Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Método de Las Rigideces JAML PDF
Transféré par
jose2017Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Método de Las Rigideces JAML PDF
Transféré par
jose2017Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
INSTITUTO TECNOLGICO DE DURANGO
NOTAS DE ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL II
MTODO DE LAS RIGIDECES
ING.JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 1 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
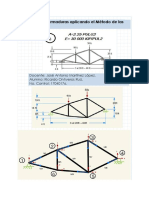
APLICACIN DEL MTODO DE LAS RIGIDECES EN EL ANLISIS
DE ARMADURAS
Para la armadura que se muestra en la Fig.1, determine el valor de los desplazamientos en nodos libres,
fuerzas en los elementos y reacciones.
5 kips
1 10 pulg 2
10 pulg 10 pulg
144 pulg
15 pulg 15 pulg
3 144 pulg 4
Fig.1 Armadura estticamente indeterminada de primer orden.
TOPOLOGA ESTRUCTURAL
Elemento Inicio Trmino Longitud Area Mdulo de
Coseno Seno
a b ( pulgadas ) ( pulg ) Elasticidad
( kips/ pulg
1 1 2 144 10 29000 0 1 0
2 1 3 144 10 29000 270 0 -1
3 1 4 203.6468 15 29000 315 0.7071 -0.7071
4 2 3 203.6468 15 29000 225 -0.7071 -0.7071
5 2 4 144 10 29000 270 0 -1
Grados de Libertad de la armadura
2 4
1 2
1 3
5 7
3 4
6 8
Fig.2 Grados de Libertad
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 2 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Clculo de la matriz de rigidez de los elementos en coordenadas locales
AE AE
L 0 0
L
0
(k ) = 0AE 0 0
AE
0 0
L L
0 0 0 0
Elemento 1 = Elemento 2 = Elemento 5
2013.8889 0 2013.8889 0
0 0 0 0
(k )1 = (k )2 = (k )5 =
2013.8889 0 2013.8889 0
0 0 0 0
Elemento 3 = Elemento 4
2136.0517 0 2136.0517 0
0 0 0 0
(k )3 = (k )4 =
2136.0517 0 2136.0517 0
0 0 0 0
Matriz de Rotacin de Ejes
Elemento 1
1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
(1 ) =
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
Elemento 2 = Elemento 5
0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
( 2 ) = (5 ) =
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 3 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Elemento 3
0.7071 0.7071 0 0
0.7071 0.7071 0 0
(3 ) =
0 0 0.7071 0.7071
0 0 0.7071 0.7071
Elemento 4
0.7071 0.7071 0 0
0.7071 0.7071 0 0
( 4 ) =
0 0 0.7071 0.7071
0 0 0.7071 0.7071
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DE LOS ELEMENTOS EN COORDENADAS GLOBALES
K = ( ) t (k ) ( )
Ai Ei Ai Ei
c s 0 0 0 0 c s 0 0
L Li
K aai K abi s c 0 0 i
(K )
i
= = 0 0 0 0 s c 0 0 =
K i 0 0 c s Ai Ei
0 0 0 c s
i Ai Ei
ba
K bb
0
L Li 0 0 s c
0 0 s c i
0 0 0 0
c2 sc c 2 sc
s 2 sc s2
[K ] =
i Ai Ei sc
Li c 2 sc c 2 sc
sc s 2 sc s 2
Elemento 1
2013.8889 0.0000 2013.8889 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
K =
1
2013.8889 0.0000 2013.8889 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 4 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Elemento 2 = Elemento 5
0.0000 0 0 0
0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889
K2 = K5 =
0 0 0 0
0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889
Elemento 3
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
K =
3
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
Elemento 4
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
K =
4
1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 11068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
De la matriz de conectividad (tabla de incidencias de los elementos), se genera la matriz de la
estructura: El nmero ms grande nos indica el orden de la matriz de rigidez de la estructura.
K 1aa + K aa
2
+ K aa
3
K 1ab 2
K ab 3
K ab
1
K ba 1
K bb + K aa
4
+ K aa
5 4
K ab 5
K ab
K =
2
K ba 4
K ba 2
K bb + K bb
4
0
3 5 3 5
+ K bb
K ba K ba 0 K bb
Cada lugar de esta matriz es una submatriz de orden de 2x2
Los elementos de la diagonal principal nos representan la rigidez del nodo.
2013.8889 0 0 0 1068.0259 1068.02590
K11 = + +
0 0 0 2013.8889 1068.02590 1068.0259
3081.9148 1068.0259
K11 =
1068.0259 3081.9148
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 5 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
2013.8889 0 1068.0259 1068.02590 0 0
K 22 = + +
0 0 1068.02590 1068.0259 0 2013.8889
3081.9148 1068.0259
K 22 =
1068.0259 3081.9148
0 0 1068.0259 1068.02590
K 33 = +
0 2013.8889 1068.02590 1068.0259
1068.0259 1068.0259
K 33 =
1068 . 0259 3081 . 9148
1068.0259 1068.02590 0 0
K 44 = +
1068.02590 1068.0259 0 2013.8889
1068.0259 1068.0259
K 44 =
1068 . 0259 3081 . 9148
Matriz de Rigidez de la Estructura ( 8 x 8 )
3081.9148 1068.0259 2013.8889 0 0 0 1068.0259 1068.0259
2013.888 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 3081.9148 0 0 0
2013.888 0 3081.9148 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 0 0
K =
0 0 1068 .0259 3081 .9148 1068 .0259 1068 .0259 0 2013 .889
0 0 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 0 0
0 2013.888 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 3081.9148 0 0
1068.0259 1068.0259 0 0 0 0 1068.0259 1068.0259
1068.0259 1068.0259 0 2013.8889 0 0 1068.0259 3081.9148
Clculo de los desplazamientos en los nodos libres
(U a ) = (K aa )1(Pa )
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 6 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
U1x 3081.9148 1068.0259 2013.8889 0
1
5 4.1117 x103
U 1068.0259 3081.9148 3
(U a ) = U1y =
0 0 0 = 1.4247 x10
0 3.0531x103
2 x 2013.8889 0 3081.9148 1068.0259
U 2 y
