Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
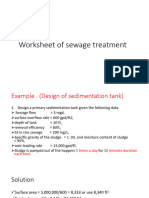
Case Study For Soap Waste Water
Transféré par
Kari ConwayTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Case Study For Soap Waste Water
Transféré par
Kari ConwayDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ISSN 2319-8885
Vol.03,Issue.10
May-2014,
Pages:2052-2057
www.semargroup.org,
www.ijsetr.com
Proposal of Wastewater Treatment Process and Design for Soap Industry
SU SUNDY MAUNG1, TIN TIN HTWE2
1
Dept of Civil Engineering, Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar, Email: susundymaung@gmail.com.
2
Dept of Civil Engineering, Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar, Email: tthtwe@gmail.com.
Abstract: This study presents the wastewater treatment plant for soap industry. Soap industry generates relatively large
quantities of wastewater that may contain various potentially organic matters. Therefore, the proper management of industrial
wastewater is essential. The quality and quantity of wastewater from this industry are studied and the suitable method for
wastewater treatment system is considered. The wastewater from soap industry is collected for three times and analysed at the
laboratory of ISO TECH in Yangon (Myanmar). Physical, chemical and biological parameters of wastewater are measured.
Then, the results are compared into public sewer of Indian Standards. According to the experimental results, the concentrations
of pH, suspended solids, BOD, COD are higher than acceptable level of Indian Standards. The wastewater production from the
soap industry is 595000 l/day with the BOD content of 43000 mg/l and COD content of 99200 mg/l. Based on the test results
and wastewater discharge, there are two proposes of wastewater treatment plant in the study. The first propose is wastewater
treatment including neutralization basin, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket, alum dosing, flocculation, primary settling, activated
sludge process and final sedimentation tank. After passing the treatment plant, the effluent BOD, COD and suspended solids are
347 mg/l, 3456 mg/l and 430 mg/l. Alternatives propose includes screening, alum dosing, flocculation, primary sedimentation
tank, trickling filter, aeration tank and secondary sedimentation tank with effluent BOD (347 mg/l). The result values of two
methods are less than the acceptable BOD quality of 350 mg/l for discharging into public sewer.
Keywords: Industrial Wastewater, Soap Industry, Unit Operations and Processes, Wastewater Treatment.
I. INTRODUCTION
Wastewater or sewage is essentially the water supply of
the community after it has been fouled by a variety of uses.
Wastewater may be defined as a combination of the liquid or
water carried wastes removed from residences, institutions,
and commercial industrial establishments, together with such
groundwater, surface water, and stormwater as may be
present. The wastewater production from urban areas is about
evenly divided between industrial and municipal sources.
Therefore, the use of water by industry can significantly
affect the water quality of receiving waters. Soap industries
are the major sources of pollution in all environments. Based
on the type of industry, various levels of pollutants can be
discharged into the environment directly or indirectly through
public lines. Wastewater from industries includes employees
sanitary waste, process wastes from manufacturing, wash
waters and relatively uncontaminated water from heating and
cooling operations. Industries consumes huge amount of
fresh water, depleting a valuable resource required for
everyday human activities.
Figure1. Manufacturing Process of Soap Industry.
In addition, wastewater effluents loaded with pollutants
the amount of organic material in the water. If the industrial
often pose significant hazards to the environment. It is
wastewater is thrown away without any treatment, there will
therefore important to have high-performance and low-cost
be much pollution to the environment. Due to this condition,
wastewater treatment plants to treat and reuse industrial
treatment plant is essentially needed from the aspect of public
effluents. The strength of the wastewater is determined by
health. The objective of this study is to reduce wastewater
measuring the amount of suspended material in the water and
Copyright @ 2014 SEMAR GROUPS TECHNICAL SOCIETY. All rights reserved.
SU SUNDY MAUNG, TIN TIN HTWE
pollution and environmental pollution. The raw materials for commonly used to define the strength of wastewaters, to
the manufacturing process of soap are pead fatty acid evaluate the efficiency of treatment by measuring oxygen
distillate, refined bleached deodorised palm stearine, coconut demand remaining in the effluent, and to determine the
oil, and tallow. These materials react with caustic soda, salt amount of organic pollution in surface waters [5].
and water. The soap manufacturing process flow diagram is
shown in figure 1. 8.Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD): The chemical oxygen
demand (COD) of wastewater or polluted water is a measure
II. WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS of the oxygen equivalent of the organic matter susceptible to
Wastewater is characterized in terms of its physical, oxidation by a strong chemical oxidant. The organic matter
chemical, and biological composition. The physical, chemical destroyed by the mixture of chromic and sulphuric acids is
and biological examinations are performed to know the converted to CO2 and water. The COD test is also used to
wastewater characteristics. measure the organic matter in industrial and municipal
1. Total Solids: The total solids in a wastewater consist of wastes that contain compounds that are toxic to biological
the insoluble or suspended solids and the soluble compounds life [2].
dissolved in water. The suspended solids content is found by
drying and weighing the residue removed by the filtering of The results of soap wastewater characteristics are shown
the sample. When this residue is ignited the volatile solids are in table I. The test results are described that they contain
burned off. Between 40 and 65 % of the solids in an average highest pollutents such as BOD, COD, suspended solids and
wastewater are suspended. Settleable solids, expressed as total solids.
miligram per litre, are those that can be removed by
sedimentation [1]. TABLE I. RESULTS OF WASTEWATER ANALYSIS
2. Colour: Colour is a qualitative characteristic that can be
used to assess the general condition of wastewater.
