Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Horizontal Pan Dryer
Transféré par
Diana Isis VelascoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Horizontal Pan Dryer
Transféré par
Diana Isis VelascoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
HORIZONTAL PAN DRYER
DESIGN PROBLEM
DESIGN SELECTION
Among the different types of rotary dryer, the horizontal pan dryer was selected.
This type is heated by steam condensing in the inner surface of the shell while the material
inside the shell is being pushed on its walls by the agitator. This is appropriate because
it is used for relatively free flowing materials. It is also well-suited for low and medium
temperature operations. It has a high thermal efficiency and relatively low capital and
labor costs. (Perrys Chemical Engineering Handbook, 7th edition, sec. 12-52).
DESIGN DESCRIPTION
A pan dryer consists of a circular vessel with a flat or ellipsoidalshaped bottom;
and an agitator. Heated jackets are provided on the vessel sidewall and base. The top
head of the vessel can also be heated. The presence of an agitator provides good mixing
and efficient contact between the product and the heated vessel surfaces, including the
agitator itself. It also helps discharge the dried solids; as a large nozzle, mounted on the
side wall, is opened after a batch of operation, and the agitator arms push the product
through the opening whenever they pass by it.
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 1
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
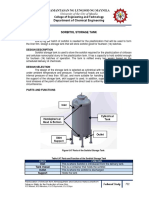
PARTS AND FUNCTION
Figure 6 Parts of a Horizontal Pan Dryer
Table 6 Parts and Function of a Horizontal Pan Dryer
PARTS FUNCTION
Feed Inlet Where the feed to be dried enters the pan dryer
Provides good mixing and efficient contact between the
Agitator/Impeller
product and the heated vessel surfaces
Steam Inlet Where the steam enters the jacket of the pan dryer vessel
Opens after every batch operation where the product is
Exit Nozzle
discharged
DESIGN ASSUMPTIONS
1. The amount of sugarcane stalks to be dried is 4000 kg/batch.
2. The initial moisture content of the feed is 10%.
3. The final moisture content of the dried sugarcane stalk is 5%.
4. The density of sugarcane stalks is 794 kg/m3.
5. The heat duty of the dryer is 1.10x106 Btu.
6. Assume an elevation of 0.5 m from the ground.
7. The dryer has cylindrical shell with ellipsoidal head and bottom.
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
1. Use a safety factor of 20% (Peters and Timmerhaus, Plant Design and Economics
for Chemical Engineers, 5th ed.).
2. The efficiency of the lap-welded joints is 70% (Peters and Timmerhaus, Plant
Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers, 5th ed.).
3. The insulating material used for the reactor is calcium silicate and the thermal
conductivity is 0.44 Btu/ft2-hr-oF (Geankoplis, Principles of Transport Processes
and Phenomena).
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 2
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
4. The length to diameter ratio of the vessel is 2 (Perrys Chemical Engineering
Handbook, 7th ed., pages 10-139).
5. The diameter of the ellipsoidal head and bottom is of the cylinder diameter.
6. The agitator used is a flat-blade turbine.
7. Agitator elevation to tank diameter is 1/3 (Geankoplis, Principles of Transport
Processes and Separation Processes, 4th ed., p. 158, Table 3.4-1).
8. Agitator width to impeller diameter is 1/5 (Geankoplis, Principles of Transport
Processes and Separation Processes, 4th ed., p. 158, Table 3.4-1).
9. Agitator length to impeller diameter is (Geankoplis, Principles of Transport
Processes and Separation Processes, 4th ed., p. 158, Table 3.4-1).
10. Use a corrosion allowance of 1/16 inch (Hesse and Rushton, Process Equipment
Design, p. 73).
11. The material of construction is carbon steel (Peters and Timmerhaus, Plant Design
and Economics, page 448, Table 10-4).
