Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Performance Summary Revision Lesson 1
Transféré par
Mega Pop LockerCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Performance Summary Revision Lesson 1
Transféré par
Mega Pop LockerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lesson One
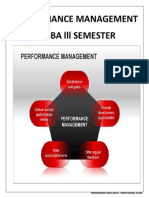
1. Define Performance management?
Continuous process of Identifying, Measuring, Developing the performance of
individuals and teams. Performance management is aligning performance with the
strategic goals of the organization.
2. Compare between Performance management and performance appraisal?
Performance management Performance appraisal
- Strategic business considerations - Driven by HR
- Driven by line manager - Assesses employee
- Ongoing feedback and coaching, So - Strengths
employee can improve performance - Weaknesses
- Once a year, Lacks ongoing feedback or
coaching
3. Discuss and explain what contributions of performance management are?
1. Contributions of Performance Management for Employees
- Clarify definitions of Job and Success criteria
- Increase motivation to perform
- Increase self-esteem
- Enhance self-insight and development
2. Contributions of Performance Management for Managers
- Communicate supervisors views of performance more clearly
- Managers gain insight about subordinates
- Better and more timely differentiation between good and poor
performers
- Employees become more competent and engaged
3. Contributions of Performance Management for Organization/HR Function
- Clarify organizational goals
- Facilitate organizational change
- Fairer, more appropriate administrative actions
- Better protection from lawsuits
- More motivated and loyal employees
- Less counterproductive and deviant behavior and more voice behavior
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 1
Lesson One
4. What are components of an Effective Performance Management Process?
- Direction sharing
- Role clarification
- Goal alignment
- Developmental goal setting
- Ongoing performance monitoring
- Ongoing feedback
- Coaching and support
- Performance assessment (appraisal)
- Rewards, recognition, and compensation
- Workflow and process control and return
5. What are Disadvantages/Dangers of Poorly Implemented PM Systems?
For employees
Lowered self-esteem and bad health
Employee burnout and job dissatisfaction
Damaged relationships
Use of false or misleading information
for Managers
Increased turnover
Decreased motivation to perform
Unjustified demands on managers resources
Varying and unfair standards and ratings
for Organization/HR Function
Wasted time and money
Demotivated or worse angry workforce
Unclear ratings system and so poor ability for HR planning and meeting HR
needs
Emerging biases and inability to distinguish between good and bad
performers
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 2
Lesson One
Increased risk of litigation
Missed opportunities and unachieved goals
Difficulties in other HR systems like talent management and succession
planning
6. Define Reward Systems ? what are components of tangible and intangible
return?
Reward system is a Set of mechanisms for distributing Tangible returns and
Intangible or relational returns as part of an employment relationship.
A. Tangible Returns
1. Cash compensation
Base pay: Hourly wages and Salary
Cost-of-Living & Contingent Pay: Usually permanent increases in pay based on either
cost of living or performance
Incentives (short- and long-term): Used to increase performance
E.g., bonuses (short term) or stock options/ownership (long term)
2. Benefits
Income Protection: Sometimes required under law, such as , Social Security ,
Disability pay, medical insurance, pension plans, savings plans
Allowances: housing and transportation.
B. Intangible Returns
1. Work/life focus (to help employee balance work/home life): Such as
vacation time,flextime and telecommuting, services (e.g., counseling,
financial planning, fitness activities)
2. Relational Returns: Such as recognition, status, employment security,
challenging work, opportunities to learn, opportunities to form personal
relationships.
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 3
Lesson One
7. What are Returns and Their Degrees of Dependency on the Performance
Management System?