0 0 1068.0259 3081.9148 0 1.058x103
Clculo de fuerzas en elementos (coordenadas locales)
( pi ) = (i )(Pi ) = (i )(K )i (Ui )
Elemento 1
p1x 1 0 0 0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889 0 4.1117 x103 2.1426
p 0 0 1.4247 x103
( p1) = p1y =
1 0 0 0 01 0 0
=
2x 0 0 1 0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889 0 3.0531x103 2.1426
p2 y 0 1 0 1.058x103
0 0 0 0 0
0
Elemento 2
p1x 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 4.1117 x103 2.8692
p1y 0 0 0 0 0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889 1.4247 x103
( p2 ) = p =
0
=
3x 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 2.8692
p3 y 0 0 0 0 0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889
0
0
Elemento 3
p1x 0.7071 0.7071 0 0 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 4.1117 x103 4.0585
p1y 0.70710 0.7071 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1.4247 x103
( p3) = p =
0 0 0
=
4x 0 0 0.7071 0.7071 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 0
4.0585
p4 y 0 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
0 0. 7071 0 .7071 0
0
Elemento 4
p2 x 0.7071 0.7071 0 0 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 3.0531x103 3.0134
p2 y 0.70710 0.7071 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1.058x103
( p4 ) = p = 0 0
=
0
3x 0 0 0.7071 0.7071 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259 0
3.0134
p3 y 1068.0259 1068.0259 1068.0259
0 0 0. 7071 0. 7071 1068.0259 0
0
Elemento 5
p2 x 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.0531x103 2.1307
p 0 0 0 2013.8889 1.058x103
( p5 ) = p2 y =
0 0 0 2013.8889 0
=
4x 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0
2.1307
p4 y 0 0 0 0 0 2013.8889 0 2013.8889
0
0
REACCIONES
(Pb ) = (Kba )(U a ) = (Kba )(K aa )1(Pa )
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 7 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
R3x 0 0 1068.0280 1068.0280 4.1117 x103 2.1308
R3 y 2013.8889 1068.0280 1068.0280 1.4247 x103 5.0002
(Pb ) = R =
0
=
4 x 1068.0280 1068.0280 0 0 3
3.0531x10 2.8697
R4 y 1068.0280 1068.0280
0 2013 . 8889 1.058x103 5.0004
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 8 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Energa de Deformacin y Energa de Deformacin Complementaria
Si se tiene un incremento de esfuerzo, este produce un incremento en el desplazamiento,
dependiendo del tipo de esfuerzo es la deformacin por ejemplo cuando las deformaciones en el
elemento son lineales estas producen esfuerzos normales, asi como una deformacin angular
produce un esfuerzo cortante.
Si en el ESTADO DE ESFUERZO que se muestra en la Fig.2, nicamente acta un
esfuerzo normal x, este esfuerzo producir un incremento en la direccin "x":
yy
yx
xy
y yz zy
xx
zx xz
zz
x
z
Fig.2 Esfuerzos xyz en un paraleleppedo rectangular
El incremento de trabajo interno es igual a la fuerza por el desplazamiento:
dWi = d = ( x dy dz )(d x dx )
como dV = dx dy dz (5)
d = x d x dV
a medida de que el material se deforma desde x = 0 hasta x =x , el trabajo realizado sobre el
volumen diferencial es igual a : dU =x dx dV , a la relacin entre dU/dV se le conoce como
densidad de energa y es igual a u= dU/dV o u= x d ,si los esfuerzos son diferentes de cero, la
densidad de energa de deformacin es igual a:
= ( x d x + y d y + z d z + x y d x y + x z d x z + y z d yz )
si "y" es una funcin de desplazamiento tridimensional u= dx i +dy j +dz k y el trabajo externo es
igual a We = Px dx +Py dy +Pz dz .
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 9 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Para un material elstico lineal si las cargas se aplican en forma gradual desde cero hasta un valor
determinado de p, la energa de deformacin interna es igual a::
v
1
2 0
= x x dv
como el material es elstico lineal x = x E , si sustituimos esta ecuacin en se tiene:
v
E
= x 2 dv
20
De los mtodos geomtricos se determin que la pendiente sobre la curva elstica Fig.2 es
igual a:
L
M
= dx
0
EI
w(x)
M M
dx
Fig.2 Viga sometida a cualquier tipo de carga
ds + du
tang = = ds = de esta ecuacin:
+c
ds +c ds = ds + du
1 M 1 du
== = =
EI c ds c
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 10 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
De esta ltima ecuacin:
M d 2v
= c = c 2
EI dx
sustituyendo esta ecuacin en la energa de deformacin interna:
2 2
E d 2v E 2 d 2v
v v
= c 2 dv = c dv
2 0 dx 2 0 dx 2
si la diferencial de volumen: dv= dAdx,
2 A 2
E d 2v
l l 2
= c 2 dA dx = EI d v dx
2 0 dx 2 2 0 dx 2
0
Ecuacin de Desplazamiento para la siguiente barra con seis grados de libertad
yi yj
A, E, I j
i
Condiciones de frontera o de borde:
v(o) = yi
dv
(0) = (0) = i
dx
v( L ) = y j
dv
( L) = ( L) = j
dx
El modelo matemtico que gobierna esta barra es la ecuacin diferencial
d 4v
= w( x)
dx 4
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 11 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
en este caso w(x) nos representa una funcin de carga en la barra, para este caso como la barra
d 4v
no tiene carga w(x)=0 y la ecuacin diferencial es igual a = 0 , en esta ecuacin se puede
dx 4
encontrar una funcin de desplazamiento v que satisfaga esta ecuacin diferenciall integrando
cuatro veces por separacin de variables. v = ao + a1 x + a 2 x 2 + a3 x 3 , en esta ecuacin a0 ,a1, a2
,a3 son parmetros que se obtienen de las condiciones de frontera o borde.
