Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
3
Transféré par
Vicente TurasTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
3
Transféré par
Vicente TurasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
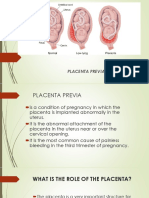
Placenta Previa
Placenta previa is the low implantation of the placenta. The types of placenta previa are
the following:
1. Low-lying placenta previa the implantation took place in the lower portion rather than the
upper portion of the uterus.
2. Marginal placenta previa the placental edges are approaching the cervical os.
3. Partial placenta previa a portion of cerval os is occluded by the placental portion.
4. Total placenta previa implantation that totally obstructs the cervical os.
Risk factors
Increased parity
Advanced maternal age
Past cesarean births
Past uterine curettage
Multiple gestation
Signs and Symptoms
Bleeding bright red blood. The lower uterine segment begins to differentiate with the
upper segment later in pregnancy. Placenta has the inability to stretch to accommodate
the differeing shape of the lower uterine segment or the cervix, thus, abrupt and bright red
bleeding occurs.
Painless bleeding
Sudden bleeding
Abruptio Placenta
In this condition, the placenta has been implanted correctly, however the placenta
separates prematurely.
Incidence
It occurs in about 10% of pregnancies and is the most common cause of perinatal death.
Risk factors
High parity
Advanced maternal age
A short umbilical cord
Chronic hypertensive disease
Pregnancy-induced hypertension
Direct trauma
Vasoconstriction from cigarette use
Thrombophilitic conditions that lead to thrombosis such as autoimmune antibodies
Signs and symptoms
Sharp, stabbing pain high in the uterine fundus (during initial separation)
Tenderness felt on uterine palpation
Heavy bleeding (not readily apparent). Blood can either pool under the placenta and be
hidden from view. External bleeding is only present if the placenta separates first at the
edges and blood escapes freely from the cervix.
Hard, boardlike uterus with no apparent or minimally apparent bleeding
Dark red blood (in bleeding episodes)
Difference Between Placenta Previa and Abruption Placenta
Category Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta
Problem Low implantation of the placenta Premature separation of the placenta
Incidence It occurs in approximately 5 in every 1000 It occurs in about 10% of pregnancies and is
pregnancies the most common cause of perinatal death.
Bleeding Always present May or may not be present
Color of blood in Bright red Dark red
bleeding episodes
Pain during PAINLESS SHARP, STABBING PAIN
bleeding
Management Bed rest (side lying position) Fluid replacement
NO vaginal or pelvic examinations Oxygen by mask
Assessment of FHR and bleeding Monitor FHR
Lateral position Keep the woman in a lateral position
No vaginal or pelvic examinations DO NOT perform any vaginal or
Termination of pregnancy pelvic examinations or give enema
Pregnancy must be terminated
Therapeutic Management because the fetus cannot obtain
1. Place the woman immediately on bed adequate oxygen and nutrients. If
rest in a side-lying position. birth does not seem imminent,
2. Weight perineal pads. cesarean birth is method of choice
3. NEVER attempt a pelvic or rectal for delivery.
examination because it may initiate
massive blood loss.
Ectopic Pregnancy
For pregnancy to happen, the ovary has to release an egg into the fallopian tube, where it
stays for about 24 hours. There it has to come in contact with a sperm to be fertilized. The fertilized
egg stays in the fallopian tube for 3 or 4 days before it heads to the uterus. There it attaches to the
lining and continues to grow until a baby is born.
But if the fertilized egg implants in your fallopian tube or somewhere else in your abdomen,
you end up with whats called an ectopic pregnancy. In these cases, the pregnancy cant continue
normally, and it requires emergency treatment.
Symptoms. Most of the time, an ectopic pregnancy happens within the first few weeks of
pregnancy. You might not even know you're pregnant and may not have signs of a problem.
Light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain are usually the first symptoms, but others could include:
Nausea and vomiting with pain
Sharp abdominal cramps
Pain on one side of your body
Dizziness or weakness
Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum
Ectopic pregnancy can lead to fallopian tube rupture. If that happens, you could have major pain
and severe bleeding. Call your doctor immediately if you have heavy vaginal bleeding that causes
lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain.