Wastewater that is light brown in colour is less than 6 h old,
while a light-to-medium grey colour is characteristic of
wastewaters that have undergone some degree of
decomposition or that have been in the collection system for
some time [1].
3.Odour: The determination of odour has become
increasingly important, as the general public has become
more concerned with the proper operation of wastewater
treatment facilities. The odour of fresh wastewater is usually
not offensive, but a variety of odorous compounds are
released when wastewater is decomposed biologically under
anaerobic conditions [1].
4.Temperature: The measurement of temperature is
important because most wastewater treatment schemes
include biological processes that are temperature dependent.
In addition, oxygen is less soluble in warm water than in cold
water [1].
5.Alkalinity: Alkalinity in wastewater results from the
presence of the hydroxide, carbonates, and bicarbonates of
elements such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, or
ammonia [1]. The alkalinity in wastewater helps to resist
changes in pH caused by the addition of acids.
6.Dissolved Oxygen: Dissolved oxygen is required for the
respiration of aerobic microorganisms as well as all other
aerobic life forms. However, oxygen is only slightly soluble
in water [4].
III. TREATMENT METHOD
7.Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD): Biological oxygen Wastewater treatment objectives are based primarily on
demand (BOD) is the quantity of oxygen used by aesthetic and environmental concerns. The objectives of
microorganisms in the aerobic stabilization of wastewaters reduction and removal of BOD, suspended solids and
and polluted waters. The standard 5-day BOD value is
International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Technology Research
Volume.03, IssueNo.10, May-2014, Pages: 2052-2057
Proposal of Wastewater Treatment Process and Design for Soap Industry
pathogenic micro-organisms continued but at higher levels. slots. The materials removed by these devices are known as
The degree of treatment can be determined by comparing the screening.
influent wastewater characteristics to the required effluent 3. Coagulation and Flocculation
wastewater characteristics. A number of different treatment Coagulation is employed for the removal of waste
and disposal or reuse alternatives are then developed and materials in suspended or colloidal form. Colloids are
evaluated, and the best alternative is selected. Wastewater presented by particles over a size range of 1 nm (10-7 cm) to
treatment is a combination of physical, chemical, and 0.1 nm (10-8 cm). These particles do not settle out on
biological processes. Methods of treatment in which the standing and cannot be removed by conventional physical
application of physical forces predominate are known as unit treatment processes. Coagulation reduces the net electrical
operations while methods of treatment in which chemical or repulsive forces at particle surfaces by adding coagulant
biological activities are involved are known as unit processes. chemicals, whereas flocculation is agglomeration of the
There are three types of unit operations and processes: 1. destabilized particles by chemical joining and bridging. In
Physical unit operations, 2. Chemical unit processes, and 3. wastewater treatment, coagulation and flocculation are used
Biological unit processes. to destabilize turbidity, color, odor-producing compounds,
pathogens, and other contaminants in surface waters.
A. Physical Unit Operation Flocculation is agitation of chemically treated water to
Treatment methods in which the applications of physical induce coagulation. In this manner, very small suspended
forces predominate are known as physical unit operations. particles collide and agglomerate into larger heavier floc that
Because most of these methods evolved directly from man's settles out by gravity. Flocculation is a principal mechanism
first observations of nature, they were the first to be used for in removing turbidity from water.
wastewater treatment. Screening, mixing, flocculation,
sedimentation, flotation, filtration, and gas transfer are 4. Primary Sedimentation Tank
typical unit operations [5]. The objective of treatment by sedimentation is to remove
readily settleable solids and floating and thus reduce the
B. Chemical Unit Processes suspended-solids content. Sedimentation is the removal of
Chemical unit processes are those in which removal of solids particles from suspension by gravity. In water
contaminants are brought about by chemical activity. In the treatment, the common application of sedimentation is after
field of wastewater treatment, chemical unit operations are chemical treatment to remove flocculated impurities and
usually used in conjunction with physical unit operations and precipitates. In wastewater processing, sedimentation is used
biological unit processes. Precipitation, absorption, and to reduce suspended solids in the influent wastewater and to
disinfection are the most common examples used in remove settleable solids after biological treatment.
wastewater treatment [5].