De la funcin de desplazamiento, vamos a derivar esta con respecto de x para obtener la
ecuacin de la pendiente:
v = ao + a1 x + a 2 x 2 + a3 x 3
dv
= a1 + 2a 2 x + 3a3 x 2
dx
si se sustituyen las condiciones de frontera se tiene:
v(0) = y i = ao
dv
(0) = i = a1
dx
v( L) = y j = a o + a1 x + a 2 x 2 + a3 x 3
dv
(0) = j = a1 + 2a 2 L + 3a3 x 2
dx
Ordenando este sistema de ecuaciones en forma matricial se tiene:
1 0 0 0 ao yi
0 1 0 0 a1 i
=
1 L L2 L3 a 2 y j
0 1 2 L 3L2 a3 j
1
ao 1 0 0 0 yi
a1 0 1 0 0 i
a = 1 L L2 L3 y
2 j
a 0 1 2 L 3L2 j
3
la solucin de este sistema de ecuaciones es:
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 12 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
1 0 0 0
ao y
0 1 0 0 i
a1 3 2 3 1 i
a =
2 L L2 L y j
2 2L 1 j
a 1 2
3 3
L L2 L3 L2
Efectuando la multiplicacin para el clculo de estos parmetros se tiene:
ao = yi
a1 = i
3 2 3 1
a2 = yi i + 2 y j
2 j
L L L L
2 1 2 1
a3 = 3 yi + 2 i 3 y j + 2 j
L L L L
sustituyendo estos parmetros en la funcin de desplazamiento v se tiene:
3 2 3 1 2 1 2 1
v = yi + i x + 2 yi i + 2 y j j x
2
+ 3 yi + 2 i 3 y j + 2 j x
3
L L L L L L L L
agrupando trminos en funcin de los grados de libertad se tiene:
3x 2 2 x3 2 x 2 x3 3x 2 2 x3 x 2 x3
v = 1 2 + 3 yi + x 2 i+ 2 3 y j + + 2
L L L
j
L L L L L
esta ecuacin la podemos escribir de la siguiente forma:
v = N1 yi + N 2 i + N3 y j + N 4 j
en donde N1,N2,N3,N4 se les llama polinomios hermitianos:
3x 2 2 x3
N1 = 1 +
L2 L3
2 x 2 x3
N2 = x 2
L L
3x 2 2 x3
N3 =
L2 L3
x 2 x3
N4 = + 2
L L
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 13 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
En notacin matricial :
v = (N )(U )
Propiedades de los polinomios hermitianos:
En el nodo i
yi = 1 .y j = i = j = 0
i =1 . yi = y j = j = 0
En el nodo j
yj =1 . yi = i = j = 0
j =1 . yi = y j = i = 0
yi + y j = 1 para cualquier valor de x
derivando dos veces con respecto de x la funcin de desplazamiento v
dv dN
= (U )
dx dx
d 2v d 2 N
= (U ) = ( B)(U )
dx 2 dx 2
elevando esta ecuacin al cuadrado y aprovechando las propiedades de simetra de los polinomios
hermitianos se tiene:
2
d 2v
= (U )t (B )t (B )(U )
dx 2
Sustituyendo esta ecuacin en la energa de deformacin interna se tiene:
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 14 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
L 2 2 L
(U ) (B ) (B )(U )dx
EI d v dx = EI
= dx 2
t t
2 0 2 0
(U )
t L
EI (B )t (B )dx (U )
2 0
=
de esta ecuacin
L
k i = EI (B )t (B )dx = matriz de rigidez del elemento en forma desglosada:
0
B12 B1B2 B1B3 B1B4
L
B22
k = EI 2 1
i B B B2 B3 B2 B4
dx
B B B3 B2 B32 B3 B4
0 3 1
B4 B1 B4 B2 B4 B3 B42
Aplicando el paquete MATHEMATICA para la obtencin de los trminos Bi Bj
B1=D[1-3x^2/l^2+2x^3/l^3,{x,2}]
-6 12 x
-- + ----
2 3
l l
Integrate[B1^2,{x,0,l}]
12
--
3
l
B1=D[1-3x^2/l^2+2x^3/l^3,{x,2}]
-6 12 x
-- + ----
2 3
l l
B2=D[x-2x^2/l+x^3/l^2,{x,2}]
-4 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
K12=(-6/l^2+12x/l^3)(-4/l+6x/l^2)
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 15 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
-6 12 x -4 6 x
(-- + ----) (-- + ---)
2 3 l 2
l l l
Expand[K12]
2
24 84 x 72 x
-- - ---- + -----
3 4 5
l l l
Integrate[K12,{x,0,l}]
6
--
2
l
K22=(-4/l+6x/l^2)^2
-4 6 x 2
(-- + ---)
l 2
l
Expand[K22]
2
16 48 x 36 x
-- - ---- + -----
2 3 4
l l l
Integrate[K22,{x,0,l}]
4
-
l
B1=D[1-3x^2/l^2+2x^3/l^3,{x,2}]
-6 12 x
-- + ----
2 3
l l
B3=D[3x^2/l^2-2x^3/l^3,{x,2}]
6 12 x
-- - ----
2 3
l l
K13=(-6/l^2+12x/l^3)(6/l^2-12x/l^3)
6 12 x -6 12 x
(-- - ----) (-- + ----)
2 3 2 3
l l l l
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 16 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Integrate[K13,{x,0,l}]
-12
---
3
l
B1
-6 12 x
-- + ----
2 3
l l
B3=D[-x^2/l+x^3/l^2,{x,2}]
-2 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
K14=(-6/l^2+12x/l^3)(-2/l+6x/l^2)
-6 12 x -2 6 x
(-- + ----) (-- + ---)
2 3 l 2
l l l
Integrate[K14,{x,0,l}]
6
--
2
l
B3
6 12 x
-- - ----
2 3
l l
K33=(6/l^2-12x/l^3)^2
6 12 x 2
(-- - ----)
2 3
l l
Integrate[K33,{x,0,l}]
12
--
3
l
B1
-6 12 x
-- + ----
2 3
l l
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 17 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
B4=D[-x^2/l+x^3/l^2,{x,2}]
-2 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
K14=(-6/l^2+12x/l^3)(-2/l+6x/l^2)
-6 12 x -2 6 x
(-- + ----) (-- + ---)
2 3 l 2
l l l
Integrate[K14,{x,0,l}]
6
--
2
l
B2=D[x-2x^2/l+x^3/l^2,{x,2}]
-4 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
B3
-2 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
K23=(-4/l+6x/l^2)(-2/l+6x/l^2)
-4 6 x -2 6 x
(-- + ---) (-- + ---)
l 2 l 2
l l
Integrate[K23,{x,0,l}]
2
-
l
B4
-2 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
B2
-4 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 18 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
K24=(-2/l+6x/l^2)(-4/l+6x/l^2)
-4 6 x -2 6 x
(-- + ---) (-- + ---)
l 2 l 2
l l
Integrate[K24,{x,0,l}]
2
-
l
B4
-2 6 x
-- + ---
l 2
l
K44=B4^2
-2 6 x 2
(-- + ---)
l 2
l
Integrate[K44,{x,0,l}]
4
-
l
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DEL ELEMENTO EN COORDENADAS LOCALES
1 3
2 A, E, I 4
12 EI 6 EI 12 EI 6 EI
L3 L2 L3 L2
6 EI 4 EI 6 EI 2 EI
k =
i L2 L L2 L
12 EI 6 EI 12 EI 6 EI 2
L3 L2 L3 L
6 EI 2 EI 6 EI 4 EI
L2 L L2 L
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 19 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
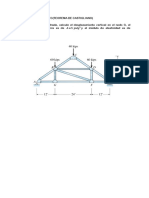
Para la siguiente estructura, determine el valor de las fuerzas en los elementos y las reacciones.
