Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
EE09 701 Power System Analysis APR 2014
Transféré par
Praveen PanickerDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EE09 701 Power System Analysis APR 2014
Transféré par
Praveen PanickerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
"Vidya Digital Library"
C 62961 (Pages: 4) Name................................... ..
Reg. No................................ .
SEVENTH SEMESTER B.TECH. (ENGINEERING) DEGREE
(SUPPLEMENTARy] EXAMINATION, APRIL 2014
(2009 Scheme)
EEIPTEE 09 701-POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS
Time: Three Hou rs Maximum: 70 Marks
Part A
Answer all the questions.
Each question carries 2 marks.
1. What are the different buses in Load Flow studies?
2. Give the objective function and the system constraints in Economic Load Dispatch.
3. What do you mean by short circuit capacity of a Bus and its importance?
4. Explain Sw~ng Equation.
5. Give the advantages and disadvantages of Fast de-coupled load flow method.
(5 x 2 = 10 marks)
Part B
Answer four questions out of si':.
6. Compare Gauss -Seidal method and Newton-Raphson method used for load flow studies.
7. Explain with neat diagram how critical clearing angle is calculated during fault conditions?
8. Explain the selection of circuit breakers based on the fault level and interruption time.
9. Explain hydrothermal coordination.
10. Explain per unit system. How impedance diagram can be drawn from single line diagram of power
system.
11. Explain how generating units are committed on the basis of forecasted load and operating
requirements and also state the difference between this method and economic load dispatch?
(4 x 5 = 20 marks)
Turn over
"Vidya Digital Library"
"Vidya Digital Library"
2 C 62961
Part C
Answer anyone question from each module,
12, (a) Explain Y bus formulation by singular transformation.
(b) The below figure shows the one line diagram of a simple four bus system, The table gives the
line impedances identified by the buses on which they terminate. The shunt admittance at all
the buses is assumed negligible.
(i) Find Ybus assuming that the line shown dotted is not connected.
ii) What modifications need to be carried out in Ybus if the line shown dotted is
connected
1--r----,
2
3 --+-_.1--
4
Line, R,p.u. X,p.u.
Bus to Bus
1-2 0.05 0.15
1-3 0.10 0.30
2-3 0.15 0.45
2-4 0.10 0.30
3-4 0.05 0.15
Or
"Vidya Digital Library"
"Vidya Digital Library"
3 C 62961
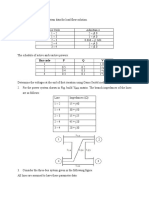
13. la) Explain the algorithm of Gauss-Seidel iterative method for the solution ofload flow equations.
(b) Tlw following is the system data for a load flow solution
The line admittances:
Bus code Admittance
1-2 2-j 8.0
1-3 I-j 4.0
2-3 0.666-j 2.664
2-4 I-j 4.0
3-4 2-j 8.0
The schedule of active and reactive powers:
Bus code P Q V Remarks
1 - - 1.06 Slack
2 0.50 0.20 1+ j 0.0 PQ
3 0.40 0.30 1+ j 0.0 PQ
4 0.30 0.10 1+ j 0.0 PQ
Determine the voltages at the end of first iteration using Gauss-Seidel method. Take 0. = 1.6
14. Give the detailed explanation of load frequency control of an isolated power system along with
complete block diagram representation.
Or
15. (a) Formulate optimum load dispatch problem considering transmission losses.
(b) A two bus system is shown in figure. Ifthe load of 125 MW is transmitted from plant 1 to the
load, a loss of 15.625 MW is incurred. Determine the generation schedule and the load demand
if th(' cost of received power is Rs. 241 MWhr. Solve the problem using coordinating equations
and penalty factor method approach. The incremental production costs of the plants are
(dF 11 dP 1) :;:: 0.025 PI + 15
idF21 dP2 ):;: 0.05 P 2 + 20
Turn over
"Vidya Digital Library"
"Vidya Digital Library"
4 C 62961
Load
16. A 25 MVA, 13.3 KV alternator with solidly grounded neutral has a subtransient reactance of
0.25 p.u The negative and zero sequence reactances are 0.35 and 0.1 p.u. respectively. A single
line to ground fault occurs at the terminals of an unloaded alternator; determine the fault current
and the line to line voltages, neglect resistance. Also determine the fault current and the line to
line voltage at the fault occurs at the terminals of the alternator.
