conventional tablets. This
approach increase therapeutic efficiency of Convenient dosing
pharmaceutical actives by avoiding hepatic first pass No water needed
metabolism, deliver drug molecule in control manner, No risk of chocking
enhance absorption and improves patient compliance. Taste masking
Enhanced stability
Keywords: Oral route, Fast dissolving film, pediatric and Improved patient compliance
geriatric patients, rapid absorption, enhanced The drug enters the systemic circulation with
Bioavailability.
reduced hepatic first pass effect.
Site specific and local action
I. INTRODUCTION
Availability of large surface area that leads to rapid
disintegration and dissolution within oral cavity.
Fast-dissolving drug-delivery systems were first developed
in the late 1970s as an alternative to tablets, capsules, and
B. Special Features of Fast Dissolving films [4]
syrups for paediatric and geriatric patients which rapidly
disintegrate and dissolve in saliva and then easily swallowed
without need of water. A film or strip can be defined as a Film should be thin and elegant.
dosage form that employs a water-dissolving Films are available in various size and shapes.
polymer(generally a hydro colloid, which may be a It should be Unobstructive.
bioadhesive polymer),which allows the dosage form to It should be easily adhere to the oral cavity.
quickly hydrate, adhere, and dissolve when placed on the Fast disintegration without water and Rapid drug
tongue or in the oral cavity(i.e. buccal, palatal, gingival, release.
lingual, or sublingual) to provide rapid local or systemic
drug delivery(1). These oral strips may be flexible or brittle, C. Ideal Characteristics Of A Drug To Be Selected [5]:
opaque or transparent.
The drug should have pleasant taste.
Buccal mucosa is an attractive route for systemic delivery of The drug should preferably have a minimum dose.
drugs since it is relatively permeable with a rich blood The drug should have small or moderate molecular
supply. A drug can be easily applied and localized to the weight.
application site, and can be removed from there if necessary. The drug should have good stability and solubility
Attempt has been made earlier to formulate various in water and in saliva.
mucoadhesive buccal devices, including tablets, films, It should be partially unionized at the pH of oral
patches, disks, strips, ointments and gels(2). cavity.
It should have the ability to permeate oral mucos.
Formulation of fast dissolving buccal film involves the
application of both aesthetic and performance characteristics
IJISRT17JU135 www.ijisrt.com 277
Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No: - 2456 2165
D. Comparison between orally fast dissolving films and oral disintegrating Tablets [6]
Orally Dissolving Films Oral Disintegrating Tablets
It is a film It is a tablet
Greater dissolution due to larger surface area Lesser dissolution due to less surface area
Better durable than oral disintegrating tablets Less durable as compared with oral films
More patient compliance Less patient compliance than film
Low dose can only be incorporated High dose can be incorporated
No risk of chocking It has a fear of chocking
II. MECHANISM OF ORAL THIN FILM [7]
Oral thin film
Keep in mouth
Disintegrate into small particles by saliva
Through buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, provide
better absorption
Quick onset of action-More bio-availability
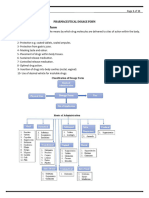
III. CLASSIFICATION OF ORAL THIN FILM [8]
a) Flash Release wafer
b) Mucoadhesive melt-away wafer
c) Mucoadhesive sustained-release wafer
A. Three types of oral films are differentiate from each other as follows:
Type Flash Release wafer Mucoadhesive melt-away wafer Mucoadhesive sustained-
Properties release wafer
Area (cm2) 2-8 2-7 2-4
Thickness (m) 20-70 50-500 50-250
Structure Film: Single layer Single or multilayer system Multilayer system
Excipients Hydrophilic polymers Hydrophilic polymers Low non soluble polymer
Drug Phase Solid solutions Solid solutions or suspension Suspension or solid solution
Application Tongue (upper palate) Buccal region Other region in oral cavity
Dissolution Max. 60 sec. Disintegration in few minutes Max. 8-10 hrs.
