Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SI (International System of Units) : (Technical Data)
Transféré par
anoopkntpcTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SI (International System of Units) : (Technical Data)
Transféré par
anoopkntpcDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
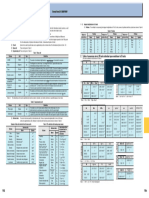
[Technical Data]
SI(International System of Units) Excerpt from JIS Z 8203(2000)
1. International System of Units(SI)and Usage. 1-3. Multiples of 10 of SI Units
1-1. Scope of Application This standard specifies how to use the International System of Units(SI)and other international unitary systems, as well as (1)Prefix The multiples and the names and symbols of prefixes to express integer multiples of 10 of SI Units are shown in Table 4.
units used in correlation with units from international systems, and other units which may be used. Table 4 prefix.
1-2. Terms and Definitions Terminology used in this specification and definitions thereof are as follows. Prefix Prefix Prefix
Multiples Multiples Multiples
(1) International System of Units(SI) Coherent system of units adopted and recommended by the International Committee on Weights and Measures. of Unit Name Symbol of Unit Name Symbol of Unit Name Symbol
It contains base units and supplementary units, units derived from them and their integral exponents to the 10th power. 1018 Exsa E 102 Hecto h 109 Nano n
(2) SI Unit Generic term used to describe base units, supplementary units or derived units of the International System of Units(SI). 1015 Peta P 101 Deca da 1012 Pico p
(3) 1 Base Unit Those units are given in Table 1. 1012 Tera T 101 Deci d 1015 Femto f
(4) 2 Supplementary Units Those supplementary units are given in Table 2. 109 Giga G 102 Centi c 1018 Atto a
106 Mega M 103 Milli m
Table 1. Base Units 103 Kilo k 106 Micro
Base Quantity Unit Symbol Definition 2. Conversion Tables for SI and Conventional Units
1 (The units enclosed by thick lines are the SI units.)
Length Meter m A meter is the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 299 792 458 of a second.
N Ibf kgf Pas cP P
A kilogram is a unit of mass(neither weight nor force), it is equal to the mass of the
Mass Kilogram kg
Viscosity
international prototype of the kilogram. 1 0.22481 1.01972101 1 1103 110
Force
A second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of radiation corresponding to the transition 4.448 1 0.4536 1103 1 1102
Time Second s
between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium 133 atom.
1 2
An ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of 9.806 65 2.205 1 110 110 1
Current Ampere A infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in a vacuum, Note) 1P=1dyns/cm2=1g/cms
would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2107 Newton per meter of length. 1Pas=1Ns/m2, 1cP=1mPas
1
Thermodynamic Temperature Kelvin K Kelvin, a unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.
273.16
Kinematic Viscosity
A mole is the amount of substance of a system that contains as many elementary particles(1) Pa or N/m2 MPa or N/mm2 Ibf/in2 kgf/cm2 m2/s cSt St
Amount of Substance Mole mol or aggregation of elementary particles as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon 12 and 1 110 6
0.14510 3
1.019 7210 5
1 1106 1104
when the mole is used, the elementary particles must be specified.
Stress
1106 1 145 1.019 7210 1106 1 1102
A candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of
Luminance Intensity Candela cd 1 6896.55 6.89710 3
1 0.0703 1104 1102 1
frequency 5401012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 683 watt per steradian.
9.806 65104 9.806 65102 14.22 1 Note) 1St=1cm2/s, 1cSt=1mm2/s
Note(1) The elementary particles here must be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or other particles.
Note) 1Pa=1N/m2, 1MPa=1N/mm2
Table 2. Supplementary Units
Base Quantity Unit Symbol Definition
mmHg
A radian is the plane angle between two radii of a circle that cuts off an arc on the Pa kPa MPa bar kgf/cm2 atm mmH2O or
Plane Angle Radian rad
circumference equal in length to the radius. Torr
A steradian is the solid angle which, having its vertex in the center of a sphere, cuts off an area of the 1 1 103 1 106 1105 1.019 72105 9.869 23106 1.019 72101 7.500 62103
Solid Angle Steradian sr
surface of the sphere equal to that of a square with sides equal in length to the radius of the sphere.