Or
17. Explain different types of shunt type faults with neat diagram. Also explain how the sequence
networks are connected in all the above cases with the expression for fault current in each
phase?
18. A 60 Hz synchronous generator having inertia constant H = 5 MJIMVA and direct axis transient
reactance Xd '= 0.3 per unit is connected to an infinite bus through a purely reactive circuit as
shown in figure. Reactances are marked on the diagram on a common system base. The generator
is delivering real power Pe = 0.8 per unit and Q ::: 0.074 per unit to the infinite bus at a voltage of
V::: 1 per unit
(a) A temporary three phase fault occurs at the sending end of the line at point F ~ When the
fault is cleared both the line are intact. Determine the critical clearing angle and the
critical fault clearing time.
(b) A three phase fault occurs at the middle of one of the lines, the fault is cleared and the
fault line is isolated. Determine the critical clearing angle.
Or
19. Explain with a neat diagram the role ofAutomatic Voltage Regulators (AVR) in improving stability.
[4 x 10 ::: 40 marks]
---- --- ---- -~~-----~--------
"Vidya Digital Library"
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit 036 - Assembling and Testing Electronic CircuitsDocument10 pagesUnit 036 - Assembling and Testing Electronic CircuitsDaved John100% (9)
- EE2351-Power System Analysis PDFDocument15 pagesEE2351-Power System Analysis PDFRK K0% (1)
- Tutorial Power System Analysis - Power Flow Analysis-SolutionDocument12 pagesTutorial Power System Analysis - Power Flow Analysis-SolutionAdriana Shoppe67% (3)
- Fundamentals of Protection SystemDocument464 pagesFundamentals of Protection Systemapi-2723737178% (9)
- PowerFlex 755 Install ManualDocument116 pagesPowerFlex 755 Install Manualkande666Pas encore d'évaluation
- 15ee71 Question Paper VtuDocument5 pages15ee71 Question Paper VtuPuneeth N RanapurPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationDocument5 pagesModel Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationVinod KohliPas encore d'évaluation
- National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur (HP) BDocument2 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Hamirpur (HP) BShivam GangwarPas encore d'évaluation
- 13.605 Power System Analysis and Stability B Tech Degree Examination Sixth Semester (2013 Scheme) Model Question Paper (Kerala University)Document4 pages13.605 Power System Analysis and Stability B Tech Degree Examination Sixth Semester (2013 Scheme) Model Question Paper (Kerala University)Abhiram DonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pow370s Ga4 Scope 2023Document9 pagesPow370s Ga4 Scope 2023Nompumelelo GabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gomputer Techniques Power System Analysis: I A. B,:4,11rDocument3 pagesGomputer Techniques Power System Analysis: I A. B,:4,11rAbhishek ChandelPas encore d'évaluation
- Seventh Sem 2015 BDocument3 pagesSeventh Sem 2015 BMonisha S.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dayananda Sagar College of EngineeringDocument3 pagesDayananda Sagar College of EngineeringPower System Analysis-1Pas encore d'évaluation
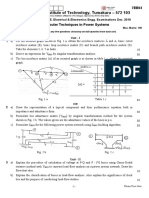
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDocument4 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemestermahesPas encore d'évaluation
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee Iii Year 2017-2018Document48 pagesEee Iii Year 2017-2018J JulietPas encore d'évaluation
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 05 2017 2170901 IcpsDocument2 pages04 05 2017 2170901 IcpsHImanshu JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAlesso RossiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocument4 pages9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSrîkår SríPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Flow AnalysisDocument38 pagesLoad Flow Analysisoluwasesan salauPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Flow AnalysisDocument38 pagesLoad Flow Analysisoluwasesan salauPas encore d'évaluation
- The University of Derby: Electrical Power Applications (6EJ503) TUTOR: DR Mahmud ShafikDocument38 pagesThe University of Derby: Electrical Power Applications (6EJ503) TUTOR: DR Mahmud Shafikoluwasesan salauPas encore d'évaluation