5. Trickling Filter
C. Biological Unit Processes Trickling filters are used for biological treatment of
Biological unit processes are those in which removal of domestic sewage and industrial wastes which are amenable to
contaminants are brought about by biological activity. In aerobic biological processes. Trickling filters, also known as
biological treatment of wastewater, the objectives are to percolating filters or sprinkling filters are similar to contact
coagulate and remove the non-settleable colloidal solids and beds in construction, but their operation is continuous and
to stabilize the organic matter. Basically, these substances are they allow constant aeration. The trickling filter is always
converted into gases that can escape to the atmosphere and preceded by primary sedimentation along with skimming
into biological cell tissue that can be removed by settling [5]. devices to remove the scum. This will prevent the clogging of
the filter by settleable solids. The effluent from the filter is
In order to treat wastewater, it is necessary to know the then taken to secondary sedimentation tanks for settling out
function of treatment process. organic solids oxidized while passing through the filter.
1. Collection Tank
6. Activated Sludge Process
In this study, storage tank is considered as tank on ground
The activated sludge is the sludge which is obtained by
with concrete.
settling sewage in presence of abundant oxygen so as to be
2. Screening supercharged with favourable aerobic micro-organisms. The
The first step in wastewater treatment is the removal or activated sludge process of sewage treatment is based on
reduction of coarse solids. The usual procedure is to pass the providing intimate contact between the sewage and biological
untreated wastewater through bar racks or screens. A screen active sludge. The effluent from the primary settling tank is
is a device with openings, generally of uniform size, that is mixed with a dose of activated sludge and is aerated in an
used to retain the coarse solids found in wastewater. The aeration tank for a period of some hours. During the aeration,
screening element may consists of parallel bars, rods or the micro-organisms in the sewage multiply by assimilating
wires, grating, wire mesh, perforated plate, and the openings part of the influent organic matter. In this process, part of
may be of any shape but generally are circular or rectangular organic matter is synthesized into new cells and part is
oxidized to derive energy. The synthesis reaction, followed
International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Technology Research
Volume.03, IssueNo.10, May-2014, Pages: 2052-2057
SU SUNDY MAUNG, TIN TIN HTWE
by subsequent separation of the resulting biological mass and Based on the characteristics of soap wastewater, the
the oxidation reaction are the main mechanisms of BOD appropriate treatment process such as neutralization,
removal in the activated sludge process. The biomass is anaerobic process, alum dosing and flocculation, primary
generally flocculant and quick settling. It is separated from settling, activated sludge processes are chosen and designed
the aerated sewage in a secondary settling tank and is according to their respective design criteria to obtain the
recycled continuously to the aeration tank as an essential acceptable wastewater quality of into public sewers Indian
feature of the process. The BOD removal is evaluated based Standards. In secondary treatment, activated sludge process
on the BOD5 of the aeration tank influent and the BOD5 of (suspended growth process) is used. In this process includes
the final effluent after sludge separation. The effluent is of aeration tank, secondary clarifier and returned sludge line.
high quality, usually having a lower BOD than that of a The proposal 1 for the treatment plant of soap industry is
trickling filter. The BOD removal is up to 80-95 percent and shown in figure 2.
the degree of bacteria removal is up to 90-95 percent.
7. Neutralization
Many industrial wastes contain acidic or alkaline
materials that require neutralization prior to discharge to
receiving waters or prior to chemical or biological treatment.
For biological treatment, a pH in the biological system
should be maintained between 6.5 and 8.5 to ensure optimum
biological activity. The biological process itself provides a
neutralization and a buffer capacity as a result of the
production of CO2, which reacts with caustic and acidic
materials. The degree of preneutralization required depends,
therefore, on the ratio of BOD removed and the causticity or
acidity present in the waste.
8. Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
Anaerobic decomposition involves in the breakdown of
organic wastes to gas (methane and carbon dioxide) in the
absence of oxygen. The quantity of organic matter converted
to gas will vary from 80 to 90 percent. In the upflow
anaerobic sludge blanket wastewater is directed to the bottom
of the reactor where it must be distributed uniformly. The
wastewater flows upward through a blanket of biologically Figure 2. Proposal 1 for treatment plant of soap industry.
formed granules which consume the waste as it passes
through the blanket. Methane and carbon dioxide gas bubbles 1. Design of Collection and Neutralization Tank
rise and are captured in the gas dome. Liquid passes into the Raw wastewater from the industry flows into the
settling portion of the reactor where solids-liquid separation collection tank. In this study, collection tank is considered as
takes place. The solids return to the blanket area while the tank on ground with concrete. For the design of the collection
liquid exists over the wires. To keep the blanket in tank, wastewater is stored for 1hrs. Dimension of tank is 2 m
suspension, an upflow velocity of 2 to 3 ft/h (0.6 to 0.9 m/h) 8.5 m 1.5 m. For the design of neutralization tank,
has been used. wastewater is passed for 6 minutes with the average air rate
(0.6 m3/min-m2). Dimension of tank is 1 m 1 m 2.5 m.