Causes. You may never know why you have an ectopic pregnancy. One cause could be a
damaged fallopian tube. It could prevent the fertilized egg from getting into your uterus, leaving it to
implant in the fallopian tube or somewhere else.
But you are more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy if you have any of the following:
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Sexually-transmitted diseases
Scarring from previous pelvic surgeries
History of ectopic pregnancy
Unsuccessful tubal ligation or tubal ligation reversal
Use of fertility drugs
Infertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF)
It could also happen if you become pregnant with an intrauterine device (IUD) in place.
Diagnosis. If your doctor thinks you have an ectopic pregnancy, she will probably perform some
tests, including a pregnancy test and a pelvic exam. An ultrasound test may be performed to view
the uterus and fallopian tubes condition.
If she confirms you have an ectopic pregnancy, she will talk to you about the best treatment based
on your medical condition and your future plans for pregnancy.
Treatments.
Medication. If your fallopian tube hasnt ruptured and your pregnancy hasnt progressed
very far, your doctor can give you an injection of methotrexate (Trexall). It stops the cells from
growing, and your body will simply absorb them. Most ectopic pregnancies can be treated with
methotrexate if theyre caught early.
Surgery. In other cases, surgery is required. The most common is laparoscopy. Your doctor
will make very small incisions in your lower abdomen and insert a thin, flexible instrument
(laparoscope) to remove the ectopic pregnancy. If your fallopian tube is damaged, she may have to
remove it as well.If youre bleeding heavily or your doctor suspects your fallopian tube is ruptured,
you might need emergency surgery with a larger incision. This is called laparotomy.
After an Ectopic Pregnancy. There is a good chance you can have a normal pregnancy again,
but it might be hard. You should consider talking to a fertility specialist early, especially if you had a
fallopian tube removed.
And talk to your doctor about how long to wait before trying again. Some doctors suggest at least 3
to 6 months. If youve already had an ectopic pregnancy, your chances of having another one go up.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesEctopic PregnancyforbiddenleiPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief Description: Ectopic PregnancyDocument6 pagesBrief Description: Ectopic PregnancyQueenet BelingonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding in Late PregnancyDocument76 pagesBleeding in Late PregnancySamia Abu AishiaPas encore d'évaluation
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookD'EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- OB/GYN For EMS ProvidersDocument94 pagesOB/GYN For EMS ProvidersPaulhotvw67100% (6)
- Ass Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesAss Ectopic PregnancyPriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Triemster BleedingDocument69 pages3rd Triemster BleedingRaiden VizcondePas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesUterus: Signs and SymptomsJoy Parallag - BautoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument11 pagesEctopic PregnancyPrincess BalloPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 4 Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta....Document51 pagesDay 4 Placenta Previa Abruptio Placenta....Marga WreathePas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument81 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageOmar mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Document10 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Diane Celine SantianoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk Conditions During Labor and DeliveryDocument14 pagesHigh Risk Conditions During Labor and DeliveryEdgar HinotanPas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta Previa A Case StudyDocument27 pagesPlacenta Previa A Case StudyJustin AlejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Medlineplus TopicsDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Medlineplus TopicsJonathan BendecioPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Renhe Hospital Wang JunjieDocument51 pagesAbortion: Renhe Hospital Wang JunjieMadhu Sudhan PandeyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralDocument45 pagesHemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralAngel Mae BaborPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaginal Bleeding in Late PregnancyDocument139 pagesVaginal Bleeding in Late PregnancygibreilPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding in Early Pregnancy Slide WorldDocument57 pagesBleeding in Early Pregnancy Slide Worlddashing_ritamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument17 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanLizcelle Bihasa86% (7)
