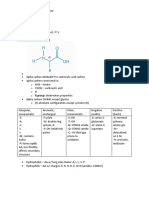
Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Next-Step MCAT Outline
Transféré par
Sage Norrie0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
257 vues24 pagesMCAT Outline
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMCAT Outline
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
257 vues24 pagesNext-Step MCAT Outline
Transféré par
Sage NorrieMCAT Outline
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 24
Next
Step MCAT Outline
The following outline details all of the information you need to know for the MCAT. You will see each
topic listed under a Concept Category with code like 2C or 5E. The AAMC has organized the MCAT
content around general concepts that cut across disciplinary boundaries. To make the material more
manageable for you, we have sorted the content into the seven MCAT sciences: biology, chemistry,
biochemistry, organic chemistry, physics, psychology, and sociology.
You will see certain topics listed more than once under multiple sciences. For example, amino acids
are listed in both the biochemistry and biology sections. When a topic can be covered under multiple
sciences, you may get questions that ask about that topic as its normally taught in a biochemistry
class, or as its normally taught in a biology class.
Biology
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
1A: Proteins
A. Structure
a. Protein Structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
b. Protein Stability: Folding, Denaturing, Hydrophobic interactions
c. Separation Techniques: Isoelectric Point, Electrophoresis
B. Protein Function: Immune System, Motors
C. Enzymes
a. Catalysts: Reduction of Activation Energy, Cofactors, Coenzymes
b. Classification
c. Substrate interactions: Active Site, Induced Fit
d. Vitamins
e. Effects on Enzyme Activity: pH, temperature, etc.
D. Enzyme Control
a. Kinetics: Michaelis-Menten, Cooperativity
b. Feedback
c. Inhibition: Competitive, Non-competitive
d. Regulatory Enzymes: Allosteric enzymes, Zymogens, Covalently-modified enzymes
1B: Molecular Genetics
A. Nucleic Acids
a. Structure, Function
b. Nucleotides, Nucleosides: Sugar-Phosphate Backbone, Purines, Pyrimidines
c. Watson-Crick Model: Double-Helix, Base-Pair Specificity
d. Transmission of genetic information
e. Denaturation, Reannealing, Hybridization
B. DNA Replication and Repair
a. Replication Mechanism: Semi-Conservative, Enzymes, Replication Origin
b. Replicating the ends of DNA
c. Repair: During Replication, Mutation Repair
C. Genetic Code
a. Triplets: Codon-Anticodon, Degeneracy, Wobble Pairing, Missense, Nonsense,
Initiation, Termination
b. Transcription
i. tRNA, mRNA, rRNA, snRNPs, snRNAs
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
ii. introns, exons
c.
Translation
i. mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
ii. ribosomes, initiation, termination co-factors
iii. post-translational processing
D. Chromosomes: Proteins, Repetitive DNA, Supercoiling, Heterochromatin, Euchromatin,
Telomeres, Centromeres
E. Gene Expression
a. Prokaryotes: Operons, Jacob-Monod Model, Repression, Positive Control
b. Eukaryotes
i. transcriptional regulation, DNA binding proteins, transcription factors
ii. gene amplification, duplication
iii. post-transcriptional control, introns, exons
iv. cancer
v. regulation of chromatic structure: methylation
vi. non-coding RNAs
F. Biotechnology: Cloning, Restriction Enzymes, cDNA, Hybridization, PCR, Blotting,
Electrophoresis, Stem Cells, Applications, Ethics
1C: Classical Genetics
A. Mendelian Genetics: Phenotype, Genotype, Gene, Locus, Allele, Zygosity, Wild-type,
Recessive, Dominant, Co-dominant, Incomplete Dominance, Leakage, Penetrance,
Expressivity, Hybridization, Gene Pool
B. Meiosis and Variability
a. Significance, Differences with Mitosis
b. Gene Segregation: Independent Assortment, Linkage, Recombination
c. Sex-Linkage, Y Chromosome, Sex Determination
d. Extranuclear Inheritance
e. Mutation: Types, Effects, Errors of Metabolism, Mutagens and Carcinogens
f. Genetic Drift
g. Crossing-over
C. Analysis: Hardy-Weinberg, Test Cross, Crossover Frequency, Biometry
D. Evolution
a. Natural Selection: Fitness, Differential Reproduction, Group Selection
b. Speciation: Polymorphism, Adaptation, Inbreeding, Outbreeding, Bottlenecks
c. Time as gradual random changes in genome
1D: Metabolism
A. Glycolysis
a. Aerobic: Substrates and Products
b. Anaerobic: Fermentation
c. Net Results
B. Regulation of Pathways
C. Krebs Cycle: Reactions, Substrates, Products, Regulation
D. Metabolism of Fat and Protein
a. Fats: Digestion, Transport
b. Fatty Acids: Oxidation, Saturated Fats, Unsaturated Fats
c. Proteins: Metabolism
d. Anabolism: Synthesis of Lipids and Polysaccharides
E. Oxidative Phosphorylation
a. Electron Transport Chain: Substrates, Products, Function
b. NADH, NADPH, Flavoproteins, Cytochromes
c. ATP Synthase, Chemiosmosis
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
d. Net Results
e. Regulation
2A: Cell Biology
A. Plasma Membrane
a. Composition: Phospholipids, Steroids, Waxes, Proteins
i. Receptors
b. Solute transport: Thermodynamics, Osmosis, Passive, Active, Na/K Pump, Channels
c. Membrane Potential
d. Exocytosis, Endocytosis
e. Gap Junctions, Tight Junctions, Desmosomes
B. Membrane-Bound Organelles
a. Nucleus: Genetic Information, Nucleolus, Nuclear Envelope, Pores
b. Mitochondria: Function, Membranes, Replication
c. Lysosomes: Function
d. ER: Rough vs. Smooth, Double Membrane, Biosynthesis
e. Golgi: Structure and Function
f. Peroxisomes: Function
C. Cytoskeleton: Microfilaments, Microtubules, Intermediate Filaments, Cilia, Flagella,
Centrioles, Microtubule Organizing Centers