3 3 2 2 3 2
1 10 1 1 10 110 1.019 7210 9.869 2310 1.019 7210 7.500 62
(5)3 Derived Units The supplementary units algebraically expressed using mathematical symbols such as plus, minus, etc.
Pressure
The SI derived units with special names and symbols are given in Table 3. 1 106 1 103 1 110 1.019 7210 9.869 23 1.019 72105 7.500 62103
5 2 1 1 4
1 10 1 10 1 10 1 1.019 72 9.869 2310 1.019 7210 7.500 62102
Examples of SI Derived Units Expressed in Terms of Base Units Table 3 SI Derived Units with Special Names and Symbols
4 2 1 1 4
9.806 65 10 9.806 65 10 9.806 65 10 9.806 6510 1 9.678 4110 110 7.355 59102
Base Quantity Base Quantity Expression in Terms of Base
Base Quantity Units or Supplementary 1.013 25 10 5
1.013 25 10 2
1.013 25 10 1
1.013 25 1.033 23 1 1.033 2310 4
7.600 00102
Name Symbol Base Quantity
Units, Supplementary Units 3 6 5 4 5
Area Square m2 Name Symbol or Other SI Units 9.806 65 9.806 65 10 9.806 65 10 9.806 6510 110 9.678 4110 1 7.355 59102
2 1 4 3 3 3
Volume Cubic Meter m3 Frequency Hertz Hz 1 Hz =1 s1 1.333 22 10 1.333 22 10 1.333 22 10 1.333 2210 1.359 5110 1.315 7910 1.359 5110 1
Velocity Meter/Second m/s Force Newton N 1 N =1 kgm/s2 Note) 1Pa=1N/m2
Acceleration Meter/Second2 m/s2 Pressure, Stress Pascal Pa 1 Pa =1 N/m2
Work, Energy, Quantity of Heat
Conductivity
Energy, Work, Heat Quantity Joule J 1 J =1 Nm J foot-Ibf kgfm kcal W/(mK) kcal/(hmC)
m1
Thermal
Wave Number Every Meter
Density Kilogram Every Cubic Meter kg/m3 Work Rate, Process Rate, Power, Electric Power Watt W 1 W =1 J/s 1 0.7376 1.019 72101 2.388 89104 1 8.600 0101
Current Density Ampere Every Square Meter A/m2 Electric Charge, Quantity of Electricity Coulomb C 1 C =1 As 1.356 1 1.38274101 0.00001 1.162 79 1
Magnetic Field Strength Ampere Every Meter A/m Electric Potential, Potential Dif erence, Voltage, Electromotive Force Volts V 1 V =1 J/C
9.806 65 7.2334 1 2.342 70103
Electrostatic Capacity, Capacitance Farad F 1 F =1 C/V
Concentration of(Substance) Mole Every Cubic Meter mol/m3 kcal/(hm2C)
Heat Transfer
W/(m2K)
Coefficient of
Electric Resistance Ohm 1 =1 V/A 4.186 05103 3087.59 4.268 58102 1
Specific Volume Cubic Meter Every Kilogram m3/kg 1 8.600 0101
Conductance Siemens S 1 S =1 1 Note) 1J=1Ws, 1J=1Nm
Luminance Candela Every Square Meter cd/m2
Magnetic Flux Weber Wb 1 Wb =1 Vs 1.162 79 1
Power Heat Flow Rate
W foot-Ibf/sec PS kcal/h
Magnetic Flux Density Tesla T 1 T =1 Wb/m2
3 1
1 0.7376 1.359 6210 8.600 0 10
Inductance Henry H 1 H =1 Wb/A kcal/(kgC)
Specific Heat
J/(kgK) cal/(gC)
Celsius Temperature Degree elsius or Degree C 1 tC =(t+273.15)k 1.356 1 0.001817 1.16658
1 2.388 89104
Luminous Flux Lumen lm 1 lm =1 cdsr 7.355 102 550.2213 1 6.325 29102
3
Illuminance Lux lx 1 lx =1 lm/m2 4.186 0510 1
1.162 79 0.8572 1.580 95103 1
Radioactivity Becquerel Bq 1 Bq =1 s1
Absorbed Dose Gray Gy 1 Gy =1 J/kg Note) Note1W=1J/s, PS:French Horsepower
Dose Equivalent Sievert Sv 1 Sv =1 J/kg
2795 2796
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanical Design Technical InfomationDocument36 pagesMechanical Design Technical InfomationPaco LMPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Design Technical Infomation - 2Document15 pagesMechanical Design Technical Infomation - 2Paco LMPas encore d'évaluation
- Units & DetailsDocument1 pageUnits & DetailssantoshcipetPas encore d'évaluation
- (Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical DataDocument1 page(Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical Datailo iloPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDS0912Document10 pagesFMDS0912Cesar RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 The International System of Units: TABLE 1-1Document2 pages1.3 The International System of Units: TABLE 1-1noman581Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 1000Document32 pagesIso 1000choirulbiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2428 6079 1 SMDocument11 pages2428 6079 1 SMAgilll ThoriqPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 10005:1994Document29 pagesIso 10005:1994Razvan IonescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of SI (Metric) Units in Maritime Applications (Committee F-25 Supplement To IEEE/ASTM SI 10)Document12 pagesUse of SI (Metric) Units in Maritime Applications (Committee F-25 Supplement To IEEE/ASTM SI 10)தர்மா வெங்கடேசன்Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metrication Guidelines: PAES 020:2005Document60 pagesMetrication Guidelines: PAES 020:2005Lhizel ClaveriaPas encore d'évaluation