- Power SystemDocument3 pagesPower SystemMogaka LucasPas encore d'évaluation
- Psa QuestionDocument8 pagesPsa QuestionSumathra KPas encore d'évaluation
- 07a70202 PowersystemanalysisDocument12 pages07a70202 PowersystemanalysisSamiullah MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- 7EE03Document3 pages7EE03MSGPas encore d'évaluation
- EE75 August 2014Document2 pagesEE75 August 2014MSGPas encore d'évaluation
- JNTUH 3-2 R16 QP Power Systems Analysis May - 2019Document3 pagesJNTUH 3-2 R16 QP Power Systems Analysis May - 2019Kiran KunchamPas encore d'évaluation
- BIBcDocument6 pagesBIBcAsmaa NasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Case StudyDocument18 pagesPower System Case Studysmurf aldous100% (1)
- PSA FileDocument63 pagesPSA FileSiddartha AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr410203 Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument9 pagesRr410203 Computer Methods in Power SystemsandhracollegesPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Ps 2 - Test 2 PDFDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Ps 2 - Test 2 PDFKRISHNA AGARWALPas encore d'évaluation
- Psa All Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesPsa All Questions and AnswersMODERN TELUGAMMAYIPas encore d'évaluation
- CMPSA Notes 3Document57 pagesCMPSA Notes 3priyanshum230825eePas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 - EE5102 - Distribution SystemsDocument6 pages2017 - EE5102 - Distribution SystemsChathura SenanayakePas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Document29 pagesPower System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Jishnuraj KubandrarajPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel P-Q Control Algorithm For Combin PDFDocument8 pagesA Novel P-Q Control Algorithm For Combin PDFvidya_sagar826Pas encore d'évaluation
- B.E/B.Tech. Degree Examination, May / June 2012 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesB.E/B.Tech. Degree Examination, May / June 2012 Sixth Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringVarun ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments - 1 July-December 2021Document7 pagesAssignments - 1 July-December 2021Ayush AgrwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Inter Connected Power System - CombinedDocument11 pagesInter Connected Power System - CombinedPalak AriwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-Ii Power Flow AnalysisDocument25 pagesUnit-Ii Power Flow AnalysisNmg KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Psa Unitwise Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesPsa Unitwise Important QuestionsyvkrishnareddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Flow AnalysisDocument68 pagesPower Flow AnalysisLuiz Pa100% (1)
- PTEE7403 April 2019Document3 pagesPTEE7403 April 2019imman46920Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis ImportantDocument8 pagesPower System Analysis Importantsparkle couragePas encore d'évaluation
- DC-Lab Report 05Document9 pagesDC-Lab Report 05Shahriar Ahsan JohaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 1Document2 pagesModel 1ponselvanvPas encore d'évaluation
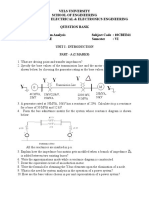
- Manukau Institute of Technology Professional Engineering Bachelor of Engineering TechnologyDocument14 pagesManukau Institute of Technology Professional Engineering Bachelor of Engineering TechnologyRana AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Document14 pagesUnit I - Introduction Part - A (2 Marks)Ragul RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis of The IEEE 14-Bus Test System Using PSAT and MATLABDocument25 pagesPower System Analysis of The IEEE 14-Bus Test System Using PSAT and MATLABAkinbode Sunday OluwagbengaPas encore d'évaluation
- PEE212 Tut Sheets 1-8 PDFDocument6 pagesPEE212 Tut Sheets 1-8 PDFArash GhumanPas encore d'évaluation
- PV 2017 FinalDocument3 pagesPV 2017 FinalUmarShahrozPas encore d'évaluation
- PV 2017 FinalDocument3 pagesPV 2017 FinalUmarShahrozPas encore d'évaluation
