Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Headache OSCE Yy Edit
Transféré par
Sorong KivalabelDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Headache OSCE Yy Edit
Transféré par
Sorong KivalabelDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Headache OSCE
Anamnesis
Time: onset, frequency, pattern, duration
Characteristic: intensity, quality, site, spreading, associated symptoms
Course: trigger factor, aggravating factor, risk factor, family history
Response: what patient do, how it affect daily life, medicine, state of health between
attack, fear/ anxiety of recurrent
Risk Factor: smoking, alcohol, execise, diet
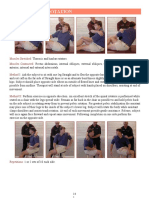
Physical Examination
1. vital sign
2. extra cranial structure evaluation
a. sinusitis
b. scalp superficial temporal artery tenderness
c. cervical paraspinal muscle stiffness
3. fundoscopy check presence of papiledema
4. cranial nerve examination
i. N II: Snellen chart
ii. N III, IV, VI: confrontation, pupil response
iii. N V: clench teeth, open jaw, corneal reflex
iv. N VII: smile + show teeth, close eye, facial symetry
v. N IX: menelan
vi. N XII: julur lidah
5. Brudzinski Neck, Brudzinski contralateral, (Reciprocal Brudzinski), Kernig
Brudzinski Neck flex the neck, see whether the leg will flex.
Brudzinski Contralateral leg flex one leg at the knee, see whether the other leg will flex
Brudzinskis reciprocal contralateral leg-flexion of one hip and knee; extension of another hip and knee; positive if
lower flexion knee, the extension one will flex
Kernig attempt to extend patient leg at knee level after flexing the tight at right angle. Fail to extend the knee
(not more than 135)
6. Neuromotor examination (examiner try to resist all patient movement)
- Patient can resist motor power 5
- Patient cannot resist but can raise up on their own motor power
3
Upper Extremities
1. Deltoidask patient to raise both arm
2. Test lower arm(biceps) flexion ask patient to flex their elbow
3. Test tricpes muscle ask patient to extend their elbow
4. Ask patient to extend their wrist
5. Test finger flexion ask patient to hold your second finger in their fist tightly.
6. Test finger abduction ask patient to fan out/abduct their finger, but examiner try to compress/close them
back
7. Test thumb opposition ask patient to touch the tip of thumb to tip of little finger
Lower Extremities
1. Hip flexion ask patient to raise their leg.
2. Adduction of hip ask patient to bring both leg together
3. Abduction of hip ask patient to move their leg apart
4. Hip extension ask patient to press down on your hand which is placed underneath patients thigh
5. Knee extension flex the knee first, then ask patient to extend the knee/kick out
6. Ham stringfloe the knee first, ask patient to pull their lower leg towards their buttock
7. Ankle dorsiflexion ask patient to pull their foot up
8. Ankle plantar floexion -- ask patient to press down their foot
9. Extensor hallucis longus ask patient to move the toes up towards their face
7. Pathologic reflex: Hoffman, Tromner, Babinski
Hoffman: Snap the nail of middle finger from above direction nail
Tromner: tap the volar surface of middle finger from the below direction
Babinski: make a smoothe J stroke, from lateral sole to medial sole
Red flags potential secondary headache (refer for CT scan)
-new or different headache in a patient aged over 50;
-Worst headache ever
-thunderclap onset (abrupt and severe);
-Subacute-progressive over month
Keep in mind to screen for
-abnormal neurological signs;
all these during amanmesis!!
