Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Mam Helen
Transféré par
Thea Eya Faye0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues14 pagesDOCS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDOCS
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues14 pagesDrug Study Mam Helen
Transféré par
Thea Eya FayeDOCS
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 14
RANITIDINE
DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ROUTE
DOSAGE
Zantac, Potent anti-ulcer Hypersensitivity to Blocks CNS: Headache, Assessment & Drug Effects
Zantac drug that ranitidine; acute daytime and malaise,
EFFERdose, competitively and porphyria; OTC nocturnal dizziness, Potential toxicity
Zantac reversibly inhibits administration in basal gastric somnolence, results from
GELdose, histamine action at children <12 y. acid secretion insomnia, decreased clearance
Zantac-75 H2-receptor sites stimulated by vertigo, mental (elimination) and
on parietal cells, histamine and confusion, therefore prolonged
Classifications thus blocking reduces agitation, action; greatest in the
: gastric acid gastric acid depression, older adult patients or
GASTROINTES secretion. release in hallucinations in those with hepatic or
TINAL AGENT; Indirectly reduces response to older renal dysfunction.
ANTISECRETO pepsin secretion food, adults. CV: Brady Lab tests: Periodic
RY (H2- but appears to pentagastrin, cardia (with rapid liver functions.
RECEPTOR have minimal and insulin. IV Monitor creatinine
ANTAGONIST effect on fasting Shown to push). GI: Constip clearance if renal
) Prototype: and postprandial inhibit 50% of ation, nausea, dysfunction is present
Cimetidine serum gastrin the stimulated abdominal pain, or suspected. When
Pregnancy concentrations or gastric acid diarrhea. Skin: Ra clearance is <50
Category: B secretion of gastric secretion. sh. Hematologic: mL/min,
intrinsic factor or Reversible manufacturer
mucus. decrease in WBC recommends
count, reduction of the dose
thrombocytopeni to 150 mg once q24h
a. Body as a with cautious and
Whole: Hypersen gradual reduction of
sitivity the interval to q12h or
reactions, anaphy less, if necessary.
laxis (rare). Be alert for early signs
of hepatotoxicity
(though low and
thought to be a
hypersensitivity
reaction): jaundice
(dark urine, pruritus,
yellow sclera and
skin), elevated
transaminases
(especially ALT) and
LDH.
Long-term therapy
may lead to vitamin
B12 deficiency.
Patient & Family Education
Note: Long duration
of action provides
ulcer pain relief that is
maintained through
the night as well as
the day.
Be aware that even if
symptomatic relief is
provided by
ranitidine, this should
not be interpreted as
absence of gastric
malignancy. Follow-up
examinations will be
scheduled after
therapy is
discontinued.
Adhere to scheduled
periodic laboratory
checkups during
ranitidine treatment.
Do not supplement
therapy with OTC
remedies for gastric
distress or pain
without physician's
advice (e.g., Mylanta II
reduces ranitidine
absorption).
Do not smoke;
research shows
smoking decreases
ranitidine efficacy and
adversely affects ulcer
healing.
Do not breast feed
while taking this drug
without consulting
physician.
PARACETAMOL
DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ROUTE
DOSAGE
Classifications: Adrenal Body as a
CENTRAL insufficiency Whole: Negligible Assessment & Drug Effects
NERVOUS concomitantly with with Monitor for S&S of:
SYSTEM AGENT; a recommended
hepatotoxicity, even
NONNARCOTIC mineralocorticoid; It provides dosage; with moderate
ANALGESIC, inflammatory temporary rash. Acute acetaminophen doses,
ANTIPYRETIC conditions, allergic analgesia for poisoning: Anore
especially in
Pregnancy states, collagen mild to xia, nausea, individuals with poor
Category: B diseases, moderate vomiting,
nutrition or who have
hematologic Hypersensitivity to pain. In dizziness, ingested alcohol over
Mild to disorders, cerebral acetaminophen or addition, lethargy, prolonged periods;
Moderate Pain, edema, and phenacetin; use with acetaminophe diaphoresis, poisoning, usually
Fever Adult: PO addisonian shock. alcohol. n lowers body chills, epigastric from accidental
325650 mg q4 Also palliative temperature or abdominal
ingestion or suicide
6h (max: 4 g/d) treatment of in individuals pain, diarrhea; attempts; potential
PR 650 mg q4 neoplastic disease, with a fever. onset
abuse from
6h (max: 4 g/d) as adjunctive of hepatotoxicity psychological
Child: PO 1015 short-term therapy elevation of dependence
mg/kg q46h PR in acute rheumatic serum
(withdrawal has been
25 y, 120 mg disorders and GI transaminases associated with
q46h (max: 720 diseases, and as a (ALT, AST) and
restless and excited
mg/d); 612 y, diagnostic test for bilirubin;
325 mg q46h Cushing's hypoglycemia, he responses).