Low Dependency
1. Cost of Living Adjustment
2. Income Protection
Moderate Dependency
- Work/Life Focus
- Allowances
- Relational Returns
- Base Pay
High Dependency
- Contingent Pay
- Short-Term Incentives
- Long-Term Incentives
8. What are Purposes of PM Systems Strategic Purpose
1. Strategic
- Link individual goals with organizations goals
- Communicate most crucial business strategic initiatives
2. Administrative
Provide information for making decisions regarding:
1. Salary adjustments
2. Promotions
3. Retention or termination
4. Recognition of individual performance
5. Layoffs
3. Informational Purpose
1. Communicate to employees:
2. Expectations
3. What is important
4. How they are doing
5. How to improve
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 4
Lesson One
4. Developmental Purpose
1. Performance feedback/coaching
2. Identification of individual strengths and weaknesses
3. Identification of causes of performance deficiencies
4. Tailor development of individual career path
5. Organizational Maintenance Purpose
1. Plan effective workforce
2. Assess future training needs
3. Evaluate performance at organizational level
4. Evaluate effectiveness of HR interventions
6. Documentation Purpose
1. Validate selection instruments
2. Document administrative decisions
3. Help meet legal requirements
9. What are An ideal system of Performance management system?
1. Strategically Congruent
Consistent with organizations strategy
Aligned with unit and organizational goals
2. Contextually Congruent
Congruent with the organizations culture as well as the broader cultural context of
the region or country
3. Thorough
- All employees are evaluated
- All major job responsibilities are evaluated
- Evaluations cover performance for entire review period
- Feedback is given on both positive and negative performance
4. Practical
- Available
- Easy to use
- Acceptable to decision makers
- Benefits outweigh costs
5. Meaningful
- Standards are important and relevant
- System measures ONLY what employee can control
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 5
Lesson One
- Results have consequences
- Evaluations occur regularly and at appropriate times
- System provides for continuing skill development of evaluators
6. Specific
Concrete and detailed guidance to employees
7. Identifies effective and ineffective performance
- Distinguish between effective and ineffective: Behaviors and Results
- Provide ability to identify employees with various levels of performance.
8. Reliable
- Consistent
- Free of error
- Inter-rater reliability
9. Valid
- Relevant (i.e., measures what is important)
- Not deficient (i.e., doesnt measure unimportant facets of job)
- Not contaminated (i.e., only measures what the employee can control)
10. Acceptable and Fair
a. Perception of Distributive Justice: Work performed Evaluation
received Reward
b. Perception of Procedural Justice: Fairness of procedures used to:
Determine ratings and Link ratings to rewards
11. Inclusive
Represents concerns of all involved
When system is created, employees should help with deciding: What should be
measure and How it should be measured
Employee should provide input on performance prior to evaluation meeting.
12. Open (No Secrets)
- Frequent, ongoing evaluations and feedback
- Two-way communications in appraisal meeting
- Clear standards and ongoing communication
- Communications are factual, open, and honest
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 6
Lesson One
13. Correctable
- Recognizes that human judgment is fallible
- Appeals process provided
14. Standardized
- Ongoing training of managers to provide
- Consistent evaluations across: People and Time
15. Ethical
- Supervisor suppresses self-interest
- Supervisor rates only where (s)he has sufficient information about the
performance dimension
- Supervisor respects employee privacy
10. Discuss Integration with other Human Resources and Development Activities
PM provides information for:
Development of training to meet organizational needs
Workforce planning
Recruitment and hiring decisions
Development of compensation systems
11. Why burnout happiness ?what are warning signs and symptoms of burnout
?and impact of spillover of the burnout ?
Causes
1. No support 2. Demands 3. No feedback 4. Role ambiguity 5. No resources
Warning signs
Withdrawing from responsibility
Isolating self from others
Taking long to get things done
Exhausted all time
Skipping work or coming in late and leaving early
Spillover burnout :negative impact on professional, personal and social life , makes
body weak to illness.
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 7
Lesson One
True/False Questions
1.1 A performance management system is the systematic description of an employees strengths
and weaknesses.
Answer F: A performance management system is the continuous process of aligning a given set of
organizational goals with individual/team performance, which are, also continuously, identified,
measured, and developed.
1.2 Linking each individuals performance to the organizations mission involves explaining to each
employee how the employees activities are helping the organization gain a competitive
advantage.