-postural;
-valsalva headache
-Seizure
-Symptoms of systemic illness: fever, history of HIV, cancer
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- First Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaD'EverandFirst Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro PEDocument36 pagesNeuro PEkhaderbasha2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCNS Cranial Nervesdenise joyce19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological ExaminationDocument8 pagesNeurological Examinationg8048658Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Neurological Exam: Respect and Kindness. When You Enter TheDocument9 pagesThe Neurological Exam: Respect and Kindness. When You Enter TheRemelou Garchitorena Alfelor100% (1)
- F& C OSCE Notes - University of Manchester, WL GanDocument57 pagesF& C OSCE Notes - University of Manchester, WL GanWeh Loong Gan100% (7)
- Professional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Document25 pagesProfessional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Noora AlmuailiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 pagesNeurological AssessmentJamaica Manuel IglesiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand and WristDocument12 pagesHand and WristnicholePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction, Deep ReflexesDocument10 pagesIntroduction, Deep ReflexesQairul AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological AssessmentDocument7 pagesNeurological AssessmentSharon LawrencePas encore d'évaluation
- PX NN CranialDocument35 pagesPX NN CranialZenithaMeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paces 7 - Cns - Upper LimbDocument11 pagesPaces 7 - Cns - Upper LimbDrShamshad KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyDocument2 pagesMUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyKristinelou Marie N. ReynaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor SystemDocument8 pagesMotor SystemEman LabPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper & Lower Limb ExaminationDocument20 pagesUpper & Lower Limb Examinationcvmqx7yppd100% (1)
- Ortho Neuro ExamsDocument0 pageOrtho Neuro ExamsMaybs Palec Pamplona-ParreñoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011Document35 pages2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011suaqaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical SkillsDocument15 pagesPractical SkillsAyni SindhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas DR Jeffrey 1Document15 pagesTugas DR Jeffrey 1Steven MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Examination and CoordinationDocument7 pagesSensory Examination and CoordinationFatimah Alsultan100% (1)
- Neurologic AssessmentDocument7 pagesNeurologic AssessmentFerric Lapenas100% (1)
- Sem 2 Week 4Document30 pagesSem 2 Week 4Fong Yu-hengPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal Exam Teaching OutlineDocument12 pagesMusculoskeletal Exam Teaching OutlineAngeliki KostakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment Mid-Term Evaluation Fall23Document6 pagesPhysical Assessment Mid-Term Evaluation Fall23Anna DrakePas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Back Examination ٢Document6 pages4-Back Examination ٢رغد رشيدPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr.K.sellahewa Cardiovascular System ExaminationDocument8 pagesDr.K.sellahewa Cardiovascular System ExaminationNilaaharan RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Paces 6 - Cns - Lower LimbDocument18 pagesPaces 6 - Cns - Lower LimbDrShamshad Khan100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument5 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentBAdz TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesNeuro Exam ReviewDianne Flores100% (2)
- Jarvis Neurological Assessment SummaryDocument11 pagesJarvis Neurological Assessment Summaryaderonke bello100% (2)
- The Motor System ExaminationDocument42 pagesThe Motor System ExaminationHelend ChildDj100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument11 pagesScoliosisHengkai NeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurologic System Physical Assessment GuideDocument4 pagesNeurologic System Physical Assessment GuideJeff Shaun Claude PalaparPas encore d'évaluation
- David Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Document11 pagesDavid Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Himani BhondgePas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial Nerve Examination: OverviewDocument8 pagesCranial Nerve Examination: OverviewMuhammed BarznjiPas encore d'évaluation
- PE CompreDocument5 pagesPE Comprejustme12345mPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of The Peripheral Neurological SystemDocument2 pagesExamination of The Peripheral Neurological Systemkenners100% (12)
- Neurological Examination of The Limbs TextDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination of The Limbs Textvidur_talrejaPas encore d'évaluation
- PACES 8 - CNS - Cranial NervesDocument7 pagesPACES 8 - CNS - Cranial NervesDrShamshad KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument3 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentMuthu KumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Physical ExamDocument10 pagesComplete Physical ExamSohayb Abu TabanjehPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Exam Internal FINALDocument27 pagesPhysical Exam Internal FINALMohammad AlrefaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity # 6 Neurovascular AssessmentDocument3 pagesActivity # 6 Neurovascular AssessmentGem Himenace100% (1)