- VM Apr 30 l2Document9 pagesVM Apr 30 l2SomilPas encore d'évaluation
- Walgreens 810Document146 pagesWalgreens 810Sri VarriPas encore d'évaluation
- Units and MeasurementsDocument8 pagesUnits and Measurementsernestnyondo63Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unidades y DimensionesDocument10 pagesUnidades y DimensionesVanessa Paulino GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- MP Avt 157 08Document14 pagesMP Avt 157 08Saeed ZamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 1 NotesDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 1 NotesNicole de los ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) IntroductionDocument7 pages1) IntroductionLESLIE JANE MERCADOPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 12478-1 1997 (E) - Image 600 PDF DocumentDocument12 pagesISO 12478-1 1997 (E) - Image 600 PDF DocumentRicardo CardosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipefitting: Basic EngineeringDocument40 pagesPipefitting: Basic Engineeringmohamed Abo-EwishaPas encore d'évaluation
- 58 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric StandardDocument39 pages58 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric Standardrizal tri susiloPas encore d'évaluation
- SI Unit EDocument1 pageSI Unit EEvangelin GuardamanoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Telecommunication Union: RecommendationDocument92 pagesInternational Telecommunication Union: Recommendationsivasundar77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Es BuDocument8 pagesEs Buhadiranji4Pas encore d'évaluation
- TCAP MessageDocument2 pagesTCAP MessageSubhajit GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- 155MAT00008 Manuel Technique DreamStar enDocument66 pages155MAT00008 Manuel Technique DreamStar enNattawut ZuesatPas encore d'évaluation
- Docrefund - Initrefund 09.2: Technical ReferenceDocument57 pagesDocrefund - Initrefund 09.2: Technical ReferencemerpdarpPas encore d'évaluation
- ROS Window: 2008 SeminarDocument3 pagesROS Window: 2008 SeminarJagadeesh PvsnPas encore d'évaluation
- Kolhan University BBA SEM 5 Previous Year Question Papers of 2018 and 2022Document19 pagesKolhan University BBA SEM 5 Previous Year Question Papers of 2018 and 2022rahulmehtagamesPas encore d'évaluation
- IEEE Recommended Practice For Preferred Metric Units For Use in Electrical and Electronics Science and TechnologyDocument20 pagesIEEE Recommended Practice For Preferred Metric Units For Use in Electrical and Electronics Science and Technologyأمين توات الجزائريPas encore d'évaluation
- 518201521601PMAIS 049 Draft F TotalDocument24 pages518201521601PMAIS 049 Draft F TotalGopalakrishnan ManikandanPas encore d'évaluation
- VJ 1310 Section 10 Parts List PDFDocument62 pagesVJ 1310 Section 10 Parts List PDFCristian Marcelo Morales LaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic and Social Council: United NationsDocument28 pagesEconomic and Social Council: United Nationsneu978693874Pas encore d'évaluation
- JCB 3230 FASTRAC Service Repair Manual SN 01270000-01271999 PDFDocument68 pagesJCB 3230 FASTRAC Service Repair Manual SN 01270000-01271999 PDFfjksemfmmdPas encore d'évaluation
- Rolling Bearings For Industrial Machinery Part E Appendix TableDocument14 pagesRolling Bearings For Industrial Machinery Part E Appendix TableInamMuradPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability of Systems: - Series SystemDocument42 pagesReliability of Systems: - Series Systemmarta100% (1)
