Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Preterm Labour
Transféré par
cgao300 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
112 vues3 pagesThis document defines and discusses preterm labour, which occurs between 24-36 weeks gestation. It outlines the epidemiology, risk factors, signs and symptoms, investigations, prevention strategies, and management of preterm labour. Investigations may include CTG, tocodynamcis, ultrasound, cervical length measurement, and tests for infection. Management involves administering steroids to aid fetal lung maturation if delivery is likely before 34 weeks, use of tocolytic drugs to delay delivery, antibiotics if membranes have ruptured, and consideration of vaginal versus cesarean delivery depending on the situation. The goal is to delay delivery long enough to complete steroid administration when possible.
Description originale:
Preterm labour matrix
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document defines and discusses preterm labour, which occurs between 24-36 weeks gestation. It outlines the epidemiology, risk factors, signs and symptoms, investigations, prevention strategies, and management of preterm labour. Investigations may include CTG, tocodynamcis, ultrasound, cervical length measurement, and tests for infection. Management involves administering steroids to aid fetal lung maturation if delivery is likely before 34 weeks, use of tocolytic drugs to delay delivery, antibiotics if membranes have ruptured, and consideration of vaginal versus cesarean delivery depending on the situation. The goal is to delay delivery long enough to complete steroid administration when possible.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
112 vues3 pagesPreterm Labour
Transféré par
cgao30This document defines and discusses preterm labour, which occurs between 24-36 weeks gestation. It outlines the epidemiology, risk factors, signs and symptoms, investigations, prevention strategies, and management of preterm labour. Investigations may include CTG, tocodynamcis, ultrasound, cervical length measurement, and tests for infection. Management involves administering steroids to aid fetal lung maturation if delivery is likely before 34 weeks, use of tocolytic drugs to delay delivery, antibiotics if membranes have ruptured, and consideration of vaginal versus cesarean delivery depending on the situation. The goal is to delay delivery long enough to complete steroid administration when possible.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
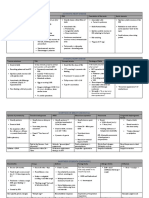
Preterm labour
Definition Investigations
Onset of labour occurring between 24+0/40 to 36+6/40 Test Findings
weeks of gestation. CTG Presence of foetal heartbeat
Tocography >1 contraction every 10 mins
Preterm: 34 36+6 weeks gestation Transvaginal U/S Significant if cervix <2cm long
+ VE
Very preterm: 28 33+6 weeks gestation Cervico-vaginal If positive:
swab for foetal 20% chance will deliver in next
Extremely preterm: <28 weeks gestation
fibronectin 10 days
If negative:
97 99% will not delivery
Epidemiology prematurely
FBE Hb in APH
Occurs in up to 10% of babies born in WBC in infection
Australia High Look for GBS
<1% are extremely preterm (<28/40 weeks) vaginal/rectal Amnisure to test is
swab membranes have ruptured
Majority of preterm birth is due to iatrogenic
Kleihauer test To look for presence of foetal cells
induction for maternal/foetal cx e.g. pre-
in maternal circulation used to
eclampsia, IUGR calculate how much anti-D to give
Rh- mothers to prevent iso-
Risk factors/Aetiology
immunisation
Maternal Foetal
PROM Multiple pregnancy Prevention
Uterine abnormalities Foetal abnormalities
Infection (e.g. Polyhydramnios 1. Address risk factors
chorioamnionitis, GBS) Diet & lifestyle limit:
Cervical Indications for o Smoking
incompetence/short premature induction o Alcohol
cervix <2cm FGR o Illicit drug use
Foetal distress Having children at a healthy age (22 40)
Congenital >12 18 months between pregnancies
abnormalities
Hx of preterm labour
2. Treat & manage infections pre-pregnancy
(4x risk)
Social factors (smoking, Asymptomatic bacteuria MSU at first
alcohol, recreational antenatal checks
drug abuse, poor diet, Bacterial vaginosis, GBS, STI needs to be
coffee intake) tested for
3. Need for cervical suture
Signs & symptoms
If there is hx of shortened cervix, or U/S
Uterine contractions (>1 in 10 minutes less indications
likely to be Braxton-Hicks contractions) Suture is put into cervix to prevent dilatation
P-PROM pooling of liquor on spec exam before ripening
Cervical length <2cm
+/- Dilatation of cervix 4. Consider the role of vaginal progesterone
+/- Non-specific lower abdo or back pain To balance out the oestrogen:progesterone
+/- PV bleed (assoc with APH due to placental ratio to promote myometrial quiescence &
abruption) delay labour
+/- Maternal/foetal tachycardia
Management pPROM without chorioamnionitis
o Amoxy/ampicillin 2g IV, 6hrly for
STATIN
48hrs followed by amoxycillin 250mg
Steroids (if <34 weeks) 2 x doses of betamethasone PO, 8hrly for 7/7
(celestone) 11.4mg IM, 24 hrs apart PLUS
o Erythromycin 250mg PO, 6hrly for 7/7
Foetal lung maturation - ARDS
Gut closure promotes sphincter formation Tocolysis (to give time to administer steroids)
Renal differentiation - glomerular units
Nifedipine (CCB)
HgB stimulates change from HbF to adult Hb o Peripheral acting Ca2+ antagonist that