- Clinical Examinations For PLAB 2Document12 pagesClinical Examinations For PLAB 2Mandeep KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Case PresentationDocument37 pagesCase PresentationRevan NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Blueprint For Final Exam - Doc Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesBlueprint For Final Exam - Doc Health AssessmentKim DepapePas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Bedah HafizDocument43 pagesTugas Bedah HafizEmir Rasyid HafizPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological AssessmentDocument76 pagesNeurological Assessmentjcabatit3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spine 2020Document1 pageSpine 2020fihimeh581Pas encore d'évaluation
- Central Integration of Motor FunctionDocument3 pagesCentral Integration of Motor FunctionM51785Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological ExaminationDocument240 pagesNeurological Examinationramadan0% (1)
- Cranial Nerve Exam RoutineDocument9 pagesCranial Nerve Exam Routine5kqmn798rfPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial Nerves ExamDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves ExamCnursePPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist Week 3 - Shoulder, Elbow & Wrist - MSKDocument4 pagesChecklist Week 3 - Shoulder, Elbow & Wrist - MSKAMY CHOIPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyshical Examination OrthopaediDocument67 pagesPyshical Examination OrthopaediSheryl ElitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome You AllDocument51 pagesWelcome You AllRam PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 8and9 Flow of The Exam2008Document3 pagesSession 8and9 Flow of The Exam2008tony_chrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Centre For Excellence in HomœopathyDocument239 pagesCentre For Excellence in HomœopathyYaniv AlgrablyPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Examination For Year 1 Residents in Orthopaedics SurgeryDocument15 pagesMCQ Examination For Year 1 Residents in Orthopaedics SurgeryTefera Letebo100% (3)
- Revision 1.Document9 pagesRevision 1.Sebayari RiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For High Jump Gary Bourne Style 1Document2 pagesLesson Plan For High Jump Gary Bourne Style 1api-430874470Pas encore d'évaluation
- Active Isolated Stretching The Mattes Method 151 184Document38 pagesActive Isolated Stretching The Mattes Method 151 184Nazareth Varas AlonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Fix Flat Feet (Pes Planus) - Posture Direct PDFDocument77 pagesHow To Fix Flat Feet (Pes Planus) - Posture Direct PDFBosco DominicPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Extremity Stretching ProtocolDocument3 pagesLower Extremity Stretching ProtocolHello RainbowPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy For Artists Eliot GoldfingerDocument231 pagesHuman Anatomy For Artists Eliot GoldfingerQueen B100% (2)
- Proper Body Mechanics For NursesDocument3 pagesProper Body Mechanics For NursesRaquel RamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rehabilitation of Features On Hip DislocationDocument5 pagesRehabilitation of Features On Hip Dislocationjuan donayrePas encore d'évaluation
- P e - 1-Prefi PDFDocument12 pagesP e - 1-Prefi PDFSairah Camille ArandiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ier Pe ADocument27 pagesIer Pe ATrixia Delgado100% (1)
- PE Assign 2Document3 pagesPE Assign 2Mhar EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomechanics Thefoot and Ankle UnitDocument19 pagesBiomechanics Thefoot and Ankle Unitshannithushan43Pas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Tendon Reflexes The What Why Where and How ofDocument11 pagesDeep Tendon Reflexes The What Why Where and How ofRahul Rai100% (1)
- Distractor AoDocument15 pagesDistractor AoGenni Jose Leli HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Monstermass Mike ChangDocument27 pagesMonstermass Mike Changjohn spencerPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Ortho Case YashikaDocument47 pagesFinal Ortho Case YashikaYashika GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brunnstrom's Movement Therapy in Hemiplegic Patient (Lower Limb)Document71 pagesBrunnstrom's Movement Therapy in Hemiplegic Patient (Lower Limb)Barney Cordova100% (1)
- 3 - 5-Strengthening The Gluteus Maximus in Subjects With Sacroiliac Dysfunction - Uswatun HasanahDocument7 pages3 - 5-Strengthening The Gluteus Maximus in Subjects With Sacroiliac Dysfunction - Uswatun HasanahIndahMardhPas encore d'évaluation
- Gals ExmDocument2 pagesGals ExmFina Syafinaz SuhaimiPas encore d'évaluation
- MovSciLec MSC 2101 Week16Document11 pagesMovSciLec MSC 2101 Week16Mary SotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ise Basic Biomechanics 9Th Edition Susan J Hall Full ChapterDocument40 pagesIse Basic Biomechanics 9Th Edition Susan J Hall Full Chapterdarrell.berry639100% (6)
- Chapter 21Document37 pagesChapter 21Ivan Olo SarumpaetPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 Annual Conference of Biomechanics in Sports - Melbourne 2012Document3 pages30 Annual Conference of Biomechanics in Sports - Melbourne 2012Osolemio MerPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles (Origin, Insertion and Action)Document4 pagesMuscles (Origin, Insertion and Action)Telle AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Test For All JointsDocument42 pagesSpecial Test For All JointsVinothini Adaikkalasamy91% (46)
- High-Resolution Sonography of The Peripheral Nervous System - A Review of The LiteratureDocument10 pagesHigh-Resolution Sonography of The Peripheral Nervous System - A Review of The LiteratureJP ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)