Answer T
1.3 Feedback often decreases motivation to perform because it points out what an employee does
wrong.
Answer F: If done correctly, receiving feedback about ones performance increases the motivation for
future performance.
1.4 Dangers of a poorly implemented performance management system include wasted time and
money, lack of standardized employee ratings, and confusion on how ratings are obtained.
Answer T
1.5 Intangible returns include benefits and work/life programs.
Answer F: Intangible returns, also known as relational returns, include recognition and status,
employment security, challenging work, opportunities to form personal relationships at work
(including friendships and romances), and learning opportunities. In contrast, tangible rewards include
cash compensation (i.e., base pay, cost-of-living pay, merit pay, short-term incentives, and long-term
incentives) and benefits (i.e., income protection, work/life focus including vacation time, tuition
reimbursement, and allowances).
1.6 Exempt employees are often employees in managerial or professional roles on salaries, and
are not eligible for overtime pay.
Answer T
1.7 Short-term incentives are one-time payments typically given quarterly or annually.
Answer T
1.8 The strategic purpose of PM systems involves constructing the strategic vision for the
organization.
Answer F: The strategic purpose of PM systems is to link an organizations goals with individuals
goals.
1.9 A reliable performance management system includes all relevant performance facets and does
not include irrelevant performance facets.
Answer F: This describes a systems validity, not reliability. A reliable performance management
system is consistent. For example, if two supervisors provided ratings of the same employee, or if one
supervisor rated the same employee twice over a short period of time during which nothing noticeable
occurs, then the ratings should be similar or identical.
1.10 Distributive justice is the perception that the performance evaluation received is fair relative to
the work performed.
Answer T
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 8
Lesson One
1.11 Performance management systems in foreign subsidiaries often differ from those in home
country headquarters as differences in the power distance (i.e., the degree to which a society
accepts unequal distribution of power) increase between/among countries.
Answer T
Multiple-Choice Questions
1.12 ________________ is a continuous process of identifying, measuring, and developing the
performance of individuals and teams and aligning performance with the strategic goals of
the organization.
A. Strategic planning
B. Performance management
C. Reward system
D. Performance appraisal
1.13 Dangers of a poorly implemented performance management system include all of the
following EXCEPT:
A. Increased emphasis on behaviors rather than results
B. Lawsuits/internal complaints of discrimination
C. Biased performance ratings
D. Decreased employee motivation
1.14 When employees of an organization do not see the PM system as fair, the organization may
witness from its employees all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Job burnout
B. Lowered self-esteem
C. Increased turnover
D. Lawsuits
1.15 Income protection programs include:
A. Pension Plans
B. Medical Insurance
C. Social Security
D. All of the above
1.16 _____________ focuses on positions and duties, rather than on an individuals contribution.
A. Contingent pay
B. Base pay
C. Cost-of-living adjustments
D. Short-term incentives
1.17 The ___________ purpose of PM systems is to furnish valid and useful information for making
employment decisions including salary adjustments, promotions, and terminations.
A. strategic
B. informational
C. administrative
D. developmental
1.18 Information gained from the organizational maintenance purpose of a PM system is used for
all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Workforce planning
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 9
Lesson One
B. Evaluating the effectiveness of job descriptions
C. Evaluating the effectiveness of HR programs
D. Creating talent inventories
1.19 Performance management systems should be thorough, meaning that:
A. All employees should be evaluated
B. An employees flaws should be discussed at length
C. The review should cover the entire review period
D. A and C
1.20 An ideal PM system is __________, which means that performance is evaluated and feedback
is given on an ongoing basis, the appraisal meeting consists of two-way communication, and
performance standards are clear.
A. open
B. standardized
C. ethical
D. specific
1.21 PM system information is important for the effective implementation of which of the following
HR function(s)?
A. Workforce planning
B. Training
C. Recruitment and selection
D. All of the above
1.22 All of the following are possible benefits of a performance management system EXCEPT:
A. Protection from lawsuits
B. Employees become more ethical
C. Employees become more competent
D. The definitions of job and criteria are clarified
1.23 Which of the following does the text identify as a possible danger of a poorly implemented
performance management system?