12. The density of carbon steel is 7861.09 kg/m3.
DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
1. Dryer Capacity a. Agitator Diameter
2. Geometric Configuration b. Agitator Height
a. Dryer Dimension c. Agitator Elevation
i. Dryer Diameter d. Agitator Width
ii. Dryer Height e. Agitator Length
iii. Dryer Length 4. Shell Thickness
b. Dryer Cross-Sectional 5. Shell Insulation
Area 6. Power Requirement
3. Agitator Design
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 3
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
DESIGN CALCULATIONS
1. Dryer Capacity
Compute for the dryer capacity using the equation:
=
4000
= = 5.0378 3
794 /3
Using a 20% safety factor,
V = 5.0378 m3 x 1.20 = 6.0454 m3
Use: V = 6.10 m3
2. Geometric Configuration
a. Dryer Dimension
i. Dryer Diameter
The total volume of the dryer is equal to the volume of the vessel, its top and bottom
head:
V=Vcylinder + Vhead + Vbottom
2 4
= +
4 3
Since L/D = 2 and Dhead&bottom = D,
2 4 2
= (2) + ( )
4 3 4 4
3 3
= +
2 12
7 3
=
12
7 3
6.10 3 =
12
D = 1.4931 m
Use: D = 1.5 m
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 4
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
ii. Dryer Height
Since the orientation of the cylindrical tank is horizontal, the height of the dryer is
equal to the diameter of the tank added by the 0.5 m metal support.
H = Dc + 0.5 m
H = 1.5 m + 0.5 m = 2.0 m
Use: H = 2.0 m
iii. Dryer Length
Using the L/D = 2,
L = 2Dc
L = 2(1.5 m) = 3.0 m
Use: L = 3.0 m
b. Dryer Cross-sectional Area
2
=
4
(1.5 )2
= = 1.76712
4
Use: A = 1.80 m2
3. Agitator Design
a. Agitator Diameter
From Table 3.4-1 Geometric Proportions for Standard Agitation System (Principles
of Transport Processes and Separation Processes by Geankoplis, 4th ed., p. 158):
= 0.4
where,
Da = Agitator Diameter, m
DT = Tank Diameter, m
Calculating for the diameter of the agitator:
Da = 0.4 (1.5 m) = 0.6 m
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 5
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
Use: Da = 0.6 m
b. Agitator Height
From Table 3.4-1 Geometric Proportions for Standard Agitation System (Principles
of Transport Processes and Separation Processes by Geankoplis, 4 th ed., p. 158):
=1
where,
H = Height of Agitator, m
DT = Tank Diameter, m
Calculating for the height of the agitator:
H = DT
H = 1.5 m
Use: H = 1.5 m
c. Agitator Elevation
From Table 3.4-1 Geometric Proportions for Standard Agitation System (Principles
of Transport Processes and Separation Processes by Geankoplis, 4th ed., p. 158):
1
=
3
where,
C = Elevation of Agitator, m
DT = Tank Diameter, m
Calculating for the elevation of the agitator:
C = 1/3(1.5 m)
C = 0.5 m
Use: C = 0.5 m
d. Agitator Width
From Table 3.4-1 Geometric Proportions for Standard Agitation System (Principles
of Transport Processes and Separation Processes by Geankoplis, 4th ed., p. 158):
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 6
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
1
=
5
where,
W = Width of Agitator, m
Da = Agitator Diameter, m
Calculating for the elevation of the agitator:
W = 1/5 (0.6 m) = 0.12 m
Use: W = 0.12 m
e. Agitator Length
From Table 3.4-1 Geometric Proportions for Standard Agitation System (Principles
of Transport Processes and Separation Processes by Geankoplis, 4th ed., p. 158):
1
=
4
where,
L = Length of Agitator, m
Da = Agitator Diameter, m
Calculating for the elevation of the agitator:
L = 1/4 (0.6 m) = 0.15 m
Use: L = 0.15 m
4. Shell Thickness
Shell thickness formula (Process Equipment Design, Hesse and Rushton, Eq. 4-
3, p. 85):
= +
2
where,
ts shell thickness
P internal pressure
D inside diameter of the shell
S allowable working stress
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 7
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
e joint efficiency
C corrosion allowance
Allowable Working Stress formula (Rules of Thumbs for Chemical Engineers, 4th ed.)