- Ectopic Pregnancy Final EditDocument11 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Final EditBRAIMA JOHNPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuDocument44 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuLiangkiuwiliuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy - OMDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - OMrheindPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaginal Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument8 pagesVaginal Bleeding in Early PregnancyBal Ri Mekoleu100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument17 pagesEctopic PregnancyB.HemavarshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy Kehamilan Luar RahimDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Kehamilan Luar RahimMuhamad Aminuddin Abu BakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanJack BangcoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo ManongdoDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo Manongdoliam0831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Ectopic PregnancyDocument8 pagesManagement of Ectopic PregnancySulaiman WalizadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesUterus: Signs and SymptomsmoigomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesUterus: Signs and SymptomsmoigomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Information For You: An Ectopic PregnancyDocument25 pagesInformation For You: An Ectopic PregnancyAnonymous layszXmsPas encore d'évaluation
- EctopicDocument13 pagesEctopicZoe Jeanne GarcianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta PreviaDocument43 pagesPlacenta PreviaAngela Joy AmparadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta PreviaDocument19 pagesPlacenta Previarosekatekate929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument10 pagesAbruptio PlacentaDoc DudayPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Abortion& Ectopic PXDocument33 pages2 Abortion& Ectopic PXabrhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5 - 1Document40 pagesComplications During Pregnancy - Chapt 5 - 1Bob IrsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDocument9 pagesSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Process - Placenta PreviaDocument56 pagesNursing Process - Placenta PreviaRicardo Robianes BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cesarean Birth (Breech Presentation)Document5 pagesCesarean Birth (Breech Presentation)Dave Noel AytinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2C Orev Compilation TopicDocument56 pages2C Orev Compilation TopicPaolo AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Trimester RisksDocument67 pages3rd Trimester RisksCrisha SaguidPas encore d'évaluation
- Perdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaDocument26 pagesPerdarahan Antepartum - EmiliaEmilia NazmaPas encore d'évaluation
- M102 Remedial ModuleDocument14 pagesM102 Remedial ModuleMA. JYRELL BONITOPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy JournalDocument3 pagesEctopic Pregnancy JournalSiska FriedmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Togdher University Lectural Asma Da, Ud Kahin Class of Midwifery and Nursing Course Title Reproductive HealthDocument18 pagesTogdher University Lectural Asma Da, Ud Kahin Class of Midwifery and Nursing Course Title Reproductive HealthHoodo AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Aph Family MedicineDocument79 pagesAph Family MedicineMohammad Nahel SorourPas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta PreviaDocument2 pagesPlacenta PreviaSilverius Seantoni SabellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy - ClinicalKeyDocument21 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - ClinicalKeyFirmandi ArafatPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of Labor Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesStages of Labor Nursing Considerationsneleh gray100% (2)
- High-Risk Labor & Delivery Client & Her FamilyDocument68 pagesHigh-Risk Labor & Delivery Client & Her FamilyJAMES ROD MARINDUQUEPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument4 pagesEctopic PregnancyJovie Anne BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Unit 04 ObDocument9 pagesCourse Unit 04 ObDenise FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion and MiscarriageDocument38 pagesAbortion and MiscarriageJane Ann AlolodPas encore d'évaluation
- Shubrat Singh: EctopicDocument25 pagesShubrat Singh: Ectopicshubham royalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument4 pagesEctopic PregnancySyahriana AnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding DisordersDocument20 pagesBleeding DisordersSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy 1Document8 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 1Nansy DaasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesEctopic PregnancyMary Anne Yap100% (1)