- TechRef FOP CreateFormOfPayment 15.4 001Document141 pagesTechRef FOP CreateFormOfPayment 15.4 001Andrei Gogu50% (2)
- TR 10207002v010101pDocument17 pagesTR 10207002v010101pAbdalmalek shamsanPas encore d'évaluation
- T Rec Z.120 201102 I!!pdf eDocument146 pagesT Rec Z.120 201102 I!!pdf eJorgef CondegPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Quantities and Measurements PresentationDocument60 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurements Presentation金 Abigail RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- T REC Q.773 TcapDocument39 pagesT REC Q.773 TcapsimirajPas encore d'évaluation
- DT15 (83 85)Document35 pagesDT15 (83 85)Сергей СергейPas encore d'évaluation
- Is 10005 1994 PDFDocument29 pagesIs 10005 1994 PDFsunilrauloPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Torsional Vibration Damper (TVD) Pulley, Implementation of A Rubber Elastomeric Behavior, Simulations and ExperimentsDocument20 pagesDynamics of Torsional Vibration Damper (TVD) Pulley, Implementation of A Rubber Elastomeric Behavior, Simulations and Experimentsstefan.vince536Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Relaiblity of SystemsDocument42 pagesLecture 3 - Relaiblity of Systemsnickokinyunyu11Pas encore d'évaluation
- TechRef Insurance Proposal 13.1 002Document63 pagesTechRef Insurance Proposal 13.1 002Andrei GoguPas encore d'évaluation
- Itu-T: Enhanced Telecom Operations Map (eTOM)Document14 pagesItu-T: Enhanced Telecom Operations Map (eTOM)lazaro maizPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm d1914Document6 pagesAstm d1914Jose Luis Villegas EchalarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide For The Use of The International System of Units (SI) : NIST Special Publication 811 2008 EditionDocument89 pagesGuide For The Use of The International System of Units (SI) : NIST Special Publication 811 2008 EditionCarlos TrejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide For The Use of The International System of UnitsDocument89 pagesGuide For The Use of The International System of UnitsAndré Dias BrochadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gears Engineering InformationDocument138 pagesGears Engineering InformationoperationmanagerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 MetricGears PDFDocument9 pages1 MetricGears PDFGerardo Franco Rava0% (1)
- The SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitDocument3 pagesThe SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitMathilda YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Gears Engineering InformationDocument138 pagesGears Engineering InformationxeyesightPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Helpful InformationDocument16 pages10 Helpful InformationAndy YanPas encore d'évaluation
- ETS2.2 Monitoring Plan Template: The Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trading Scheme Regulations 2005 Confidentiality StatementDocument21 pagesETS2.2 Monitoring Plan Template: The Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trading Scheme Regulations 2005 Confidentiality StatementAsebaho BadrPas encore d'évaluation
- Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunications TermsD'EverandTelecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunications TermsPas encore d'évaluation
- A Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsD'EverandA Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsW. R. MacconnellPas encore d'évaluation
- LyricsDocument1 pageLyricsanoopkntpcPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME - Performance Test CodesDocument1 pageASME - Performance Test CodesanoopkntpcPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Answers On Steam TurbinesDocument4 pagesQuestion Answers On Steam TurbinesanoopkntpcPas encore d'évaluation
