Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Exigo: 8 MG, 16 MG, 24 MG Tablet Anti-Vertigo
Transféré par
Nyume Lathifah HanumTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Exigo: 8 MG, 16 MG, 24 MG Tablet Anti-Vertigo
Transféré par
Nyume Lathifah HanumDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BETAHISTINE
HYDROCHL ORIDE
EXIGO 8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg Tablet
Anti-Vertigo
FORMULATION
Each tablet contains:
Betahistine hydrochloride............................................... 8 mg, 16 mg or 24 mg
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Betahistine 8 mg is an off-white tablet, round, flat tablet, bisected on one side and
plain on the other.
Betahistine 16 mg is an off-white tablet, round, biconvex, bisected on one side and
plain on the other.
Betahistine 24 mg is an off-white tablet, round, flat tablet, bisected on one side and
plain on the other.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACODYNAMICS
The exact mechanism of action of betahistine is unclear. However, animal studies
have shown that betahistine improves blood flow in the striae vascularis of the inner
ear, resulting in reduced endolymphatic pressure.
Pharmacologic evaluation showed that betahistine may exert weak H1 receptor
agonistic activity and H3 antagonistic properties in the central and autonomic
nervous systems. Betahistine also appears to inhibit spike generation of neurons in
the lateral and medial vestibular nuclei in a dose-dependent manner.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Betahistine is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration. It is rapidly
and almost completely metabolized into 2-pyridylacetic acid (2-PAA), its main
metabolite which has no pharmacological activity. Since plasma betahistine levels
are very low, pharmacokinetic analyses are therefore based on 2-PAA
measurements in plasma and urine. Peak plasma concentrations of 2-PAA
achieved one hour after oral administration in fasting subjects and declines with a
half-life of about 3.5 hours. Tissue distribution of betahistine in humans is unknown.
The drug has little or no binding to either serum albumin, or other plasma proteins.
It is not known to what extent the drug crosses the placenta. The effects of hepatic
and renal disease on the kinetics of betahistine are unknown.
Betahistine is eliminated in the kidney with 85 to 90% of the radioactivity of an 8 mg
dose appearing in the urine over 56 hours. The maximum rates of excretion are
reached within 2 hours of administration. The drug is excreted in the urine as 2-PAA
with no unchanged betahistine being detected
INDICATIONS
For the treatment of vertigo, tinnitus and hearing loss associated with
Meniere's syndrome.
For the symptomatic treatment of vertigo of peripheral origin.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Orally, to be taken preferably with meals.
Recommended Initial Dose: 8 to 16 mg given three times a day; OR 24 mg
given two times a day
Maintenance Dose: 24 to 48 mg per day given in divided doses
Maximum dose: 48 mg per day
Individualize dosage according to patient's response and tolerance.
Re-assess patient periodically to determine the need for maintenance
treatment with an appropriate dose.
Or, as prescribed by a physician.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to betahistine or any component of the product.
Patients with pheochromocytoma since betahistine, a synthetic histamine
analog, may provoke release of epinephrine and/or norepinephrine from the
tumor, precipitating a hypertensive crisis.
Active peptic ulcer or a history of this condition
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Use with caution in patients with the following conditions:
Bronchial asthma and COPD with bronchospastic component
History of allergic skin conditions
Porphyria
Avoid concurrent use with antihistamines. (see Drug Interactions)
Mild gastrointestinal irritation may be expected with betahistine. Patients should be
advised to take the drug with food. Otherwise, dose may be reduced.
INTERACTIONS WITH OTHER MEDICAMENTS
There have been no reports of potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs.
No in vivo studies have been performed. In vitro data revealed no inhibition of
cytochrome P450 enzymes.
In vitro data showed an inhibition of betahistine metabolism by drugs that inhibit
monoamine-oxidase (MAO) including MAO subtype B (e.g., Selegiline). Caution is
recommended when using betahistine and MAO inhibitors (including MAO-B
selective) concomitantly.
Although antagonism between betahistine and antihistamines may be expected
theoretically, no such interactions have been reported.
The effects of Beta2 agonists may be decreased by betahistine.
There is a case report of potentiation of betahistine with salbutamol and a case
report of interaction with ethanol and maloprim.
STATEMENT ON USAGE FOR HIGH RISK GROUPS
Pregnancy
Clinical data regarding the safe use of betahistine during pregnancy are
unavailable. Betahistine should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly
necessary.