A. Salaries must be increased.
B. Poorly performing employees will always stay at the organization.
C. No time or money is spent on the system.
D. Motivation to perform is decreased.
1.24 Tangible returns include:
A. Base pay
B. Learning opportunities
C. Respect from coworkers
D. None of the above
1.25 Relational returns include:
A. Income protection
B. Recognition and status
C. Challenging work
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 10
Lesson One
D. B and C
1.26 Pay that focuses on position and duties performed rather than on a specific individuals
contribution is called:
A. Base pay
B. Pay raises
C. Salary
D. Relational returns
1.27 Pay added to base pay that depends upon an employees performance is called:
A. An allowance
B. Contingent pay
C. Relational return
D. A benefit
1.28 Relational returns include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Challenging work
B. Performance bonuses
C. Employment security
D. Recognition and status
1.29 All of the following are characteristics of an ideal performance management system EXCEPT:
A. Reliability
B. Meaningfulness
C. Inexpensive
D. Thorough
1.30 Which of the following are examples of work/life focus?
A. Counseling
B. Financial planning
C. Relational returns
D. A and B
1.31 A purpose of a performance management system is to:
A. Get rid of poorly performing employees
B. Provide documentation
C. Increase profits
D. Give the HR department something to do
1.32 An ideal performance management system is correctable. What does this mean?
A. If an employee is dissatisfied with a rating, it will be changed.
B. If an employee is dissatisfied with a rating, there is a process to appeal the rating
decision.
C. An ideal performance management system is not correctable.
D. None of the above is correct.
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 11
Lesson One
1.33 In the context of performance management, validity means that the measures of performance
are trusted and perceived as fair by the employees.
A. True
B. False
1.34 In the context of performance management, validity means that all the employees agree with
the rating process.
A. True
B. False
1.35 In which country is PM usually adapted to the countrys unique culture?
A. South Korea
B. South Africa
C. Australia
D. All of the above
1.36 In what manner is performance management typically similar around the world?
A. Standardization of performance measurement
B. Emphasis on behavior versus results of employee performance
C. Interpersonal aspects
D. None of the above
1.37 In what aspect is performance management generally different around the world?
A. Interpersonal aspects
B. Standardization of performance measurement
C. Alignment of individual and organizational goals
D. All of the above
1.38 Since the 1997 Asian financial crisis, the main ongoing challenge for many organizations in
South Korea has been to __________.
A. incorporate the traditional emphasis on social harmony to PM systems
B. recruit and incentivize a more internationally and racially diverse workforce
C. reconcile a merit-based approach with more traditional, seniority-based values
D. develop greater sensitivity to equal opportunity and due process issues
Performance management summer, 2017 Tel: 01002410113 Page 12
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Performance ManagementDocument15 pagesPerformance ManagementrajbobadePas encore d'évaluation
- Force Table LabDocument6 pagesForce Table Labquestionmark786100% (1)
- Performance Management 5Document65 pagesPerformance Management 5jeankahoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 HRM544Document31 pagesChapter 1 HRM544fazleyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance ManagementDocument9 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Performance ManagementsaidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Measuring Results and BehaviorDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Measuring Results and BehaviorTin Portuzuela100% (1)
- PM105 Module 1Document51 pagesPM105 Module 1ArneldNiguelAriolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capstone ReportDocument36 pagesCapstone Reportapi-446884357Pas encore d'évaluation
- Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Physical Education and Health-3 GradeDocument16 pagesWhole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Physical Education and Health-3 GradeVERDADERO LevisthonePas encore d'évaluation
- Competency-Based Performance Management 1Document22 pagesCompetency-Based Performance Management 1hardik_panchal183Pas encore d'évaluation
- Discuss The Advantage of Competency Based Performance Management Over Traditional AppraisalDocument7 pagesDiscuss The Advantage of Competency Based Performance Management Over Traditional Appraisalakansha toppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-2 Performance Management ProcessDocument29 pagesChapter-2 Performance Management ProcessDr.Nadeem SyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Competency Based Performance Management SystemDocument11 pagesCompetency Based Performance Management SystemWaqar Malik0% (1)