IV. PROPOSAL AND DESIGN OF WASTEWATER
TREATMENT PLANT 2. Design of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
Depending on the constituents that must be removed, an To keep the blanket in suspension, an upflow velocity of
almost limitless number of different flowsheet can be 2 to 3 ft/h (0.6 to 0.9 m/h) has been used with retention time
developed using unit operations and processes. In the study, (4 hours). Dimension of tank is 5 m diameter and 4.95 m
there are two types of proposed flowsheet for soap depth. After passing this tank, the effluent BOD and COD are
wastewater treatment. In order to design wastewater 4300 mg/l with removal efficiency (90%) and 9920 mg/l with
treatment plant, it is necessary to determine the design removal efficiency (90%).
discharge. In this study, the discharge from soap wastewater
is considered for the treatment plant. According to 3. Design of Alum Dosage Per Day
wastewater generation standards, 1 kilogram (1kg) of soap The required dosage of alum varies from 75mg/l 250
produces 23.4L of wastewater. The soap production per day mg/l depending upon the condition [2]. Chemical
is 25424 kg. Therefore, wastewater flow rate from soap precipitation (alum coagulant) can be removed from 40
industry is 595 m3/day. to70% of BOD, 80 to 90% of suspended solids and 30 - 60 %
of COD. Considering for the average percentage removal, the
A. Proposal 1 effluent BOD is obtained as 1720 mg/l, effluent suspended
International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Technology Research
Volume.03, IssueNo.10, May-2014, Pages: 2052-2057
Proposal of Wastewater Treatment Process and Design for Soap Industry
solids is 1512 mg/l and effluent COD is 5456 mg/l . Alum is returned sludge line. The proposal 2 for the treatment plant of
in more use than other coagulants because it is very cheap. It soap industry is shown in figure 3.
reduces taste and odor in addition to turbidity. Alum required
per day is 59.5 kg/day. 1. Design of Collection Tank
Raw wastewater from the industry flows into the
4. Design of Flocculation Tank collection tank. In this study, collection tank is considered as
Flocculation is an essential operation designed to force tank on ground with concrete. For the design of the collection
agitation in the fluid and induced coagulation. For the design tank, wastewater is stored for 1hrs. Dimension of tank is 2 m
of flocculation tank, wastewater is passed for 30 minutes. 8.5 m 1.5 m.
Dimension of tank is 4 m 2 m 1.5 m and provide
revolving paddles attached to two horizontal shafts tranverse
to basin length. Let each shaft should be located at mid depth
of tank. Let provide three paddles to each shaft. Paddle size is
0.03 m wide and each of length 1 m with 31 watts of power
requirement.
5. Design of Primary Sedimentation Tank
Sedimentation tanks are designed to reduce the velocity of
flow so as to permit suspended solids to settle out of water by
gravity. In this study, the circular shaped primary
sedimentation tank is used radically flow. Dimension of tank
is 4.5 m diameter and 3 m depth with detention time (2
hours). The effluent BOD, COD and SS become 1118 mg/l,
3546 mg/l and 403 mg/l respectively.
6. Design of Aeration Tank
It is a biological treatment process in which biologically
activated mass, called activated sludge is continuously mixed
with the sewage flow in the aeration basin in the presence of
oxygen. The oxygen is supplied to the mixed liquor either by
diffused compressed air or by mechanical aeration. In the
study, conventional activated sludge process is used.
Conventional activated sludge processes can be removed 80
to 95 % of BOD, 80 to 90 % of suspended solids, 80-85 % of
COD and 10- 25 % of phosphorus. Tank dimension is 6.5 m
38 m 4.5 m. Total air required is 16 m3/min. Standard Figure3.Proposal 2 for Treatment Plant of Soap Industry.
diffuser plates of 0.3 m 0.3 m 25 mm passing 1.2 m3 of
air/m2 with pore sizes of 0.3 mm are chosen. Total number of 2. Design of Screen
plates is 148 plates. A screen is a device with openings generally of uniform
size. In this study, fine screen of rotary drum type is used and
7. Design of Secondary Sedimentation Tank designed according to the criteria. Dimension of drum screen
In conventional activated sludge process, the aeration tank is 1.5 m diameter and 2.45 m length. The effluent of BOD
is followed by the secondary sedimentation tank. Tank and SS are 34400 mg/l and 7812 mg/l.