D. Epithelial and Connective Cells
2B: Microbiology
A. Cell Theory: History, Development, Impact
B. Prokaryotes
a. Archaea, Bacteria, Bacilli, Spirilli, Cocci
b. Lack of Eukaryotic Features
c. Cell Wall, Flagella
d. Fission, Exponential Growth
e. Quick Adaptation, Antibiotic Resistance
f. Types: Aerobic, Anaerobic, Parasitic, Symbiotic
g. Chemotaxis
h. Genetics: Plasmids, Transformation, Conjugation, Transposons
C. Viruses
a. Structure, Size, Lack of Organelles
b. Bacteriophages
c. Genome: DNA, RNA
d. Life Cycle: Intracellular Reproduction, Attachment, Replication, Release
e. Transduction
f. Retroviruses
g. Prions, Viroids
2C: Cell Division, Cell Development, Reproduction, Embryology
A. Mitosis: Phases, Structures, Growth Arrest, Control and Loss of Control
B. Reproduction
a. Gametogenesis, Meiosis
b. Ovum, Sperm: Formation, Morphology, Contribution to Zygote
c. Sequence: Fertilization to Birth
C. Embryogenesis
a. Stages: Fertilization, Cleavage, Blastula, Gastrula, Cell Movements, Neurulation
b. Germ Layers: Endoderm, Mesoderm, Ectoderm
c. Neural Crest
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
d. Environmental Effects
D. Cell Development
a. Specialization: Determination, Differentiation, Tissue Types, Cell communication
b. Cell Migration
c. Stem Cells
d. Gene Regulation
e. Apoptosis
f. Regeneration, Senescence, Aging
3A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
A. Nerve Cell
a. Structures: Soma, Dendrites, Axon, Myelin, Nodes of Ranvier
b. Synapse: Structure, Neurotransmitters
c. Resting Potential, Action Potential
d. Excitatory, Inhibitory Fibers, Summation, Firing Frequency
e. Glia, Neuroglia
B. Nervous System
a. Function, Organization
b. Efferent, Afferent
c. Sympathetic, Parasympathetic
d. Reflexes: Reflex Arc, Spinal Cord, Supraspinal Circuits
e. Endocrine System Integration
C. Endocrine System
a. Function, Major Glands, Major Hormones
b. Mechanism of Hormone Action
c. Transport of Hormones and Second Messengers
3B: Physiology
A. Respiratory System: Structure, Function, Thermoregulation, Henrys Law, pH control,
Regulation
B. Circulatory System
a. Structures, Functions, Regulation
b. Heart: Chambers
c. Systolic, Diastolic Pressure
d. Pulmonary, System Circulations
e. Arteries, Veins, Capillaries
f. Blood Composition: Plasma, Cells, Chemicals
g. Clotting
h. Gas Transport: Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit
i. Lymphatic System: Structures, Functions
C. Immune System
a. Innate: Macrophages, Phagocytes
b. Adaptive: T-cells, B-cells
c. Tissues: Marrow, Spleen, Thymus, Lymph Nodes
d. Antigens, Antibodies: Ag Presentation, Ag-Ab Recognition, Structure of Ab
e. Autoimmune Diseases
f. Major Histocompatibility Complex
D. Digestive System
a. Ingestion, Peristalsis
b. Organs: Stomach, Liver, Gall Bladder, Pancreas, Small Intestine, Large Intestine
c. Control: Muscular, Endocrine, Nervous
E. Excretory System
a. Homeostasis: bp, osmoregulation, acid balance, nitrogenous waste
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
b.
Kidney: Cortex, Medulla
c.
Nephron: Glomerulus, Bowmans Capsule, Tubules, Loop of Henle, Collecting Duct
i. filtration, counter-current multiplier, secretion, reabsorption, concentration
d. Storage: ureter, bladder, urethra
F. Reproductive System: Gonads, Genitals, Sexual Development, Menstrual Cycle, Pregnancy,
Lactation
G. Muscle System
a. Function: Mobility, Circulatory Assistance, Thermoregulation, Shivering
b. Smooth, Striated, Cardiac
c. Muscle Structure: T-tubule, Contractile Apparatus, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum,
Contractile Velocity
d. Cardiac Muscle: Regulation
e. Oxygen Debt
f. Control: Motor Neurons, Neuromuscular Junction, Motor End Plates, Sympathetic
and Parasympathetic, Voluntary, Involuntary
g. Sarcomeres
h. Troponin, Tropomyosin
H. Skeletal System
a. Function: Support, Protection, Calcium Storage
b. Bone Types, Joint Types
c. Composition of Bone Matrix and Cells
d. Cartilage, Ligaments, Tendons
e. Endocrine Regulation
I. Skin System
a. Structure: Layers, Cell Types, Impermeability to Water
b. Function: Homeostasis, Osmoregulation, Thermoregulation, Physical Protection
c. Hormonal Control
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
4B: Fluids
A. Circulatory System: Pressure and Flow in Arteries and Veins
4C: Electrochemistry and Circuits
A. Nerve Cell Propagation: Myelin, Schwann Cells, Insulation, Nodes of Ranvier
5D: Biological Molecules
A. Nucleotides and Nucleosides: Composition, Purines, Pyrimidines, DNA, Double-Helix
5E: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
A. Enzymes
a. Reaction Types
b. Mechanisms: Active Site, Induced-fit, Cofactors, Coenzymes, Vitamins
c. Kinetics: Catalysis, Michaelis-Menten, Cooperativity, Environmental Effects
d. Inhibition and Regulation
Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior
6A: Sensation
A. Sensory Processing: Thresholds, Adaptation, Pathways, Receptor Types
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
B. Vision
a. The Eye: Structure and Function
b. Visual Processing: Brain Pathways
C. Hearing
a. The Ear: Structure and Function, Hair Cells
b. Auditory Processing: Brain Pathways
D. Other Senses
a. Somatosensation, Nociception
b. Taste, Smell: Pheromones
c. Vestibular Sense
6B: Cognition, Consciousness, and Memory
A. Biological Factors Affecting Cognition
B. Alertness
C. Sleep and Circadian Rhythms
D. Emotional Effect on Memory Retrieval
E. Memory: Changes in Synaptic Connections, Neural Plasticity, Long-Term Potentiation
F. Language: Brain Areas of Language and Speech
Emotion and Stress
A. Biological Factors in Perceiving Emotion
B. Physiological Response to Stress
7A: Behavior
A. Biological Basis of Behavior