- Organizational EthicDocument15 pagesOrganizational EthicAji SegaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Income Statement - Kieso 4Document34 pagesIncome Statement - Kieso 4Muhammad RezaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Proposal For Improving and Preparing of Curriculum and Instruction For K To 12 of PLP-CONDocument71 pagesA Proposal For Improving and Preparing of Curriculum and Instruction For K To 12 of PLP-CONAngela Carla JoveroPas encore d'évaluation
- CHD ScorecardDocument3 pagesCHD Scorecard지창욱Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paternity LeaveDocument24 pagesPaternity LeaveLei AdapPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Rights and DisciplineDocument15 pagesEmployee Rights and Disciplinesayedamin0Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Critical Survey of The Different Normative EthicalDocument19 pagesA Critical Survey of The Different Normative EthicalDesiree RebarterPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate StrategyDocument4 pagesCorporate Strategy"DocAxi" Maximo B Axibal Jr MD FPSPPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Qualities For BusinessmenDocument36 pagesGood Qualities For BusinessmenPradeepKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance and Special Education 1Document53 pagesGuidance and Special Education 1kepvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic Act No. 6615 - An Act Requiring Government and Private Hospitals and Clinics To Extend Medical Assistance in Emergency CasesDocument1 pageRepublic Act No. 6615 - An Act Requiring Government and Private Hospitals and Clinics To Extend Medical Assistance in Emergency CasesNingClaudio100% (1)
- Assisting Patient in Oral CareDocument30 pagesAssisting Patient in Oral CareSean Maghinay BanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal and External Assessment PDFDocument3 pagesInternal and External Assessment PDFGieees StrecaPas encore d'évaluation
- EthicsDocument6 pagesEthicsJanelAlajasLeePas encore d'évaluation
- (RC-U007-DA) Chryss Universal TV RemoteDocument5 pages(RC-U007-DA) Chryss Universal TV RemoteDionne Sebastian Doromal100% (1)
- Performance Management SystemDocument11 pagesPerformance Management Systemscholta00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Performance AppraisalsDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalsSaif HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 5 - PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL PDFShariful Islam100% (2)
- Unit - IV Performance Management: Training & Development Definition of Performance ManagementDocument27 pagesUnit - IV Performance Management: Training & Development Definition of Performance ManagementPrachiPas encore d'évaluation
- II Shreeram II MOdule 4 Performance Monitoring and RewardsDocument6 pagesII Shreeram II MOdule 4 Performance Monitoring and RewardskedarambikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Recording Reflection: PRN - 20200212060135 NAME - Rohit Patwari Subject - Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesRecording Reflection: PRN - 20200212060135 NAME - Rohit Patwari Subject - Human Resource ManagementAbhishek mudaliarPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Management: Definition:: Y S N Murthy, Pvpsit Page 1 of 14Document14 pagesPerformance Management: Definition:: Y S N Murthy, Pvpsit Page 1 of 14realguy556789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Performance Management and Reward SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Performance Management and Reward SystemDeviane CalabriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Management: Semester-5Document8 pagesPerformance Management: Semester-5Ruhani AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Managment System Chapter 11Document12 pagesPerformance Managment System Chapter 11misbah ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Management 1Document6 pagesPerformance Management 1Kajal kumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 5 - Key Issues in Managing Employees' PerformanceDocument10 pagesSession 5 - Key Issues in Managing Employees' PerformanceShumbusho ConsultingtzPas encore d'évaluation
- HAFIZH RAIN (Performance Management Assignment)Document7 pagesHAFIZH RAIN (Performance Management Assignment)anuarPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Performance ApprisalDocument50 pagesEmployee Performance Apprisalshaik karishmaPas encore d'évaluation
- HRM-II Class NotesDocument8 pagesHRM-II Class NotesVishal kr. SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance ManagementDocument52 pagesPerformance ManagementpriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- PTM PDFDocument36 pagesPTM PDFAthira NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics, Contribution and PrerequisitiesDocument7 pagesCharacteristics, Contribution and PrerequisitiesSoni MainaliPas encore d'évaluation
