Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study (Pyrazinamide)
Transféré par
Kristine Artes Aguilar67%(3)67% ont trouvé ce document utile (3 votes)
3K vues2 pagesPyrazinamide is an oral antituberculotic drug used for initial treatment of active TB in conjunction with other antituberculotics. It is contraindicated in those with allergy to pyrazinamide or acute hepatic disease. Common side effects include hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, rashes, photosensitivity, and hyperuricemia leading to gout. Nursing considerations include assessing for allergies or conditions like hepatic disease or gout, administering the drug once daily in conjunction with other antituberculotics, monitoring for side effects, and discontinuing if liver damage occurs.
Description originale:
aaaa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPyrazinamide is an oral antituberculotic drug used for initial treatment of active TB in conjunction with other antituberculotics. It is contraindicated in those with allergy to pyrazinamide or acute hepatic disease. Common side effects include hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, rashes, photosensitivity, and hyperuricemia leading to gout. Nursing considerations include assessing for allergies or conditions like hepatic disease or gout, administering the drug once daily in conjunction with other antituberculotics, monitoring for side effects, and discontinuing if liver damage occurs.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
67%(3)67% ont trouvé ce document utile (3 votes)
3K vues2 pagesDrug Study (Pyrazinamide)
Transféré par
Kristine Artes AguilarPyrazinamide is an oral antituberculotic drug used for initial treatment of active TB in conjunction with other antituberculotics. It is contraindicated in those with allergy to pyrazinamide or acute hepatic disease. Common side effects include hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, rashes, photosensitivity, and hyperuricemia leading to gout. Nursing considerations include assessing for allergies or conditions like hepatic disease or gout, administering the drug once daily in conjunction with other antituberculotics, monitoring for side effects, and discontinuing if liver damage occurs.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
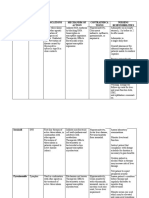
MECHANISISM SIDE EFFECTS/ NURSING
DRUG NAME OF ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE EFFECTS CONSIDERATIONS
Generic Name: Bacteriostatic or Initial treatment of Contraindicated with Dermatologic: Assessment:
Pyrazinamide bactericidal active TB in allergy to Rashes, History:
against adults and pyrazinamide, acute photosensitivity Allergy to
Brand Name: mycobacterium children with hepatic disease, Gastro Intestinal: pyrazinamide, acute
Tebrazid tuberculosis combined with lactation, acute gout. Hepatotoxicity, hepatic disease, gout,
other Use cautiously with nausea, vomiting, diabetes mellitus,
Classification: antituberculotic diabetes mellitus, diarrhea, anorexia acute intermittent
Antituberculotic Treatment of acute intermittent Hematologic: porphyria, pregnancy.
drug-resistant TB porphyria, pregnancy. Sideroblastic Physical:
Dosage: as part of an anemia, Skin color, lesions,
15 to 30 mg/kg once individualized thrombocytopenia, joint status, TB, liver
daily regimen. adverse effects on evaluation, LFTs,
clotting mechanism serum and urine uric
Route: or vascular integrity acid levels, blood and
Oral Other: urine glucose, CBC.
Active gout
Intervention:
Administer only in
conjunction with
other
antituberculotics.
Administer once a
day.
Discontinue drug if
liver damage or
hyperuricemia in
conjunction with
acute gouty
arthritis occurs.
Teaching pionts:
Take drugs once a
day, it will need to
be taken with other
tuberculosis drugs.
Take drugs
regularly, avoid
missing doses.
Do not discontinue
drug without first
consulting
healthcare
provider.
Have regular,
periodic medical
check-ups,
including blood test
to evaluate drug
effects.
