Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Power Point ch1s2
Transféré par
api-320485715Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Power Point ch1s2
Transféré par
api-320485715Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 1 Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
TEKS The student is expected to:
4A differentiate between physical and chemical
changes and properties
4B identify extensive and intensive properties
4C compare solids, liquids, and gases in terms of
compressibility, structure, shape, and volume
4D classify matter as pure substances or mixtures
through investigation of their properties
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Chapter 1 Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Preview
Lesson Starter
Objectives
Matter
Basic Building Blocks of Matter
Properties and Changes in Matter
Properties of Matter
Physical Properties and Physical Changes
Water in Three States
Chemical Properties and Chemical Changes
Evidence of a Chemical Change
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Lesson Starter
Mass of deflated balloon _______________
Mass of inflated balloon ________________
The matter in the balloon must have a mass.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Objectives
Distinguish between the physical properties and
chemical properties of matter.
Classify changes of matter as physical or chemical.
Explain the gas, liquid, and solid states in terms of
particles.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Objectives, continued
Explain how the law of conservation of energy
applies to changes of matter.
Distinguish between a mixture and a pure
substance.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Matter
Volume is the amount of three dimensional space an
object occupies.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter.
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up
space.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Matter
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Basic Building Blocks of Matter
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that
maintains the chemical identity of that element.
An element is a pure substance that cannot be
broken down into simpler, stable substances and is
made of one type of atom.
A compound is a substance that can be broken down
into simple stable substances. Each compound is
made from the atoms of two or more elements that
are chemically bonded.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Atom
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Element
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Molecule
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Compounds
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Basic Building Blocks of Matter, continued
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Properties and Changes in Matter
Extensive properties depend on the amount of
matter that is present.
volume
mass
the amount of energy in a substance.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Properties and Changes in Matter
Intensive properties do not depend on the amount
of matter present.
melting point
boiling point
density
ability to conduct electricity
ability to transfer energy as heat
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Properties of Matter
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Comparing Extensive and Intensive Properties
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Physical Properties and Physical Changes
A physical property is a characteristic that can be
observed or measured without changing the identity
of the substance.
melting point and boiling point
A physical change is a change in a substance that
does not involve a change in the identity of the
substance.
grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Physical Properties and Physical Changes,
continued
A change of state is a physical change of a
substance from one state to another.
states of mattersolid state, liquid state, gas state,
plasma
In the solid state, matter has definite volume and
definite shape.
In the liquid state, matter has a definite volume but
an indefinite shape.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Physical Properties and Physical Changes,
continued
In the gas state, matter has neither definite volume
nor definite shape.
Plasma is a high-temperature physical state of matter
in which atoms lose most of their electrons, particles
that make up atoms.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Liquid
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Gas
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Water in Three States
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Chemical Properties and Chemical Changes
A chemical property relates to a substances ability
to undergo changes that transform it into different
substances
A change in which one or more substances are
converted into different substances is called a
chemical change or chemical reaction.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Chemical Reaction
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Chemical Properties and Chemical Changes,
continued
The reactants are the substances that react in a
chemical change.
The products are the substances that are formed by
the chemical change.
reactants product
Carbon plus oxygen yields (or forms) carbon dioxide.
carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Evidence of a Chemical Change
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Electrolysis
of Water
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Comparison of Physical and Chemical
Properties
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Comparing Physical and Chemical Properties
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Comparing Chemical and Physical Changes
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Energy and Changes in Matter
Energy is always involved when physical or chemical
changes occur.
Energy can be in various forms.
heat
light
Energy can be absorbed or released in a change, it is
not destroyed or created.
law of conservation of energy
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Classification of Matter
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Classification Scheme for Matter
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Classifying Matter
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Classification of Matter
A mixture is a blend of two or more kinds of matter,
each of which retains its own identity and properties.
mixed together physically
can usually be separated
Homogeneous mixtures are called solutions
uniform in composition (salt-water solution)
Heterogeneous mixtures
not uniform throughout (clay-water mixture)
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Types of Mixtures
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Pure Substances
A pure substance has a fixed composition.
Pure substances are either compounds or elements.
A pure substance differs from a mixture in the
following ways:
Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the
same characteristic properties.
Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the
same composition.
Water is always 11.2% hydrogen and 88.8% oxygen by
mass.