- PID Windup PDFDocument4 pagesPID Windup PDFOualid LamraouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pid Loop ShapingDocument7 pagesPid Loop ShapingCAFECHINOPas encore d'évaluation
- TES P 119 05 R0 Insulation CoordinationDocument8 pagesTES P 119 05 R0 Insulation CoordinationZain-Ul- AbdeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Data SheetDocument5 pagesData SheetMindSet MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- ACT01Document56 pagesACT01imtherr01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation Equations For Mass Momentum and EnergyDocument12 pagesConservation Equations For Mass Momentum and Energypuja kochPas encore d'évaluation
- Chziri zvf330 Ac Drive User Manual E375Document59 pagesChziri zvf330 Ac Drive User Manual E375Diego Armando Carrera palmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4che syakirPas encore d'évaluation
- Equivalent Circuit of Transformer Referred To Primary and SecondaryDocument4 pagesEquivalent Circuit of Transformer Referred To Primary and SecondaryAbdullah Al AsikPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.11 Combined Gas Law (SPA10) Edited Ver.Document17 pages1.11 Combined Gas Law (SPA10) Edited Ver.Jimin ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- ODB - PhysicsDocument3 pagesODB - PhysicsJerric CristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Gelombang Dan BunyiDocument31 pagesSoal Gelombang Dan BunyiSaeful GhofarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gibbs Helmholtz ChemTexDocument4 pagesGibbs Helmholtz ChemTexVineet klPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Scheme Form 1Document8 pagesMath Scheme Form 1Ben walkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnatic InductionDocument1 pageElectromagnatic InductionMahes JeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuits 9TH 106Document5 pagesElectric Circuits 9TH 106Richard DapitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Impedance CalculationsDocument4 pagesCable Impedance CalculationsJoseph PoplingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Engr. Bon Ryan AnibanDocument7 pagesEngr. Bon Ryan AnibanBillie Ian. Salamante JrPas encore d'évaluation
- Quest Circular Motion 1 KeyDocument5 pagesQuest Circular Motion 1 KeyCarlos OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet (Métrico) - 2BH1900Document2 pagesDatasheet (Métrico) - 2BH1900Rafael BalakPas encore d'évaluation
- Clicker Chapter 30Document74 pagesClicker Chapter 30riffyjiffyPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5 Paper 1 ANSWERSDocument16 pagesTopic 5 Paper 1 ANSWERSHarsh ShrivPas encore d'évaluation
- Breakthrough PropulsionDocument28 pagesBreakthrough PropulsionChu Tiến ThịnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Oedipus III 02 (1974-01-14) PDFDocument8 pagesAnti-Oedipus III 02 (1974-01-14) PDFMoon FrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Electricity and Magnetism: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIp_k_soni_iit_physicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Solve Combine VariationDocument4 pagesSolve Combine VariationAimee Rose GaliciaPas encore d'évaluation
- MagnetismDocument4 pagesMagnetismTalha MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Work: Chapter Iv. Work, Power and EnergyDocument14 pagesWork Work: Chapter Iv. Work, Power and EnergyDiane Joy Fojas PanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12th Physics Chapter 2 Test 1 SQDocument1 page12th Physics Chapter 2 Test 1 SQEeman AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- CUPY106 - CUMS 102 Assignment 2Document6 pagesCUPY106 - CUMS 102 Assignment 2Takunda T. NgorimaPas encore d'évaluation
- TYM - JCT - For NEET - UT-01 - 03-06-2023 - Question PaperDocument20 pagesTYM - JCT - For NEET - UT-01 - 03-06-2023 - Question Papersyed kingPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - ResistorsDocument3 pages01 - ResistorsKaushik BhattacharyaPas encore d'évaluation