- MB0049-Fall Drive-Assignment-2011 - Set 1 & 2Document29 pagesMB0049-Fall Drive-Assignment-2011 - Set 1 & 2dineshhegdekhPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance ManagementDocument47 pagesPerformance ManagementPremendra SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Management Material II MBADocument53 pagesPerformance Management Material II MBAJERINPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Performance Appraisal SystemDocument3 pagesEssentials of Performance Appraisal SystemHarshita KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Management & Appraisal MethodsDocument8 pagesPerformance Management & Appraisal MethodsJunaid MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 Organisational Control and Reward SystemsDocument4 pagesModule 4 Organisational Control and Reward SystemsBaher WilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Appraisal Private Sectors Banks Roll No 11Document40 pagesPerformance Appraisal Private Sectors Banks Roll No 11pareshgholapPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Overview of ManagementDocument59 pagesModule 1 - Overview of ManagementAdrian GallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- PMS Unit 3Document7 pagesPMS Unit 3Hensel SevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors That Might Lead To Increases in Productivity Include Technological Innovation, Capital Accumulation, Increased Skill of Workers, Increased Access ToDocument6 pagesFactors That Might Lead To Increases in Productivity Include Technological Innovation, Capital Accumulation, Increased Skill of Workers, Increased Access ToSusanne BellPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignement No. 2Document4 pagesAssignement No. 2Clifford Jay CalihatPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm ReviewerDocument20 pagesMidterm ReviewerJINKY TOLENTINOPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance AppraisalDocument16 pagesPerformance Appraisalmaria ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- HR Project On Performance AppraisalDocument20 pagesHR Project On Performance AppraisalRizwanasaleem100% (2)
- Finncial Statement AnalysisDocument3 pagesFinncial Statement AnalysisMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Statistics: Telephone SurveysDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Statistics: Telephone SurveysMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Major Differences Between U.S GAAP and IFRSDocument12 pagesThe Major Differences Between U.S GAAP and IFRSMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Lived Assets Through U.S. GAAPDocument17 pagesLong Lived Assets Through U.S. GAAPMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- UG022527 International GCSE in Mathematics Spec A For WebDocument77 pagesUG022527 International GCSE in Mathematics Spec A For WebJohn Hopkins100% (1)
- Lec3 STATISTICSDocument9 pagesLec3 STATISTICSMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter+15+Monopoly AbbreviatedDocument7 pagesChapter+15+Monopoly AbbreviatedMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra QuestionsDocument2 pagesExtra QuestionsMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Single AssetsDocument4 pagesSingle AssetsMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- CH One QuestDocument2 pagesCH One QuestMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 VBDocument2 pagesQ1 VBMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 2Document2 pagesTask 2Mega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced TheoraticalDocument9 pagesAdvanced TheoraticalMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- tb1 ch14Document84 pagestb1 ch14Mega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire Grad IIDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire Grad IIMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Acu ch4 MCQDocument3 pagesAcu ch4 MCQMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- POM ch1Document5 pagesPOM ch1Mega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 Summer Managerial Account 1Document4 pagesCH 2 Summer Managerial Account 1Mega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Fac 408 NewDocument7 pagesFac 408 NewMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 The Law of Comparative AdvantageDocument10 pagesChapter 2 The Law of Comparative AdvantageMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions About Corporate Governance BenefitsDocument6 pagesQuestions About Corporate Governance BenefitsMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- H1: There Is Significant Relationship Between Website Quality and The Firm ProfitabilityDocument2 pagesH1: There Is Significant Relationship Between Website Quality and The Firm ProfitabilityMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1Document3 pagesTask 1Mega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 