B. Component of fast dissolving film [9]:
1) Drug (API)
2) Film Forming Polymers
3) Plasticizers
4) Sweetening Agents
5) Saliva Stimulating Agents
6) Cooling Agent
7) Flavouring Agent
8) Colouring Agent
9) Surfactants
10) Stabilizing and thickening agents
IJISRT17JU135 www.ijisrt.com 278
Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No: - 2456 2165
Sr. No. Ingredient Amount Role of contents Example
1 Drug(API) 5-30% Active pharmaceutical Antimigrain, Antacid,
ingredients Vasodilator, Antiallergic,
Anti-diabetic
2 Water Soluble 45% Film forming capability Hydroxy propyl methyl
polymer celullose, Pullulan,
Maltodextrin
3 Plasticizer 0-20% It improves the flexibility Glycerol, ,Dibutyl Pthalate
and reduces the brittleness
of the film
4 Saliva 2-6% Production of saliva tofaster Citric acid, Malic acid, Ascorbic
Stimulating disintegrationt. acid.
agent
5 Surfactant Q.S. To reduce interfacial tension Tween-80
6 Sweetening 3-6% Tasking masking agent. Sucrose, Dextrose, Mannitol,
agent Aspartame, Sorbitol, fructose
7 Flavours,Colou Q.S. It imparts attractiveness to United State Food and Drug
rs,Fillers film. Administration approved
1) Drug (API): Variety of API can delivery through and to enhance the mouth-feel effect of the product. Other
FDOTF. It is always used to have microionised API which cooling agents like WS3, WS23and Utracoll II can also be
will improves the texture of the film and allows for better used in conjunction with flavours.
dissolution. eg. Ondansetron HCL, Montelukast Sodium etc.
7) Flavouring Agent: The acceptance of oral disintegrating
2) Film Forming Polymers: Water-soluble polymers are films depends on flavoring agent. Selection of drug is
used as film formers as they provide rapid disintegration, depend on type of drug in the formulation. eg.
good mouth feel and mechanical strength to the films. Peppermintoil, cinnamon oil etc.
Water-soluble polymers film adheres to the bucosal mucosa
and rapidly delivers medication into the systemic 8) Colouring Agent: Titanium dioxide or FD&C approved
circulation. e.g. Gelatin, Hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, colouring agents are incorporated (not exceeding
Modified starches, Hydroxyl ethyl cellulose etc. concentration levels of 1%w/w) in FDF formulation when
some of the formulation ingredients or drugs are present in
3) Plasticizers: It is a essential ingredient of the oral films. insoluble or suspension form
The selection of plasticizer depends upon itscompatibility
with the polymer and also the type of solvent employed in 9) Surfactants: Surfactants are used as wetting or
the casting of film. Itimproves the flexibility of the film and dispersing agent. By the use of surfactant the film gets
reduces the brittleness of the film. eg. Glycerol, Propylene dissolved within seconds and release active agent
glycol, Low molecular weight polyethylene glycols, immediately. Solubility of poorly soluble drugs in fast
Citratederivatives like triacetin, acetylcitrate, Phthalate dissolving oral films can be improved by using surfactant.
derivatives likedimethyl,diethyl,dibutyl derivatives, Castor eg. polaxamer 407, benzalkonium chloride, tweens and
oil etc. spans etc.
4) Sweetening Agents: This is used for taste masking of 10) Stabilizing and thickening agents: Generally, to
bitter drugs. Natural sweeteners as well as artificial improve the viscosity and consistency of dispersion or
sweeteners are used. Following are the sweetenerswhich are solution of the filmpreparation the stabilizing and thickening
Suitable in FDF formulation: agents are employed before casting. Natural gumslike
(a) Water soluble natural sweetener: xylose, ribose, glucose, xanthan gum, locust bean gum, carragenan and cellulosic
sucrose, maltose, stevioside etc. derivatives are few examplesof stabilizing and thickening
(b) Water soluble artificial sweetener: sodium or calcium agents.
saccharin salts, cyclamate salts,acesulfame-k etc.
