Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Tissues G-IX
Transféré par
Srinivas Venkataraman0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
239 vues3 pagesassignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentassignment
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
239 vues3 pagesBiology Tissues G-IX
Transféré par
Srinivas Venkataramanassignment
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
AECS MAGNOLIA MAARUTI PUBLIC SCHOOL
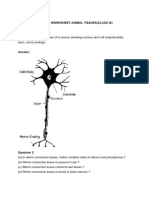
Arekere, B.G. Road, Bangalore 76
Question Bank
Subject: Science (Biology)
Grade: IX Topic: Tissues
Answer the following question:
1. What are the utility tissues in multicellular organisms?
2. What is the name given to a group of cells? Are these group of cells same for
plants and animals? What is the difference between them?
3. Which tissue is responsible for growth in plants? Why growth of plant takes
place only in specific regions.
4. What are the various types of tissues in plants?
5. State the functions of
a) parenchyma
b) collenechyma
c) sclerenchyma
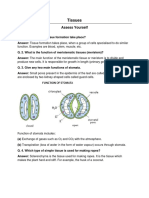
6. State the functions and location of the following meristems.
a) apical meristem
b) intercalary meristem
c) lateral meristem
7. What are complex tissues? What constitute them and why are they called so?
8. What are the functions of xylem and phloem?
9. Name the different types of tissues found in you.
10. Name the tissues which is found on the surface of your skin and what is it
composed of?
11. Which type of muscles/tissues are found in the
a) Iris of the eyes.
b) Viscera
c) Ureters/Kidney tubule of excretory system
d) nose, ear
e) aquatic plants for buoyancy.
12. Why are smooth muscles called involuntary muscles?
13. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut? What is the function of this tissue
in the plant body?
14. Give reasons.
a) Meristamatic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they
lack vacuole.
b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissue.
c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
d) Blood is a fluid connective tissue.
15. Name the following tissues:
a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of mouth.
b) Tissue that connects muscles to bone in human.
c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
f) Tissue present in the brain.
g) The plant tissues used for making ropes.
h) Bark of a tree.
16. Differences between striated, smooth and cardiac muscle.
17. Growth in plants is restricted to certain regions. Give reason for this fact.
Mention two growth regions in plant.
18. Do the roots of a plant continue growing after their tips are removed? Explain
giving reason.
19. How are meristematic tissues different from permanent tissues?
20. What are the small pores present in the epidermis of leaf called as? What are
the functions performed by such pores?
21. Draw a neat labeled diagram of location of the meristematic tissues in the
plant body.
22. Draw a well labeled diagram of a neuron.
23. What is the specific function of cardiac muscle?
24. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
25. Give the schematic diagram/flowchart for the classification of plant tissues.
26. Animal of colder region and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of
subcutaneous fat? Describe why?
27. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall
of glass jar? Explain why?
28. Water hyacinth floats on water surface. Explain.
29. Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
30. What are the characteristic features to identify a nerve cell?
31. Write one word for the following.
a) Tissue present in soft parts of the plant like cortex and pith of stem.
b) Long and unbranched extension of a neuron.
c) A component of phloem formed by end to end fusion of cells with
perforated transverse walls.
d) Thickenings present in sclerenchyma cells.
e) Water proof layer present on the outer wall of epidermal cells.
f) Zig-zag thickenings in cardiac muscles.
32. What will happen if the phloem at the base of a branch is removed?
33. Name the tissue that smoothens bone surface at joints. Describe its structure
with the help of a diagram.
34. Name three different types of blood cells and give their functions. Draw a
diagram of any one of them.
35. Draw a neat diagram of leaf epidermal peel showing stomata label any two
parts.
