Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Organic
Transféré par
Schimmel Repelin Velud AytresogresTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Organic
Transféré par
Schimmel Repelin Velud AytresogresDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
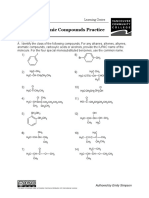
Chemistry 0871 Learning Centre
Naming Organic Compounds Practice
EXERCISES
A. Identify the class of the following compounds. For any alkanes, alkenes, alkynes,
aromatic compounds, carboxylic acids or alcohols, provide the IUPAC name of the
molecule. For the four special monosubstituted benzenes, use the common name.
1) I 8)
Br CH3
2) H2C CH3 9) H2C CH3
H3C CH CH2CH2 CH3 H3C C C CH CHCH3
H3C
3) O 10) O
H3C C CH2 CH3 H3C CH2CH2 CH2 CH
4) Cl CH3 11) O
H3C CH CH C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 HO C CH2CH2CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3 CH2CH3
5) CH 2CH 3 12) OH
CH 2CH 3 H3C CH CH CH CH3
CH3 H3C
6) CH3 13) H3C
H2C CH CH CH2 H3C C C C CH3
CH3 CH3 CH2CH3
7) O 14) H2C CH3
H3C CH C O CH3 H3C CH CH O CH2 CH3
CH3 CH3
2013 Vancouver Community College Learning Centre. Authored by
by Emily
EmilySimpson
Simpson
Student review only. May not be reproduced for classes.
B. Draw the structural formulas for the following compounds:
1) 1-pentene 7) 4-methylhexanoic acid
2) 2-methyl-3-heptyne 8) 2,3-dichloro-4-ethyl-2-hexene
3) 3-ethyl-4,5-dimethylpentane 9) 2,4-dinitrotoluene
4) 2-ethyl-1-pentanol 10) 3-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-2-pentanol
5) m-bromophenol 11) 5-chloro-4-methyl-3-heptanone
6) 3,3,6,6-tetraethyl-4-octyne 12) 3-phenyl-1-propyne
C. Draw all possible open-chain structures for the following molecular formulas and
name them:
1) C5H12
2) C5H10
3) C3H8O
2013 Vancouver Community College Learning Centre.
Student review only. May not be reproduced for classes. 2
SOLUTIONS
A. (1) aromatic compound: iodobenzene (2) alkane: 3-methylhexane (3) ketone
(4) alkane/alkyl halide: 3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,4-dimethyloctane (5) aromatic compound:
o-diethylbenzene or ortho-diethylbenzene (6) alkene: 3-methylpentene (7) ester
(8) aromatic compound: p-bromotoluene or para-bromotoluene (9) alkyne:
4-ethyl-5-methyl-2-hexyne (10) aldehyde (11) carboxylic acid: hexanoic acid
(12) alcohol: 2,4-dimethyl-3-pentanol (13) alkene: 2,4,4-trimethyl-2-hexene
(14) ether
B. (1) H2C=CHCH2CH2CH3 (2) H3CCHCCCH2CH2CH3 (3) CH3
CH3 H3CCH2CHCHCH2CH3
CH2CH3
(4) HOCH2CHCH2CH2CH3 (5) OH (6) H3CCH2 CH2CH3
CH2CH3 H3CCH2CCCCCH2CH3
Br H3CCH2 CH2CH3
(7) O=CCH2CH2CHCH2CH3 (8) C (9) CH3
OH CH3 H3CC=CCHCH2CH3 NO2
C CH2CH3
NO2
(10) H3C CH3 (11) O (12)
H3CCCCH2CH3 H3CCH2CCHCHCH2CH3
HO CH2CH3 H3C C HCCCH2
C. (1) pentane 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpropane
H3CCH2CH2CH2CH3 H3CCH2CH2CH3 CH3
CH3 H3CCH2CH3
CH3
(2) 1-pentene 2-pentene 2-methyl-1-butene
H2C=CHCH2CH2CH3 H3CCH=CHCH2CH3 H2C=CCH2CH3
CH3
3-methyl-1-butene 2-methyl-2-butene
H2C=CHCHCH3 H3CC=CHCH3
CH3 CH3
(3) 1-propanol 2-propanol methoxyethane (methyl ethyl ether)