(c) Dipeptide based sweetener: aspartame IV. METHODS OF PREPARATION [10]
5) Saliva Stimulating Agents: The saliva stimulating One or combination of the following process can be used to
agents are used to increase the rate of production of saliva manufacture the mouth dissolving films:
that is helpful in the faster dissolution of the film 1) Solvent casting method:
formulations. eg. Citric acid, malic acid, lactic acid, ascorbic In solvent casting method water soluble polymers are
acid and tartaric acid etc. dissolved in water and the drug along with other excipients
is dissolved in suitable solvent then both the solutions are
6) Cooling Agent: Monomethyl succinate is used as mixed and stirred and finally casted in to the petri plate
Cooling agents which helps to improve the flavour strength dried and cut in to uniform dimensions
IJISRT17JU135 www.ijisrt.com 279
Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No: - 2456 2165
Fig 1. Steps involved in Solvent casting method
2) Semisolid casting: - Fewer operation units
In semisolid casting method firstly a solution of water- - Better content uniformity
soluble film forming polymer is prepared. The resulting - An anhydrous process
solution is added to a solution of acid insoluble polymer
(e.g. cellulose acetate phthalate, cellulose acetate butyrate), 4) Solid dispersion extrusion:
which was prepared in ammonium or sodium hydroxide. In this method immiscible components are extrude with
Then appropriate amount of plasticizer is added so that a gel drug and then solid dispersions are prepared. Finally the
mass is obtained. Finally the gel mass is casted in to the solid dispersions are shaped in to films by means of dies.
films or ribbons using heat controlled drums. The thickness
of the film is about 0.015-0.05 inches. 5) Rolling Method:
In rolling method a solution or suspension containing drug is
3) Hot melt extrusion: rolled on a carrier. The solvent is mainly water and mixture
In hot melt extrusion method firstly the drug is mixed with of water and alcohol. The film is dried on the rollers and
carriers in solid form. Then the extruder having heaters cutted in to desired shapes and sizes.
melts the mixture. Finally the melt is shaped in to films by
the dies. There are certain benefits of hot melt extrusion.
V. COMMERCIAL THIN FILM ORAL DOSAGE FORM PRODUCTS[11]
Product Manufacturer Active Pharmaceutical Agent Strength (mg)
Triaminic Novartis Dextromethorphan HBr 7.5
Triaminic Novartis Diphenhydramine HCl 12.5
Theraflu Novartis Dextromethorphan HBr 15
Gas-X Novartis Simethicone 62.5
Sudafed Pfizer Phenylephrine HCl 10
Benadryl Pfizer Diphenhydramine HCl 12.5
Chloraseptic Prestige Benzocaine Menthol 3/3
Suppress InnoZen Menthol 2.5
Orajel Del Menthol/Pectin 2/30
Listerine Pfizer Cool mint -
IJISRT17JU135 www.ijisrt.com 280
Volume 2, Issue 6, June 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No: - 2456 2165
VI. PATENTED TECHNOLOGIES OF FAST Latha, A Review On Oral Thin Fast Dissolving Films
DISSOLVING ORAL FILMS RecentTrend Of Dosage Form For Quick Release,
Department of pharmaceutics, CMR College of pharmacy,
A. XGel[12] Hyderabad, India, Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2014 Oct; 5(4): (P)
XGel film technology is developed by BioProgress which 54 - 67.
causes a revolution in the product offerings and 2. Bingi Manasa,Ganesh Kumar Gudas, N. Sravanthi, R.
manufacturing methods which is now available to the Anusha Madhuri, Y. Lavanya AndC. Pranitha.:
pharmaceutical industry. These films may be coloured or Formulation and evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal
printed during manufacture for branding and coding which patches ofRiesperidone. J. A chemical. Pharmacy.
is quite helpful in product identification and also developed Research., 2010, 2(4):866-872.
