Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Arnoldbridgett Portfolioi
Transféré par
api-356951570Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Arnoldbridgett Portfolioi
Transféré par
api-356951570Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
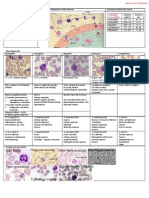
Biologic Damage to Tissue
The most sensitive human cells to ionizing radiation are blood cells, a whole body dose
of 0.25 Gy will begin to show depletion of blood cells, they may repopulate within weeks
for a small dose of radiation at least less than 1 Gy, for amounts more than 1 Gy a longer
amount of time will be needed if permanent damage to stem cells has not occurred. There
are many different types of blood cells, erythrocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils,
granulocytes and thrombocytes.
Cell Dose Recovery
Erythrocyte 0.25 Gy 1 week
Lymphocyte 0.25 Gy Shortly after radiation
0.5-1 Gy Several months
Neutrophil 0.5 Gy A few months
Granulocyte Varying dose 2 months
Thrombocyte >0.5 Gy 2 months
Epithelial tissue is the next most sensitive type of tissue. These cells comprise a number
of organs and undergo mitosis often. The organ systems comprised of epithelial cells are
skin and hair, mucous linings, intestines, pulmonary alveoli, and blood and lymphatic
vessel lining.
Cell Dose Recovery
Skin 4 - >40 Gy 2 hours 6 weeks
Digestive tract 7-15 Gy 3-5 days
Immature reproductive cells are sensitive to radiation while mature reproductive cells are
less sensitive.
Cell Dose Recovery
Immature spermatogonia 0.1 Gy A few months
2 Gy 12 months
5-6 Gy Permanent damage
Immature ova 0.1 Gy 30 days to expel ova
Mature ova 2 Gy Temporary sterility
0.1-20 Gy (fractioned) Tolerated
5 Gy Permanent damage
Because muscle tissue does not divide often it is not as radiosensitive.
Nervous tissue cells do not divide and therefore are also not as radiosensitive. Adult
nerve cells are less sensitive than fetal nerve cells. If exposed to a certain threshold of
radiation the nerve cells may become impaired but still function.
Cell Dose Recovery
Fetal neuron 0.1 Sv fetal EqD 4% chance of mental
retardation
Adult neuron >50 Gy Death
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Leukocytes Benign DisordersDocument3 pagesLeukocytes Benign DisordersGerardLum100% (3)
- I. Differentiate Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. (With Illustration)Document3 pagesI. Differentiate Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. (With Illustration)Cris Ryan Mercado DulangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 9 - Quality AssuranceDocument41 pagesLecture 9 - Quality AssuranceLindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus RTTDocument114 pagesSyllabus RTTGrace NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Units and Biological Effects in 40 CharactersDocument67 pagesRadiation Units and Biological Effects in 40 CharactersSivirahul100% (2)
- Review: Cell Structures and Functions: Stem 12 General Biology 1Document114 pagesReview: Cell Structures and Functions: Stem 12 General Biology 1Mariz GenandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Protection in The Design of Radiotherapy FacilitiesDocument145 pagesRadiation Protection in The Design of Radiotherapy FacilitiesPalani Vel Rajan100% (1)
- Plant Animal CellsDocument19 pagesPlant Animal Cellsits jycdlcrzPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobius3D White PaperDocument10 pagesMobius3D White Paperjfg350Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Medicine Exam Revised PDFDocument79 pagesNuclear Medicine Exam Revised PDFAina Mira PalouPas encore d'évaluation
- ICRU - 50 - Prescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam TherapyDocument81 pagesICRU - 50 - Prescribing, Recording and Reporting Photon Beam TherapyzxoncoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensitivity of organs and tissues to radiation exposureDocument21 pagesSensitivity of organs and tissues to radiation exposureWhite MochiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells Communicate and Genistein Fools ReceptorsDocument2 pagesCells Communicate and Genistein Fools ReceptorsJayleen Coy Sabling LadyongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell-DivisionDocument143 pagesCell-DivisionDonisha Janah DonairePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Sensitivity to RadiationDocument18 pagesCell Sensitivity to RadiationLouella ArtatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune System Disorders ExplainedDocument9 pagesImmune System Disorders ExplainedFrancheskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hatchability Problem Analysis1Document13 pagesHatchability Problem Analysis1AbdisamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyDocument28 pagesCharacteristics of Cancer Cells: Obituary Brings To Light The Tragedy of One Local FamilyRoxie SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- DeBoer Bucharest Treating FutureDocument4 pagesDeBoer Bucharest Treating FutureGeorgianaGabrielaPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Protection in Nuclear Medicine1Document27 pagesRadiation Protection in Nuclear Medicine1Marian JonahPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocument16 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsTodd SilversteinPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 09 Science Chapter05 the Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesGrade 09 Science Chapter05 the Fundamental Unit of Lifeadhithyanb345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Radiation Induced ErithemaDocument47 pagesTreatment of Radiation Induced ErithemaDimitar FilevskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Cell PhysiologyMarc Andreo MalalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Radbio