dimension is 4 m diameter and 4.5 m depth with detention
time (2.28 hours). The final effluent of BOD is 347 mg/l with 3. Calculation of Alum Dosage Per Day
69 % removal efficiency. Considering for the average percentage removal, the
effluent BOD is obtained as 13760 mg/l, effluent suspended
B. Proposal 2
solids is 1172 mg/l and effluent COD is 54560 mg/l . Alum is
Alternative method of wastewater treatment plant is
in more use than other coagulants because it is very cheap. It
considered. Based on the characteristics of soap wastewater,
reduces taste and odor in addition to turbidity. Alum required
the appropriate treatment process such as screening, alum
per day is 59.5 kg/day.
dosing and flocculation, primary settling, trickling filter,
aeration tank and secondary sedimentation tank are chosen 4. Calculation of Flocculation Tank
and designed according to their respective design criteria to Flocculation is an essential operation designed to force
obtain the acceptable wastewater quality of into public agitation in the fluid and induced coagulation. For the design
sewers Indian Standards. In secondary treatment, activated of flocculation tank, wastewater is passed for 30 minutes.
sludge process (suspended growth process) is used. In this Dimension of tank is 4 m 2 m 1.5 m and provide
process includes aeration tank, secondary clarifier and revolving paddles attached to two horizontal shafts tranverse
International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Technology Research
Volume.03, IssueNo.10, May-2014, Pages: 2052-2057
SU SUNDY MAUNG, TIN TIN HTWE
to basin length. Let each shaft should be located at mid depth second. And then, neutralization basin is the reduction of
of tank. Let provide three paddles to each shaft. Paddle size is alkalinity for the soap wastewater. . Finally, the results of
0.03 m wide and each of length 1 m. effluent are within the BOD (350 mg/l), COD (10000 mg/l),
SS (600 mg/l) and dissolved solids (2100 mg/l) for disposal
5. Design of Primary Sedimentation Tank into public sewer of Indian Standard.
Sedimentation tanks are designed to reduce the velocity of
flow so as to permit suspended solids to settle out of water by VI. ACKNOWLEDGMENT
gravity. In this study, the circular shaped primary The author would like to express her heart felt gratitude to
sedimentation tank is used radically flow. Dimension of tank Dr. Kyaw Moe Aung, Associate Professor and Head of Civil
is 4.5 m diameter and 3 m depth with detention time (2 Engineering Department, Mandalay Technological
hours). The effluent BOD, COD and SS become 8256 mg/l, University. The author is deeply grateful to her supervisor
35464 mg/l and 469 mg/l respectively. Dr. Tin Tin Htwe, Associate Professor, Department of Civil
Engineering, Mandalay Technological University, for her
6. Design of High Rate Trickling Filter valuable guidance, criticisms, encouragement comments,
In the first stage of secondary treatment, high rate suggestions and advice throughout the whole length of the
trickling filter is designed according to the criteria. research work. The author would like to her gratefulness to
Dimension of filter is 37 m diameter and 3 m depth. The all people in soap industry (Mandalay). Finally, specially
effluent BOD, COD and SS are 1651 mg/l, 7092.8 mg/l and thanks to her parents, for their moral support, patience,
117.25 mg/l respectively. understanding and encouragement.
7. Design of Aeration Tank VII. REFERENCES
Conventional activated sludge processes can be removed [1] Metcalf & Eddy, third edition, Wastewater Engineering
80 to 95 % of BOD, 80 to 90 % of suspended solids, 80-85 % Treatment, Disposal, Reuses, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing
of COD and 10- 25 % of phosphorus. Tank dimension is 6.5 Company Limited, New Delhi, 1995.
m 56 m 4.5 m. Total air required is 27 m3/min. In this [2] W.Wesley Eckenfelder, Jr, second edition, 1989,
process, mechanical aeration is used with paddle mechanism. Industrial Wate Pollution Control, Tata McGraw-Hill
Provide revolving paddles attached to three horizontal shafts Publishing Company Limited.
running parallel to the length. Let each shaft should be [3] Lawrence K. Wang , 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group,
located at mid depth of tank. Let provide thirty paddles to Treatment of Soap and Detergent Industry Wastes, The
each shaft. Paddle size is 0.58 m wide and each of length 0.6 Cooper Union, New York, U.S.A.
m with 4128 watts of power requirement. [4] Mark J Hammer Jr. fourth edition, Water and
Wastewater Technology, Prentic- Hall of India Private
8. Design of Secondary Sedimentation Tank Limited, New Delhi, 2003.
In conventional activated sludge process, the aeration [5] Environmental Engineering for B.E course (Department
tank is followed by the secondary sedimentation tank. Tank of Technical and Vocational Education).
dimension is 4 m diameter and 4.5 m depth with detention [6] Environmental Engineering for B.Tech course
time (2.28 hours). The final effluent of BOD is 347 mg/l with (Department of Technical and Vocational Education).
79 % removal efficiency.
V. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
From the test result, the value of BOD, COD, suspended
solids and total dissolved solids are 43000 mg/l, 99200 mg/l,
10080 mg/l and 40300 mg/l respectively. These are high
content over the limit for public sewer of Indian Standard.