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Laboratory Chemicals and Purity
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Section 2 Matter and Its Properties
Chapter 1
Examples of Mixtures
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Scienteer Plan 2018Document4 pagesScienteer Plan 2018api-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mixed Scientific Notation Problems 2-8Document7 pagesMixed Scientific Notation Problems 2-8api-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific NotationDocument1 pageScientific Notationapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Power NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Power Notesapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Average Atomic Mass Worksheet 2Document1 pageAverage Atomic Mass Worksheet 2api-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
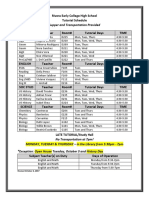
- Tutorial Flyer 10-2-2017Document1 pageTutorial Flyer 10-2-2017api-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Y IsotopepracticewkDocument1 pageY Isotopepracticewkapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: Name - PeriodDocument5 pagesLab Equipment Worksheet: Name - Periodapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sci Notation PracticeDocument1 pageSci Notation Practiceapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Notation Guided NotesDocument3 pagesScientific Notation Guided Notesapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Equipment ActivityDocument2 pagesLab Equipment Activityapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cal Using Sig FigDocument1 pageCal Using Sig Figapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Significant Figures WorksheetDocument2 pagesSignificant Figures Worksheetapi-320485715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 4327 Corrosive Sulphur Flyer PDFDocument2 pages4327 Corrosive Sulphur Flyer PDFMichael Angelo VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cafflano Ç Klassic User TipsDocument14 pagesCafflano Ç Klassic User TipsismuPas encore d'évaluation
- DGT-eex Brochure Eng 2020Document2 pagesDGT-eex Brochure Eng 2020Ali SadiqPas encore d'évaluation
- D7GDocument8 pagesD7Gfirman manaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Steven Thomas ResumeDocument1 pageSteven Thomas ResumestevenmthomasPas encore d'évaluation
- D-11 Chapter 9 Turb Alignment and S P ClearancesDocument17 pagesD-11 Chapter 9 Turb Alignment and S P ClearancesHernan Giraut100% (2)
- Magpul Industries M-Lok Information BookletDocument10 pagesMagpul Industries M-Lok Information BookletTwobirds Flying PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Polymers PPT PDFDocument47 pagesPolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevPas encore d'évaluation
- PadajucebrtveDocument11 pagesPadajucebrtveMonk3y MPas encore d'évaluation
- Battery ChargingDocument7 pagesBattery Charging123olympiakosPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering Competitive QuestionsDocument46 pagesCivil Engineering Competitive QuestionsSantosh Rai67% (3)
- 2 SinteringDocument32 pages2 SinteringGopikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Monitor m8-m9 User ManualDocument242 pagesMonitor m8-m9 User Manualcarlos6696Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yvoh8 18HP SM 0114 (En) PDFDocument224 pagesYvoh8 18HP SM 0114 (En) PDFTirta Noegraha100% (4)
- Uk Oti 66 1.7.06Document44 pagesUk Oti 66 1.7.06Nassar Al-shabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current Array TutorialDocument13 pagesEddy Current Array TutorialsameerPas encore d'évaluation
- CR800 Hybrid Low ResDocument8 pagesCR800 Hybrid Low RestappannPas encore d'évaluation
- Riko Technical Brochure PDFDocument29 pagesRiko Technical Brochure PDFGrigoreOzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Snamprogetti Saipem Urea Process AmmoniaDocument23 pagesSnamprogetti Saipem Urea Process AmmoniaTu Hai50% (2)
- Computer-Integrated ManufacturingDocument12 pagesComputer-Integrated ManufacturingGagandeep Singh SidhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Modular CNC Mini Mill Assy-01Document1 pageModular CNC Mini Mill Assy-01ModularCNC100% (1)
- What Defines An Industrial GasDocument2 pagesWhat Defines An Industrial GasYuri YamirnovPas encore d'évaluation
- Explosion of An Aqueous Ammonia Scrubber Tank at Yara Italia, FerraraDocument8 pagesExplosion of An Aqueous Ammonia Scrubber Tank at Yara Italia, Ferraravaratharajan g rPas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statement For Pipeline WeldingDocument21 pagesMethod Statement For Pipeline WeldingKhwanas Luqman100% (1)
- TLC PDFDocument5 pagesTLC PDFAV&P Lord100% (1)
- CE2021 ME2010 2016 Tute 05 PDFDocument3 pagesCE2021 ME2010 2016 Tute 05 PDFAAKIL AHAMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusprajari ghoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase Changes Independent Practice Spring 2016Document3 pagesPhase Changes Independent Practice Spring 2016Jarrod CollinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 Filtration-Grp. 5Document20 pagesExperiment 3 Filtration-Grp. 5Claudine Valdez100% (1)
- Stabilised Mud Block Production With Mardini Block PressDocument16 pagesStabilised Mud Block Production With Mardini Block PressMahesh ConstructionPas encore d'évaluation