a. Nervous System: Neurons, Neurotransmitters
i. central and peripheral nervous systems
ii. brain: forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, lateralization, methods of study
iii. spinal cord
b. Endocrine System: Components, Effects on Behavior
c. Genetics: Temperament and Heredity, Adaptive Value of Behaviors
i. Regulatory Genes and Behavior
ii. Behavior Variation Between Populations
B. Disorders: Schizophrenia, Depression, Alzheimers, Parkinsons, Stem-Cell Therapy
C. Motivation: Biological Drives
7C: Learning
A. Classical Conditioning: Conditioned and Unconditioned Response, Processes
B. Operant Conditioning
a. Shaping, Extinction
b. Reinforcement Schedules and Types
c. Punishment, Escape, Avoidance
C. Biological Effects on Associative Learning
8C: Social Interaction
A. Animal Signals and Communication
B. Social Behavior in Animals: Foraging, Mating, Game Theory, Altruism, Inclusive Fitness
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Biochemistry
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
1A: Proteins
A. Amino Acids: configuration, dipolar ions, acidic/basic, hydrophobic/hydrophilic
B. Structure
a. Protein Structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
b. Protein Stability: Folding, Denaturing, Hydrophobic interactions, Solvation and
Entropy
c. Separation Techniques: Isoelectric Point, Electrophoresis
C. Protein Function: Immune System, Motors
D. Enzymes
a. Catalysts: Reduction of Activation Energy, Cofactors, Coenzymes
b. Classification
c. Substrate interactions: Active Site, Induced Fit
d. Vitamins
e. Effects on Enzyme Activity: pH, temperature, etc.
E. Enzyme Control
a. Kinetics: Michaelis-Menten, Cooperativity
b. Feedback
c. Inhibition: Competitive, Non-competitive, Mixed, Uncompetitive
d. Regulatory Enzymes: Allosteric enzymes, Zymogens, Covalently-modified enzymes
1B: Molecular Genetics
A. Nucleic Acids
a. Structure, Function
b. Nucleotides, Nucleosides: Sugar-Phosphate Backbone, Purines, Pyrimidines
c. Watson-Crick Model: Double-Helix, Base-Pair Specificity
d. Denaturation, Reannealing, Hybridization
1D: Metabolism
A. Bioenergetics
a. Thermodynamics/Bioenergetics: G, Keq, Concentrations, Spontenaiety
b. Phosphoryl Groups: ATP Hydrolysis, Group Transfers
c. Redox: Half-Reactions, Soluble Electron Carriers, Flavoproteins
B. Carbohydrates: Classification, Configuration, Hydrolysis of Glycosides, Monomers and
Polymers
C. Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
a. Aerobic: Substrates and Products
b. Anaerobic: Fermentation
c. Net Results
d. Gluconeogenesis and Pentose Phosphate Pathway
D. Regulation of Pathways
a. Regulation of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
b. Glycogen Synthesis and Breakdown, Regulation
c. Analysis of Metabolic Regulation
E. Krebs Cycle: Acetyl CoA Production, Reactions, Substrates, Products, Regulation
F. Metabolism of Fat and Protein
a. Fats: Digestion, Transport
b. Fatty Acids: Oxidation, Saturated Fats, Unsaturated Fats, Ketone Bodies
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
G. Oxidative Phosphorylation
a. Electron Transport Chain: Substrates, Products, Function
b. NADH, NADPH, Flavoproteins, Cytochromes
c. ATP Synthase, Chemiosmosis
d. Net Results
e. Regulation
f. Mitochondria: Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress
H. Hormonal Regulation: High Level Integration, Tissue Specific Metabolism, Obesity
2A: Cell Biology
A. Plasma Membrane
a. Composition: Phospholipids, Steroids, Waxes, Proteins
i. Receptors
b. Solute transport: Thermodynamics, Osmosis, Passive, Active, Na/K Pump, Channels
c. Membrane Potential
d. Exocytosis, Endocytosis
3A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
A. Biosignalling: Gated Ion Channels, Voltage and Ligand Gated, Receptor Enzymes, G protein-
coupled receptors
B. Lipids: Structure, Steroids, Terpenes, Terpenoids
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
5A: Solution Chemistry and Acid/Base
A. Brnsted-Lowry Definitions, Auto-Ionization of Water, Conjugates
B. Weak Acids/Bases: Salts, pH Calculations
C. Constants: Ka, Kb, Kw
D. Buffers: Common Systems, Titration Curves
E. Ions: Common Names and Charges, Hydration and Hydronium
5C: Separation and Purifications
A. Extraction
B. Distillation
C. Chromatography: Column, HPLC, Paper, TLC
D. Peptides: Electrophoresis, Quantitative Analysis, Size-Exclusion, Ion-Exchange, Affinity
5D: Biological Molecules
A. Nucleotides and Nucleosides: Composition, Purines, Pyrimidines, DNA, Double-Helix,
Chemistry, Other Functions
B. Amino Acids and Pepties
a. Amino Acids: Configuration, Dipolar, Acid/Base, Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic
b. Peptides: Sulfur Linkage, Polypeptides, 1 - 4 Structure, Isoelectric Point
C. 3D Protein Structure: Conformational Stability, Hydrophobic Interactions, Solvation and
Entropy, 4 Structure, Folding and Denaturing
D. Non-Enzymatic Protein Function: Binding, Immunoglobulins, Motors
E. Lipids: Storage, Triacyl Glycerols, Saponification, Phospholipids, Phosphatids, Sphingolipids,
Waxes, Fat-Soluble Vitamins, Steroids, Prostaglandins
F. Cyclic Molecules: Phenols, Hydroquinones, Ubiquinones, 2e- Redox Centers, Aromatic
Heterocycles
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
5E: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
A. Enzymes
a. Reaction Types
b. Mechanisms: Active Site, Induced-fit, Cofactors, Coenzymes, Vitamins
c. Kinetics: Catalysis, Michaelis-Menten, Cooperativity, Environmental Effects
d. Inhibition and Regulation
B. Bioenergetics: G, Keq, Phosphorylation, ATP, ATP Group Transfers, Redox, Soluble Electron
Carriers, Flavoproteins
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Chemistry