(max: 2.6 g/d) syndrome and for patic coma, acute
Neonate: PO 10 differential renal Patient & Family Education
15 mg/kg q68h diagnosis of failure (rare). Chr
Do not take other
adrenal onic
hyperplasia and ingestion: Neutro medications (e.g., cold
adrenal adenoma.. penia, preparations)
pancytopenia, containing
leukopenia, acetaminophen
thrombocytopeni without medical
c advice; overdosing
purpura, hepatot and chronic use can
oxicity in cause liver damage
alcoholics, renal and other toxic
damage. effects.
Do not self-medicate
adults for pain more
than 10 d (5 d in
children) without
consulting a physician.
Do not use this
medication without
medical direction for:
fever persisting longer
than 3 d, fever over
39.5 C (103 F), or
recurrent fever.
Do not give children
more than 5 doses in
24 h unless prescribed
by physician.
Do not breast feed
while taking this drug
without consulting
physician.
DEXAMETHASONE
DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ROUTE
DOSAGE
Classifications: Adrenal Systemic fungal Aerosol Assessment & Drug Effects
HORMONES AND insufficiency infection, acute therapy: Nasal
SYNTHETIC concomitantly with infections, active or irritation, dryness Monitor and report
SUBSTITUTES, a resting tuberculosis, , epistaxis, S&S of Cushing's
ADRENAL mineralocorticoid; vaccinia, varicella, rebound syndrome (see
CORTICOSTEROI inflammatory administration of live congestion, Appendix F) or other
D; conditions, allergic virus vaccines (to bronchial systemic adverse
GLUCOCORTICOI states, collagen patient, family asthma, effects.
D; STEROID diseases, members), latent or Drug has anosomia, Monitor neonates
Prototype: hematologic active antiinflammat perforation of born to a mother who
Prednisone disorders, cerebral amebiasis. Ophthalm ory and nasal has been receiving a
Pregnancy edema, and ic use:Primary open- immunosuppr septum. Systemic corticosteroid during
Category: C addisonian shock. angle glaucoma, eye ession Absorption pregnancy for
Also palliative infections, superficial properties. CNS: Euphoria, symptoms of
Allergies, treatment of ocular herpes insomnia, hypoadrenocorticism.
Inflammation, neoplastic disease, simplex, keratitis and convulsions, Monitor for S&S of a
Neoplasias as adjunctive tuberculosis of eye. increased ICP, hypersensitivity
Adult: PO 0.254 short-term therapy Safe use during vertigo, reaction (see
mg b.i.d. to q.i.d. in acute rheumatic pregnancy (category headache, Appendix F). The
IM 816 mg q1 disorders and GI C), lactation, or in psychic acetate and sodium
3 wk or 0.81.6 diseases, and as a children is not disturbances. CV: phosphate
mg intralesional diagnostic test for established. CHF, formulations may
q13 wk Child: Cushing's hypertension, ed contain bisulfites,
PO/IV/IM 0.08 syndrome and for ema. Endocrine: parabens, or both;
0.3 mg/kg/d differential Menstrual these inactive
divided q612h diagnosis of irregularities, hyp ingredients are
Cerebral Edema adrenal erglycemia; cushi allergenic to some
Adult: IV 10 mg hyperplasia and ngoid state; individuals.
followed by 4 mg adrenal adenoma. growth
q4h, reduce suppression in Patient & Family Education
dose after 24 d children;
Take drug exactly as
then taper over hirsutism. Special
57 d Child: Senses: Posterior prescribed.