S = Su
Where Su workable pressure (11000 psi) for carbon steel (Process Equipment
Design, Hesse and Rushton)
S = (11000 psi) = 2750 psi
2.205 0.3048 3
= 794 3 ( ) = 49.5763 3
1 1
Internal Pressure: H=D
1
49.5763 3 32.174 2 (1.5 0.3048 )
= + = + 25 = 26.6943
144 2
32.174
2 1 2
= 26.6943
26.6943 (1500 ) 1 25.4
= + ( ) = 12.0605
(2 2750 0.70) 26.6943 16 1
ts = 12.0605
Use: ts = 12.10 mm
5. Shell Insulation
The operating temperature of the dryer is 100oC and the temperature surrounding
is assumed to be 25oC.
T = (100 25) oC = 75oC = 167oF
Using equation 10.8, from Unit operations of Chemical Engineering, 6th ed., by
McCabe, Smith, and Harriott (p. 294):
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 8
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
=
Arranging the equation and substituting the surface area of the cylinder,
= ()
where x = thickness of the insulation used.
3,28 2
(1.5 3 ( 1 ) ) 0.44 2 167
1
1,100,000 =
1.25
x = 0.0127 ft = 3.8709 mm
Use: x = 4 mm
6. Power Requirement
From Eq. 3.4-2 of Principles of Transport Processes and Separation Processes,
Geankoplis, p. 158:
=
3 5
where,
Np = power number, dimensionless
P = power, J/s
Da = impeller diameter, m
= Fluid density
N = rotational speed, rev/s
= 3 5
The power number and angular velocity for a flat-blade turbine is 7 and 50 rpm.
(Rules of Thumbs for Chemical Engineers)
1 3
= 7 794 3 (50 ) (0.6 )5 = 250.11
60
1
= 250.11 = 0.3354
745.7
Use: 0.50 hp
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 9
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS
HORIZONTAL PAN DRYER
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
Method of Operation Batch
Number of Units 1
Residence Time 75 minutes
Material Handled Sugarcane Stalks
Feed Initial Moisture Content 10%
Final Moisture Content 5%
EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATIONS
Design Parameter Proposed Existing
DRYER
Capacity 6.10 m3 4 150 m3
Cross-Sectional Area 1.80 m 2 2 -10 m2
Diameter 1.5 m 0.9 - 4.5 m
Height 2m 0.5 3 m
Length 3m 2 24.5 m
Shell Thickness 12.10 mm -
Thickness of Insulation 4 mm -
Power Requirement 0.50 hp Up to 3 hp
AGITATOR
Diameter 0.6 m 0.5 1 m
Height 1.5 m 12m
Length 0.15 m -
Width 0.12 m -
Elevation 0.5 m 0.5 1 m
MATERIALS OF CONSTRUCTION
Dryer Carbon Steel
Insulation Calcium Silicate
Agitator Carbon Steel
SUPPLIER INFORMATION
Company Name J.J. Esteban Enterprises
Company Address Daan Sarile, Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
Contact Number +63 (0916) 281-9570
E-mail Support@Jjeenterprises.com
Price Php
ACCESSORIES
Fan Centrifugal
Dryer Exhaust Control Bag Filter
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 10
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG MAYNILA
College of Engineering and Technology
Chemical Engineering Department
DESIGN CONFIGURATION
CHE 513 EQUIPMENT DESIGN | PROJECT IN EQUIPMENT DESIGN 11
Cruz | Maninang | Velasco | Villaluna
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Design and Construction of A Tunel Dryer For Food Crops DryingDocument8 pagesDesign and Construction of A Tunel Dryer For Food Crops DryingMathilda Jowito PasaribuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Muneer BeriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Prediction of Drying Uniformity in Tray Dryer System Using CFD SimulationDocument5 pagesThe Prediction of Drying Uniformity in Tray Dryer System Using CFD SimulationSiraj AL sharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Paper Recycling Machine DesignDocument6 pagesManual Paper Recycling Machine DesignLakshmanan Arunachalam100% (1)
- CFD Drying SimulationDocument6 pagesCFD Drying SimulationAdonis A. ClosasPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Yr Project Chapter 3Document19 pagesFinal Yr Project Chapter 3Moses IdokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of A Cyclone Rice DryerDocument312 pagesDevelopment of A Cyclone Rice DryerShankar AcharPas encore d'évaluation
- MicrofilterDocument23 pagesMicrofilterArrianne Jaye MataPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Paper Recycling MachineDocument6 pagesManual Paper Recycling MachineShubhamDabralPas encore d'évaluation