The Law of Comparative AdvantageDocument10 pagesChapter 2 The Law of Comparative AdvantageMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Cost of Division B: Items Estimate Actual VarainceDocument1 pageTotal Cost of Division B: Items Estimate Actual VarainceMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 OB Organizational Behavior AcuDocument4 pagesChapter 3 OB Organizational Behavior AcuMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of The Organizational Change On Employees' ProductivityDocument19 pagesThe Impact of The Organizational Change On Employees' ProductivityMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 9 Group Behavior OB ACUDocument6 pagesCH 9 Group Behavior OB ACUMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pom After MidDocument6 pagesPom After MidMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pom After MidDocument6 pagesPom After MidMega Pop LockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Wetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsDocument3 pagesWetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsManish thapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Into TypeDocument114 pagesMathematics Into TypeSimosBeikosPas encore d'évaluation
- Skype OptionsDocument2 pagesSkype OptionsacidwillPas encore d'évaluation
- JD For Library Interns Sep 2023Document2 pagesJD For Library Interns Sep 2023Bharat AntilPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordination Compounds 1Document30 pagesCoordination Compounds 1elamathiPas encore d'évaluation
- IBM Unit 3 - The Entrepreneur by Kulbhushan (Krazy Kaksha & KK World)Document4 pagesIBM Unit 3 - The Entrepreneur by Kulbhushan (Krazy Kaksha & KK World)Sunny VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationMira ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemAbdulhakam Abubakar YusufPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Document9 pagesCAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Christina FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Communication PlanDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Communication PlanRev Richmon De ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- FIREXDocument2 pagesFIREXPausPas encore d'évaluation
- Rele A Gas BuchholtsDocument18 pagesRele A Gas BuchholtsMarco GiraldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Irregular Verbs-1Document1 pageIrregular Verbs-1timas2Pas encore d'évaluation
- BP TB A2PlusDocument209 pagesBP TB A2PlusTAMER KIRKAYA100% (1)
- Jurnal UlkusDocument6 pagesJurnal UlkusIndri AnggraeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013Document1 pageCambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th Edition © Hodder & Stoughton LTD 2013RedrioxPas encore d'évaluation
- Project TitleDocument15 pagesProject TitleadvikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Roberts, Donaldson. Ante-Nicene Christian Library: Translations of The Writings of The Fathers Down To A. D. 325. 1867. Volume 15.Document564 pagesRoberts, Donaldson. Ante-Nicene Christian Library: Translations of The Writings of The Fathers Down To A. D. 325. 1867. Volume 15.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisPas encore d'évaluation
- Tangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFDocument32 pagesTangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFRashid BumarwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Church A Rchitecture Abbey: Throne" Ecclesia Cathedralis (In Latin)Document18 pagesChurch A Rchitecture Abbey: Throne" Ecclesia Cathedralis (In Latin)Pat GeronzPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance MeasurementDocument13 pagesPerformance MeasurementAmara PrabasariPas encore d'évaluation
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Document106 pagesDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Mai PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- BRAC BrochureDocument2 pagesBRAC BrochureKristin SoukupPas encore d'évaluation
- Sayyid DynastyDocument19 pagesSayyid DynastyAdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Immediate Life Support PDFDocument128 pagesImmediate Life Support PDFShilin-Kamalei Llewelyn100% (2)
- DHBVNDocument13 pagesDHBVNnitishPas encore d'évaluation
- Government by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesDocument122 pagesGovernment by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesRone Eleandro dos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- MSC in Healthcare Management (Top-Up) Degree From ARU - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKDocument19 pagesMSC in Healthcare Management (Top-Up) Degree From ARU - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKLSBRPas encore d'évaluation
- 123456Document4 pages123456Lance EsquivarPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseDocument11 pagesAnimal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseZarin Tanjim WoyshorjoPas encore d'évaluation