Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Choledocholithiasis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Transféré par
Sheana TmplCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Choledocholithiasis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Transféré par
Sheana TmplDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
X.
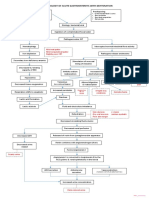
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
CHOLEDOCHOLITHIASIS
Non Modifiable Modifiable
- Age: 58 years old
- Diet: High fatty
foods and alcohol
intake
- Lack of physical
activity
Bile becomes supersaturated with cholesterol/calcium/excess
unconjugated bilirubin/both and has decrease bile salt
Solutes precipitate from solution to solid crystals
Crystals come together to form stones
Small stones may pass from the gall bladder to common bile duct
Tx:
- Cholecystomy
Intraoperative
Cholangiogram Obstruction in the common bile duct
- T-tube insertion
- Exploration of the
Bile duct
Body tries to dislodge No bile reaches the GIT Backflow of conjugated
the stones bilirubin to liver
Spasm of the decreased bile in decrease bile in duodenum Conjugated bilirubin
biliary tracts small intestine for enters blood stream
fat digestion decreased Sterobilin
S/Sx: S/Sx:
- Biliary colic decreased emulsification S/Sx: - Jaundice
- RUQ pain of fats - Clay-colored stool - Icterus Sclera
- Yellow skin
S/Sx:
- Nausea and vomiting
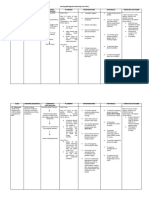
X. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Elevated intramural pressure
Walls of the biliary tract becomes
distended/inflammation occurs
Occlusion of lymphatic Diminished host antibacterial defenses
channels then the venous
return and arterial Immune system dysfunction
supply to the biliary
tract becomes undermined Bacteria form access to the biliary tree
Reduced blood supply
to the biliary tract
Decrease oxygenation
Walls of the biliary Bacteria
tract starts to break starts to Bacteremia
multiply
Retro gate ascends from duodenum
to the hepatic ducts
S/Sx:
- Charcots triad:
Fever. RUQ pain, and Jaundice
- Reynolds pentad:
Altered mental status, Hypotension,
Fever. RUQ pain, and Jaundice
Symbols:
Leads to :
Diagnostics :
Signs and Symptom :
Patient based : Bold Letter
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/774245-overview#a5
Brunner and Suddarths Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, Twelfth Edition
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, Sixth Edition
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CHOLANGITISDocument1 pageCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Nontoxic Nodular GoiterDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nontoxic Nodular GoiterKaila Abeleda100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of the urinary tractDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of the urinary tractMarjorie CarganillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Gastroenteritis Pathophysiology ExplainedDocument2 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Pathophysiology ExplainedMareeze Hatta100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument4 pagesConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Gallstones: Risk Factors and ComplicationsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gallstones: Risk Factors and ComplicationsBernalene Sy100% (3)
- TRIAGE Sorting Patients in EDDocument10 pagesTRIAGE Sorting Patients in EDRocelyn CristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- You Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeDocument2 pagesYou Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeWen Silver100% (1)
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisDocument3 pagesEtiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisGerriPas encore d'évaluation
- TextOfBioethics PDFDocument228 pagesTextOfBioethics PDFNgoc HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Laryngeal CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Laryngeal CancerKimber Maniulit67% (6)
- Acute PainDocument4 pagesAcute PainIvan Jules P. PALMARESPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgBryan Voltaire Santos LannuPas encore d'évaluation
- COPAR Community Organizing Pre-Entry Phase ProcessDocument2 pagesCOPAR Community Organizing Pre-Entry Phase ProcessLegendXPas encore d'évaluation
- CONZACEDocument2 pagesCONZACEDanielle Desiree RamasPas encore d'évaluation
- Myoma PathoniixDocument1 pageMyoma PathoniixRendel FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Naprex Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNaprex Drug StudyAngelica shane NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Myoma PathoDocument3 pagesMyoma PathoJan Michael Artiaga100% (1)