RadiosensitivityDocument3 pagesRadbio Radiosensitivityfrancoise wyanet rualoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle ExpDocument24 pagesCell Cycle ExpIvan GalletoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 WorksheetDocument2 pagesLesson 1 WorksheetJoon Bok NamleePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiology ReviewerAngela SernatPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Notes Chapter 6Document17 pagesBio Notes Chapter 6Tanvir KauraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Cellular Aberration: Normal Cell vs. Cancer CellDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Cellular Aberration: Normal Cell vs. Cancer CellAdiel CalsaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMOTHERAPYDocument28 pagesCHEMOTHERAPYDwi CahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells 1.1-1.4Document6 pagesCells 1.1-1.4bommoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Effect of Ionizing Radiation Lecture MODIFIEDDocument58 pagesBiological Effect of Ionizing Radiation Lecture MODIFIEDHitesh RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- AIDS: Late-Stage HIV Infection Weakens Immune SystemDocument6 pagesAIDS: Late-Stage HIV Infection Weakens Immune SystemMihir SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Aging PhysiologicalDocument37 pagesAging PhysiologicalNico WirawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaching The Topic: Cells: Unit 1Document13 pagesApproaching The Topic: Cells: Unit 1tychrPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of EM RadiationDocument47 pagesEffects of EM RadiationFelix FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Culture, Plaque, Embryonated EggDocument26 pagesCell Culture, Plaque, Embryonated Eggalexiel1815Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleChad LabradorPas encore d'évaluation
- Announcements and Exam InfoDocument32 pagesAnnouncements and Exam Inforaiashish123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek3 EditDocument20 pagesQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek3 EditInele Ellia AgRePas encore d'évaluation
- School NewsletterDocument3 pagesSchool Newsletterapi-351642214Pas encore d'évaluation
- ENSC 3520 - Chemical-Induced Carcinogenesis - Students PDFDocument123 pagesENSC 3520 - Chemical-Induced Carcinogenesis - Students PDFSamuel WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle Regulation and CheckpointsDocument3 pagesCell Cycle Regulation and Checkpointsʀᴇɢᴇʟʏɴ ʙᴀʟɪᴅPas encore d'évaluation
- BTEC Exam Revision BookletsDocument21 pagesBTEC Exam Revision BookletsMahmoud FawzyPas encore d'évaluation
- End of The Year Review II Part 1 2020Document42 pagesEnd of The Year Review II Part 1 2020Shreya ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesCell BiologyArmie Rose FaldasPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal and Plant CellDocument16 pagesAnimal and Plant CellDarlPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicha-Cancer PresentationDocument13 pagesNicha-Cancer Presentationapi-452284231Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell CycleDocument81 pagesCell CycleSandara AsinguaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem CellDocument14 pagesStem CellPinhsing WenPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology CH1Document1 pageBiology CH1rei0pkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Limuz 6Document4 pagesLimuz 6api-354399053Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Division Regulation and Cancer GrowthDocument7 pagesCell Division Regulation and Cancer GrowthFRISKA CHRISTININGRUMPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Cells vs Plant Cells ComparisonDocument6 pagesAnimal Cells vs Plant Cells ComparisonEszterPas encore d'évaluation
- Prostate Health Sensor DemoDocument31 pagesProstate Health Sensor Demoonce_8Pas encore d'évaluation
- To Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksDocument34 pagesTo Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksPawpaw Chan0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeKay TangPas encore d'évaluation
- RADBIOLOGY Ievan Dred Balmores OriginalDocument15 pagesRADBIOLOGY Ievan Dred Balmores OriginalMichaela Marie DimasPas encore d'évaluation
- Dom 2Document2 pagesDom 2jenrosemPas encore d'évaluation
- L1.Introduction To OncologyDocument7 pagesL1.Introduction To OncologyEslam EltayebPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Test ReviewDocument10 pagesBio Test ReviewOlivia LauterbachPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cells For Students Part 1Document14 pagesStem Cells For Students Part 1AkshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument71 pagesCell Structure and Functionkylev100% (1)
- 16Document3 pages16api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Particulate ElectromagneticDocument2 pagesParticulate Electromagneticapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14Document2 pages14api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- SI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & FormulaDocument3 pagesSI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formulaapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10Document2 pages10api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6Document3 pages6api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9Document3 pages9api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8Document2 pages8api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4Document1 page4api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11Document1 page11api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- (C) - Within The Main X-Ray Circuit There Are Two Sides, The Primary (Low Voltage) Side (A), and TheDocument2 pages(C) - Within The Main X-Ray Circuit