Transfer to Tertiary centre with access to neonatal prevents uterine contraction
resuscitation facilities & blood transfusion Terbutaline (-antagonist)
o Inhibits -receptors, SNS
Antibiotics (if pPROM) stimulation of uterine myometrium
Pre-partum: Erythromycin 250mg PO, QID relaxation
Intra-partum o Can also be used to maternal HR
o Benpen 3g IV loading dose, then 1.8g Intrapartum care consider vaginal vs C-section
IV 4hrly until delivery delivery + continuous CTG
o If hypersensitive: Cephazolin 2g IV
8hrly until delivery Neuroprotection (if <30/40) maternal IV MgSO4
o Anaphylactic: clindamycin 600mg IV, infusion
8hrly until delivery
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 30 Minutes in HeavenDocument11 pages30 Minutes in HeavenValpo Valparaiso100% (1)
- Squirting For DummiesDocument31 pagesSquirting For DummiesGustavoCalderin75% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemLiangkiuwiliuPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of InfertilityDocument22 pagesTreatment of InfertilityAlina ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- IMMUNIZATION TIPSDocument14 pagesIMMUNIZATION TIPSETCPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Exam' Questions For V - Year Studying Students I Group of QuestionsDocument7 pagesOral Exam' Questions For V - Year Studying Students I Group of QuestionsShreya SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Infants Nutritional NeedsDocument5 pagesInfants Nutritional NeedsSukQin KongPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv in PregnancyDocument98 pagesHiv in PregnancyAkrit DahalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Notes (3&7) - CompleteDocument11 pagesDna Notes (3&7) - Completecgao30100% (1)
- Oxytocics and TocolyticsDocument6 pagesOxytocics and TocolyticsFarheen khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension: DefinitionDocument7 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension: Definitionkristine hinaresPas encore d'évaluation
- ENDOCRINE DISORDERS DURING PREGNANCYDocument223 pagesENDOCRINE DISORDERS DURING PREGNANCYSTEPHANIE TALILAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyDocument9 pagesSigns and Symptoms of PregnancyTrina Joy DomantayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pap Smear - Overview, Indications, PreparationDocument11 pagesPap Smear - Overview, Indications, PreparationBayu Surya DanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Dysfunctions and ParaphiliasDocument10 pagesSexual Dysfunctions and ParaphiliasGino Al Ballano BorinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCH Epidemiology Issues MagnitudeDocument25 pagesMCH Epidemiology Issues MagnitudeRatna KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Undescended TestisDocument25 pagesUndescended TestisAmir ShafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Friedman VTE Bundle PDFDocument24 pagesFriedman VTE Bundle PDFGerman Parra CPas encore d'évaluation
- HELLP SyndromeDocument3 pagesHELLP SyndromeWidyawati TjahjadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Use in Labour RoomDocument22 pagesDrug Use in Labour RoomManoj Dongarwar100% (1)
- Simple Queen Rearing MethodsDocument8 pagesSimple Queen Rearing MethodsAyvz Martija LambioPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical DisordersDocument225 pagesMedical DisordersWael GaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of structured teaching on gestational hypertensionDocument18 pagesImportance of structured teaching on gestational hypertensionمالك مناصرةPas encore d'évaluation
- Skills Training Manual BookDocument51 pagesSkills Training Manual BookAndi RahmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument4 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Concise Paediatric BookDocument561 pagesConcise Paediatric BookWai Kwong ChiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Monitoring Tests and TherapiesDocument46 pagesFetal Monitoring Tests and TherapiesAumrin Fathima100% (1)
- 9fetal Well Being in PregnancyDocument10 pages9fetal Well Being in PregnancyuouoPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual DisordersDocument8 pagesMenstrual DisordersBangkit Pank BuminataPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Amniotic Fluid LevelsDocument2 pagesLow Amniotic Fluid LevelspramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of Newborn AssessmentDocument15 pagesNursing Care of Newborn AssessmentMary RosePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing the NeonateD'EverandNursing the NeonateMaggie MeeksPas encore d'évaluation
- Medications and Labor FactorsDocument8 pagesMedications and Labor FactorsKimberly Sharah Mae FortunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzhymas DiseaseDocument12 pagesAlzhymas Diseasekids dance BPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Fertilization Techniques ExplainedDocument180 pagesAssisted Fertilization Techniques ExplainedPaul Kevin Mendoza67% (3)
- Emergencias ReproductivasDocument24 pagesEmergencias ReproductivasYami SuperPas encore d'évaluation