- Falling Head Permeability - 011Document8 pagesFalling Head Permeability - 011Bee-thumb FairusPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Washing Machine For Cleaning of Small Components: Tandale P, Shivpuje S, Ladkat S, Simran KDocument7 pagesDesign of Washing Machine For Cleaning of Small Components: Tandale P, Shivpuje S, Ladkat S, Simran Kqudus adedamolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Zhang Hang, Deng ShengxiangDocument10 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Zhang Hang, Deng ShengxiangSai Santhosh ManepallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Article 2Document6 pagesArticle 2sami Tub ftPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Reticulation Pipe Design ReportDocument24 pagesWater Reticulation Pipe Design Reportrozita kadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Engineering Design of The Spray DryerDocument6 pagesChemical Engineering Design of The Spray Dryervictor100% (2)
- FYP Presentation-Fall 2019Document11 pagesFYP Presentation-Fall 2019Salman Tariq100% (1)
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj BanhattiDocument3 pagesDesign and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj Banhattidurgesh3guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drying - Mass Transfer OperationDocument6 pagesDrying - Mass Transfer OperationShivani PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 328916782-Spray-Dryer-Design-UPDATED3 جدا جداDocument14 pages328916782-Spray-Dryer-Design-UPDATED3 جدا جداeidPas encore d'évaluation
- Indirect Dryers For Biomass Drying-Comparison of Experimental Characteristics For Drum and Rotary ConfigurationsDocument11 pagesIndirect Dryers For Biomass Drying-Comparison of Experimental Characteristics For Drum and Rotary ConfigurationsRenalyn TorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluidized Bed DryerDocument13 pagesFluidized Bed DryerjimmiePas encore d'évaluation
- Ijett V30P234Document5 pagesIjett V30P234Nyoto BagusPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of A Solar Dryer ForDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Solar Dryer ForYousup AliPas encore d'évaluation
- ICETAS 2018 Paper 142Document5 pagesICETAS 2018 Paper 142Snunkhaem EcharojPas encore d'évaluation
- 47 Sorbitol Storage Tank Oct20Document6 pages47 Sorbitol Storage Tank Oct20Karl RaymundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Olumide DryingDocument34 pagesOlumide DryingAnthony Oyindamola AdekoleoyePas encore d'évaluation
- Air Pollution Treatment MethodsDocument64 pagesAir Pollution Treatment Methodssagbvn100% (1)
- Manual Paper Recycling Machine DesignDocument6 pagesManual Paper Recycling Machine DesignJashandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- RenewableDocument222 pagesRenewableTaimur AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Rotary DryerDocument24 pages4 - Rotary DryerkhawarPas encore d'évaluation
- The International Journal of Science & Technoledge: Optimization of Water TankDocument10 pagesThe International Journal of Science & Technoledge: Optimization of Water Tanktvpavan666Pas encore d'évaluation
- 38 Ijmperddec201838Document14 pages38 Ijmperddec201838TJPRC PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and CFD Analysis of Food Dryer UsDocument14 pagesDesign and CFD Analysis of Food Dryer UsShubham kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic Can Crushing MachineDocument22 pagesPneumatic Can Crushing MachineBoopathi KalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acknowledgement: Technology and Management. Who Give The Opportunity. It Was Very Easy For Me "Document10 pagesAcknowledgement: Technology and Management. Who Give The Opportunity. It Was Very Easy For Me "Ojasv kalyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 CH 414Document38 pages2017 CH 414Mian GulshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Test Analysis 2080-03-02Document3 pagesWeekly Test Analysis 2080-03-02SHUBHASH CHANDRA PATHAKPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 - Hydrometer Testnvxjkcvbcxckvbckjvjkvknvck.Document6 pagesLab 4 - Hydrometer Testnvxjkcvbcxckvbckjvjkvknvck.Amirah ShafeeraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2214157X21005475 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2214157X21005475 Mainduraid ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutsche Filter 2Document15 pagesNutsche Filter 2Sadie100% (2)