Report fever,
malaise loss of
appetite, nausea,
vomiting, darkened
urine, yellowing of
skin and eyes,
severe pain in
great toe or wrist.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- RifampicinDocument2 pagesRifampicinFlorenz Gatchalian100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyFlorenz Gatchalian100% (1)
- IsoniazidDocument2 pagesIsoniazidAlberto Creo Jr.100% (3)
- Drug Study RifampicinDocument2 pagesDrug Study RifampicinJamil Lorca100% (5)
- Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument2 pagesClinical Medications WorksheetsMichael Kuzbyt0% (1)
- Rifampicin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRifampicin Drug StudyNicole Louize CaloraPas encore d'évaluation
- Rifampicin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRifampicin Drug StudyMaila Joy Pring Fuentes67% (3)
- Pyrazinamide Drug StudyDocument1 pagePyrazinamide Drug Studyanreilegarde100% (2)
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument2 pagesETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoPas encore d'évaluation
- STREPTOMYCINDocument3 pagesSTREPTOMYCINChad InongPas encore d'évaluation
- Streptomycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesStreptomycin Drug Studym B100% (1)
- GentamicinDocument1 pageGentamicinreinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument3 pagesDrug Study IsoniazidJamil Lorca100% (4)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosPas encore d'évaluation
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClindamycin Drug StudyAlex MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - ClarithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ClarithromycinTrisha Lapid MatulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name: Amikacin SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amikacin Sulfateichiro017100% (7)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudysarahtotPas encore d'évaluation
- ISONIAZIDDocument2 pagesISONIAZIDXerxes DejitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDocument4 pagesDrug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDeinielle Magdangal Romero100% (1)
- Drug Study Iron SucroseDocument1 pageDrug Study Iron SucroseAkiraMamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Salbutamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol Drug StudyVinz Khyl G. CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolDocument3 pagesIpratropium Bromide Plus SalbutamolA sison100% (1)
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLee JennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gentamicin Drug SummDocument1 pageGentamicin Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG AmikacinDocument2 pagesDRUG Amikacinrholiboi100% (1)
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDocument4 pagesTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- CefiximeDocument2 pagesCefiximenarucute01224Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyArabelle GOPas encore d'évaluation
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userPas encore d'évaluation
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- CetirizineDocument1 pageCetirizineGabby Robles PajePas encore d'évaluation
- IsoniazidDocument2 pagesIsoniazidMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- DRUG STUDY (Amoxicilin)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Amoxicilin)Gerly LagutingPas encore d'évaluation
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyMark Angelo LorzanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Levofloxacin (Levocin)Document1 pageLevofloxacin (Levocin)Diego ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤─ IrisariPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BaylePas encore d'évaluation
- Amoxicillin TrihydrateDocument1 pageAmoxicillin TrihydrateHoney Que BullivantPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name:: Antituberculot IcDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Antituberculot IcPrincess Erika C. MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugggstudyyDocument6 pagesDrugggstudyycataleya mesaPas encore d'évaluation
- KETOROLACDocument1 pageKETOROLACJugen Gumba Fuentes AlquizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Anti TBDocument2 pagesDrugs Anti TBLeo_Rabacca_3610Pas encore d'évaluation
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosPas encore d'évaluation
- New Employee Orientation Policy: PurposeDocument10 pagesNew Employee Orientation Policy: PurposeKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Intravenous FluidsDocument3 pagesIntravenous FluidsKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Shangri-La Hotel, Manila 1 Garden Way, Ortigas Centre Mandaluyong CityDocument2 pagesShangri-La Hotel, Manila 1 Garden Way, Ortigas Centre Mandaluyong CityKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory and Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic TestKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical AssessmentDocument9 pagesPhysical AssessmentKristine Artes Aguilar0% (1)
- Patient'S Profile:: Patient's Name: Address: Date of Birth: Age: Gender: Religion: NationalityDocument1 pagePatient'S Profile:: Patient's Name: Address: Date of Birth: Age: Gender: Religion: NationalityKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Mechanisism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects/Advers E Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanisism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects/Advers E Effects Nursing ConsiderationsKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- HemodialysisDocument9 pagesHemodialysisKristine Artes Aguilar100% (2)
- IbuprofenDocument3 pagesIbuprofenKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mefenamic AcidDocument1 pageMefenamic AcidKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Sa Sawma Wound Cleansing and Dressing Procedure Nov 07Document23 pages2007 Sa Sawma Wound Cleansing and Dressing Procedure Nov 07Kristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reasoning Planning Intervention Evaluation Standard CriteriaDocument1 pageCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reasoning Planning Intervention Evaluation Standard CriteriaKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemo DrugDocument1 pageChemo DrugKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Affidavit of LossDocument1 pageAffidavit of LossKristine Artes Aguilar0% (1)
- Cues Problem Scientific Reasoning Planning Intervention With Rationale Evaluation Standard Criteria Subjective: Short TermDocument2 pagesCues Problem Scientific Reasoning Planning Intervention With Rationale Evaluation Standard Criteria Subjective: Short TermKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Drug StudyKristine Artes Aguilar67% (3)