- NAME: A. Sai Hitesh Reddy ROLL No: B170711EE Experiment: 7 Load Flow Analysis AimDocument4 pagesNAME: A. Sai Hitesh Reddy ROLL No: B170711EE Experiment: 7 Load Flow Analysis Aimsaihitesh adapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailDocument3 pagesAishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailSujesh ChittarikkalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee6203 Power System Ii (Mid - SP20)Document2 pagesEe6203 Power System Ii (Mid - SP20)Samaira SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2007 Paper 1Document2 pagesMarch 2007 Paper 1many1tothe11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Sem 3Document11 pagesMid Sem 3BROJO CHAND GAYENPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8D'EverandElectronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsD'EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hsg230 Keeping Electrical Switchgear SafeDocument60 pagesHsg230 Keeping Electrical Switchgear Safelifemillion2847Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Group - 16 - Engine - Electrical - Triton PDFDocument4 pages10 - Group - 16 - Engine - Electrical - Triton PDFlaudi shofaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Alumoweld ProductsDocument28 pagesAlumoweld Productsjpnovoa2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gmail - Order 8117270258209721 Is Good To Go! PDFDocument4 pagesGmail - Order 8117270258209721 Is Good To Go! PDFEug. Sam.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Series: 100 Series Low-Profile Plug-In Smoke DetectorsDocument2 pages100 Series: 100 Series Low-Profile Plug-In Smoke DetectorsLogan Marquez AguayoPas encore d'évaluation
- PFC Javier Mohedano MartinezDocument88 pagesPFC Javier Mohedano MartinezmiguelpaltinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanmatnogalfredPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal and SystemDocument15 pagesSignal and Systemswap_k007100% (1)
- The Implementation of Solar Tracker Using Arduino With ServomotorDocument26 pagesThe Implementation of Solar Tracker Using Arduino With Servomotorsoumen goraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Report GSM Based Remote Monitoring of 3 Parameters On TransformersDocument16 pagesReport GSM Based Remote Monitoring of 3 Parameters On TransformersJilly ArasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Proposal: Wireless Mobile ChargerDocument13 pagesProject Proposal: Wireless Mobile ChargerJerin TasnimPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4Document8 pagesUnit 4Sri ChandanaPas encore d'évaluation
- LG Ac Error CodesDocument93 pagesLG Ac Error CodesbrianPas encore d'évaluation
- III 7 Hall EffectDocument8 pagesIII 7 Hall EffectHa ZimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cathodic Protection System Using Ceramic AnodesDocument132 pagesCathodic Protection System Using Ceramic Anodesadeoye_okunoyePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatic Field Lec2Document7 pagesElectrostatic Field Lec2Sudesh Fernando Vayanga SubasinghaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Derive The Instrumentation Amplifier Transfer FunctionDocument1 pageHow To Derive The Instrumentation Amplifier Transfer FunctionHelioBernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Fiber Optics A Brief History of Fiber Optics Lesson 4Document5 pagesChapter 2 Fiber Optics A Brief History of Fiber Optics Lesson 4elevitas2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design, Simulate and Implement A 5V DC Power Supply With Filter - Group No 14Document15 pagesDesign, Simulate and Implement A 5V DC Power Supply With Filter - Group No 14HARSHIL HARSHIL GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiator AmplifierDocument5 pagesDifferentiator AmplifierAhmed ShaabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature Control With SCRDocument3 pagesTemperature Control With SCRRoberto Fernandez100% (3)
- Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesElectrical Engineeringkim jeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Himax: Analog Input Module With Sequence of Events Recording ManualDocument60 pagesHimax: Analog Input Module With Sequence of Events Recording ManuallinhPas encore d'évaluation
- IEEE Xplore Full-Text PDFDocument10 pagesIEEE Xplore Full-Text PDFpshyciPas encore d'évaluation
- AC DisconnectsDocument2 pagesAC DisconnectsFidel CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Pec CodesDocument10 pagesPec CodesMujeeb AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- CosimatDocument27 pagesCosimatmatPas encore d'évaluation