There Are Two Sides, The Primary (Low Voltage) Side (A), and Theapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7Document1 page7api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document3 pages2api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook11qcDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook11qcapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook12storageDocument1 pageArnoldbridgett Notebook12storageapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circui 4Document2 pagesElectrical Circui 4api-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook2gridsDocument6 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook2gridsapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook10fluorosDocument4 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook10fluorosapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook6digitalprocessingDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook6digitalprocessingapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook8detaildistortionDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook8detaildistortionapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook9artifactsDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook9artifactsapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook3filmscreensDocument4 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook3filmscreensapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook4pspDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook4pspapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook7densitycontrastDocument2 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook7densitycontrastapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook5drDocument3 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook5drapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook1formulasDocument4 pagesArnoldbridgett Notebook1formulasapi-356951570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eye Lens Dose During CT ExamDocument7 pagesEye Lens Dose During CT ExamSamu SimamesaPas encore d'évaluation
- EOTA Tr010 Report Exposure Procedure For Artificial WeatheringDocument10 pagesEOTA Tr010 Report Exposure Procedure For Artificial Weatheringmatersci_ebayPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2, WEEK-6-SF10FE-IIEe-f-49 - IIg-50Document12 pagesQ2, WEEK-6-SF10FE-IIEe-f-49 - IIg-50CRISTINE MAE AREVALO50% (2)
- Proton Therapy for Cancer Treatment Using High-Energy ProtonsDocument48 pagesProton Therapy for Cancer Treatment Using High-Energy ProtonsSUBHA100% (1)
- Radiation Monitoring Systems and Equipment CatalogDocument28 pagesRadiation Monitoring Systems and Equipment CatalogYamin AliPas encore d'évaluation
- A - New - Process - Simulator - For - The - Optimization of Electron Beam Crosslinking ProcessesDocument7 pagesA - New - Process - Simulator - For - The - Optimization of Electron Beam Crosslinking ProcessesAroop Ratan SenPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Protection 2021 1Document44 pagesRadiation Protection 2021 1Marriel AmodiaPas encore d'évaluation
- (NBS Special Publication, 330) International Bureau of Weights and Measures - The International System of Units (SI) PDFDocument2 pages(NBS Special Publication, 330) International Bureau of Weights and Measures - The International System of Units (SI) PDFMihay BerlinschiPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 Final DraftDocument19 pagesGroup 2 Final Draftapi-428300261Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eurados Report 201203Document67 pagesEurados Report 201203Sylwia WojdanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On The Awareness On Occupational Health Safety Among Health Care Professionals in Radiology Department in A Selected Hospital 1 2 2Document7 pagesA Study On The Awareness On Occupational Health Safety Among Health Care Professionals in Radiology Department in A Selected Hospital 1 2 2alni diniatiPas encore d'évaluation
- RSM 2008 RevisionDocument51 pagesRSM 2008 RevisionphanthanhhungPas encore d'évaluation
- SAHPGL RDN XR 01 v1 Guideline For QC in Medical Diagnostic X Ray Imaging SystemsDocument37 pagesSAHPGL RDN XR 01 v1 Guideline For QC in Medical Diagnostic X Ray Imaging Systemscollestein christdianPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Dose Setting - Tech TipDocument6 pagesRadiation Dose Setting - Tech Tipjchav004ucrPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Goshu 3Document18 pages3 Goshu 3nega cheruPas encore d'évaluation
- TG 244 Anal Write UpDocument14 pagesTG 244 Anal Write Upapi-347149977Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigDocument8 pagesPhys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigWael ElsawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahlberg Hi Rad Xs enDocument3 pagesAhlberg Hi Rad Xs enPLANNING PPPas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental Optimization of The Energy For BreastDocument14 pagesExperimental Optimization of The Energy For BreastJuan CumbradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerb Safety Guidelines No. Aerb/Rf-Igd/Sg-1Document55 pagesAerb Safety Guidelines No. Aerb/Rf-Igd/Sg-1Ardh0072Pas encore d'évaluation
- Radcal 9015Document111 pagesRadcal 9015samuel mPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Monitoring Devices: Mr. Deepak Aheer M.Sc. (Nuclear Medicine) AIIMS New DelhiDocument82 pagesPersonal Monitoring Devices: Mr. Deepak Aheer M.Sc. (Nuclear Medicine) AIIMS New Delhihussain samaahPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation PhysicsDocument307 pagesRadiation PhysicsHarley Alejo MPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Basic RadiotherapyDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Basic Radiotherapyhendra2darmawanPas encore d'évaluation