HOCH2CH2CH3 H3CCHCH3 H3COCH2CH3
OH
2013 Vancouver Community College Learning Centre.
Student review only. May not be reproduced for classes. 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- (Open Drugs) A Complete MDMA Synthesis For The First Time ChemistDocument13 pages(Open Drugs) A Complete MDMA Synthesis For The First Time Chemistfelipecam586% (7)
- General Chemistry Questions and AnswersDocument38 pagesGeneral Chemistry Questions and AnswersGarcia RaphPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Exam QuestionsNasser Gemina PantaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rosales and Brassicales Lab ReportDocument11 pagesRosales and Brassicales Lab ReportKoreen Bayani100% (1)
- Moment of Inertia and Angular Momentum: VocabularyDocument6 pagesMoment of Inertia and Angular Momentum: VocabularybyronPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2gdgDocument4 pagesNaming Alkanes Ws 1 and Ws 2gdgusmanzubair100% (1)
- Organic Chem (Online Review)Document211 pagesOrganic Chem (Online Review)Spencer Thomas100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsNajmusawwa Aulia RahmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Meat Curing Lab ReportDocument6 pagesMeat Curing Lab ReportSaha Norrazief Abdul Hakim100% (1)
- Pharchem Lecture Chap 6Document12 pagesPharchem Lecture Chap 6Charm MatiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoichiometry HomeworkDocument10 pagesStoichiometry HomeworkFrancis TayagPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic vs Inorganic: Key DifferencesDocument2 pagesOrganic vs Inorganic: Key DifferencesMarlo Cardinez100% (1)
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument84 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsHey itsJamPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry ReviewerDocument22 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReviewerKaren Kate LozadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Electrochemistry Tutorial 1-2016Document2 pagesAdvanced Electrochemistry Tutorial 1-2016kasun1237459Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry: Bettelheim / Brown / Campbell / Farrell / TorresDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Bettelheim / Brown / Campbell / Farrell / TorresEli Jah0% (1)
- Journal-1-Molecular Modeling in Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesJournal-1-Molecular Modeling in Organic ChemistryRochelle Joyce Olmilla BersaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Informational Passages RC - ElementsDocument2 pagesInformational Passages RC - ElementsandreidmannnPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument6 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionsKyla AngellePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Lab Operations PDFDocument5 pagesBasic Lab Operations PDFErzhan OmarbekovPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Intramolecular Forces of AttractionDocument5 pagesTypes of Intramolecular Forces of AttractionGrazielle AlmazanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structural Theory of Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesThe Structural Theory of Organic ChemistryAlhely HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties and Structure of Matter and AtomsDocument8 pagesProperties and Structure of Matter and AtomsMelissa SueltoPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesSummary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundsstreetcribdealer100% (1)
- Group IV Cations Anions FlowchartsDocument2 pagesGroup IV Cations Anions FlowchartsFaith DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry - HybridizationDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry - HybridizationOyedotun TundePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM 108) M1C1 - Introduction To Chemistry-Matter and MeasurementDocument29 pages(CHEM 108) M1C1 - Introduction To Chemistry-Matter and MeasurementVladimir TimbrezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Chemistry ReviewDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Chemistry ReviewRugi Vicente Rubi100% (1)
- Intro To OrganicDocument47 pagesIntro To OrganicAlexandria Baldedara100% (1)
- Reviewer Organic Chemistry LectureDocument9 pagesReviewer Organic Chemistry LectureAlyanna Elisse Vergara100% (1)
- CH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFDocument10 pagesCH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFAnonymous caERsAPas encore d'évaluation
- CuSO4 Biuret Test for ProteinsDocument2 pagesCuSO4 Biuret Test for ProteinsChristian Villanueva100% (4)
- Classification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Hope SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsBilal Khan100% (1)
- Chem 31 Experiment 4 in Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesChem 31 Experiment 4 in Organic ChemistryBelle AnasarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoker C17 1Document15 pagesStoker C17 1yawahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment ExamDocument5 pagesAssessment ExamCristine ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocument17 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesSUBHENDU5174124Pas encore d'évaluation
- LecithinDocument14 pagesLecithinMichael UrrutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Which of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidDocument10 pagesWhich of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidCorrine PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification Tests Reveal Hydrocarbon PropertiesDocument5 pagesClassification Tests Reveal Hydrocarbon PropertiesKyle Guzman100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesDocument55 pagesLecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesS JPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry Worksheet 6Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Worksheet 6Daniel WalshPas encore d'évaluation
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument18 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureSachin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 7: Stereochemistry and PolarimetryDocument3 pagesExperiment 7: Stereochemistry and PolarimetryKeke AuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument74 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To BiologyMichael PapioPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions and Solubility ExplainedDocument64 pagesSolutions and Solubility ExplainedSohila A. MabroukPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry - AlkanesDocument87 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry - Alkanessevero97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument11 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionsNelsonMoseM100% (1)