1 2 3 4
3 k/pie
0.5 k/pie
30WF108 33WF118 30WF108
144
12WF87 12WF120 12WF12O 12WF87
360 540 360
5 6 7 8
GRADOS DE LIBERTAD DE LA ESTRRUCTURA
2 1 25 3 4
8
11
3 6 9 12
10
1 4 7
1 3 5
4 7
6
14 17 20
2 23
15 18 21
13 16 19 22
24
5 6 7 8
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 20 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Topologa estructural
ELEMENTO INICIO TERMINO PERFIL LONG. AREA INERCIA E
PULG PULG PULG4 KIPS/PULG
1 1 2 30WF108 360 31.7 5770 30000
2 1 5 12WF87 144 25.6 740 30000
3 2 3 33WF118 540 34.7 5900 30000
4 2 6 12WF120 144 35.3 1070 30000
5 3 4 30WF108 360 31.7 5770 30000
6 3 7 12WF120 144 35.3 1070 30000
7 4 8 12WF87 144 25.6 740 30000
Matriz de Rigidez del elemento en coordenadas locales:
AE 0 0 AE 0 0
L L
0 12 EI 6 EI 0 12 EI 6 EI
L3 L2 L3 L2
0 6 EI 4 EI 6 EI 2 EI
( )
0
k =
i L2 L L2 L
AE 0 0 AE 0 0
L L
0 12 EI 3 6 EI 0 12 EI 6 EI 2
L L2 L3 L
0 6 EI 2 EI 0 6 EI 4 EI
L2 L L2 L
Matriz de rotacin
c s 0 0 0 0
s c 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
( ) =
0 0 0 c s 0
0 0 0 s c 0
0 0 0 0 0 1
Matriz de rigidez en coordenadas globales:
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 21 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
( K ) i = ( )t (k i )( )
AE 0 0 AE 0 0
L L
c s 0 0 0 0 0 12 EI 6 EI 0 12 EI 6 EI c s 0 0 0 0
L3 L2 L3 L2 s c
s c 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 EI 4 EI 6 EI 2 2 EI
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 L2 L
0
L 0 0 1 0 0 0
( K )i = AE L
0 AE 0 0 s 0
0 0 0 c s
L
0 0
L
0 0
0 c
0 0 0 s c
0 0 c 0
12 EI 3 6 EI 0 12 EI 6 EI 2 0 0 0 s
L L2 L3
L 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1
0 4 EI
0 0 0 1
6 EI 2 EI 0 6 EI
L2 L L2 L
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DE LA ESTRUCTURA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1
K aa + K aa
2
K 1ab 0 0 2
K ab 0 0 0 1
K1 1
K bb + K aa
3
+ K aa
4 3
K ab 0 0 4
K ab 0 0 2
ba
0 3
K ba 3
K bb + K aa
5
+ K aa
6 5
K ab 0 0 6
K ab 0 3
(K ) = 0 0 5
K ba 5
K bb + K aa
7
0 0 0 7
K ab 4
K ba 2
0 0 0 2
K bb 0 0 0 5
4 4
0 K ba 0 0 0 K bb 0 0 6
0 0 6
K ba 0 0 0 6
K bb 0 7
0 0 0 7
K ba 0 0 0 7
K bb 8
Matriz de Rigidez de nodos libres
1 2 3 4
K1 + K 2 K 1ab 0 0 1
aa aa
Kaa = 1
K ba 1
K bb + K aa
3
+ K aa
4 3
K ab 0 2
0 3
K ba 3
K bb + K aa
5
+ K aa
6 5
K ab 3
0 0 5
K ba 5
K bb + K aa
7
4
Cada submatriz es de orden de 3x3
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 22 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Utilizando el programa STACKER se generan las matrices de rigidez en coordenadas locales y
globales del elemento as como la matriz de rotacin de ejes-
Element 1
Length,Area,theta,I,E
360,31.7,0,5770,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u1',v1',t1',u2',v2',t2',,,,,,,,,u1,v1,t1,u2,v2,t2,,FEE'
2642, 0, 0,-2642, 0, 0,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 2641.66666666667, 0, 0,-
2641.66666666667, 0, 0,,0
0, 44.52, 8014, 0,-44.52, 8014,, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 44.5216049382716,
8013.88888888889, 0,-44.5216049382716, 8013.88888888889,,-7.5
0, 8014, 1923333, 0,-8014, 961667,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 0,
8013.88888888889, 1923333.33333333, 0,-8013.88888888889,
961666.666666667,,450
-2642, 0, 0, 2642, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,,-2641.66666666667, 0, 0,
2641.66666666667, 0, 0,,0
0,-44.52,-8014, 0, 44.52,-8014,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,, 0,-44.5216049382716,-
8013.88888888889, 0, 44.5216049382716,-8013.88888888889,,-7.5
0, 8014, 961667, 0,-8014, 1923333,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 0,
8013.88888888889, 961666.666666667, 0,-8013.88888888889,
1923333.33333333,,-450
Element 2
Length,Area,theta,I,E
144,25.6,270,740,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u1',v1',t1',u5',v5',t5',, , , , , , ,,u1,v1,t1,u5,v5,t5,,FEE'
5333, 0, 0,-5333, 0, 0,, 0,-1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 89.2168209876543, 0,
6423.61111111111,-89.2168209876543, 0, 6423.61111111111,,0
0, 89.22, 6424, 0,-89.22, 6424,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 5333.33333333333,
0, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0,,-67.50
0, 6424, 616667, 0,-6424, 308333,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 6423.61111111111, 0,
616666.666666667,-6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333,,6075
-5333, 0, 0, 5333, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 0,-1, 0,,-89.2168209876543, 0,-
6423.61111111111, 89.2168209876543, 0,-6423.61111111111,,0
0,-89.22,-6424, 0, 89.22,-6424,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,, 0,-5333.33333333333,
0, 0, 5333.33333333333, 0,,-67.50
0, 6424, 308333, 0,-6424, 616667,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 6423.61111111111, 0,
308333.333333333,-6423.61111111111, 0, 616666.666666667,,-6075
Element 3
Length,Area,theta,I,E
540,34.7,0,5900,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u2',v2',t2',u3',v3',t3',, , , , , , ,,u2,v2,t2,u3,v3,t3,,FEE'
1928, 0, 0,-1928, 0, 0,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 1927.77777777778, 0, 0,-
1927.77777777778, 0, 0,,0
0, 13.49, 3642, 0,-13.49, 3642,, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 13.4887974394147,
3641.97530864198, 0,-13.4887974394147, 3641.97530864198,,
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 23 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
0, 3642, 1311111, 0,-3642, 655556,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 0,