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
1D: Metabolism
A. Bioenergetics
a. G, Keq
b. Concentration, Le Chateliers Principle
c. Exo- and Endo-thermic, Spontaneity
d. ATP hydrolysis, G << 0
e. Redox: Half-reactions, Soluble Electron Carriers, Flavoproteins
2A: Cell Biology
A. Plasma Membrane: Osmosis, Osmotic Pressure, Colligative Properties
3A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
A. Electrochemistry: Concentration cell, direction of flow, Nernst Equation
3B: Physiology
A. Respiratory System: Henrys Law
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
4B: Gas Phase
A. Absolute Temp, Kelvin Scale, Pressure, Mercury Barometers, 22.4 L/mol @ STP
B. Ideal Gas: Ideal Gas Law, Boyles Law, Charless Law, Avogadros Law
C. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
D. Real Gases: Qualitative, Quantitative, Van der Waalss Equation
E. Partial Pressure, Mole Faction, Daltons Law
4C: Electrochemistry and Circuits
A. Electrochemistry
a. Electrolytic Cell: Electrolysis, Anodes and Cathodes, Electrolytes, Faradays Law,
Electron Flow
b. Galvanic Cells: Half-reactions, Potential, Electron Flow
c. Concentration Cell
d. Batteries: EMG, Voltage, Lead-Storage, Nickel-Cadmium
4E: Atomic Nucleus, Periodic Table, Stoichiometry
A. Atomic Nuclei: Atomic Number and Weight, Nucleons, Nuclear Forces, Radioactive Decay,
Mass Spectrometer
B. Electronic Structure
a. Hydrogen Atoms, Bohr Model, Effective Nuclear Charge
b. Quantum Numbers
c. Ground vs. Excited States
d. Pauli Exclusion Principle
e. Paramagnetic and Diamagnetic Elements
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
f. Photoelectric Effect
g. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
C. The Periodic Table
a. Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Halogens, Noble Gases, Transition Metals
b. Representative Elements
c. Metals and Non-Metals
d. Oxygen Group
e. Valence Electrons
f. Ionization Energy, Electron Affinity, Electronegativity, Atomic and Ionic Radius
D. Stoichiometry: Molecular Weight, Molecular and Empirical Formula, Metric Units, Percent
Mass, Avogadros Number, Density, Oxidation, Disproportionation Reactions, Chemical
Equations, Yields, Limiting Reagents
5A: Solutions and Acid/Base
A. Acid/Base
a. Brnsted-Lowry, Auto-ionization of Water, Conjugate Acids and Bases
b. Strong Acids, Weak Acids
c. Weak Acids: Dissociation, Salts, Hydrolysis, pH Calculations
d. Ka, Kb, Kw
e. Buffers: Concepts, Titration Curves
B. Ions and Solutions
a. Anions, Cations, Familiar Ions, Hydration, Hydronium, Units of Concentration, Ksp,
Common-Ion Effect, Complex Ions
C. Titration: Indicators, Neutralization, Titration Curves, Redox Titration
5B: Covalent Bonds
A. Lewis Dot Formulas: Resonance, Formal Charge, Lewis Acids and Bases
B. Partial Ionic Bonds: Electronegativity, Dipole Moment
C. Sigma and Pi Bonds
a. Hybrid Orbitals, VSEPR, Resonance
b. Structural Formulas involving H, C, N, O, F, S, P, Si, Cl
D. Double and Triple Bonds: Bond Length, Bond Energy, Rigidity
E. Liquids: Intermolecular Forces, H-bonding, Dipoles, Van der Waals, London Dispersion
5E: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
A. Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics
a. Zeroth Law, First and Second Laws
b. PV Diagrams: Work
c. Entropy: Disorder, Phases
d. Calorimetry: Heat Capacity, Specific Heat
e. Conduction, Convection, Radiation
f. Hesss Law, Enthalpy, Bond Dissociation Energy
g. Free Energy, Spontaneity
h. Phase Changes: Phase Diagram, Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
B. Kinetics and Equilibrium
a. Rate Law, Rate Constants, Reaction Order, Rate-Determining Step
b. Temperature and Rate: Activation Energy, Transition State, Reaction Profiles,
Arrhenius Equation
c. Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic Control
d. Catalysts
e. Reversible Reactions: Law of Mass Action, Keq and G, Le Chateliers Principle
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Organic Chemistry
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
1A: Proteins
A. Amino Acids: configuration, dipolar ions, acidic/basic, hydrophobic/hydrophilic
B. Structure
a. Protein Structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
b. Protein Stability: Folding, Denaturing, Hydrophobic interactions, Solvation and
Entropy
c. Separation Techniques: Isoelectric Point, Electrophoresis
1D: Metabolism
A. Carbohydrates: Classification, Configuration, Hydrolysis of Glycosides, Monomers and
Polymers
2A: Cell Biology
A. Plasma Membrane: Composition: Phospholipids, Steroids, Waxes, Proteins
3A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
A. Lipids: Structure, Steroids, Terpenes, Terpenoids
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
4D: Light and Sound
A. Molecular Structure and Absorption Spectra
a. IR, UV-Vis, Proton NMR
5C: Separation and Purifications
A. Extraction
B. Distillation
C. Chromatography: Column, HPLC, Paper, TLC
D. Peptides: Electrophoresis, Quantitative Analysis, Size-Exclusion, Ion-Exchange, Affinity
E. Racemic Mixtures, Separation of Enantiomers
5D: Biological Molecules
A. Amino Acids and Peptides
a. Amino Acids: Configuration, Dipolar, Acid/Base, Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic
b. Peptides: Sulfur Linkage, Polypeptides, 1 - 4 Structure, Isoelectric Point
B. Lipids: Storage, Triacyl Glycerols, Saponification, Phospholipids, Phosphatids, Sphingolipids,
Waxes, Fat-Soluble Vitamins, Steroids, Prostaglandins
C. Carbohydrates: Classification, Configuration, Cyclic Conformation
a. Hydrolysis of Glycosides
b. Keto-Enol Tautomers
D. Carbonyl Compounds
a. Nomenclature and Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
b.
Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Carbon: Acetal, Ketal, Imine, Enamine, Hydrides,
Cyanohydrin
c. Oxidation of Aldehydes
d. Enolates: Tautomerism, Aldol Condensation, Retro-Aldol, Kinetic and
Thermodynamic Enolate
e. Steric Hindrance of Carbonyl Bond
f. Acidity of hydrogens, Carbanions
E. Alcohols
a. Nomenclature, Physical Properties
b. Reactions: Oxidation, Sn1, Sn2, Protection, Mesylates, Tosylates
F. Carboxylic Acids
a. Nomenclature, Physical Properties
b. Reactions: Amides, Lactam, Esters, Lactones, Anhydrides, Reduction,
Decarboxylation, Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
G. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
a. Nomenclature, Physical Properties
b. Reactions: Nucleophilic Substitution, Transesterification, Amide Hydrolysis
c. Reactivity, Steric Effects, Electronic Effects, Strain, lactams
H. Cyclic Molecules: Phenols, Hydroquinones, Ubiquinones, 2e- Redox Centers, Aromatic
Heterocycles
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Physics
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems
4A: Kinematics
A. Translational Motion: Units, Vectors, Velocity, Acceleration
B. Force: Newtons Laws, Friction, Center of Mass
C. Equilibrium: Vector Analysis, Torque
D. Work: Mechanical Advantage, Work Energy Theorem, Conservative Forces
E. Energy: Kinetic, Potential (Gravity, Spring), Conservation, Power, Units
F. Periodic Motion
a. Amplitude, Frequency, Phase
b. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves: Wavelength, Speed
4B: Fluids
A. Liquids: Density, Specific Gravity, Buoyancy, Pressure, Viscosity, Continuity, Turbulence,
Surface Tension, Bernoullis Equation, Venturi Effect, Pitot Tube
B. Gas Phase
a. Temperature in Kelvin, Pressure and Barometer
b. Ideal Gases: Boyles Law, Charless Law, Avogadros Law
c. Kinetic Molecular Theory: Heat Capacity, Boltzmanns Constant
d. Real Gases: Qualitative and Quantitative
e. Partial Pressure, Daltons Law
4C: Electrostatics and Circuits
A. Electrostatics: Charge, Conservation, Coulombs Law
a. Electric Field: Field Lines, Charge Distribution
b. Electrostatic Energy, Potential
B. Circuits
a. Current, EMF, Voltage, Ammeters, Voltmeter
b. Resistance: Ohms Law, Series, Parallel, Resistivity
c. Capacitance: Parallel Plate Capacitor, Energy, Series, Parallel, Dielectric
d. Conductivity: Metallic, Electrolytic
C. Magnetism: Field, Lorentz Force
4D: Light and Sound
A. Sound
a. Sound Production
b. Pitch, Speed, Intensity, Attenuation
c. Doppler Effect
d. Resonance
e. Ultrasound
f. Shock Waves
B. Light
a. Interference, Young Double-Slit, Thin Films, Diffraction Grating, Single-Slit
Diffraction, X-ray Diffraction
b. Polarization: Linear, Circular
c. Speed, Oscillating E and B Fields
d. EM Spectrum, Visual Spectrum, Color, Photon Energy
C. Optics
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
a. Reflection, Refraction, Snells Law, Dispersion
b. Total Internal Reflection
c. Mirrors: Curvature, Focal Length, Real and Virtual Images
d. Lenses: Converging, Diverging, Diopters, Combinations of Lenses
e. Aberrations
f. Optical Instruments, the Eye
4E: Nuclear and Electronic Structure
A. Nucleus: Atomic Number and Weight, Nucleons, Decay
B. Electronic Structure
a. Ground State, Excited State, Bohr Model
b. Absorption and Emission Spectra
c. Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism
d. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
e. Photoelectric Effect
5E: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
A. Thermodynamic System: Zeroth Law, First Law, Second Law
a. PV Diagram, Work
b. Conduction, Convection, Radiation
c. Coefficient of Expansion
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Psychology
Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior
6A: Sensation
1. Threshholds
2. Weber's Law
3. Signal Detection theory
4. Sensory adaptation
Particular Senses
1. Vision
a) Parallel Processing
b) Feature detection
2. Hearing and Auditory Processing
3. Auditory processing
4. Somatosensation and Pain
5. Kinesthetic sense
Perception
1. Bottom-up / Top-down processing
2. Perceptual organization depth, form, motion, constancy
3. Gestalt principles
6B: Consciousness and Thinking
Consciousness
1. States of consciousness
a) Alertness
b) Sleep
i. Stages and cycles of sleep
ii. Dreaming
iii. Sleep disorders
c) Hypnosis
d) Meditation
2. Drugs that change conscious perception
a) Types of drugs
b) Drug addiction
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Memory and Attention
1. Selective Attention
2. Divided Attention
3. Memory encoding process and how to increase it
4. Memory storage
a) Types
b) Semantic networks
c) Spreading activation
5. Memory retrieval, effect of emotion
a) Recall
b) Recognition
c) Relearning
d) Retrieval cues
6. Memory loss
a) Aging
b) Alzheimer's disease
c) Korsakoff's syndrome
d) Decay
e) Interference
f) Memory construction and source monitoring
Cognition and Language
1. Cognitive development
a) Piaget
b) Later adulthood
c) Effect of language
d) Role of culture, heredity, environmental
2. Problem solving
a) Approaches
b) Barriers
c) Hueristics
i. Biases
ii. Intuition
iii. Emotion
iv. Overconfidence
v. Belief perseverance
3. Intelligence
a) Various definitions and levels of ability
b) Effect of heredity, environment
4. Theories of language development
a) Learning
b) Nativist
c) Interactionist
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
6C: Emotion and Stress
Emotion
1. Cognitive component
2. Physiological component
3. Behavioral component
4. Universal emotions
5. James-Lange theory
6. Cannon-Bard theory
7. Schachter-Singer theory
Stress
1. Stress appraisal
2. Stressors
3. Responses to stress: physiological, emotional, behavioral
4. Stress management
7A: Behavior and Personality
Biology influences behavior