Based on the characteristics, the appropriate treatment
processes are chosen to design the soap wastewater treatment
plant. In the study, two types of treatment processes are
considered. In proposal 1 includes neutralization, anaerobic
process, alum dosing and flocculation, primary settling,
activated sludge processes. After passing through the
treatment process, the effluent of BOD, COD and SS become
347 mg/l, 3546 mg/l and 403 mg/l respectively. In proposal 2
includes screening, alum dosing and flocculation, primary
settling, trickling filter, aeration tank and secondary
sedimentation tank. After passing treatment plant, the
effluent BOD, COD and SS become 347 mg/l, 7092.8 mg/l
and 117.25 mg/l respectively. The effluent BOD of two types
of treatment is the same with the value of 347 mg/l. But the
effluent COD of the first treatment process is lower than the
International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Technology Research
Volume.03, IssueNo.10, May-2014, Pages: 2052-2057
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mini Project ReportDocument5 pagesMini Project ReportSaj BhaiPas encore d'évaluation
- SEKO Solenoid Dosing Pumps Kompact SeriesDocument3 pagesSEKO Solenoid Dosing Pumps Kompact SeriesmauiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficiency Comparison of Various Sewage Treatment Plants in BangaloreDocument36 pagesEfficiency Comparison of Various Sewage Treatment Plants in BangalorePRETTY MARY100% (1)
- Module - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRDocument39 pagesModule - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRFaran Masood100% (1)
- R1 Bep WTP Aurangabad 27012023Document42 pagesR1 Bep WTP Aurangabad 27012023Rajesh Gangwal100% (1)
- FRP Media PSF, AcfDocument25 pagesFRP Media PSF, Acfluckynaveenraj100% (1)
- M13 - L17 Grit ChamberDocument6 pagesM13 - L17 Grit ChamberBerliana Cahya Ningtias0% (1)
- Tech City-STP 100 KLD Price Comparison (03092016)Document10 pagesTech City-STP 100 KLD Price Comparison (03092016)Preston VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Standards STPs NGT OrderDocument14 pagesRevised Standards STPs NGT OrderBhaskar Challa100% (1)
- Advanced Wastewater TreatmentDocument16 pagesAdvanced Wastewater TreatmentvikkykamblePas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 11Document11 pagesHandout 11shivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bar Screen-Grit ChamberDocument10 pagesBar Screen-Grit ChamberRaja ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sewage Treatment WorksheetDocument18 pagesSewage Treatment WorksheetRemedanPas encore d'évaluation
- Handover Document - Yaden KatunayakeDocument39 pagesHandover Document - Yaden KatunayakeUTY ENGPas encore d'évaluation
- Today'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"Document57 pagesToday'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"saravan1891Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Processes - 5th EditionDocument24 pagesDesign of Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Processes - 5th EditionTheeva RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Removal of Removal of Iron (Fe) and Manganese (MN) : DR Liu YuDocument20 pagesRemoval of Removal of Iron (Fe) and Manganese (MN) : DR Liu YuChuah Chong YangPas encore d'évaluation
- GN Buildtech Private LTD: Proposal For, Supply& Installation of 10000 LPH Ro PlantDocument9 pagesGN Buildtech Private LTD: Proposal For, Supply& Installation of 10000 LPH Ro Plantgnbuildtech Pvt ltdPas encore d'évaluation
- Removal of Chromium From Tannery Solid WasteDocument7 pagesRemoval of Chromium From Tannery Solid WasteLuis Paz Soldán G100% (1)
- Main UASB ReactorDocument23 pagesMain UASB ReactorsasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Waste Water TreatmentDocument5 pagesHospital Waste Water TreatmentNP100% (1)
- 40 KLD MBR QuoteDocument15 pages40 KLD MBR QuoteV Narasimha RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Treatment CalculatorDocument3 pagesWater Treatment CalculatorgrabettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tank Bottom Scraper Zickert - enDocument22 pagesTank Bottom Scraper Zickert - enzxc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- 225 H Engg DataDocument8 pages225 H Engg DataPravin BotePas encore d'évaluation
- Envirenmental EngineeringDocument87 pagesEnvirenmental Engineering4919404Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical AdditionsDocument103 pagesChemical AdditionsAlvin Kim100% (1)
- CPI BrochureDocument2 pagesCPI Brochuremashonk okPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesWaste Water TreatmentIbrar ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Drum FlakerDocument20 pagesDrum FlakerAna Quintana100% (2)
- 7.operational Problems PDFDocument42 pages7.operational Problems PDFDeva VaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 45 KLD STP PROPOSAL VRANDAVAN GREENS PDFDocument9 pages45 KLD STP PROPOSAL VRANDAVAN GREENS PDFTech MongerPas encore d'évaluation
- DBDocument25 pagesDBAbhijit MondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Laundry Wastewater Treatment Using CoaguDocument20 pagesLaundry Wastewater Treatment Using CoaguAnggy de Rincon100% (1)
- Treatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Document4 pagesTreatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Dương Ánh100% (1)
- Sulphuric Acid Process Flow ChartDocument1 pageSulphuric Acid Process Flow ChartPoon CYPas encore d'évaluation
- Deferum 1Document12 pagesDeferum 1Azuwa NizamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Zetag 8140 - 0710Document6 pagesChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Zetag 8140 - 0710PromagEnviro.comPas encore d'évaluation
- DESIGN OF OIL AND GREASE TRAPS CalculationsDocument1 pageDESIGN OF OIL AND GREASE TRAPS Calculationsahsan maqsoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Enpro Project ReportDocument51 pagesEnpro Project ReportYadav VirendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation Example of Extended AerationDocument30 pagesCalculation Example of Extended AerationHRK65100% (1)
- Cod BodDocument4 pagesCod Bodgurubakkiamjai100% (1)
- MBR V Conv ComparisonDocument10 pagesMBR V Conv ComparisonJayakrishnan RadhakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sugar IndustryDocument27 pagesSugar IndustryChali HainePas encore d'évaluation
- Manual ENG - Kristal 600ER0820 V1.3b (221110)Document49 pagesManual ENG - Kristal 600ER0820 V1.3b (221110)merifie renegado67% (3)
- Rubber Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument2 pagesRubber Wastewater Treatment ProcessStan MacapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On: Sewage Treatment PlantDocument8 pagesPresentation On: Sewage Treatment PlantLeo VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Liu Yi-Design and Construction of Biogas Digester 2017Document74 pagesLiu Yi-Design and Construction of Biogas Digester 2017Stanley Wishmore MukuraPas encore d'évaluation
- DNIT Vol 2 Part 1Document196 pagesDNIT Vol 2 Part 1JitendraHatwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Report of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentDocument10 pagesReport of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentJulie MahadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ammonia StrippingDocument4 pagesAmmonia StrippingthirumuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- 19.2. Dewatering of Sludge by FiltrationDocument46 pages19.2. Dewatering of Sludge by FiltrationClaudia AvramPas encore d'évaluation
- Clarifier Settling Tank PDFDocument25 pagesClarifier Settling Tank PDFvenustasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 KLD STP Upgreation PROPOSAL-GMCPLDocument7 pages20 KLD STP Upgreation PROPOSAL-GMCPLTech Monger100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment Plant Revamping ReportDocument4 pagesSewage Treatment Plant Revamping Reportjeykumar.BalannairPas encore d'évaluation
- Utility List - Compressed Air Consumption DF - Rev0Document1 pageUtility List - Compressed Air Consumption DF - Rev0Aditya PranotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Watse ReportDocument17 pagesWatse ReportPrasenjit GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Characterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesMaliha CheemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Treatment Plant For Dyeing IDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Treatment Plant For Dyeing ISaravanaKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Production: Effluent Treatment PlantDocument12 pagesSustainable Production: Effluent Treatment PlantKush SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Silica Fouling On Fluoride Rejection in RO Membrane System (1) General IntroductionDocument8 pagesEffect of Silica Fouling On Fluoride Rejection in RO Membrane System (1) General IntroductionERENSKYPas encore d'évaluation
- Argal Chemical PumpDocument1 pageArgal Chemical PumpKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Argal PumpDocument1 pageArgal PumpKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- DOC040.52.10005.Oct12 Nutrients - Web PDFDocument8 pagesDOC040.52.10005.Oct12 Nutrients - Web PDFKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- 02.meir Kaisserman - Krakow PresentationDocument8 pages02.meir Kaisserman - Krakow PresentationKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Water 03 00157 v2 PDFDocument20 pagesWater 03 00157 v2 PDFKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 PDFDocument7 pages01 PDFKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- ACI APP D Supplemental Reinf PDFDocument2 pagesACI APP D Supplemental Reinf PDFKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- CG Water Sampling For Microbiological AnalysisDocument2 pagesCG Water Sampling For Microbiological AnalysisVasanthan VasPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflex G 2000, Grey, Standing Expansion Vessel, 10/3,5 Bar Article-No.:8527005Document1 pageReflex G 2000, Grey, Standing Expansion Vessel, 10/3,5 Bar Article-No.:8527005Kari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 FlotationDocument27 pages4 FlotationKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Bridge Lee.JDocument11 pages2017 Bridge Lee.JKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Manganese Removal in Drinking Water SystemsDocument9 pagesManganese Removal in Drinking Water SystemsKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Typical PDFDocument24 pagesTypical PDFKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 FlotationDocument27 pages4 FlotationKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- JHRv50n02 Article07 Cameron-Shah AppendixDocument6 pagesJHRv50n02 Article07 Cameron-Shah AppendixKari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuthill Blower Spec - 02Document8 pagesTuthill Blower Spec - 02Kari ConwayPas encore d'évaluation