3641.97530864198, 1311111.11111111, 0,-3641.97530864198, 655555.555555556,,
-1928, 0, 0, 1928, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,,-1927.77777777778, 0, 0,
1927.77777777778, 0, 0,,
0,-13.49,-3642, 0, 13.49,-3642,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,, 0,-13.4887974394147,-
3641.97530864198, 0, 13.4887974394147,-3641.97530864198,,
0, 3642, 655556, 0,-3642, 1311111,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 0,
3641.97530864198, 655555.555555556, 0,-3641.97530864198, 1311111.11111111,,
Element 4
Length,Area,theta,I,E
144,35.3,270,1070,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u2',v2',t2',u6',v6',t6',, , , , , , ,,u2,v2,t2,u6,v6,t6,,FEE'
7354, 0, 0,-7354, 0, 0,, 0,-1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 129.002700617284, 0,
9288.19444444445,-129.002700617284, 0, 9288.19444444445,,0
0, 129, 9288, 0,-129, 9288,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 7354.16666666667, 0,
0,-7354.16666666667, 0,,
0, 9288, 891667, 0,-9288, 445833,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 9288.19444444445, 0,
891666.666666667,-9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333,,
-7354, 0, 0, 7354, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 0,-1, 0,,-129.002700617284, 0,-
9288.19444444445, 129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445,,
0,-129,-9288, 0, 129,-9288,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,, 0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0,
7354.16666666667, 0,,
0, 9288, 445833, 0,-9288, 891667,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 9288.19444444445, 0,
445833.333333333,-9288.19444444445, 0, 891666.666666667,,
Element 5
Length,Area,theta,I,E
360,31.7,0,5770,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u3',v3',t3',u4',v4',t4',, , , , , , ,,u3,v3,t3,u4,v4,t4,,FEE'
2642, 0, 0,-2642, 0, 0,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 2641.66666666667, 0, 0,-
2641.66666666667, 0, 0,,0
0, 44.52, 8014, 0,-44.52, 8014,, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 44.5216049382716,
8013.88888888889, 0,-44.5216049382716, 8013.88888888889,,
0, 8014, 1923333, 0,-8014, 961667,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 0,
8013.88888888889, 1923333.33333333, 0,-8013.88888888889, 961666.666666667,,
-2642, 0, 0, 2642, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,,-2641.66666666667, 0, 0,
2641.66666666667, 0, 0,,
0,-44.52,-8014, 0, 44.52,-8014,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,, 0,-44.5216049382716,-
8013.88888888889, 0, 44.5216049382716,-8013.88888888889,,
0, 8014, 961667, 0,-8014, 1923333,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 0,
8013.88888888889, 961666.666666667, 0,-8013.88888888889, 1923333.33333333,,
Element 6
Length,Area,theta,I,E
144,35.3,270,1070,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u3',v3',t3',u7',v7',t7',, , , , , , ,,u3,v3,t3,u7,v7,t7,,FEE'
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 24 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
7354, 0, 0,-7354, 0, 0,, 0,-1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 129.002700617284, 0,
9288.19444444445,-129.002700617284, 0, 9288.19444444445,,0
0, 129, 9288, 0,-129, 9288,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 7354.16666666667, 0,
0,-7354.16666666667, 0,,
0, 9288, 891667, 0,-9288, 445833,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 9288.19444444445, 0,
891666.666666667,-9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333,,
-7354, 0, 0, 7354, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 0,-1, 0,,-129.002700617284, 0,-
9288.19444444445, 129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445,,
0,-129,-9288, 0, 129,-9288,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,, 0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0,
7354.16666666667, 0,,
0, 9288, 445833, 0,-9288, 891667,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 9288.19444444445, 0,
445833.333333333,-9288.19444444445, 0, 891666.666666667,,
Element 7
Length,Area,theta,I,E
144,25.6,270,740,30000
Local Element Matrix,,,,,,,Transformation Matrix,,,,,,,Global Element
Matrix,,,,,,,FEE Vector
u4',v4',t4',u8',v8',t8',, , , , , , ,,u4,v4,t4,u8,v8,t8,,FEE'
5333, 0, 0,-5333, 0, 0,, 0,-1, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 89.2168209876543, 0,
6423.61111111111,-89.2168209876543, 0, 6423.61111111111,,0
0, 89.22, 6424, 0,-89.22, 6424,, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,, 0, 5333.33333333333,
0, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0,,
0, 6424, 616667, 0,-6424, 308333,, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,, 6423.61111111111, 0,
616666.666666667,-6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333,,
-5333, 0, 0, 5333, 0, 0,, 0, 0, 0, 0,-1, 0,,-89.2168209876543, 0,-
6423.61111111111, 89.2168209876543, 0,-6423.61111111111,,
0,-89.22,-6424, 0, 89.22,-6424,, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,, 0,-5333.33333333333,
0, 0, 5333.33333333333, 0,,
0, 6424, 308333, 0,-6424, 616667,, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,, 6423.61111111111, 0,
308333.333333333,-6423.61111111111, 0, 616666.666666667,,
Global Structure Stiffness Matrix
,u 1,v 1,t 1,u 2,v 2,t 2,u 3,v 3,t 3,u 4,v 4,t 4,u 5,v 5,t 5,u 6,v 6,t 6,u
7,v 7,t 7,u 8,v 8,t 8,,,, FEE,
PX 1, 2730.88348765432, 0, 6423.61111111111,-2641.66666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0,-89.2168209876543, 0, 6423.61111111111, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0,,,PX 1,-67.5,