1. Neurotransmitters
2. Endocrine effects
3. Genetic factors
a) Temperament
b) Interaction between heredity and environment
4. Environment and experience effect behavior
Attitudes and Motivation
1. Influences on motivation
a) Instinct
b) Arousal
c) Drive
d) Needs
2. Link between motivation and behavior
a) Drive Reduction Theory
b) Incentive Theory
c) Cognitive Theories
d) Need-based Theories
3. Specific behaviors explained by theories
a) Eating, Sex
b) Drug use
c) Others
4. Regulation of motivation: biological factors, cultural factors
5. Components of attitudes
a) Cognitive
b) Affective
c) Behavioral
6. Cognitive dissonance
7. Behavior and attitude affect each other
Personality
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
1. Perspectives on Personality
a) Psychoanalytic
b) Humanistic
c) Trait
d) Social cognitive
e) Biological
f) Behaviorist
2. Explaining behavior situationally
Psychological Disorders
1. Psychological disorders
a) Biomedical approach
b) Biopsychosocial approach
c) Classification schemes and types
i. Anxiety
ii. Somatoform
iii. Mood
iv. Schizophrenia
v. Dissociative
vi. Personality
d) Incidence and prevalence
2. Psychological disorders as nervous system disorders
a) Schizophrenia
b) Depression
c) Alzheimer's
d) Parkinson's
7B: The Presence of Other People
1. Social facilitation
2. Deindividuation
3. Bystander effect
4. Social loafing
5. Peer pressure
7C: Behavior Change and Learning
1. Habituation
2. Classical Conditioning
a) Stimuli
i. Neutral
ii. Conditioned
iii. Unconditioned
b) Responses
i. Conditioned
ii. Unconditioned
c) Acquisition
d) Extinction
e) Spontaneous recovery
f) Generalization
g) Discrimination
3. Operant Conditioning
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
a) Shaping
b) Extinction
c) Reinforcement
i. Positive
ii. Negative
iii. Primary
iv. Conditional
d) Reinforcement Schedules
i. Fixed ratio
ii. Variable ratio
iii. Fixed interval
iv. Variable interval
e) Punishment
f) Escape
g) Avoidance
4. Observational learning
a) Modeling
b) Mirror Neurons
c) Vicarious Emotions
5. Attitude change
a) Elaboration Likelihood Model
i. Central and Peripheral route processing
b) Social Cognitive theory
c) Factors that affect attitude change
i. Changing behavior
ii. Characteristics of the message and target
iii. Social factors
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
8A: Identity and Interaction
Identity
1. Self-concept
2. Identity
3. Social Identity
4. Self-esteem
5. Self-efficacy
6. Locus of control in self-identity
7. Stages of identity development
a) Erikson
b) Vygotsky
c) Kohlberg
d) Freud
8. Social factors on identity development
a) Imitation
b) Role-taking
c) Reference group
8B: Interaction
1) Attribution theory
a) Fundamental attribution error
b) Cultural impact on attribution
2) Self-perception shapes perception of others
3) Perception of environment affects perception of others
4) Prejudice
a) Power
b) Prestige
c) Class
d) Emotion
e) Cognition
f) Discrimination
i. How power, prestige, class affect discrimination
5) Stereotypes
a) Self-fulfilling prophecy
b) Stereotype threat
6) Interaction between animals
a) Signals used by animals
8C: Social behaviors
1) Attraction
2) Aggression
3) Attachment
4) Social support
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Sociology
Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior
7B: Social Influences on Behavior
1. Peer pressure
2. Group polarization
3. Groupthink: Culture: Assimilation, Multiculturalism, Subculture
4. Socialization
a) Norms
b) Socializing Agents
i. Family
ii. Peers
iii. Media
iv. Workplace
5. Deviance
a) Stigma
6. Obedience
a) Conformity
8C: Social Interactions
1. Types of Group
a) Status
b) Roles
c) Groups
d) Networks
e) Organizations
2. Influences on interaction
a) Responses to emotional displays
i. Gender
ii. Culture
3. Manipulating perception by others
a) Front stage vs. Back stage
b) Dramaturgy
4. Discrimination
a) Individual discrimination
b) Institutional discrimination
5. Ethnocentrism
a) In-group vs. Out-group
b) Cultural relativism
9A: Structure of Society
Analyzing social structures
1. Functionalism
2. Conflict theory
3. Symbolic interaction
4. Social constructionism
5. Institutions that shape society
a) Education
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
b) Family
c) Religion
d) Government
e) Economy
f) Health care
6. Culture
a) Material culture
b) Symbolic culture
c) Language
d) Values
e) Beliefs
i. Norms
f) Rituals
7. Social groups placement within the culture
8. Evolution
9B: Demographics
1. Age
2. Gender
3. Race
4. Ethnicity
5. Immigration
6. Sexual orientation
7. Demographic shifts
a) Fertility
b) Migration
c) Mortality
8. Social movements
9. Globalization
10. Urbanization
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
10A: Social Inequality
1. Spatial Inequality
a) Segregation
b) Environmental inequality
c) Globalization
2. Social Class
a) Stratification into classes
i. Status
ii. Power
b) Cultural capital
c) Social capital
d) Social reproduction
e) Privilege
f) Prestige
3. Class and race, gender, age
4. Social mobility
a) Intergenerational
b) Intragenerational
c) Downward
d) Upward
e) Meritocracy
5. Povery
a) Relative
b) Absolute
c) Segregation
d) Isolation
6. Healthcare Disparities
a) Inequality in health status
i. Race
ii. Gender
iii. Class
b) Unequal access to healthcare
i. Race
ii. Gender
iii. Class
2014 Next Step Pre-Med, LLC. All rights reserved.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Choosing The Perfect PlanDocument3 pagesChoosing The Perfect PlanNeil CPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics ReviewDocument57 pagesMCAT Physics ReviewrinieroxPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content Organic ChemistryLoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsD'EverandSterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Sample Questions Template 1Document42 pagesMCAT Sample Questions Template 1gendut_novri0% (1)