Lactation
It is now known whether betahistine is excreted in human breast milk. The benefits
of the drug to the mother should be weighed against the potential risk to the baby
when considering betahistine treatment.
Children
The safety and efficacy of betahistine in pediatric patients less than 18 years old
have not been established.
Geriatric
There is no special precaution required for treatment of the elderly; therefore, the
same dosage as in the general population may be used.
Effect on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Betahistine does not affect driving or psychomotor ability.
UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS
In general, betahistine is well tolerated. However, a few adverse effects associated
with the drug have been reported:
Gastrointestinal: Vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal pain, nausea, dyspepsia,
abdominal cramps, abdominal distention, bloating
Body as a Whole: Tiredness, malaise
CNS: Dizziness, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, and throbbing pulsation; rarely,
convulsions, somnolence, confusions, hallucinations
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Angioneurotic edema, rash, pruritus,
and urticaria; Stevens Johnson syndrome
Cardiovascular: Vasodilation, postural hypotension, tachycardia, and ventricular
extrasystoles
Respiratory: Dyspnea, asthma, bronchospasms
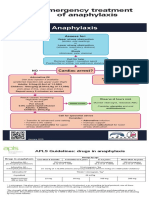
Immune System: Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions such as anaphylaxis
OVERDOSAGE & MANAGEMENT
Few cases of overdose have been reported with some patients experiencing mild to
moderate symptoms with doses above 200 mg. Clinical features of betahistine
overdose may include nausea, dry mouth, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain,
headache, somnolence, hypotension, itching; convulsion, pulmonary or cardiac
complications, ataxia, and seizures at higher doses. A case of convulsion was
reported at a dose of 728 mg.
There is no specific antidote to betahistine overdose; gastric lavage and
symptomatic treatment are recommended.
Store at temperatures not exceeding 30OC.
Caution: Foods, Drugs, Devices, and Cosmetics Act prohibits dispensing without
prescription.
AVAILABILITY
Betahistine hydrochloride (Exigo) 8 mg Tablet - Box of 30 Tablets (in flex foil)
Betahistine hydrochloride (Exigo) 16 mg Tablet - Box of 30 Tablets (in flex foil)
**Betahistine hydrochloride (Exigo) 24 mg Tablet - Box of 30 Tablets (in flex foil)
Manufactured by Amherst Laboratories, Inc.
UNILAB Pharma Campus, Barangay Mamplasan
Bian, Laguna, Philippines
for BIOMEDIS, INC.
6/F Dynavision Bldg., 108 Rada St., Legaspi Village
Makati City, Philippines
** Manufactured by Amherst Laboratories, Inc.
UNILAB Pharma Campus, Barangay Mamplasan
Bian, Laguna, Philippines
Distributed by United Laboratories, Inc.
66 United St., Mandaluyong City, Philippines
Under authority by BIOMEDIS, INC.
6/F Dynavision Bldg., 108 Rada St., Legaspi Village P30000009578
Makati City, Philippines Revision Date: July 2013
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Francis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneDocument8 pagesFrancis Peteros Drug Study 2 BetamethasoneFrancis PeterosPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogPas encore d'évaluation
- CimetidineDocument3 pagesCimetidineapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY Brokenshire College Study on BevacizumabDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Brokenshire College Study on BevacizumabJai GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dexamethasone and Methotrexate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDexamethasone and Methotrexate Drug StudyJunel Paolo SilvioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Pen G FuroDocument3 pagesDrug Study Pen G Furokuro hanabusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Janumet Drug StudyDocument4 pagesJanumet Drug Studykath bernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- DUPHASTON Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDUPHASTON Drug StudyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDocument2 pagesDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterPas encore d'évaluation
- RifampicinDocument1 pageRifampicinDaryl LimosPas encore d'évaluation
- Cefpodoxime Proxetil - Print VersionDocument5 pagesCefpodoxime Proxetil - Print Versionchristina_1990Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dinoprostone GelDocument7 pagesDinoprostone GelSahil AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study MsDocument10 pagesDrug Study MsAbie Jewel Joy RoquePas encore d'évaluation
- Omeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideDocument5 pagesOmeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideJenivic Empig PuedanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study AspirinMaria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Drug Study - Captopril CefuroximeDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Captopril CefuroximeJet BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Macrobid, Macrodantin (Nitrofurantoin) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and More 2 PDFDocument2 pagesMacrobid, Macrodantin (Nitrofurantoin) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and More 2 PDFNailis Sa'adahPas encore d'évaluation
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