PY 1, 0, 5377.8549382716, 8013.88888888889, 0,-44.5216049382716,
8013.88888888889, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 1,-7.5,
MZ 1, 6423.61111111111, 8013.88888888889, 2540000, 0,-8013.88888888889,
961666.666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,MZ 1,6525,
PX 2,-2641.66666666667, 0, 0, 4698.44714506173, 0, 9288.19444444445,-
1927.77777777778, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-129.002700617284, 0,
9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PX 2, 0,
PY 2, 0,-44.5216049382716,-8013.88888888889, 0, 7412.17706904435,-
4371.91358024691, 0,-13.4887974394147, 3641.97530864198, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 2,-7.5,
MZ 2, 0, 8013.88888888889, 961666.666666667, 9288.19444444445,-
4371.91358024691, 4126111.11111111, 0,-3641.97530864198, 655555.555555556,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0,,,MZ 2,-450,
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 25 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
PX 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2770.66936728395, 0, 9288.19444444445,-
2641.66666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-129.002700617284, 0,
9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0,,,PX 3, 0,
PY 3, 0, 0, 0,-1927.77777777778, 0, 0, 1927.77777777778, 7398.68827160494,
8013.88888888889, 0,-44.5216049382716, 8013.88888888889, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 3, 0,
MZ 3, 0, 0, 0, 0,-13.4887974394147,-3641.97530864198, 9288.19444444445,
8027.3776863283, 2811358.02469136, 0,-8013.88888888889, 961666.666666667,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333, 0, 0, 0,,,MZ 3, 0,
PX 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3641.97530864198, 655555.555555556, 0,-3641.97530864198,
1311111.11111111, 89.2168209876543, 0, 6423.61111111111, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0,-89.2168209876543, 0, 6423.61111111111,,,PX 4,0,
PY 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-2641.66666666667, 0, 0, 2641.66666666667,
5333.33333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0,,,PY
4,0,
MZ 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-44.5216049382716,-8013.88888888889,
6423.61111111111, 44.5216049382716, 608652.777777778, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0,-6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333,,,MZ 4,0,
PX 5,-89.2168209876543, 0,-6423.61111111111, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8013.88888888889,
961666.666666667, 0,-8013.88888888889, 1923333.33333333, 89.2168209876543,
0,-6423.61111111111, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PX 5,-67.5,
PY 5, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
5333.33333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 5, 0,
MZ 5, 6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-
6423.61111111111, 0, 616666.666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,MZ 5,-
6075,
PX 6, 0, 0, 0,-129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PX 6, 0,
PY 6, 0, 0, 0, 0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 6, 0,
MZ 6, 0, 0, 0, 9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 891666.666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,MZ 6, 0,
PX 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 129.002700617284, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 0, 0,,,PX 7, 0,
PY 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 7354.16666666667, 0, 0, 0, 0,,,PY 7, 0,
MZ 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 9288.19444444445, 0, 445833.333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-9288.19444444445, 0, 891666.666666667, 0, 0, 0,,,MZ 7, 0,
PX 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-89.2168209876543, 0,-6423.61111111111, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 89.2168209876543, 0,-6423.61111111111,,,PX 8, 0,
PY 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-5333.33333333333, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 5333.33333333333, 0,,,PY 8,0,
MZ 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6423.61111111111, 0, 308333.333333333, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,-6423.61111111111, 0, 616666.666666667,,,MZ 8,0,
Matriz de Rigidez del elemento 1= elemento 5
( coordenadas locales )
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 26 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0
0 44.52 8013 . 88 0 44 . 52 8013 .88
8013.88 961666.67
(k )i = (k )5 =
0 8013.88 1923333.33 0
2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0
0 44 .52 8013 . 88 0 44. 52 8013 .88
8013.88 1923333.33
0 8013.88 961666.67 0
Matriz de rotacin del elemento 1= elemento 5
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0
(1) = (5 ) =
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 1
0 0 0 0
Matriz de rotacin del elemento 1= elemento 5
( coordenadas globales )
2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0
0 44.52 8013.88 0 44.52 8013.88
8013.88 961666.67
(K )i = (K )5 =
0 8013.88 1923333.33 0
2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0
0 44 . 52 8013. 88 0 44.52 8013. 88
8013.88 1923333.33
0 8013.88 961666.67 0
Matriz de Rigidez del elemento 2 = elemento 7
( coordenadas locales )
5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0 0
0 89.22 6423.61 0 89.22 6423.61
6423.61 308333.33
(k )2 = (k )7 =
0 6423.61 616666.66 0
5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0 0
0 89.22 6423.61 0 89.22 6423.61
6423.61 616666.66.