Report lack of
PO/IV/IM 12 subcapsular
mg/kg loading cataract, increase response to
dose, then 11.5 d IOP, glaucoma, medication or
mg/kg/d divided exophthalmos. GI malaise, orthostatic
q46h (max: 16 : Peptic ulcer hypotension,
mg/d) Shock with possible muscular weakness
Adult: IV 16 perforation, and pain, nausea,
mg/kg as a single abdominal vomiting, anorexia,
dose or 40 mg distension, hypoglycemic
repeated q26h nausea, reactions (see
if needed increased Appendix F), or
Dexamethasone appetite, mental depression to
Suppression Test heartburn, physician. These
Adult: PO 0.5 mg dyspepsia, symptoms may signal
q6h for 48 h pancreatitis, bow hypoadrenocorticism.
Report changes in
Inflammation el
Adult/Child: perforation, oral appearance and easy
Ophthalmic/Topi candidiasis. Musc bruising to physician.
cal/Inhalation/In uloskeletal: Musc These symptoms may
tranasal See le weakness, loss signal
Appendix A. of muscle hyperadrenocorticism
mass, vertebral .
compression Note: Hiccups that
fracture, occur for several
pathologic hours following each
fracture of long dose may be a
bones, tendon complication of high-
rupture. Skin: Ac dose oral
ne, impaired dexamethasone.
wound Keep appointments
healing, petechia for checkups; make
e, ecchymoses, sure electrolytes and
diaphoresis, BP are evaluated
allergic during therapy at
dermatitis, hypo- regular intervals.
or Add potassium-rich
hyperpigmentati foods to diet; report
on, SC and signs of hypokalemia
cutaneous (see Appendix F).
atrophy, burning Concomitant
and tingling in potassium-depleting
perineal area diuretic can enhance
(following IV dexamethasone-
injection). induced potassium
loss.
Note: Dexamethasone
dose regimen may
need to be altered
during stress (e.g.,
surgery, infections,
emotional stress,
illness, acute
bronchial attacks,
trauma). Consult
physician if change in
living or working
environment is
anticipated.
Discontinue drug
gradually under the
guidance of the
physician.
Note: It is important
to prevent exposure
to infection, trauma,
and sudden changes
in environmental
factors, as much as
possible, because
drug is an
immunosuppressor.
Do not breast feed
while taking this drug
without consulting
physician.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Histology of GI PRETRANSDocument7 pagesHistology of GI PRETRANSThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- ChestpainDocument1 pageChestpainThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- METHODOLOGYDocument6 pagesMETHODOLOGYThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- C and D AnsDocument1 pageC and D AnsThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Biochem QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiochem QuestionsThea Eya Faye100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Appendix GDocument6 pagesAppendix GThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Learning PortfolioDocument1 pageLearning PortfolioThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Programme: "Vital Signs Taking, Leads To Healthy Being"Document2 pagesProgramme: "Vital Signs Taking, Leads To Healthy Being"Thea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Histology of GI PRETRANSDocument7 pagesHistology of GI PRETRANSThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Rodesa Lara Fea V. Bongalon Reaction Paper On Martial Law: Atty. Francesco C. BritanicoDocument2 pagesRodesa Lara Fea V. Bongalon Reaction Paper On Martial Law: Atty. Francesco C. BritanicoThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Effects of Climate Change: The Adaptation of Elderly People's Healthcare Needs in Magalalag West, Enrile, CagayanDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Climate Change: The Adaptation of Elderly People's Healthcare Needs in Magalalag West, Enrile, CagayanThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Clinicaaaaaal 2Document3 pagesClinicaaaaaal 2Thea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Module VSDocument3 pagesModule VSThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Debbie Weekly ReportDocument25 pagesDebbie Weekly ReportThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- 62 67Document6 pages62 67Thea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Path o StrokeDocument1 pagePath o StrokeThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Albino Carag: February 06, 2017 Brgy. Captain Magalalag West, EnrileDocument1 pageAlbino Carag: February 06, 2017 Brgy. Captain Magalalag West, EnrileThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Debbie Rubin OooooDocument19 pagesDebbie Rubin OooooThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 24Document24 pages1 24Thea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDocument1 pageAcknowledgement ReceiptThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- Food LabelingDocument13 pagesFood LabelingThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
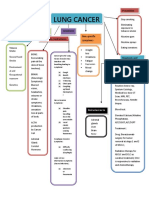