for non-ingestible applications such as cosmetic, ostomy 3.Vanksha Kushwaha, Juber Akhtar, Shazia Usmani, Satya
pouches, sanitary and healthcare pouches . These films Prakash Singh, A Review On Fast Dissolving Formulation
enhance the stability of product. Technologies, 2015, 4(7), 574-585
4.Ankita Keshari, Dr. Pramod Kumar Sharma, Dr. Nayyar
B. Soluleaves [12]: Parvez, Fast Dissolving Oral Film: A Novel and Innovative
In this technology, the film on coming in contact with saliva Drug Delivery system, IJPSR, 2014, 5(3), 92-95
releases its active ingredients, during this film adhere to the 5. Shruti C Prabhu, Sarvesh D Parsekar, Amitha Shetty,
mucous membrane in order to release the drug slowly in 15 Samuel S Monteiro, Mohd Azharuddin and AR. Shabaraya,
min. This method is useful for those who have difficulty in A Review on Fast Dissolving Sublingual Films for
swallowing conventional tablets. This technology is applied Systemic Drug Delivery, International Journal Of
to flavoured products such as mouth fresheners, Pharmaceutical And Chemical Sciences, 2014, 3(2), 501-
confectionery and vitamins 511.
6. Bhupinder Bhyan, Sarita Jangra2, Mandeep Kaur1,
C. Wafertab [13] Harmanpreet Singh, Orally Fast Dissolving Films:
Wafertab is a drug delivery system which incorporates Innovations In Formulation And Technology, International
pharmaceutically active ingredients into an ingestible film Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research,
strip. When film came in contact with saliva it provides 2011 9(2) 50-57
rapid dissolution and release of active ingredient. The 7. Pardeep Kumar Jangra, Sachin Sharma1, Rajni Bala1,
Wafertab film strip can also be flavoured for additionally Fast Dissolving Oral Films: Novel Way For Oral Drug
improved taste masking. The active ingredient is integrated Delivery, International Standard Serial Number, 2014,
into the body of a fused. 3(1), 6-28
8. Ms. Mansi M Soni, Dr. Kanu R Patel, Recent Trends in
D. Foamburst [13] OPral driug Delivery System: Fast Dissolving Film, 2016,
Foamburst is a new patent granted in September 2004 which 5(2), 188-208
is for capsules made of formed film. During production an 9. M. Sri Rekha, SK. Shaheda Sultana1, K. Mahathi1, P.
inert gas is blown into the film, results in a film with Parveen, B. Prathima, A. Seethadevi, Novel Oral Drug
honeycomb structure as a capsule which dissolve rapidly Delivery System: Fast Dissolving Buccal Film, 2014,
and causing a melt-in-the mouth sensation. The void in the 2(12), 18-41
film may be gas-filled, empty or filled with other materials 10. Rajni Bala, Pravin Pawar, Sushil Khanna, Sandeep
to produce specific taste burst characteristics or deliver Arora, Orally Dissolving Strips: ANew Approach To Oral
active drugs. Drug Delivery System, International Journal Of
PharmaceuticalInvestigation, April 2013,3 (2),67-76.
VII. CONCLUSION 11.Deepak Sharma , Daljit Kaur, Shivani Verma, Davinder
Singh, Mandeep Singh, Gurmeet Singh, Rajeev Garg, Fast
From the above, this can be concluded that fast dissolving Dissolving Oral Films Technology: A Recent Trend For An
films have proved as beneficial innovative tool for all Innovative Oral Drug Delivery System International
groups of population or all groups of patients that having Journal of Drug Delivery.2015, 7 (2), 60-75
problem of swallowing .Fast dissolving films play vital role 12. Anupama VM, Kiran RS, Rao VUM,Dileep P, Bhavani
when quick onset of action is required .Pharmaceutical D, Latha, BM. AReview on Oral Thin Fast DissolvingFilms
Industries also recognized the potential of fast dissolving recent trend of dosage form for quick release. Int J Pharm
film and also launched several products. Gaining importance Bio Sci. 2014;5(4): 54-67.