- PJN Aguilar Et AlDocument5 pagesPJN Aguilar Et AlVicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cec Post Fall Assess and Man June 2013Document3 pagesCec Post Fall Assess and Man June 2013Vicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- BGH ChartingDocument3 pagesBGH ChartingVicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheets On The Following Aspects of A Quality Improvement ProjectDocument7 pagesWorksheets On The Following Aspects of A Quality Improvement ProjectVicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- Corticosteroids and ARDS: A Review of Treatment and Prevention EvidenceDocument6 pagesCorticosteroids and ARDS: A Review of Treatment and Prevention EvidenceVicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- Asakawa 2003 BDocument10 pagesAsakawa 2003 BVicente TurasPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Procedure Protocols For Parasitological Sample Collection ProcessingDocument36 pagesLaboratory Procedure Protocols For Parasitological Sample Collection ProcessingDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (4)
- VirologyDocument27 pagesVirologyAgus Nurul HidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Deep Learning and Machine Learning in Healthcare Domain - A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesApplications of Deep Learning and Machine Learning in Healthcare Domain - A Literature ReviewIAEME PublicationPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Healing Occurs in Fractures Treated With Stress Sharing Devices Such As CastsDocument4 pagesSecondary Healing Occurs in Fractures Treated With Stress Sharing Devices Such As CastsYuva RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patofisiologi Kanker RahimDocument98 pagesPatofisiologi Kanker RahimOjo Nesu100% (1)
- Top 10 Differential Diagnoses in Family Medicine - CoughDocument2 pagesTop 10 Differential Diagnoses in Family Medicine - CoughTiza OyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nej M CPC 2103461Document10 pagesNej M CPC 2103461monaPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Pharma (NLE)Document2 pagesApplied Pharma (NLE)Maginalyn CangasPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune Dysregulation Among Students Exposed To Exam Stress and Its Mitigation by Mindfulness Training - Findings From An Exploratory Randomised TrialDocument11 pagesImmune Dysregulation Among Students Exposed To Exam Stress and Its Mitigation by Mindfulness Training - Findings From An Exploratory Randomised TrialPatricia Elena ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Npte Exam TablesDocument586 pagesNpte Exam TablesarbazPas encore d'évaluation
- Topnotch Practice Exam 1 For MARCH 2020 and SEPT 2020 BatchesDocument104 pagesTopnotch Practice Exam 1 For MARCH 2020 and SEPT 2020 BatchesJerome AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Okir A DatuDocument6 pagesOkir A DatuRonel FillomenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Additives in FoodDocument21 pagesLesson Plan Additives in FoodZahra AlkhansaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manila Standard Today - July 21, 2012 IssueDocument16 pagesManila Standard Today - July 21, 2012 IssueManila Standard TodayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cases Journal: Acquired Nonobstructive Urinary Bladder Diverticulum: A CaseDocument3 pagesCases Journal: Acquired Nonobstructive Urinary Bladder Diverticulum: A CaseIrma Suriani DarwisPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial Distribution ExercisesDocument3 pagesBinomial Distribution ExercisesAlp Eren AKYUZPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Espresso Coffee Machine ParametersDocument10 pagesImportance of Espresso Coffee Machine ParametersOssian89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology Paper 1 Question BankDocument8 pagesPhysiology Paper 1 Question BankVeshalinee100% (1)
- Saluyot (Sci2)Document8 pagesSaluyot (Sci2)Lina Quintero OdalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilation: Kinematics and Kinetics.: Thorax Structure and FunctionDocument52 pagesVentilation: Kinematics and Kinetics.: Thorax Structure and FunctionAlejandra RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortify Your Knowledge About Vitamins PDFDocument3 pagesFortify Your Knowledge About Vitamins PDFpgomperPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of BioethicsDocument7 pagesPrinciples of BioethicsNuronnisah Kalinggalan PadjiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthorexia Nervosa: HistoryDocument3 pagesOrthorexia Nervosa: HistorySimona LeafuPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodontal Therapy in Older AdultsDocument15 pagesPeriodontal Therapy in Older AdultsPathivada Lumbini100% (1)
- Define Education: Why Education Is Important To SocietyDocument5 pagesDefine Education: Why Education Is Important To SocietyzubairPas encore d'évaluation
- Cuscuta AssignmentDocument12 pagesCuscuta AssignmentAshfaq Hussain KharalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulacan State UniversityDocument5 pagesBulacan State UniversityAlexandra CamuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary Function TestDocument7 pagesPulmonary Function TestGhada HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Giannopoulos PC - AlDocument54 pagesGiannopoulos PC - AlNikosPas encore d'évaluation