- THE MORAL ISSUES OF ABORTION: ONGOING DEBATES CHAPTERDocument38 pagesTHE MORAL ISSUES OF ABORTION: ONGOING DEBATES CHAPTERBHUKYA USHARANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Milestone of Preschool AgeDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Milestone of Preschool AgeJessa Mae BacuganPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Contraceptive PillsDocument113 pagesOral Contraceptive PillsRaj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric ICU Ethical DilemmasDocument70 pagesPediatric ICU Ethical Dilemmasmay chehabPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument5 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- InfertilityDocument14 pagesInfertilityDrChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vancouver Style Referencing SystemDocument20 pagesVancouver Style Referencing SystemKarthik ManoharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Obg ResearchDocument15 pagesObg ResearchAGERI PUSHPALATHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Maternal Perception of Fetal MovementsDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Maternal Perception of Fetal MovementsNoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosi S: MalariaDocument28 pagesDiagnosi S: MalariaOm Prakash SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Pregnancies: Shanelle ThomasDocument40 pagesMultiple Pregnancies: Shanelle Thomasshanellethomas1820100% (1)
- Menstrual Cycle Fertilization and Embryogenesis 1Document71 pagesMenstrual Cycle Fertilization and Embryogenesis 1Siselle FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth - Development of Fetus - NeonateDocument40 pagesGrowth - Development of Fetus - NeonatesujidahPas encore d'évaluation
- Exclusive Breast Milk for BabyDocument4 pagesExclusive Breast Milk for BabyWindayaniayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Paper Abstract BookDocument1 047 pagesFree Paper Abstract Bookkukadiya100% (1)
- Early Signs of PregnancyDocument27 pagesEarly Signs of PregnancyYzel Vasquez AdavanPas encore d'évaluation
- ACOG Bulletin #73 PDFDocument20 pagesACOG Bulletin #73 PDFwanwan_adongPas encore d'évaluation
- FIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1Document12 pagesFIGO Guidelines - Prevention and Treatment of PPH Etc1karinasurakusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Insemination GuideDocument3 pagesArtificial Insemination Guidesagi muPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Hemorrhage GuideDocument20 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage Guidem_amroellahPas encore d'évaluation
- Multifetalpregnancy 121008074609 Phpapp02Document38 pagesMultifetalpregnancy 121008074609 Phpapp02Jagannath MaalePas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal SubgalealDocument6 pagesNeonatal SubgalealIrenLayPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Dysfunctional Labour and Cephalopelvic Disproportion (CPDDocument128 pagesGuide to Dysfunctional Labour and Cephalopelvic Disproportion (CPDDebjyoti KarmakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Labour Quiz SummaryDocument62 pagesLabour Quiz SummaryMOHAMED AZIZPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Termination of PregnencyDocument19 pagesMedical Termination of PregnencyTijilPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge of Breast EngorgementDocument17 pagesKnowledge of Breast EngorgementRoselineTigga100% (1)
- EBP NursingDocument31 pagesEBP NursingVictoria Castillo Tamayo100% (1)
- PDF Theories Applied To Midwifery CompressDocument10 pagesPDF Theories Applied To Midwifery CompressRafiqa BashirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan On Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument29 pagesLesson Plan On Iron Deficiency AnemiaGLOBAL INFO-TECH KUMBAKONAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityD'EverandHandbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityMichael H. DahanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingD'Everand2023 OB/GYN Coding Manual: Components of Correct CodingPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonwealth Statutory Declaration Form (May 2011) PDFDocument2 pagesCommonwealth Statutory Declaration Form (May 2011) PDFcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Commonwealth Statutory Declaration Form (May 2011) PDFDocument2 pagesCommonwealth Statutory Declaration Form (May 2011) PDFcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theme IV Yr 5d Content Guide - MatrixDocument9 pagesTheme IV Yr 5d Content Guide - Matrixcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras WorksheetDocument2 pagesPythagoras Worksheetcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Student Elective Rotation GuideDocument3 pagesStudent Elective Rotation Guidecgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD30 Literature Review PlanDocument1 pageCD30 Literature Review Plancgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD30 Draft CollationDocument8 pagesCD30 Draft Collationcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD marker panel guide for flow cytometry cell identificationDocument2 pagesCD marker panel guide for flow cytometry cell identificationcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lit Reviews For RX Students v7Document20 pagesLit Reviews For RX Students v7Joshua McdonaldPas encore d'évaluation