0 6423.61 308333.33 0
Matriz de rotacin del elemento 2 = elemento 7
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0
( 2 ) = ( 7 ) =
1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1
0 0 0
Matriz de Rigidez del elemento 2 = elemnto 7
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 27 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
( coordenadas globales )
89.22 0 6423.61 89.22 0 6423.61
0 5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0
6423.61
(K )2 = (K )7 =
0 616666. 67 6423 . 61 0 308333.33
89.22 0 6423.61 89.22 0 6423.61
0 5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0
6423.61 308333.33 6423.61 616666.67
0 0
Matriz de Rigudez del elemento 3
( coordenadas locales )
1927.77 0 0 1927.77 0 0
0 13.49 3641.98 0 13.49 3641.98
3641.98 655555.55
(k )3 =
0 3641.98 1311111.11 0
1927.77 0 0 1927.77 0 0
0 13.49 3641. 98 0 13. 49 3641.98
3641.98 1311111.11
0 3641.98 655555.55 0
Matriz de rotacin del elemento 3
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0
( 3 ) =
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 1
0 0 0 0
Matriz de rigidez del elemento 3
( coordenadas globales )
1927.77 0 0 1927.77 0 0
0 13.49 3641.98 0 13.49 3641.98
3641.98 655555.55
(K )3 =
0 3641.98 1311111.11 0
1927.77 0 0 1927.77 0 0
0 13.49 3641.98 0 13.49 3641.98
3641.98 1311111.11
0 3641.98 655555.55 0
Matriz de Rigudez del elemento 4 = elemento 6
( coordenadas locales )
7354.16 0 0 7354.16 0 0
0 129.00 9288.19 0 129.00 9288.19
9288.19 445833.33
(k )4 = (k )6 =
0 9288.19 891666.67 0
7354.16 0 0 7354.16 0 0
0 129.00 9288.19 0 129.00 9288.19
9288.19 891666.67
0 9288.19 445833.33 0
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 28 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Matriz de rotacin del elemento 4 = elemento 6
0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0
( 4 ) = ( 6 ) =
1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1
0 0 0
Matriz de Rigidez del elemento 4 = elemento 6
( coordenadas globales )
129.00 0 9288.19 129.00 0 9288.19
0 7354.16 0 0 7354.16 0
9288.19
(K ) = (K ) =
4 6 0 891666.67 9288 .19 0 445833 . 33
129.00 0 9288.19 129.00 0 9288.19
0 7354.16 0 0 7354.16 0
9288.19 445833.33 9288.19 891666.67
0 0
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DE LOS NODOS LIBRES K aa
2730.88 0 6423.61 2641.67 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 5377.85 8013.88 0 44.52 8013.88 0 0 0 0 0 0
6423 .61 8013 .88 2540000 0 8013 . 88 961666 .67 0 0 0 0 0 0
2641.67 0 0 4698.45 0 9288.19 1927.77 0 0 0 0 0
0 44.52 8013.88 0 7412.18 4371.91 0 13.49 3641.98 0 0 0
8013.88 961666.67 9288.19 4371.91 4126111.11 3641.98 655555.55
(K aa )=
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1927.77 0 0 4698.45 0 9288.19 2641.66 0 0
0 0 0 0 13.490 3641.98 0 7398.69 4371.91 0 44.52 8013.88
0 0 0 0 3641.98 655555.55 9288.19 4371.91 4126111.11 0 8013.88 961666.67
0 0 0 0 0 0 2641.66 0 0 2730.89 0 6423.61
5333.33 8013.88
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 44.52 8013.88 0
8013.88 2540000
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8013 .88 961666 .67 6423 . 61
Fuerzas nodales equivalenetes en los elementos
Elemento 1
w l2
= 450 k pu lg
12
wl
= 7.50 kips
2
w l2
= 450 k pu lg
12
wl
= 7.50 kips
2
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 29 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Elemento 3
w l2
= 6075 k pu lg
12
wl
= 67.50 kips
2
w l2
= 6075 k pu lg
12
wl
= 67.50 kips
2
1 2 3 4
7.5 k 7.5 k 67.5 k 67.5 k
450 450 6075 6075
kip-pulg kip-pulg kip-pulg kip-pulg
5 6 7 8
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 30 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
Sistema de fuerzas en los nodos libres (Pa )
1 2 3 4
7.5 kips 75.0 kips
450 k-pulg 562.50 k-pulg 607.50 k-pulg
5 6 7 8
Clculo de los desplazamientos en los nodos no restringidos
2730.88 0 6423.61 2641.67 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0
0 5377.85 8013.88 0 44.52 8013.88 0 0 0 0 0 0 7.5
6423 .61 8013 .88 2540000 0 8013 .88 961666.67 0 0 0 0 0 0 450
2641.67 0 0 4698.45 0 9288.19 1927.77 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 44.52 8013.88 0 7412.18 4371.91 0 13.49 3641.98 0 0 0 7.5
8013.88 961666.67 9288.19 4371.91 4126111.11 3641.98 655555.55 562.5
(U a ) =
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1927.77 0 0 4698.45 0 9288.19 2641.66 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 13.490 3641.98 0 7398.69 4371.91 0 44.52 8013.88 67.5
0 0 0 0 3641.98 655555.55 9288.19 4371.91 4126111.11 0 8013.88 961666.67 607.5
0 0 0 0 0 0 2641.66 0 0 2730.89 0 6423.61 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 44.52 8013.88 0 5333.33 8013.88 0
0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8013 . 88 961666.67 6423 .61 8013.88 2540000
u1x = 0.002507545
u1y = 0.000518411
1 = 0.000464499
u 2 x = 0.003721734
u
2 y = 0.011662024
2 = 0.001813049
Ua =
u3x = 0.003100226
u = 0.010406097
3y
3 = 0.001954894
u 4 x = 0.001356534
u 4 y = 0.001786475
4 = 0.000698241
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 31 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
CLCULO DE FUERZAS EN LOS ELEMENTOS
Elemento 1
( p1 ) = ( 1 )( K )1 (U 1 ) + ( Psc 2 )
1 0 0 0 0 0 2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0 0.00251 0 3.2075
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 44.52 8013.88 0 44.52 8013.88 0.0052 7.5 2.7649
0 0 8013.88 961666.67 0.00046 450 302.5488
( p1) =
0 1 0 0 0 8013.88 1923333.33 0
+ =
0 0 0 1 0
0 2641.66 0 0 2641.66 0 0 0.00372 0 3.2075
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 44.52 8013.88 0 44.52 8013.88 0.01166 7.5 17.7649
0 1 8013.88 1923333.33 0.00181 450 3392.7914
0 0 0 0 0 8013.88 961666.67 0
17.7649
302.55
3392.7914
3.2075
3.2075
2.7649
Elemento 2
( p 2 ) = ( 2 )( K ) 2 (U 2 )
0 1 0 0 0 0 89.22 0 6423.61 89.22 0 6423.61 0.0025 2.7649
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0 0.000518 3.2075
0 0 1 0 0 0 6423.61 0 616666.67 6423.61 0 308333.33 0.000464 302.5488
( p2 ) = =
0 0 0 0 1 0 89.22 0 6423.61 89.22 0 6423.61 0 2.7649
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 5333.33 0 0 5333.33 0 0 3.2075
0 0 308333.33 6423.61
0 0 0 1 6423.61 0 0 616666.67 0 159.3282
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 32 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
2.7649
3.2075
302.55
2.7649
3.2075
159.3282
De una manera anloga se pueden obtener las dems fuerzas en los elementos
1 2 3 4
302.55 439.796
3392.79 4974.86 4705.05 2990.72
1582.067 1714.32
773.75 842.76 224.004
159.328
5 6 7 8