- MCAT Physics Reference NotesDocument16 pagesMCAT Physics Reference NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Princeton WB ChemDocument762 pagesPrinceton WB Chemrajatgoyal20100% (1)
- McatDocument6 pagesMcatapi-383289428100% (1)
- MCAT Hyperlearning SetDocument2 pagesMCAT Hyperlearning Setbmxengineer0% (6)
- MCAT Practice PsDocument4 pagesMCAT Practice PsStephen CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- Free MCAT ResourcesDocument2 pagesFree MCAT ResourcesGeorges KoberianosPas encore d'évaluation
- AAMC Self Assesement Biology PDFDocument58 pagesAAMC Self Assesement Biology PDFsamivan27Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT ShortcutsDocument12 pagesMCAT ShortcutsShafqat Shakeel100% (2)
- MCAT PsychologyDocument113 pagesMCAT PsychologyChris WongPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT TipsDocument4 pagesMCAT TipsAndre AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 - Mcat PDFDocument158 pages2015 - Mcat PDFhuyly34Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Biology: Chapter 1 - The CellDocument16 pagesMCAT Biology: Chapter 1 - The CelljoPas encore d'évaluation
- Breaking Down The MCAT - A 3 Month MCAT Study Schedule - Student Doctor NetworkDocument28 pagesBreaking Down The MCAT - A 3 Month MCAT Study Schedule - Student Doctor NetworksafetydownPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsDocument6 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsLoraPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Approach The Mcat Tips TestimonialsDocument17 pagesHow To Approach The Mcat Tips Testimonialsapi-290840202Pas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Ways to Score Higher on Your MCAT: What You Need to Know About the Medical College Admission Test Explained SimplyD'Everand101 Ways to Score Higher on Your MCAT: What You Need to Know About the Medical College Admission Test Explained SimplyPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsD'EverandMCAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Document30 pagesMCAT Review Biology Notes (Full 1)Chris_Barber09100% (2)
- MCAT Mnemonic SDocument17 pagesMCAT Mnemonic STasneem MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- 5R Mcat PrepDocument73 pages5R Mcat Preprajatgoyal2050% (2)
- Aamc MCAT Test 7Document76 pagesAamc MCAT Test 7Kevin75% (4)
- Physics L Ecture 4 - Momentu M, Machin Nes and Ra Adioactive DecayDocument2 pagesPhysics L Ecture 4 - Momentu M, Machin Nes and Ra Adioactive DecayRobert Velázquez LucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- SB Notes Master Version 2.0Document156 pagesSB Notes Master Version 2.0anamargarita1962388Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetDocument6 pagesMCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetChris_Barber09Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Test8 ExplanationsDocument14 pagesMCAT Test8 ExplanationsRomilPatelPas encore d'évaluation
- P-S KA Notes in Q&A Format (Created From 100 PG Version)Document158 pagesP-S KA Notes in Q&A Format (Created From 100 PG Version)medmedPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Review 1Document46 pagesMCAT Physics Review 1dana milstein100% (1)
- Examkrackers General Chemistry NotesDocument16 pagesExamkrackers General Chemistry NotesddPas encore d'évaluation
- Aamc 8Document58 pagesAamc 8TravanL.Hurst100% (1)
- MCAT Lab TechniquesDocument17 pagesMCAT Lab TechniquesJim Smith100% (1)
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDocument8 pagesMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFDocument172 pagesComplete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFWollo NeftegnawPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Destroy The MCAT With Minimal Study TimeDocument11 pagesHow To Destroy The MCAT With Minimal Study TimeKristin SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsD'EverandSterling Test Prep MCAT Organic Chemistry & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryDocument25 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryLora100% (1)
- Master AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsDocument30 pagesMaster AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsSukhvir AujlaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Full Length3Document75 pagesMCAT Full Length3AliPas encore d'évaluation
- AamcDocument155 pagesAamcMyRoseBluePas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Hormones SummaryDocument1 pageMCAT Hormones Summaryrvar839Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 MCAT Leah4scimcatcheatsheetcollection2017Document50 pages1 MCAT Leah4scimcatcheatsheetcollection2017JD Ampaya100% (2)
- MCAT 4R SolutionsDocument36 pagesMCAT 4R SolutionsTravanL.HurstPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Discretes Test W. SolutionsCodie SimoneauxPas encore d'évaluation
- MadeMD MCAT Study ScheduleDocument78 pagesMadeMD MCAT Study ScheduleDerryk AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Exam Strategy EbookDocument32 pagesMCAT Exam Strategy EbookMary PPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Math PortionMCATDocument22 pagesMCAT Math PortionMCATwbowen92888100% (1)
- Ch. 1: Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesCh. 1: Amino AcidsNicole Ann LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test 8Document58 pagesPractice Test 8The LightPas encore d'évaluation
- Don's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesD'EverandDon's Tactical-Nuclear MCAT Test-Taking Tips and TechniquesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Aamc 2020 Mcat Essentials - 2 PDFDocument39 pagesAamc 2020 Mcat Essentials - 2 PDFJulienne Miguel Arguelles BarredoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Sciences: Time: 100 Minutes Questions 1-77Document79 pagesPhysical Sciences: Time: 100 Minutes Questions 1-77mattyg35Pas encore d'évaluation