- A Study of Efficient Drying Parameters For Bed Dryers: Christopher Tremblay, Dongmei ZhouDocument8 pagesA Study of Efficient Drying Parameters For Bed Dryers: Christopher Tremblay, Dongmei ZhouavgpaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of A High-Efficiency Rotary Dryer For Sewage SludgeDocument10 pagesDevelopment of A High-Efficiency Rotary Dryer For Sewage SludgeJorge VallejosPas encore d'évaluation
- Tray Dryer: Abolencia, Edin Hayel T., Derramas, Pasia, Abraham Paul L., Payongayong, Michael LDocument4 pagesTray Dryer: Abolencia, Edin Hayel T., Derramas, Pasia, Abraham Paul L., Payongayong, Michael LEdin AbolenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Stirred Batch ReactorDocument39 pagesDesign of Stirred Batch ReactorSyahir Safarudin100% (3)
- International Bag FilterDocument4 pagesInternational Bag FilterRAJAMANICKAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal 2020Document20 pagesJournal 2020vigneshkumar mechPas encore d'évaluation
- Expt Guide - F4 - Drying Under Constant Conditions Using Tray DryerDocument9 pagesExpt Guide - F4 - Drying Under Constant Conditions Using Tray DryerBabyyFacedPas encore d'évaluation
- NICTE NOMENSEN (English)Document7 pagesNICTE NOMENSEN (English)Kevin MulyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Dryer Augmenting - Natural - Convection - and - Conduction - BasedDocument9 pagesSolar Dryer Augmenting - Natural - Convection - and - Conduction - Basedpravin mundePas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization of A Solar-Assisted Drying System For Drying BananasDocument9 pagesOptimization of A Solar-Assisted Drying System For Drying BananasResearcherzPas encore d'évaluation
- Applying CFD For Studying The Dynamic and ThermalDocument20 pagesApplying CFD For Studying The Dynamic and ThermalPUBG SORRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4.4 - Preliminary-Primary Treatment (WW)Document32 pagesChapter 4.4 - Preliminary-Primary Treatment (WW)Siti Nurain mustafa kamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancang Bangun Mesin Pengering Vertikal Dengan Pengadukan Mekanik Untuk Biji-BijianDocument9 pagesRancang Bangun Mesin Pengering Vertikal Dengan Pengadukan Mekanik Untuk Biji-BijianDika WibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Simulation of Heat Exchangers Using Aspen HYSYS, and Aspen Exchanger DesignDocument8 pagesDesign and Simulation of Heat Exchangers Using Aspen HYSYS, and Aspen Exchanger DesignMehul BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tzempelikos D. Et Al - Airflow Patterns in A Laboratory Batch-Type, Tray Air Dryer - Ic-Scce2012 - ProceedingsDocument10 pagesTzempelikos D. Et Al - Airflow Patterns in A Laboratory Batch-Type, Tray Air Dryer - Ic-Scce2012 - ProceedingsAndronikos FiliosPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Simulation of Hydrogen Peroxide Plant: Manufacturing ProcessesDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation of Hydrogen Peroxide Plant: Manufacturing Processesdfeor shenoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice Meter: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument20 pagesOrifice Meter: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Waste Management ReportDocument34 pagesSolid Waste Management ReportDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Sludge DigestionDocument32 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Sludge DigestionDiana Isis Velasco0% (1)
- Polymer EngineeringDocument33 pagesPolymer EngineeringDiana Isis Velasco100% (1)
- Hydroelectric PowerDocument8 pagesHydroelectric PowerDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Management: Decision MakingDocument42 pagesEngineering Management: Decision MakingDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument33 pagesSolid Waste ManagementDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Moral FrameworksDocument16 pagesChapter 3 - Moral FrameworksDiana Isis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost EstimationDocument58 pagesCost EstimationDiana Isis Velasco100% (2)