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 33 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
ANLISIS ESTRUCTURAL METODO MATRICIAL DE RIGIDECES
JOS ANTONIO MARTNEZ LPEZ 34 OCTUBRE DEL 2001
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Losas Con Cargas ConcentradasDocument7 pagesLosas Con Cargas Concentradasjose2017100% (1)
- Act2 - 16040887Document14 pagesAct2 - 16040887jose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Armadura Con Metodo de Rigideces Hernan Hernandez RamirezDocument13 pagesArmadura Con Metodo de Rigideces Hernan Hernandez Ramirezjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Act2 - 17040150Document88 pagesAct2 - 17040150jose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Propiedades DinámicasDocument8 pagesPropiedades Dinámicasjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Armadura FinalDocument13 pagesArmadura Finaljose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problema Método de FlexibilidadesDocument34 pagesProblema Método de Flexibilidadesjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo de Armaduras Aplicando El Método de Rigideces. de La Cruz CastroDocument30 pagesTrabajo de Armaduras Aplicando El Método de Rigideces. de La Cruz Castrojose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mapa Conceptual PlacasDocument1 pageMapa Conceptual Placasjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mapa Mental - Teoría Clásica de PlacasDocument1 pageMapa Mental - Teoría Clásica de Placasjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Resueltos Analisis Est AvanzadoDocument9 pagesProblemas Resueltos Analisis Est Avanzadojose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Movimieto en La Base Del SueloDocument2 pagesMovimieto en La Base Del Suelojose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Estructura Mapa CognitivoDocument1 pageEstructura Mapa Cognitivojose2017100% (1)
- Problema Propuesto CastiglianoDocument1 pageProblema Propuesto Castiglianojose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Examen de AdmisiónDocument29 pagesExamen de Admisiónjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculo Del Peralte PDFDocument3 pagesCalculo Del Peralte PDFjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Losas PerimetralesDocument11 pagesLosas Perimetralesjose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Propuestos (Deformaciones)Document1 pageProblemas Propuestos (Deformaciones)jose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integral de DuhamelDocument4 pagesIntegral de Duhameljose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Secciones T y LDocument13 pagesSecciones T y Ljose2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3-Protección 51N-50N - CaracterísticasDocument2 pages5.3-Protección 51N-50N - Característicasheder.gajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagramas de Ellingham para CO y CO2Document5 pagesDiagramas de Ellingham para CO y CO2Jack QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Elvie-Pump Manual SpanishDocument18 pagesElvie-Pump Manual SpanishAlejandro Gonzalez BenitezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Simbología y Diagramas de InstrumentaciónDocument33 pages4 Simbología y Diagramas de InstrumentaciónClark Isaac Velasquez MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- p6 QuimicaDocument16 pagesp6 QuimicaBrandon Daniel Bobadilla LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Diccionario de La Construccion Materiales1Document55 pagesDiccionario de La Construccion Materiales1Angie GámezPas encore d'évaluation
- RadioterapiaDocument21 pagesRadioterapiaIgnacio AndrésPas encore d'évaluation
- Caso Practico 2 Desarrollo y Negocios SosteniblesDocument12 pagesCaso Practico 2 Desarrollo y Negocios Sosteniblespronature infoPas encore d'évaluation
- Proyecto Andrea S. JavierDocument28 pagesProyecto Andrea S. Javieranibal chavez zeballosPas encore d'évaluation
- Reprogramación de La Operación DiariaDocument2 pagesReprogramación de La Operación DiariaNeil Philip Galvez FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Pruebas A Transformadores de PotenciaDocument16 pagesPruebas A Transformadores de PotenciaJean CarloPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo Weleda 2013Document96 pagesCatalogo Weleda 2013Jhso TovarPas encore d'évaluation
- Proyecto Corregido Hyo SenatiDocument57 pagesProyecto Corregido Hyo SenatiElber Luis Laureano Aldana100% (1)
- Tablero de AislamientoDocument3 pagesTablero de AislamientocesarPas encore d'évaluation
- 07-Un Casco de Seguridad Puede SalvarloDocument1 page07-Un Casco de Seguridad Puede SalvarloAnalista Seguridad industrialPas encore d'évaluation
- Informe Del GeraDocument10 pagesInforme Del GeraFlorería Techi100% (2)
- Proyecto Refrigeracion 1Document12 pagesProyecto Refrigeracion 1Perico ZambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plantas AgroindustrialesDocument31 pagesPlantas AgroindustrialesWild RochaPas encore d'évaluation
- 30leroy Somer Manual Mant07 - EsDocument24 pages30leroy Somer Manual Mant07 - Esonyx_lucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Glosario de Maquinas de Inducción TrifásicasDocument13 pagesGlosario de Maquinas de Inducción TrifásicasStephen SalinasPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo Final Dibujo TecnicoDocument16 pagesTrabajo Final Dibujo Tecnicoluva lujan alvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flujo InternoDocument28 pagesFlujo InternoalexPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz Franklin ChasipantaDocument2 pagesMatriz Franklin ChasipantaFranklin ChasipantaPas encore d'évaluation
- 300663es-C Mantenimineot y RepracionDocument20 pages300663es-C Mantenimineot y RepracioncesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Valvoline Syn Power Motor Oil ILSACGradesspanish 1Document2 pagesValvoline Syn Power Motor Oil ILSACGradesspanish 1Nicolás GustavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Equipamiento v.4Document38 pagesEquipamiento v.4juan diego tezen maldonado100% (1)
- Aplicación de Los FenoliticosDocument2 pagesAplicación de Los Fenoliticosjosemgg0304Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capitulo Sobre Aspectos EconomicosDocument8 pagesCapitulo Sobre Aspectos EconomicosvodafontPas encore d'évaluation
- Pau Sept12 QuimicaDocument2 pagesPau Sept12 QuimicalincecitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Las 5 Principales Aplicaciones de Los HidrocarburosDocument5 pagesLas 5 Principales Aplicaciones de Los HidrocarburosDavid Luis GsPas encore d'évaluation