- Concept Map LungDocument1 pageConcept Map LungThea Eya FayePas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Nursing Care Plans For Lung CancerDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plans For Lung CancerThea Eya Faye100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Drugs Associated With Pregnancy, Labor and Delivery, and LactationDocument4 pagesChapter 12 - Drugs Associated With Pregnancy, Labor and Delivery, and LactationmysPas encore d'évaluation
- Lee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Document25 pagesLee Zu Ying Problem of The Spine 541-16-17Star CruisePas encore d'évaluation
- Hoarseness in AdultsDocument9 pagesHoarseness in AdultsNila Ijma SeptianaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Pedia AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesPedia AbnormalitiesRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Casauay and Pacunana Group 15 1Document4 pagesCasauay and Pacunana Group 15 1Steve EstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- Krok I 2013-17 ExplainedDocument292 pagesKrok I 2013-17 ExplainedU1GoKu0% (1)
- First Degree BurnsDocument3 pagesFirst Degree BurnsbobboxPas encore d'évaluation
- Indice Diastolico de ChoqueDocument11 pagesIndice Diastolico de ChoqueLUIS AYALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDDocument11 pagesAcute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDbanu kuhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Valosin Poultry MGDocument5 pagesValosin Poultry MGMarta DinataPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 AAHA/AAFP Fluid Therapy Guidelines For Dogs and CatsDocument15 pages2013 AAHA/AAFP Fluid Therapy Guidelines For Dogs and CatsTatiana Amaya GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study in SchizophreniaDocument11 pagesA Case Study in SchizophreniaRamin ApparaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument112 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYC100% (2)
- NRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 2: Determinants of HealthDocument44 pagesNRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health: Module 2: Determinants of HealthjustdoyourPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Non Invasive Imaging in NASHDocument3 pagesNon Invasive Imaging in NASHParul SoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Jurnal 2Document10 pagesReview Jurnal 2UlfahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Paln of Mrs Richard (Clinical Scenario-3)Document20 pagesNursing Care Paln of Mrs Richard (Clinical Scenario-3)Axsa AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Entire Asn Conference On Mp3 CD Roms: $149: Price Per Individual Download Is $14Document2 pagesEntire Asn Conference On Mp3 CD Roms: $149: Price Per Individual Download Is $14m29herePas encore d'évaluation
- Neurofibroma, Schwannoma or A Hybrid Tumor of The Peripheral Nerve Sheath?Document4 pagesNeurofibroma, Schwannoma or A Hybrid Tumor of The Peripheral Nerve Sheath?As AsPas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatric Chest ConditionsDocument59 pagesPaediatric Chest ConditionsReuben GrechPas encore d'évaluation
- A Biological Safety: Biosafety CabinetsDocument2 pagesA Biological Safety: Biosafety CabinetsJasper jay DumalagPas encore d'évaluation
- Kanker Payudara PDFDocument20 pagesKanker Payudara PDFbabehPas encore d'évaluation
- Myasthenia GravisDocument10 pagesMyasthenia Gravisnoranhassanshams0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amantadine HCLDocument4 pagesAmantadine HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lencastre Et Al-2019-Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and VenereologyDocument2 pagesLencastre Et Al-2019-Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and VenereologyMaria MogosPas encore d'évaluation
- Subjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessDocument8 pagesSubjective Cues:: Nursing Care ProcessBianca Marithè RejanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 162 Dham 8 1999Document6 pages162 Dham 8 1999Nur Sidiq Agung SPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatitis BDocument48 pagesHepatitis BHari Suthan TPas encore d'évaluation
- Hair Loss in CatsDocument6 pagesHair Loss in CatsGiulia Nădășan-CozmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recurrent Takotsubo CardiomyopathyDocument6 pagesRecurrent Takotsubo CardiomyopathyProdi S1- 1BPas encore d'évaluation
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfD'EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1458)
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissD'EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (81)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipD'EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1135)
- Deep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingD'EverandDeep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (103)