as they are idea l dosage form for use in young children, as 13.Patel JC, Patel KR, Patel NM. Review onFast Dissolving
well as geriatric patients. Film. Int J AdvancedPharmaceutics. 2013; 3(1):44-50
References
1. Venkata Anupama M, R. Shireesh Kiran, V. Uma
Maheswar Rao,P. Dileep, D. Bhavani And B. Madhavi
IJISRT17JU135 www.ijisrt.com 281
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Role of Lipid Excipients in Modifying Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: Basic Principles and Biological ExamplesD'EverandRole of Lipid Excipients in Modifying Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: Basic Principles and Biological ExamplesKishor M. WasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach To Oral Drug DeliveryDocument7 pagesFast Dissolving Films: A Novel Approach To Oral Drug DeliveryEga TrikuntiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Article 009 PDFDocument8 pagesArticle 009 PDFprasanthiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films: (Reg. No. 14421S0303)Document23 pagesA Review On Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films: (Reg. No. 14421S0303)SiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Films: A Comprehensive Review: Review Article Open AccessDocument7 pagesOral Films: A Comprehensive Review: Review Article Open AccessFarhan AmjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Films and StripsDocument22 pagesSeminar On Films and StripskeyurPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Sciences: Oral Dissolving Films: A ReviewDocument12 pagesPharmaceutical Sciences: Oral Dissolving Films: A ReviewEga TrikuntiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation Development and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Film of Ziprasidone Using Natural BioenhancerDocument12 pagesFormulation Development and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Film of Ziprasidone Using Natural BioenhancerEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Films 1 PDFDocument11 pagesOral Films 1 PDFCristian Camilo Villa100% (1)
- Review On "Mouth Dissolving Tablet As Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System"Document13 pagesReview On "Mouth Dissolving Tablet As Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System"Editor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- IJNDD 10 (2), Apr-Jun, 2018, 68-75 - Research ArticleDocument8 pagesIJNDD 10 (2), Apr-Jun, 2018, 68-75 - Research ArticleJameel MullaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3676-Article Text-10501-1-10-20191113Document5 pages3676-Article Text-10501-1-10-20191113SOUJANYA BONIPas encore d'évaluation
- Orally Dissolving Strips: A New Approach To Oral Drug Delivery SystemDocument19 pagesOrally Dissolving Strips: A New Approach To Oral Drug Delivery SystemDuong NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Film Containing RofecoxibDocument7 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Film Containing RofecoxibSathish SizzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Fast Disintegration TableDocument20 pagesDevelopment of Fast Disintegration TableKamran AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyDocument10 pagesRecent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyAnkush BhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Drug Delivery System: CollegeDocument32 pagesInnovative Drug Delivery System: CollegeSiriPas encore d'évaluation
- L-1 Tablet-1..Document11 pagesL-1 Tablet-1..Sun ShinePas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyDocument11 pagesRecent Trends of Fast Dissolving Tablet - An Overview of Formulation TechnologyAisyah Al-mumtahanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Suon Lacn SteaDocument10 pagesSuon Lacn Steaelektron2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Dissolving Oral Films An Innovative DrugDocument8 pagesFast Dissolving Oral Films An Innovative DrugHananun ZharfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Disintegrating Film of Imipramine HydrochlorideDocument13 pagesFast Disintegrating Film of Imipramine HydrochlorideChetna ModiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablet-Oral Solid Dosage FormDocument31 pagesTablet-Oral Solid Dosage FormHely PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview On Mouth Dissolving Film: Review ArticleDocument4 pagesAn Overview On Mouth Dissolving Film: Review ArticleSOUJANYA BONIPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Strip Paracetamol PDFDocument3 pagesJurnal Strip Paracetamol PDFaristhanovyraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Short Review On "A Novel Approach in Oral Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System and Their Patents"Document13 pagesA Short Review On "A Novel Approach in Oral Fast Dissolving Drug Delivery System and Their Patents"Arman DalalPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5: TabletsDocument15 pagesTopic 5: TabletsKate EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Pelletization Techniques: International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy June 2020Document6 pagesA Review On Pelletization Techniques: International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy June 2020ES MMPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablet DefectsDocument96 pagesTablet DefectsUmair HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Buccal Drug Delivery System: Presenting ByDocument29 pagesBuccal Drug Delivery System: Presenting ByKuldip KuldipPas encore d'évaluation