- No. 10 SANAANI Topic For Esophagogastric Balloon Tamponade Tubes Billroth 1 and 11Document12 pagesNo. 10 SANAANI Topic For Esophagogastric Balloon Tamponade Tubes Billroth 1 and 11Nur SanaaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology PRINTDocument1 pagePathophysiology PRINTNichole Audrey SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilPas encore d'évaluation
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- Coxa PlanaDocument13 pagesCoxa PlanaJustin Ahorro-DionisioPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument1 pageNarrative PathophysiologyJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- PatofkuDocument3 pagesPatofkunisaaa88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDocument1 pageGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainKarizza Reyes Mamaradlo100% (1)
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument5 pagesAplastic AnemiaVenice Marie GargantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesMarlon CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- IX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesIX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsCandace AlcarazPas encore d'évaluation
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocument4 pagesIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageHemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspirin Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesAspirin Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsAubrey Unique EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsKyla ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Document3 pagesChapter III Pathopysiology (Print!!!)Kismet SummonsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology VolvulusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology VolvulusHyacinth Bueser Bondad0% (2)
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan0% (1)
- Etiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument5 pagesEtiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJanelle NarcisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology Emphysemanursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYstrawberryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesDocument72 pagesCirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutPas encore d'évaluation
- With Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Document72 pagesWith Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Ainun JaariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Cholestatic Jaundice: DR - Ram Raut - JR III (Medicine) Guide - Dr.D.B. Kadam Seminar Teacher-Dr - NitinDocument68 pagesApproach To Cholestatic Jaundice: DR - Ram Raut - JR III (Medicine) Guide - Dr.D.B. Kadam Seminar Teacher-Dr - NitinAnan JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- MS-2 GallbladderDocument2 pagesMS-2 Gallbladderelijahdale.guillergan-05Pas encore d'évaluation
- About The Diseases. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract DisordersDocument10 pagesAbout The Diseases. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract DisordersJeenah HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- NML 4an3b DiscussionDocument17 pagesNML 4an3b DiscussionSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- GYNECOLOGICALNURSINGDocument4 pagesGYNECOLOGICALNURSINGSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Pareto ChartDocument1 pagePareto ChartSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- DSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesDocument7 pagesDSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Elective II ReviewerDocument4 pagesElective II ReviewerSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Pareto ChartDocument1 pagePareto ChartSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Improvement ToolsDocument5 pagesPerformance Improvement ToolsSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing TheoriesDocument2 pagesNursing TheoriesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- MS 1 PERIOPERATIVE NURSING ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIESDocument41 pagesMS 1 PERIOPERATIVE NURSING ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIESSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- ManualDocument9 pagesManualSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Choledocholithias PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCholedocholithias PathophysiologySheana Tmpl100% (2)
- DSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesDocument7 pagesDSA worksheet guides quality improvement cyclesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Elective IIDocument13 pagesElective IISheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Group QuestionsDocument7 pagesGroup QuestionsSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Surgical Procedure1Document4 pagesCommon Surgical Procedure1Sheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- ANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologySheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Prokaryotic CellDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Eeee ErDocument8 pagesReview Eeee ErSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- ObjectivesDocument2 pagesObjectivesSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing HistoryDocument2 pagesNursing HistorySheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- First ENCD Youth RallyDocument1 pageFirst ENCD Youth RallySheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- Walang LamanDocument1 pageWalang LamanSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- MỘT SỐ CÂU HỎI TRẮC NGHIỆM ÁP DỤNG CHUYÊN ĐỀ GIỚI TỪ TRONG ĐỀ THI ĐHDocument6 pagesMỘT SỐ CÂU HỎI TRẮC NGHIỆM ÁP DỤNG CHUYÊN ĐỀ GIỚI TỪ TRONG ĐỀ THI ĐHPhương ThảoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wattgate 381 Audio Grade Duplex Socket - y CableDocument20 pagesWattgate 381 Audio Grade Duplex Socket - y Cableapi-11530725100% (1)
- MSE Admission and Degree RequirementsDocument6 pagesMSE Admission and Degree Requirementsdeathbuddy_87Pas encore d'évaluation
- 405 Econometrics Odar N. Gujarati: Prof. M. El-SakkaDocument27 pages405 Econometrics Odar N. Gujarati: Prof. M. El-SakkaKashif KhurshidPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing characteristics and properties of various crude oilsDocument2 pagesComparing characteristics and properties of various crude oilsnishant bhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC Ag Syllabus 5th DeanDocument150 pagesBSC Ag Syllabus 5th Deansaurabh rPas encore d'évaluation
- AIA Design Development Deliverable ListDocument8 pagesAIA Design Development Deliverable Listpeterhwilliams100% (1)
- Week 2 - Risk AssessmentDocument35 pagesWeek 2 - Risk AssessmentTahir BashirPas encore d'évaluation
- Eko 75 Spare Part ListDocument23 pagesEko 75 Spare Part ListРустам Хайретдинов100% (1)
- CQ B TECHNIQUESDocument37 pagesCQ B TECHNIQUESeddie6355100% (3)
- Land Rover Range Rover Owners Manual 2007Document358 pagesLand Rover Range Rover Owners Manual 2007PetreCaracaleanu0% (1)
- Premchand Deliverance Download in PDFDocument4 pagesPremchand Deliverance Download in PDFRiya W100% (3)
- Manual CastingDocument64 pagesManual CastingDjRacksPas encore d'évaluation
- Incorrect Fuel Level Indication RepairDocument3 pagesIncorrect Fuel Level Indication RepairBogdan StefanPas encore d'évaluation
- Crusher Type Part Number Description Weight (KG)Document3 pagesCrusher Type Part Number Description Weight (KG)Juvenal CorreiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Data Sheet Permatreat® Pc-191T: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet Permatreat® Pc-191T: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationMajd DraidiPas encore d'évaluation
- VMA 2520 eDocument7 pagesVMA 2520 eVijaya SimhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbozinc 859: Selection & Specification Data Substrates & Surface PreparationDocument2 pagesCarbozinc 859: Selection & Specification Data Substrates & Surface PreparationAmy JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Max 223C Pipeline Welding InverterDocument2 pagesMax 223C Pipeline Welding InvertermtonellyPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F477-08Document4 pagesAstm F477-08ALARCONISTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Information: Traffic Management AccessoryDocument12 pagesProduct Information: Traffic Management AccessoryCORAL ALONSOPas encore d'évaluation
- GRT9165 Product GuideDocument23 pagesGRT9165 Product GuideEslamAldenAbdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Problems Involving Kinds of Propotion StudentDocument18 pagesSolving Problems Involving Kinds of Propotion StudentJohn Daniel BerdosPas encore d'évaluation
- Price List Grand I10 Nios DT 01.05.2022Document1 pagePrice List Grand I10 Nios DT 01.05.2022VijayPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 7 Activities Sheet Winter 2020Document7 pagesLab 7 Activities Sheet Winter 2020Mareline MendietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Raise The Limits: Eppendorf Research PlusDocument12 pagesRaise The Limits: Eppendorf Research PlusZahia Slama Ep AchourPas encore d'évaluation
- Zip Grade 100 Question V2Document1 pageZip Grade 100 Question V2Jesus Daniel Anaya AlvaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 56 - Narration and SequenceDocument14 pagesExercise 56 - Narration and SequenceLéoKostasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mahamrityunjaya MantraDocument8 pagesMahamrityunjaya MantraBalakrishnan KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Big A Tukpd 2011-2012 RevisiDocument5 pagesSoal Big A Tukpd 2011-2012 RevisiTriana WatiPas encore d'évaluation