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q2-Week 1Document26 pagesMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q2-Week 1Christian GebañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gree Dehumidifier Service ManualDocument58 pagesGree Dehumidifier Service Manualjdv1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- EIE3123 Dynamic Electronic Systems - p1-p57Document57 pagesEIE3123 Dynamic Electronic Systems - p1-p57Safwat KhairPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Quiz Direct VariationDocument2 pagesLong Quiz Direct VariationHermann Dejero LozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Connecting Piping Design in AutoCAD Plant 3D To Piping Fabrication Through Spoolgen-Ian Matthew-AU2018Document12 pagesConnecting Piping Design in AutoCAD Plant 3D To Piping Fabrication Through Spoolgen-Ian Matthew-AU2018Gabriel DezoutterPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4. Heat TransferDocument28 pagesModule 4. Heat TransferBry RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- State-Of-The-Art of Battery State-Of-Charge DeterminationDocument19 pagesState-Of-The-Art of Battery State-Of-Charge Determinationyasvanthkumar sPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasonic Insertion: Technical Information PW-4Document2 pagesUltrasonic Insertion: Technical Information PW-4Miguel ArriechePas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 69 Steering FundDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 69 Steering FundÆxis QuevedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Linear Algebra in Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesApplications of Linear Algebra in Computer ScienceSameed Ahmed Rafi100% (2)
- Inv ItemDocument127 pagesInv Itemprabhu181Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5-EN 4050-A (Dig) - 2F1CDocument9 pages5-EN 4050-A (Dig) - 2F1Cabuzer1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- TractionDocument26 pagesTractionYogesh GurjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mazda 3Document5 pagesMazda 3Jhony GranadosPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Differential Equations (Pdes)Document5 pagesPartial Differential Equations (Pdes)uploadingpersonPas encore d'évaluation
- About Planets - Vaishali's ProjectDocument3 pagesAbout Planets - Vaishali's ProjectRaj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Is 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyDocument4 pagesIs 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyCrypto AbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Rife and Philip Hoyland's 3.3 MHZ SweepDocument2 pagesDr. Rife and Philip Hoyland's 3.3 MHZ SweepKhalid Ibrahim100% (1)
- IB Lite 1 11 0 New FeaturesDocument11 pagesIB Lite 1 11 0 New Featuresm.n.malasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneDocument6 pagesSodium Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneIqmal HakimiPas encore d'évaluation
- PDPP - Presentation.3.Concurrent. Engineering - January.2021Document17 pagesPDPP - Presentation.3.Concurrent. Engineering - January.2021Ashish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Humiseal 1C49Lv Silicone Conformal Coating Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesHumiseal 1C49Lv Silicone Conformal Coating Technical Data Sheetmario230991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of Test For Rheometer - ODR: 1. ScopeDocument1 pageMethods of Test For Rheometer - ODR: 1. ScopeArun GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Equations and Matrices Unit 2Document31 pagesEquations and Matrices Unit 2Fab SPas encore d'évaluation
- An Ecient Uniform-Cost Normalized Edit Distance AlgorithmDocument12 pagesAn Ecient Uniform-Cost Normalized Edit Distance Algorithmanon-75650Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fpls 12 764103Document10 pagesFpls 12 764103Pawan MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Soda Ash PDFDocument45 pagesSoda Ash PDFM TPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Structure IIDocument3 pagesMechanics of Structure IIvenkata369Pas encore d'évaluation
- CORE JAVA (3-0-0) Module - I (10 Hours)Document3 pagesCORE JAVA (3-0-0) Module - I (10 Hours)Rupak BhuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- CTX 310 Communication With Fast Ethernet Board V2 (Fanuc)Document34 pagesCTX 310 Communication With Fast Ethernet Board V2 (Fanuc)ivePas encore d'évaluation