- Gupta 2009Document12 pagesGupta 2009hilda kurniawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Buccal Drug Delivery SystemDocument35 pagesBuccal Drug Delivery Systemshamma shahulhameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Dispersible Tablets - A ReviewDocument8 pagesOral Dispersible Tablets - A ReviewSriram NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Formulation Technology For Recent Advancements in Fast Dissolving TabletsDocument12 pagesA Review of Formulation Technology For Recent Advancements in Fast Dissolving TabletsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Dissolving TabletsDocument26 pagesFast Dissolving TabletsBilal KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Bio Availability Parameters of Pharmaceutical SuspensionDocument8 pagesFormulation and Bio Availability Parameters of Pharmaceutical SuspensionDelvia NovalisyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Park Ash 2011Document14 pagesPark Ash 2011Amiro AuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Development of Sublingual TabletDocument20 pagesFormulation and Development of Sublingual Tabletvedantyenge68Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tablet (Print) PDFDocument17 pagesTablet (Print) PDFAsif Hasan NiloyPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Films For Two Drugs in The Management of Chemotherapy Induced VomitingDocument66 pagesDesign and Evaluation of Mouth Dissolving Films For Two Drugs in The Management of Chemotherapy Induced Vomitingdheeksha puvvadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Suspension: Pharmaceutical Preparations Dr. Asra HameedDocument64 pagesSuspension: Pharmaceutical Preparations Dr. Asra HameedGutu DoinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Buccal Mucoadhesive Films: A ReviewDocument8 pagesBuccal Mucoadhesive Films: A ReviewLidya AmelianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter_6 (Tablets) (2)Document25 pagesChapter_6 (Tablets) (2)Rayonesh RayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Dispersible Tablets Novel Technology and Development PDFDocument7 pagesOral Dispersible Tablets Novel Technology and Development PDFHaider SalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Final 2023 PratikDocument24 pagesProject Final 2023 PratikPratik sablePas encore d'évaluation
- 83-Article Text-86-1-10-20180222 - 2Document6 pages83-Article Text-86-1-10-20180222 - 2Haider SalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabletmanufactureprocess Elixer PDFDocument8 pagesTabletmanufactureprocess Elixer PDFGhazanfar AyazPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Pharmaceutical Suspension and Its Advancement 9311Document7 pagesA Review On Pharmaceutical Suspension and Its Advancement 9311Lifia CahyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Some of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowDocument17 pagesSome of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Tablets Are Given BelowTasmih Rob MowPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocular Inserts - Advancement in Therapy of Eye DiseasesDocument8 pagesOcular Inserts - Advancement in Therapy of Eye DiseasesCristina Maria FranziniPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablets Part 1 - MergedDocument185 pagesTablets Part 1 - MergedTaleda AloranPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Suspension FundamentalsDocument51 pagesPharmaceutical Suspension FundamentalsMehak LubanaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Solid DispersionDocument7 pagesA Review On Solid DispersionEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- Sublingual DdsDocument20 pagesSublingual DdsrandatagPas encore d'évaluation
- Parenteral Suspension An OverviewDocument10 pagesParenteral Suspension An OverviewIrma LaumbuPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral DDF 3 2 Gupta PDFDocument13 pagesOral DDF 3 2 Gupta PDFZaki AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Dosage Forms PC IDocument29 pagesDosage Forms PC Ianeri desaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Suspension SEPT 16-1Document53 pagesPharmaceutical Suspension SEPT 16-1Subha ShankareePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2.1 Dosage FormDocument7 pagesModule 2.1 Dosage FormAbby Dimalaluan OquendoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physico-Chemical Properties of The Drug Affecting BioavailabilityDocument32 pagesPhysico-Chemical Properties of The Drug Affecting BioavailabilityLilia AndromedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparatively Design and Analyze Elevated Rectangular Water Reservoir with and without Bracing for Different Stagging HeightDocument4 pagesComparatively Design and Analyze Elevated Rectangular Water Reservoir with and without Bracing for Different Stagging HeightInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Leaf Fiber as a Main Component in Making