- AAMC7 RSolutionsDocument40 pagesAAMC7 RSolutionsharmit12Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideD'EverandMCAT Test Prep Physics Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsD'EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsD'EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuideD'EverandMCAT Test Prep Inorganic Chemistry Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 2 of 3: MCAT Exam Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- A. Continuity at A Point: FC C F FX FX FCDocument4 pagesA. Continuity at A Point: FC C F FX FX FCSage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Limits: Thomas, 13eDocument5 pagesBasic Limits: Thomas, 13eSage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- X FX X FX: B. Limits at Infinity (End Behavior)Document5 pagesX FX X FX: B. Limits at Infinity (End Behavior)Sage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- F X With Respect To X Is The Function: FXH FX F X H: MAC 2311: Calculus Section 3.2: The Derivative As A FunctionDocument5 pagesF X With Respect To X Is The Function: FXH FX F X H: MAC 2311: Calculus Section 3.2: The Derivative As A FunctionSage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- Before You Begin This Unit, Watch This Video To Find Out Why We Learn Calculus!Document6 pagesBefore You Begin This Unit, Watch This Video To Find Out Why We Learn Calculus!Sage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- Y FX PX FX: Rise RunDocument6 pagesY FX PX FX: Rise RunSage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- F X Approach F X Has An Infinite LimitDocument3 pagesF X Approach F X Has An Infinite LimitSage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- lim sin 4 π lim sec 6 π Document2 pageslim sin 4 π lim sec 6 π Sage NorriePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesRenal Physiology Notescipa920% (1)
- Renal BiochemistryDocument47 pagesRenal BiochemistryIzzah AtqaPas encore d'évaluation
- DiureticsDocument10 pagesDiureticsAyla NacariøPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretion ExerciseDocument25 pagesExcretion ExerciseKrisnhalianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Deogiri College Aurangabad: Examination 2020-2021Document7 pagesDeogiri College Aurangabad: Examination 2020-2021M SuPas encore d'évaluation
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument10 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysiskisserPas encore d'évaluation
- Elsevier Adaptive Quizzing Renal - Quiz PerformanceDocument50 pagesElsevier Adaptive Quizzing Renal - Quiz PerformanceSaul Benavidez100% (2)
- Nephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Document55 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Pavi MuruganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- KGMU B.SC Nursing Entrance Exam Bilology Previous Year PaperDocument8 pagesKGMU B.SC Nursing Entrance Exam Bilology Previous Year PaperTech GaminggPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Workbook and Study Modules - 01-01-15708067Document82 pagesStudent Workbook and Study Modules - 01-01-15708067Joe Xavier ReidyPas encore d'évaluation
- Es Racp Dwe Adult Medical Sciences 101 170Document26 pagesEs Racp Dwe Adult Medical Sciences 101 170Gurki BajwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case - Neck MassDocument78 pagesCase - Neck MassMico TanPas encore d'évaluation
- X Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24Document28 pagesX Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24chaitanya100% (3)
- Renal-System PPT 2019Document45 pagesRenal-System PPT 2019sankarPas encore d'évaluation
- MOCKBOARD PART 3 Ready To PrintDocument7 pagesMOCKBOARD PART 3 Ready To PrintJayrald CruzadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Dot Point SummaryDocument91 pagesBiology Dot Point Summaryjulz230100% (4)
- Renal MCQ 1Document2 pagesRenal MCQ 1AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 - June 1BR MS PDFDocument24 pages2015 - June 1BR MS PDFSimilar12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM - Ayesigwa GeraldDocument13 pagesANATOMY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM - Ayesigwa GeraldAyesigwa Gerald96Pas encore d'évaluation
- MANISH - KANTI - BISWASUrino-genital System2020-05-04note Kidneyfinal 4-5-20Document11 pagesMANISH - KANTI - BISWASUrino-genital System2020-05-04note Kidneyfinal 4-5-20ShangPas encore d'évaluation
- CM Exam With Answer PDFDocument27 pagesCM Exam With Answer PDFKobi Carl MangopotPas encore d'évaluation
- For Website All Questions PDFDocument26 pagesFor Website All Questions PDFAyyaz HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Base Handout (Student)Document29 pagesAcid Base Handout (Student)Joel Topf100% (8)
- Farmaco LectureDocument117 pagesFarmaco LectureanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument101 pagesCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- Syllabus of BSC Nursing, Kathmandu UniversityDocument191 pagesSyllabus of BSC Nursing, Kathmandu UniversityKamal Raj Chapagain94% (18)
- CCRN-PCCN Review RenalDocument11 pagesCCRN-PCCN Review RenalGiovanni MictilPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Excretion WsDocument3 pagesIGCSE Excretion WsAnand Kumar Shukla100% (1)
- Unit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisaclumutPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology and Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesEtiology and Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryVictor TayoPas encore d'évaluation