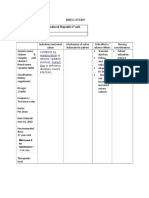
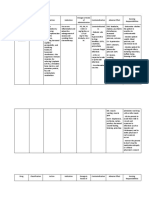
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskylePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudymYiE23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocument5 pagesAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudygabbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 pagesTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianPas encore d'évaluation
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Anoro Ellipta Pi MGDocument35 pagesAnoro Ellipta Pi MGAgusJiethoSfarmAptPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyzenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lovastatin Drug GuideDocument2 pagesLovastatin Drug GuideAngel CatalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyBlesyl Sison MabanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap. 6 - 8 MaternalDocument16 pagesChap. 6 - 8 MaternalKaryll RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Quinine SulfateDocument7 pagesDrug Study Quinine SulfateKathlyn_Matic_6376Pas encore d'évaluation
- CefazolinDocument3 pagesCefazolinintrovert ikonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Omeprazole Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesOmeprazole Nursing ResponsibilitiesRea LynPas encore d'évaluation
- Losartan Plus HydrochlorothiazideDocument18 pagesLosartan Plus Hydrochlorothiazidegmsanto7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMinaPas encore d'évaluation
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Identified Health Problems RankedDocument3 pagesIdentified Health Problems RankedKANT JAMES D. MAHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument3 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationKim SunooPas encore d'évaluation
- DS VigocidDocument1 pageDS VigocidasdasdPas encore d'évaluation
- A Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On Evening Primrose OilAlexis Khalyl Y. MontejoPas encore d'évaluation
- EMERGENCY DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesEMERGENCY DRUG STUDYGrace Santos MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Aspirin (Asa)Document5 pagesDrug Study: Aspirin (Asa)Shara Lailanie A. AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- AlbendazoleDocument7 pagesAlbendazolefinchan IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- LansoprazoleDocument3 pagesLansoprazoleJody FelizioPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicinal Product Tablets Treat Vertigo and Meniere's DiseaseDocument6 pagesMedicinal Product Tablets Treat Vertigo and Meniere's DiseaseasdwasdPas encore d'évaluation
- Vergo 16: Betahistine Dihydrochloride Tablet 16 MGDocument4 pagesVergo 16: Betahistine Dihydrochloride Tablet 16 MGmegha_okztPas encore d'évaluation
- Betahistine (DRUG LIST)Document2 pagesBetahistine (DRUG LIST)Bon- BonPas encore d'évaluation
- Betahistine Drug InfoDocument3 pagesBetahistine Drug InfoAshish KarnPas encore d'évaluation
- Serc Tablets Treat Meniere's DiseaseDocument4 pagesSerc Tablets Treat Meniere's DiseasenobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDocument124 pagesHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiPas encore d'évaluation
- AOM GuidelineDocument10 pagesAOM GuidelineaitnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Y-Site Compatibility Table-VADocument15 pagesAdditional Y-Site Compatibility Table-VANyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDocument124 pagesHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiPas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis of Dielectric Constants of Pharmaceutical Medicines Using Microwave Radiation ExposureDocument24 pagesAn Analysis of Dielectric Constants of Pharmaceutical Medicines Using Microwave Radiation ExposureNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- AOM GuidelineDocument10 pagesAOM GuidelineaitnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDocument124 pagesHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDocument124 pagesHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiPas encore d'évaluation
- CV Experiment - Determination of Acetaminophen in Childrens Pain Relief Elixir PDFDocument9 pagesCV Experiment - Determination of Acetaminophen in Childrens Pain Relief Elixir PDFNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- AOM GuidelineDocument10 pagesAOM GuidelineaitnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Urticaria Angioedema2015 PDFDocument19 pagesUrticaria Angioedema2015 PDFNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- EU Acne Guidelines Method-Report Final PDFDocument53 pagesEU Acne Guidelines Method-Report Final PDFNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- SGS USP Elemental Impurities v2 en 10Document2 pagesSGS USP Elemental Impurities v2 en 10Nyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis of Dielectric Constants of Pharmaceutical Medicines Using Microwave Radiation ExposureDocument24 pagesAn Analysis of Dielectric Constants of Pharmaceutical Medicines Using Microwave Radiation ExposureNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiemetic Drug Class ReviewDocument24 pagesAntiemetic Drug Class ReviewNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- GC 795Document7 pagesGC 795IlhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Nsaid Metaanalysis PDFDocument10 pagesNsaid Metaanalysis PDFNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Thursday - Session A01 - Finocchiaro - Update On The Management of Hyperlipidemia PDFDocument155 pagesThursday - Session A01 - Finocchiaro - Update On The Management of Hyperlipidemia PDFNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For The Management of Heroin WithdrawalDocument12 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Heroin WithdrawalNyume Lathifah HanumPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Pharmacy 18 TBDocument9 pagesPractical Pharmacy 18 TBPitarpa TongpakPas encore d'évaluation