- DS21Document3 pagesDS21vsdfsd258Pas encore d'évaluation
- EVAC Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant: Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) 40-360Document2 pagesEVAC Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant: Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) 40-360Paliwal A100% (1)
- Alldo DMXDMH MLDocument80 pagesAlldo DMXDMH MLNora PiñerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Water Treatment en April2016Document2 pagesWaste Water Treatment en April2016Ronald Figo Torres EchePas encore d'évaluation
- Bab Bahasan Buku QasimDocument2 pagesBab Bahasan Buku QasimRd Nur MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Evs Microproject 3rd YearDocument10 pagesEvs Microproject 3rd YearSwapnilPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Publications Brochure PDFDocument5 pages2018 Publications Brochure PDFnir1nstPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Design Calculations For STP and ETP by Richa Environmental Services PVT LTD PDFDocument6 pagesFree Design Calculations For STP and ETP by Richa Environmental Services PVT LTD PDFmuradali01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Course No.: BIOF216 Course Title: Water, Sanitation and Solid Waste ManagementDocument6 pagesCourse No.: BIOF216 Course Title: Water, Sanitation and Solid Waste ManagementJeswin EldhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary ClarifiersDocument51 pagesSecondary ClarifiersmakortoPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 8 Wastewater CharacterizationDocument8 pagesPart 8 Wastewater CharacterizationAhmad Mohmmed Jaradat0% (1)
- Wastewater Treatment: By: Engr. Abdul Mannan ZafarDocument21 pagesWastewater Treatment: By: Engr. Abdul Mannan ZafarWasif RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Trojan Uv Swiftect UvphoxDocument6 pagesTrojan Uv Swiftect UvphoxMonicaRossetimPas encore d'évaluation
- CEE361 HW#8 Questions Spring20Document3 pagesCEE361 HW#8 Questions Spring20Muhammad UkashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amr January 20Document96 pagesAmr January 20fernando quispialayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation For Activated Sludge ProcessDocument6 pagesCalculation For Activated Sludge ProcessNiong David78% (9)
- Water Refilling Station StudyDocument3 pagesWater Refilling Station StudyReynante Alabata63% (8)
- Calculation For Activated Sludge Process PDFDocument6 pagesCalculation For Activated Sludge Process PDFvinoohmPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Sedimentation Basins: Prof. Dr. Jabbar H. Al-BaidhaniDocument49 pagesDesign of Sedimentation Basins: Prof. Dr. Jabbar H. Al-BaidhaniFaisal Ahsan SadmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Performance Evaluation of A Down-Flow Hanging Sponge (DHS) Reactor As A Decentralized Domestic Wastewater Treatment System in Tropical RegionsDocument12 pages2020 Performance Evaluation of A Down-Flow Hanging Sponge (DHS) Reactor As A Decentralized Domestic Wastewater Treatment System in Tropical RegionsEddie D SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flat Sheet MBR MembraneDocument18 pagesFlat Sheet MBR MembraneNIHAR SHAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Wabag Biopur: Biofi Ltration For Wastewater TreatmentDocument6 pagesWabag Biopur: Biofi Ltration For Wastewater TreatmentNguyen AnPas encore d'évaluation
- DOLSAR Introduction - Jan 2019 PDFDocument77 pagesDOLSAR Introduction - Jan 2019 PDFAsad ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- MBR Membrane Bio ReactorDocument4 pagesMBR Membrane Bio ReactorecotechconsultantsPas encore d'évaluation
- Recycling of Grey Water Into Usable Water by Using Natural MaterialsDocument3 pagesRecycling of Grey Water Into Usable Water by Using Natural MaterialsVIVA-TECH IJRIPas encore d'évaluation
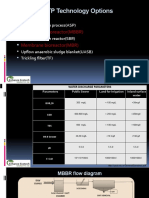
- STP Technology Options: Moving Bed Bioreactor (MBBR) Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)Document6 pagesSTP Technology Options: Moving Bed Bioreactor (MBBR) Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)amzad aliPas encore d'évaluation
- PRESENTATION CcwsDocument61 pagesPRESENTATION CcwsRamkiPas encore d'évaluation
- DWG-04.11-ME-031 Pri - Sludge - Pump - Station2 (r.6) PDFDocument5 pagesDWG-04.11-ME-031 Pri - Sludge - Pump - Station2 (r.6) PDFAhmed HussienPas encore d'évaluation
- Watersupplywastewatermanagement Ce345 190731023321Document88 pagesWatersupplywastewatermanagement Ce345 190731023321alqazitravels HARIPUR100% (1)
- CIDEX OPA Technical Info AP-2000304Document8 pagesCIDEX OPA Technical Info AP-2000304Ahmed EljenanPas encore d'évaluation