**********************
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Grade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Document3 pagesGrade 9 - Tissues - Revision WRKSHT - 23-24Yashvi PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Bio Chap 6 Tissues QSTN BankDocument7 pages9th Bio Chap 6 Tissues QSTN BankArunKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- TissuesDocument23 pagesTissuesAadarsh RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - TissuesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - Tissuesankit anandPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th TissueDocument6 pages9th TissueRanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal Tissuesvedanthendre5Pas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument19 pagesBiologyBhavyaraj GohilPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6VI A 19 Aaryan JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- 9bio AssignmentDocument2 pages9bio AssignmentKrishna GovilPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseArpan KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 09 Biology - Chapter Tissue Solved Questions - 6Document2 pagesClass 09 Biology - Chapter Tissue Solved Questions - 6Anusha AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper BiologyDocument3 pagesSample Paper BiologyMini PGPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue Q&ADocument6 pagesTissue Q&ASuman DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Class-Ix CHAPTER-2, Tissues A. Give Reasons, WhyDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class-Ix CHAPTER-2, Tissues A. Give Reasons, WhyMy Fact worldPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeDocument31 pagesTissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeAyushi VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class-8, Ch5,6Document2 pagesClass-8, Ch5,6Amit Kumar LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesleenaapPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Bio Important QuesDocument12 pages9th Bio Important QuesData SharePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Document5 pagesChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- TissuesDocument5 pagesTissuesDarshilPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocument5 pages09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- JihijiojhiDocument5 pagesJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocument11 pagesScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsDocument11 pages2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsGauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Test-1class Ix TissuesDocument5 pagesRevision Test-1class Ix TissuesAnwesh NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Questions For Class 9th - CH 6 Tissues Science Study Rankers PDFDocument6 pagesExtra Questions For Class 9th - CH 6 Tissues Science Study Rankers PDFsssPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet - 1 Biology IxDocument2 pagesWorksheet - 1 Biology Ixhoney1002Pas encore d'évaluation
- WS CH 6 - 2Document2 pagesWS CH 6 - 2ayan.aggarwallPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues: One Mark QuestionsDocument12 pagesTissues: One Mark QuestionsSrividhya ManikandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues Comprehensive NotesDocument16 pagesTissues Comprehensive NotesMuhammad SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Epithelial TissueDocument2 pagesEpithelial Tissueapi-295869261Pas encore d'évaluation
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and Function - WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function - WorksheetblackcatPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)Document11 pagesBIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)RaashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7Document7 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 7Seenu SPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocument13 pages9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData SharePas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue SubjectiveDocument1 pageTissue SubjectiveKHUSHKARAN SANDHUPas encore d'évaluation
- cell and its structure (разработка)Document8 pagescell and its structure (разработка)Ирина КривошеяPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology How Life Works 2Nd Edition Morris Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesBiology How Life Works 2Nd Edition Morris Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbierbalkgeorge3f17100% (12)
- 1695651173960.class9 Animal Tissue OnewordDocument1 page1695651173960.class9 Animal Tissue OnewordSai KaushalPas encore d'évaluation
- ST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)Document6 pagesST - John'S School Greater Noida West Subject: Science CLASS IX: BIOLOGY (2020 - 21) Chapter - 6 Tissues (Answer Key - 2)India Tech with AstitvaPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - RevisionDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Worksheet - RevisionFabioPas encore d'évaluation
- Hsslive-Xi-Zoology-Qb-Ch-3-Structural Organisation-NavasDocument9 pagesHsslive-Xi-Zoology-Qb-Ch-3-Structural Organisation-Navasashlyyyyyy33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Anatomy (Q-Bank 2020)Document22 pagesElementary Anatomy (Q-Bank 2020)Muhammad AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsDocument87 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsMahimna SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 910th Bio QuesDocument19 pages910th Bio QuesData SharePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 4 Student Packet (ANP)Document7 pagesCh. 4 Student Packet (ANP)Alex ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants: One Mark QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants: One Mark QuestionsHaripriya KotariPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Test Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesPlant Test Multiple Choice QuestionsnamratanimiPas encore d'évaluation
- A&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideDocument2 pagesA&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideJoe ChounramanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Worksheet: Biology IXDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet: Biology IXDharmendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocument11 pagesTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-01 (Solved)Document15 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-01 (Solved)cbsesamplepaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzPas encore d'évaluation