- Sample ThesisDocument1 pageSample ThesisKristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of Client With CancerDocument63 pagesNursing Care of Client With CancermikErlhPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Personal HygieneDocument4 pagesWhat Is Personal HygieneAnonymous 0FWhoTu100% (1)
- Acute Limb Ischemia: Clinical PracticeDocument9 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia: Clinical PracticeIndah MaulidawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chin Chong MinDocument3 pagesChin Chong MinSHine PukurPas encore d'évaluation
- 95 Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Gel by Using Natural PolymerDocument3 pages95 Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Gel by Using Natural PolymerJulian Kayne100% (1)
- Prospectus PDFDocument68 pagesProspectus PDFPrince Digital ComputersPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodontal InstrumentsDocument10 pagesPeriodontal Instrumentsmanishpankaj123100% (1)
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus PDFDocument23 pagesMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus PDFGerardo N. Pabón Gallino100% (1)
- 08 Chapter 3 Pyrazole AppDocument100 pages08 Chapter 3 Pyrazole AppSaima KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lastearthdistro PDFDocument24 pagesLastearthdistro PDFleonabrahamzapruderPas encore d'évaluation
- Doctors Order Form D4Document1 pageDoctors Order Form D4Marielle ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- NICU OrganizationDocument5 pagesNICU Organizationgopscharan100% (1)
- Goc Marina Reviewer PDFDocument57 pagesGoc Marina Reviewer PDFAl Jhem Geronimo60% (5)
- What Is CelecoxibDocument3 pagesWhat Is CelecoxibKevin LabbeikPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac GlycosidesDocument8 pagesCardiac GlycosidesShan Sicat100% (1)
- (Progress in Epileptic Disorders, Vol. 13) Solomon L. Moshé, J. Helen Cross, Linda de Vries, Douglas Nordli, Federico Vigevano-Seizures and Syndromes of PDFDocument283 pages(Progress in Epileptic Disorders, Vol. 13) Solomon L. Moshé, J. Helen Cross, Linda de Vries, Douglas Nordli, Federico Vigevano-Seizures and Syndromes of PDFWalter Huacani HuamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hanna Instruments Sds Hi 7033 2016-06-13Document3 pagesHanna Instruments Sds Hi 7033 2016-06-139802774Pas encore d'évaluation
- Periop QuizesDocument9 pagesPeriop QuizesAnonymous ZQ4gHahzPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and Electrolytes Study GuideDocument13 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Study GuideElizabeth McKeePas encore d'évaluation
- Thorax and Lungs SGDocument2 pagesThorax and Lungs SGDestinee Caple100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing TestDocument21 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing TestAt Day's Ward50% (2)
- Current & Future Status of Herbal MedicinesDocument4 pagesCurrent & Future Status of Herbal MedicinesimmchrPas encore d'évaluation
- V Jttu/: Prices ChangeDocument179 pagesV Jttu/: Prices ChangeKarpincho3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rekap Umr 2019-4Document52 pagesRekap Umr 2019-4Derri HafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Degnala DiseaseDocument12 pagesDegnala DiseaseSantosh Bhandari100% (1)
- Chapter - 014 Student HandoutsDocument16 pagesChapter - 014 Student Handoutsebiniyam2021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guiding Principles For Best Practices in Geriatric PTDocument16 pagesGuiding Principles For Best Practices in Geriatric PTPritesh KujurPas encore d'évaluation
- The Science of NutritionalDocument738 pagesThe Science of NutritionalMonching Adecer100% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled Documentapi-388763698Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consent Form - EmployerDocument1 pageConsent Form - EmployerShankarr Kshan100% (1)
- SEE WITHOUT Glasses PreviewDocument21 pagesSEE WITHOUT Glasses PreviewHokusyPas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingD'EverandDeep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (104)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipD'EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1135)
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfD'EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1461)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissD'EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (82)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayD'EverandThe Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayPas encore d'évaluation
- Midnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepD'EverandMidnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Peaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxD'EverandPeaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (144)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)D'EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (40)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellD'EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellPas encore d'évaluation
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouD'EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (5)
- The Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerD'EverandThe Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (58)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductD'EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (31)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningD'EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- The Self-Care Solution: A Year of Becoming Happier, Healthier, and Fitter—One Month at a TimeD'EverandThe Self-Care Solution: A Year of Becoming Happier, Healthier, and Fitter—One Month at a TimeÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (5)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayD'EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayPas encore d'évaluation
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookD'EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- 369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESD'Everand369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (50)
- The Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeD'EverandThe Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (13)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeD'EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessD'EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessPas encore d'évaluation
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)D'EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeD'EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifePas encore d'évaluation