an Improvised Water FilterDocument11 pagesThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Leaf Fiber as a Main Component in Making an Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning for Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 pagesAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning for Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro-Optics Properties of Intact Cocoa Beans based on Near Infrared TechnologyDocument7 pagesElectro-Optics Properties of Intact Cocoa Beans based on Near Infrared TechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubDocument6 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Terracing as an Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains- CameroonDocument14 pagesTerracing as an Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains- CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions on Customer SatisfactionDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions on Customer SatisfactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review: Pink Eye Outbreak in IndiaDocument3 pagesA Review: Pink Eye Outbreak in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Encoder Driven Hybrid Pipelines for Image Deblurring using NAFNETDocument6 pagesAuto Encoder Driven Hybrid Pipelines for Image Deblurring using NAFNETInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Design, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooDocument8 pagesDesign, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (3)
- A Survey of the Plastic Waste used in Paving BlocksDocument4 pagesA Survey of the Plastic Waste used in Paving BlocksInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyberbullying: Legal and Ethical Implications, Challenges and Opportunities for Policy DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCyberbullying: Legal and Ethical Implications, Challenges and Opportunities for Policy DevelopmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatic Portovenous Gas in a Young MaleDocument2 pagesHepatic Portovenous Gas in a Young MaleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Explorning the Role of Machine Learning in Enhancing Cloud SecurityDocument5 pagesExplorning the Role of Machine Learning in Enhancing Cloud SecurityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigating Digitalization: AHP Insights for SMEs' Strategic TransformationDocument11 pagesNavigating Digitalization: AHP Insights for SMEs' Strategic TransformationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Perceived Impact of Active Pedagogy in Medical Students' Learning at the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy of CasablancaDocument5 pagesPerceived Impact of Active Pedagogy in Medical Students' Learning at the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy of CasablancaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Power Factor ControllerDocument4 pagesAutomatic Power Factor ControllerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Distractions among Adolescents: Impact on Learning in the Aftermath of COVID-19 in IndiaDocument2 pagesMobile Distractions among Adolescents: Impact on Learning in the Aftermath of COVID-19 in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Biomechanics in Footwear Design and Development: An Exploration of Key Concepts and InnovationsDocument5 pagesReview of Biomechanics in Footwear Design and Development: An Exploration of Key Concepts and InnovationsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Studying the Situation and Proposing Some Basic Solutions to Improve Psychological Harmony Between Managerial Staff and Students of Medical Universities in Hanoi AreaDocument5 pagesStudying the Situation and Proposing Some Basic Solutions to Improve Psychological Harmony Between Managerial Staff and Students of Medical Universities in Hanoi AreaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Time Variables as Predictors of Senior Secondary School Students' Mathematical Performance Department of Mathematics Education Freetown PolytechnicDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Time Variables as Predictors of Senior Secondary School Students' Mathematical Performance Department of Mathematics Education Freetown PolytechnicInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Dosage Control System Using Reinforcement LearningDocument8 pagesDrug Dosage Control System Using Reinforcement LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Securing Document Exchange with Blockchain Technology: A New Paradigm for Information SharingDocument4 pagesSecuring Document Exchange with Blockchain Technology: A New Paradigm for Information SharingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhancing the Strength of Concrete by Using Human Hairs as a FiberDocument3 pagesEnhancing the Strength of Concrete by Using Human Hairs as a FiberInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Formation of New Technology in Automated Highway System in Peripheral HighwayDocument6 pagesFormation of New Technology in Automated Highway System in Peripheral HighwayInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Chain 5.0: A Comprehensive Literature Review on Implications, Applications and ChallengesDocument11 pagesSupply Chain 5.0: A Comprehensive Literature Review on Implications, Applications and ChallengesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Intelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains with AIDocument14 pagesIntelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains with AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Making of Self-Disposing Contactless Motion-Activated Trash Bin Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocument7 pagesThe Making of Self-Disposing Contactless Motion-Activated Trash Bin Using Ultrasonic SensorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- AutocoidsDocument26 pagesAutocoidsA.R. ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Parameters of An Extended Aeration Activated Sludge System - Water Tech Online PDFDocument9 pagesWhat Are The Parameters of An Extended Aeration Activated Sludge System - Water Tech Online PDFZoran KostićPas encore d'évaluation
- New Law Regarding Mental Health Part 2 1 UpDocument43 pagesNew Law Regarding Mental Health Part 2 1 UpHollister TidwellPas encore d'évaluation
- NM ObtDocument22 pagesNM ObtIlyan NastiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tourettes SyndromeDocument12 pagesTourettes Syndromeapi-238788335Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rehab-U FreeMobilityEbook PDFDocument10 pagesRehab-U FreeMobilityEbook PDFTuteraipuni POTHIERPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism of Propionibacterium Acne Necrosis by Initiation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Porphyrin AbsorptionDocument23 pagesMechanism of Propionibacterium Acne Necrosis by Initiation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Porphyrin AbsorptionCaerwyn AshPas encore d'évaluation
- Javma-Javma 21 04 0213Document5 pagesJavma-Javma 21 04 0213Black manPas encore d'évaluation
- History of PharmacyDocument81 pagesHistory of PharmacyNurdiansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Range of Pest Control Services by Pest Control (India) Pvt. LTDDocument5 pagesRange of Pest Control Services by Pest Control (India) Pvt. LTDAvinash ToranePas encore d'évaluation
- Gram08 28Document21 pagesGram08 28Hendra Wana Nur'aminPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifepak 20e: Operating InstructionsDocument218 pagesLifepak 20e: Operating InstructionsJorge ArturoPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Aspergilosis 2016 Update by AmericaDocument60 pagesPractice Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Aspergilosis 2016 Update by AmericaNur Prasetyo Nugroho100% (1)
- Child AbuseDocument5 pagesChild AbusePeng Peng LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Antiseptic Polyherbal OintmentDocument11 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Antiseptic Polyherbal OintmentandrapradeshssePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade9 STE Con.-Chem. Q4 Module-5 Wk6 ADMDocument20 pagesGrade9 STE Con.-Chem. Q4 Module-5 Wk6 ADMChelzy CatabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue Wastewater Treatment SolutionsDocument49 pagesCatalogue Wastewater Treatment SolutionsmentolPas encore d'évaluation
- Game Addiction PDFDocument9 pagesGame Addiction PDFRonaldas GadzimugometovasPas encore d'évaluation
- Asia Pacific October 2022Document24 pagesAsia Pacific October 2022Dhananjay VasuDevaPas encore d'évaluation
- AHA ACLS Provider Manual $45Document2 pagesAHA ACLS Provider Manual $45Jigar GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Critiquing 1Document3 pagesCritiquing 1Nilesh VeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Appellant MemorialDocument20 pagesAppellant MemorialKeerthana Madhavan100% (1)
- Updated February 10, 2012: Preview of The Medifocus Guidebook On: Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument30 pagesUpdated February 10, 2012: Preview of The Medifocus Guidebook On: Alzheimer's Diseaseexpedito andres prada suarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Croup NcbiDocument6 pagesCroup NcbijefrizalzainPas encore d'évaluation
- English Iii: University of Guayaquil Facultad Piloto de OdontologíaDocument4 pagesEnglish Iii: University of Guayaquil Facultad Piloto de OdontologíaDianitaVelezPincayPas encore d'évaluation
- Kimberly Callis - Stoning Demons - Complex PTSD Recovery Workbook. 6Document44 pagesKimberly Callis - Stoning Demons - Complex PTSD Recovery Workbook. 6intenselight91% (11)
- Sarana Prasarana Pelayanan Terpadu (Pandu) Penyakit Tidak Menular Di FKTPDocument3 pagesSarana Prasarana Pelayanan Terpadu (Pandu) Penyakit Tidak Menular Di FKTPdion dqPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical and Anaesthetic Instruments For OSCEs - A Practical Study Guide (Master Pass Series) 1st EditionDocument121 pagesSurgical and Anaesthetic Instruments For OSCEs - A Practical Study Guide (Master Pass Series) 1st EditionYoleima PerdomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Waste Water TreatmentDocument5 pagesHospital Waste Water TreatmentNP100% (1)
- Background: Pediatric Chickenpox Next Section: PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesBackground: Pediatric Chickenpox Next Section: PathophysiologyRachel Johann Aquinto100% (1)