- TissuesDocument7 pagesTissuesRohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 Bio PaperDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Bio PaperOm SolaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Results and Technique Comparison: in Vivo Dosimetry For Total Body Irradiation: Five-YearDocument10 pagesResults and Technique Comparison: in Vivo Dosimetry For Total Body Irradiation: Five-YearSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- NSEA - 2017: AnalysisDocument8 pagesNSEA - 2017: AnalysisSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT 17Document60 pagesRPT 17Srinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Exposures Fact Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesMedical Exposures Fact Sheet PDFSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Exposures Fact SheetDocument1 pageMedical Exposures Fact SheetSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 Special Techniques PDFDocument259 pagesChapter 15 Special Techniques PDFSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Doses Near The Surface During Total-Body Irradiation With 15 MV X-RaysDocument6 pagesDoses Near The Surface During Total-Body Irradiation With 15 MV X-RaysSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2017: AnswersDocument1 pageAakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2017: AnswersSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ 2009 Soln PDFDocument7 pagesMCQ 2009 Soln PDFSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International As and A Level ChemistryDocument557 pagesCambridge International As and A Level ChemistryAamirShafique100% (2)
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument24 pagesMetals and Non MetalsSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Units and Dimensions PDFDocument20 pagesUnits and Dimensions PDFSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International As and A Level ChemistryDocument557 pagesCambridge International As and A Level ChemistrySrinivas Venkataraman0% (1)
- Assignment: Linear Equations in One Variable: Class VIII IIT-JEE Pre-Foundation MathsDocument8 pagesAssignment: Linear Equations in One Variable: Class VIII IIT-JEE Pre-Foundation MathsSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilaterals PDFDocument2 pagesQuadrilaterals PDFSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Areas and Volumes - GSDocument2 pagesSurface Areas and Volumes - GSSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jstse Previous Years: (Mathematics: Triangles TS)Document2 pagesJstse Previous Years: (Mathematics: Triangles TS)Srinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2017: AnswersDocument1 pageAakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2017: AnswersSrinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jstse Previous Years: (Mathematics: Polynomials)Document1 pageJstse Previous Years: (Mathematics: Polynomials)Srinivas VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract Law: Offer & Acceptance CasesDocument8 pagesContract Law: Offer & Acceptance CasesAudrey JongPas encore d'évaluation
- Fail Operational and PassiveDocument1 pageFail Operational and PassiverobsousPas encore d'évaluation
- BrookfieldDocument8 pagesBrookfieldFariha Naseer Haral - 28336/TCHR/JVAITPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation For Service Platform & Pump Shelter StructureDocument36 pagesCalculation For Service Platform & Pump Shelter Structuretrian33100% (1)
- Cambridge English First Fce From 2015 Reading and Use of English Part 7Document5 pagesCambridge English First Fce From 2015 Reading and Use of English Part 7JunanPas encore d'évaluation
- BD9897FS Ic DetailsDocument5 pagesBD9897FS Ic DetailsSundaram LakshmananPas encore d'évaluation
- Sosa Ernest - Causation PDFDocument259 pagesSosa Ernest - Causation PDFtri korne penal100% (1)
- 3658 - Implement Load BalancingDocument6 pages3658 - Implement Load BalancingDavid Hung NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- School Based CPPDocument11 pagesSchool Based CPPjocelyn g. temporosa100% (1)
- Chapter 2-EER and Relational Database SchemaDocument146 pagesChapter 2-EER and Relational Database Schemagirmay tadesePas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical TestsDocument47 pagesStatistical TestsUche Nwa ElijahPas encore d'évaluation
- ch09 (POM)Document35 pagesch09 (POM)jayvee cahambingPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahasa Inggris XIIDocument1 pageBahasa Inggris XIIclaudiaomega.pPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of A Single Axis Tilting QuadcopterDocument4 pagesDevelopment of A Single Axis Tilting QuadcopterbasavasagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tfa Essay RubricDocument1 pageTfa Essay Rubricapi-448269753Pas encore d'évaluation
- They Cried MonsterDocument13 pagesThey Cried MonstermassuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ghosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthDocument7 pagesGhosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthCinthia MtzPas encore d'évaluation
- Womack - Labor History, Industrial Work, Economics, Sociology and Strategic Position PDFDocument237 pagesWomack - Labor History, Industrial Work, Economics, Sociology and Strategic Position PDFhmaravilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFDocument56 pagesMeasurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFmadivala nagarajaPas encore d'évaluation
- AD&D 2nd Edition - Dark Sun - Monstrous Compendium - Appendix II - Terrors Beyond Tyr PDFDocument130 pagesAD&D 2nd Edition - Dark Sun - Monstrous Compendium - Appendix II - Terrors Beyond Tyr PDFWannes Ikkuhyu100% (8)
- National ScientistDocument2 pagesNational ScientistHu T. BunuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Long-Distance HADR ConfigurationsDocument73 pagesAutomated Long-Distance HADR ConfigurationsKan DuPas encore d'évaluation
- Modbus Manual TD80 PDFDocument34 pagesModbus Manual TD80 PDFAmar ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Feb 1 - ScottDocument17 pagesFeb 1 - ScottNyannnPas encore d'évaluation
- Hanssen, Eirik.Document17 pagesHanssen, Eirik.crazijoePas encore d'évaluation
- Shostakovich: Symphony No. 13Document16 pagesShostakovich: Symphony No. 13Bol DigPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2cesar jimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloze Tests 2Document8 pagesCloze Tests 2Tatjana StijepovicPas encore d'évaluation
- PEBDocument4 pagesPEBDR RISKA WAHYUPas encore d'évaluation