- MauritiusDocument26 pagesMauritiusAgron ExportPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric DosesDocument20 pagesPediatric Doseshamadadodo550% (2)
- Dravyaguna Vigyan Paper ReviewDocument8 pagesDravyaguna Vigyan Paper Reviewchauhan_892277982Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP Reference Standard CatalogDocument12 pagesIP Reference Standard CatalogUrva VasavadaPas encore d'évaluation
- PROCESS VALIDATION OF ORAL SOLID DOSAGE FORM. TABLET-An Overview PDFDocument16 pagesPROCESS VALIDATION OF ORAL SOLID DOSAGE FORM. TABLET-An Overview PDFAndy Rojas100% (1)
- Analgesics & Antibiotics in Pediatric DentistryDocument77 pagesAnalgesics & Antibiotics in Pediatric DentistryJanani Gopalakrishnan100% (3)
- (Dermatology) Javier Avalos - Howard I Maibach-Dermatologic Botany-CRC Press (2000)Document418 pages(Dermatology) Javier Avalos - Howard I Maibach-Dermatologic Botany-CRC Press (2000)Julian ManongdoPas encore d'évaluation
- HALLUCINOGENDocument21 pagesHALLUCINOGENSheryl SabadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vancouver 2010 Paralympic Pharmacy GuideDocument146 pagesVancouver 2010 Paralympic Pharmacy GuideVsevolod BentsianovPas encore d'évaluation
- Algorithms - AnaphylaxisDocument1 pageAlgorithms - AnaphylaxisAdeelZ.SiddiqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Racecadotril PDFDocument3 pagesDrug Study Racecadotril PDFAndrey Mary RanolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Cannabis in Europe Report FINAL REV2 1Document52 pagesMedical Cannabis in Europe Report FINAL REV2 1Camilo Parra CuadrosPas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFNews-PressPas encore d'évaluation
- PHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Student Nurse Drug ReportDocument2 pagesPHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Student Nurse Drug ReportClaire Madriaga GidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Surat Pesanan Obat Apotek Ym 123Document4 pagesSurat Pesanan Obat Apotek Ym 123ymPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyZyryll LaoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis and Management of ADRsDocument45 pagesDiagnosis and Management of ADRspriyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 5891148413604464740Document26 pages4 5891148413604464740kelid IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- People Taking Horse IvermectinDocument5 pagesPeople Taking Horse IvermectinStephen Cooper100% (1)
- Atropine SulfateDocument2 pagesAtropine SulfateKureaa OhPas encore d'évaluation
- Obat IhcDocument3 pagesObat IhcyolandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Government of Canada Report On Emend (Aprepitant)Document6 pagesGovernment of Canada Report On Emend (Aprepitant)jennabushPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetaminophen Suppository Mechanism of Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Suppository Mechanism of Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNiziu BearsPas encore d'évaluation
- Fulhold Pharma Investor Update Regulatory ProgressDocument5 pagesFulhold Pharma Investor Update Regulatory ProgresstopwinePas encore d'évaluation
- ICH E2F Step 4 October 2010Document34 pagesICH E2F Step 4 October 2010SravyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steroid Emollient LaddersDocument2 pagesSteroid Emollient LaddersAnne Marie ScerriPas encore d'évaluation
- Proper Disposal of Expired or Unwanted DrugsDocument9 pagesProper Disposal of Expired or Unwanted Drugscarramrod2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Oral Drug DoseDocument17 pagesPediatric Oral Drug DoseTan 57Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indications: CNS: Headache CV: Chest Pain, DyspneaDocument2 pagesIndications: CNS: Headache CV: Chest Pain, Dyspneaalpha mayagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Divalproex Sodium brain disorder medicines guideDocument13 pagesDivalproex Sodium brain disorder medicines guideMiguelito Galagar GultianoPas encore d'évaluation
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionD'EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingD'EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePas encore d'évaluation
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsPas encore d'évaluation
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesD'EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsD'EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsPas encore d'évaluation
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementD'EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeD'EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeD'EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (17)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryD'EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (44)