- CPPREP4002 - Annotated Unit GuideDocument8 pagesCPPREP4002 - Annotated Unit Guidecgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD30 Literature Review PlanDocument1 pageCD30 Literature Review Plancgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD30 Literature Review PlanDocument1 pageCD30 Literature Review Plancgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- CD30+ cutaneous lymphoproliferative disordersDocument1 pageCD30+ cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorderscgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Organ ProlapseDocument5 pagesPelvic Organ Prolapsecgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatrics: Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesPaediatrics: Acyanotic Heart Diseasecgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fibroids: 1. Red DegenerationDocument2 pagesFibroids: 1. Red Degenerationcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Motor Systems: (Why Else Would You Go To The Gym, Right?)Document13 pagesIntro To Motor Systems: (Why Else Would You Go To The Gym, Right?)cgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Lesions of The Vulva & Vagina (Table)Document3 pagesBenign Lesions of The Vulva & Vagina (Table)cgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Terms: DescriptorsDocument2 pagesSkin Terms: Descriptorscgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- O&G GlossaryDocument3 pagesO&G Glossarycgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- EndometriosisDocument1 pageEndometriosiscgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lecture 2 - NeoplasiaDocument15 pagesPathology Lecture 2 - Neoplasiacgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Conditions (Disease Mechanisms)Document3 pagesInflammatory Conditions (Disease Mechanisms)cgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix TopicsDocument3 pagesMatrix Topicscgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lecture 5 - Upper GITDocument10 pagesPathology Lecture 5 - Upper GITcgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lecture 7 - LiverDocument11 pagesPathology Lecture 7 - Livercgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lecture 7 - LiverDocument11 pagesPathology Lecture 7 - Livercgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Respiration Notes (3&8)Document9 pagesCell Respiration Notes (3&8)cgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prenatal RhogamDocument3 pagesPrenatal Rhogamgshastri7Pas encore d'évaluation
- MumalDocument17 pagesMumalNidhi PiousPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones and Behavior: Jill E. Schneider, Jeremy M. Brozek, Erin Keen-RhinehartDocument16 pagesHormones and Behavior: Jill E. Schneider, Jeremy M. Brozek, Erin Keen-RhinehartKerin ArdyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Document11 pages3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Musharaf RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Velammal Vidyalaya, Viraganoor STD: X Full Portion Test Max - Marks:80 Subject: BIOLOGY Timing: 3hrs General InstructionsDocument3 pagesVelammal Vidyalaya, Viraganoor STD: X Full Portion Test Max - Marks:80 Subject: BIOLOGY Timing: 3hrs General InstructionsshanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Version BDocument6 pagesOB Version Bisapatrick8126100% (1)
- 11 Biology Notes ch05 Morphology of Flowering Plants PDFDocument7 pages11 Biology Notes ch05 Morphology of Flowering Plants PDFMeenakshi VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Reproductive Tract InfectionsDocument14 pages2 Reproductive Tract InfectionsawalsherPas encore d'évaluation
- Predisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine SegmentDocument11 pagesPredisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine Segmentjhachers100% (1)
- Reproduction MCQsDocument2 pagesReproduction MCQssuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pi Is 0002937811009379Document9 pagesPi Is 0002937811009379Mirza FinandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Biology: GametogenesisDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology: GametogenesisTapan Kumar PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Sexual Abuse A Medico-Legal AnalysisDocument8 pagesChild Sexual Abuse A Medico-Legal AnalysisYogi Ardhi IrafaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012rh CommunitymidwiferyguidelinesDocument43 pages2012rh Communitymidwiferyguidelinesgeorgeloto12100% (1)
- SWCRM Sperm CryopreservationDocument2 pagesSWCRM Sperm CryopreservationVenkata Ramanan Dasu SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculations Based On Vital StatisticsDocument14 pagesCalculations Based On Vital StatisticsRamniwasMahorePas encore d'évaluation
- Seed Propagation: I. Methods of Propagation A. Seeds or Sexual PropagationDocument36 pagesSeed Propagation: I. Methods of Propagation A. Seeds or Sexual PropagationMikaerika AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CBQDocument6 pagesCBQCarlos BaysaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Lessons: What is a nervous system and endocrine glands? (39Document28 pagesReview Lessons: What is a nervous system and endocrine glands? (39Kizyanah Palanas Bentic100% (1)
- BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009Document17 pagesBIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009Kjeld DmlPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology - Botany Ebook - Class 11Document299 pagesBiology - Botany Ebook - Class 11prashanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Positions and Mobility During First Stage Labour - Annemarie Lawrence, Lucy Lewis, G Justus Hofmeyr, Therese Dowswell & Cathy StylesDocument2 pagesMaternal Positions and Mobility During First Stage Labour - Annemarie Lawrence, Lucy Lewis, G Justus Hofmeyr, Therese Dowswell & Cathy StylesPujianti LestarinaPas encore d'évaluation
- #2 AngiospermDocument65 pages#2 AngiospermrandelPas encore d'évaluation