- The Nature of Analytical ChemistryDocument18 pagesThe Nature of Analytical ChemistryAzalia Tugade PanizalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 18 - ChromatographyDocument16 pagesChapter 18 - ChromatographyJames Miller100% (1)
- Drill 1 Nomenclature of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesDrill 1 Nomenclature of CarbohydratesRuth Stephanie P. PepañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry II Chapter22Document8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Chapter22RangikaPas encore d'évaluation
- To Contain and To DeliverDocument5 pagesTo Contain and To DeliverMariel AbatayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unknown Liquid Post Organic Chemistry ExperimentDocument4 pagesUnknown Liquid Post Organic Chemistry ExperimentKyra Estorninos AldabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument33 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsCorpus, Irene Zen P.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Review Group Analytical Chemistry Solubility and Volumetric AnalysisDocument8 pagesChemistry Review Group Analytical Chemistry Solubility and Volumetric AnalysisLouisiana SollestrePas encore d'évaluation
- Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnswer KeyJames Sparrow0% (2)
- Naming Organic Compounds Practice: ExercisesDocument3 pagesNaming Organic Compounds Practice: ExercisesSk MukulPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomeculture 2Document3 pagesNomeculture 2Ram KPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For 1 Puc Students ChemistryDocument3 pagesAssignment For 1 Puc Students Chemistrykrishnabrunda72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem0871-NamingOrganicCompoundsPracticeDocument3 pagesChem0871-NamingOrganicCompoundsPracticeSeungwoo ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Chemical Education-Old MacDonald Named A Compound-Animales de Granja en Química OrgánicaDocument2 pagesJournal of Chemical Education-Old MacDonald Named A Compound-Animales de Granja en Química OrgánicaMikhangBPas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion Notes 2Document10 pagesCombustion Notes 2Schimmel Repelin Velud AytresogresPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Acids W Kas and PkasDocument2 pagesTable of Acids W Kas and PkasKawthar Mokhtar100% (1)
- Combustion Notes 2Document10 pagesCombustion Notes 2Schimmel Repelin Velud AytresogresPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistryKim Bacit100% (3)
- Specification Guide: Chrome High Temp Fittings & FlangesDocument4 pagesSpecification Guide: Chrome High Temp Fittings & FlangesAdrian EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermoplastic Materials Used in Dental PracticeDocument4 pagesThermoplastic Materials Used in Dental PracticeSamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrading of Phosphate Ores - A ReviewDocument23 pagesUpgrading of Phosphate Ores - A Reviewtrinh xuan hiepPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT III Oils and FatsDocument36 pagesUNIT III Oils and FatsShubham WarsePas encore d'évaluation
- Testing Data Chemistry Penetron AdmixDocument2 pagesTesting Data Chemistry Penetron AdmixMirza Abbas ShirazeePas encore d'évaluation
- Hose Connectors: Advantages at A Glance ApplicationsDocument12 pagesHose Connectors: Advantages at A Glance ApplicationsMani KandanPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1.1 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument101 pagesCH 1.1 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry F5 KSSMNUR FASYAREENA BINTI HASHIM MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Manual Chemical Reactions Teacher EditableDocument20 pagesSolutions Manual Chemical Reactions Teacher EditableogmightyrizzlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyrazole Ring: University of Baghdad College of PharmacyDocument17 pagesPyrazole Ring: University of Baghdad College of Pharmacyشمس صبيح عبد الرحيمPas encore d'évaluation
- NIOSH 2549 - Compuestos Orgánicos Volátiles PDFDocument8 pagesNIOSH 2549 - Compuestos Orgánicos Volátiles PDFNoe Adrianzen MPas encore d'évaluation
- MDSReport 1257675056Document4 pagesMDSReport 1257675056s.aydinPas encore d'évaluation
- ESPP Catalogue Showcases Phosphorus Recovery TechnologiesDocument14 pagesESPP Catalogue Showcases Phosphorus Recovery TechnologiesJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 4 Chem134 Lec ModuleDocument56 pagesWeek 1 4 Chem134 Lec ModuleMay Ann RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Oriental College of Pharmacy: Practice Mcqs & Answer Key T. Y. B. Pharm. Sem V (CBCS) Bphe512TcosmeticologyDocument2 pagesOriental College of Pharmacy: Practice Mcqs & Answer Key T. Y. B. Pharm. Sem V (CBCS) Bphe512TcosmeticologyRishi YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acid Structure, Properties and FunctionsDocument39 pagesAmino Acid Structure, Properties and FunctionsGirum SolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unregularized Mutagenic Effects of Azo DyesDocument13 pagesUnregularized Mutagenic Effects of Azo DyesDanish IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- App1Document15 pagesApp1Resyel Urrea PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Roasting of Copper ConcentrateDocument12 pagesPartial Roasting of Copper ConcentrateMarceloValeriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Formulae of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemical Formulae of Ionic CompoundsYoung XYeePas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry Lab - Recrystallization of AcetanilideDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab - Recrystallization of Acetanilidelalag yanPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB #1 DiffusionDocument2 pagesLAB #1 DiffusionAmelia LlewellynPas encore d'évaluation
- Report 17 Biochem CholesterolDocument2 pagesReport 17 Biochem CholesterolBožana Tomić100% (2)
- Electricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPDocument29 pagesElectricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPGunay OmarovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrometallurgy Del Cu PDFDocument528 pagesHydrometallurgy Del Cu PDFAnonymous FfIxH2o9100% (1)
- Resolução Cap 10 AtkinsDocument40 pagesResolução Cap 10 Atkinsrcrm17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 1 and 2 PATTERNSAND PROPERTIES OF METALSDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1 and 2 PATTERNSAND PROPERTIES OF METALSgiselle veneziaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5407 14148 2 PBDocument6 pages5407 14148 2 PBKhaerul IlhamPas encore d'évaluation