Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Type Inheritance Pathogenesis Features Treatment: Iron Deficiency Anaemia
Transféré par
Na Ni0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
8 vues4 pagesSummary of the types of anaemia
Titre original
Anaemia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentSummary of the types of anaemia
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
8 vues4 pagesType Inheritance Pathogenesis Features Treatment: Iron Deficiency Anaemia
Transféré par
Na NiSummary of the types of anaemia
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
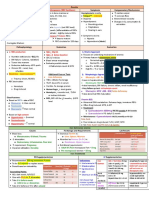
Type
Inheritance Pathogenesis Features Treatment
Iron deficiency Secondary to many diseases Occurs when there is inadequate iron for Clinical: - Find and treat the underlying
anaemia - Limited capacity for ison haemoglobin synthesis - Brittle hair cause
absorption - Presence of depleted iron stores with or - Angular stomatitis - Oral iron
- Loss of iron without functional or health impairment - Glossitis - Paraenteral iron
- Inadequate dietary intake Causes: - Atrophy of tongue papillae
- Increased demand: bleeding, growth - Brittle nails
pregnancy - Koilonychia
- Reduced supply: dietary insufficiency, - Pica
malabsorption Lab results:
Hb
MCV
MCH
- Poikilocytosis RBC of
varying shape
- Anisocytosis RBS of
varying sizes
Serum iron
Total iron binding capacity
(TIBC)
Serum ferritin
Megaloblastic - Congenital enzymes deficiencies in DNA Lab results:
anaemia synthesis Hb
- Drugs interfering in DNA synthesis MCV
- Myelodysplasia due to dyserythropoiesis - Leucopenia and
thrombocytopenia (in severe
cases)
- Oval macrocytes,
anisocytosis, poikilocytosis
- hypersegmented
polymorphonuclears
(immature WBCs)
Vitamin B12 B12 deficiency or its normal Normal function: Clinical features: - Initial: hydroxocobalamin
metabolism - Intrinsic factor: transports B12 to ileum - Gradual and progressive 1mg IM per week x 3 doses
- Transcolbamin II: transports in blood to - Lemon yellow colour - Maintenance:
bone marrow - Glossitis and angular Hydroxycobalamin 1mg IM
Factors compromising B12: stomatitis every 3 months
- Vegan diet - Neurological changes - Oral preparations:
- Gastrectomy - Peripheral polyneuropathy - 2mg tablet
- Small intestine pathology and can lead to paraplegia - 2 x 1mg tablet sublingual
- Drugs for gastritis, e.g. proton pump (due to defective methylation
inhibitors of myelin)
- Dementia
- Psychological disturbances
Vitamin B9 B9 deficiency or its normal Can be caused by: - Same as B12 clinically but - Treat the underlying cause
metabolism - Alcoholism will not manifest neuropathy - Folate 5mg tablet oral x 4
- Anorexia - Neural tube defects (NTD) in months
- Pregnancy newborn Prophylaxis:
- Old age - Normal pregnancy: 400g
daily throughout pregnancy
- With previous child with
NTD: 5mg daily throughout
pregnancy
- Also given in severe
haemolytic anaemias and
patients on chronic dialysis
Anaemia of Related to causative disease: - Defective release of iron from storage - Blood film: normocytic -Treat the underlying cause
chronic disease pulmonary TB, chronic (high level of hepcidin > decrease iron normochromic (can progress - EPO injections
inflammatory disease, release from macrophage) to microcytic hypochromic) - Non-responsive to iron
malignancy - Reduced RBC lifespan - Serum iron and Total iron supplementation
- Inadequate EPO response (due to effect binding capacity (TIBC)
of cytokines) reduced
- Serum ferritin normal or
raised
Sideroblastic - Hereditary: X-linked - Defective haem synthesis (mutation in Detected through bone - Treat the underlying cause
anaemia - Acquired ALA synthase) marrow examination - Pyridoxine (B6)
- Primary - Increase iron uptake > increase iron - Thiamine (B1)
(myelodysplastic, refractory deposition - EPO
type) - Blood transfusions
- Secondary (drugs,
alcoholism, lead poisoning
malignancy)
Sickle cell - Autosomal recessive Results from a mutation in the globin - Vaso-occlusive crisis Preventing precipitating
anaemia - Common is Africa, Middle chain - Anaemia: Hb, sickling of factors (infection, acidosis,
(Hb abnormality) east and India Clinical subtypes: RBC, sickle solubility test, Hb dehydration, cold and
- Hb SS sickle cell anaemia electrophoresis hypoxia) is the best course of
- Hb SC sickle cell disease (Mild anaemia confirmatory management
but higher incidence of retinal - Splenic sequestration: Hb,
abnormalities) abdominal pain, splenomegaly
- Hb AS sickle cell trait (no anaemia, - Bone marrow aplasia: Hb,
normal blood picture, hematuria) reticulocytes
Hb S exposed to hypoxia > polymerization
and crystallisation of Hb > sickling of RBC
> loss of membrane flexibility > rapid
degradation of RBC and blockage of
microcirculation > blood stasis > tissue
infarction
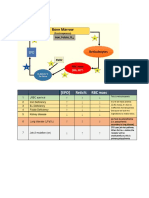
Thalassaemia
(Hb Abnormality)
Autosomal recessive disorder
Thalassaemia Mediterranean region
(excess globin
formation) Caused by point mutations
Thalassaemia major Homozygous - Failure to thrive, recurrent bacterial - RBC Management:
infection - MCV - Folic acid supplements
- Severe anaemia - Hb - Regular blood transfusions
- Extramedullary haemopoiesis (liver, - Microcytic hypochromic - Bone marrow transplant
spleen and other bones) anaemia - Gene therapy
- Genetic counselling
Thalassaemia - Becomes symptomatic in adolescence May have bone deformities Does not require blood
intermedia - Presents with mild anaemia and splenomegaly transfusion
- Still may be iron overloaded
Thalassaemia minor Heterozygous Carrier state Usually asymptomatic
(trait) Anaemia is mild or absent
Thalassaemia Far east region
(excess globin
formation) Caused by gene deletions
4-gene deletions No chain synthesised, only gamma Death in utero or shortly after
chains > Hb Barts () instead of Hb F birth
- Non-functional Hb
3-gene deletions Also known as Hb H (4) disease - Moderate anaemia Regular transfusion not need
- Splenomegaly
- Microcytosis
2-gene deletions Also know as - thalassaemia trait May or may not have anaemia
- Microcytosis
- Asymptomatic
- Normal electrophoresis
1-gene deletion Also know as - thalassaemia trait - Asymptomatic
- Clinical picture: normal
- Blood picture: normal
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandDocument13 pagesARRANGING For Marchong or Concert BandCheGus AtilanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematologi ModulDocument67 pagesHematologi ModulSyifa Mahmud Syukran Akbar100% (1)
- A Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersDocument26 pagesA Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersJohn DoePas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia - AmbossDocument10 pagesAnemia - AmbossGuga XachidzePas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Loss: Acute Chronic Inadequate Production of Normal Blood CellsDocument11 pagesBlood Loss: Acute Chronic Inadequate Production of Normal Blood CellsSheila Amor BodegasPas encore d'évaluation
- HematologyDocument20 pagesHematologyJunaid SabirPas encore d'évaluation
- HaematinicsDocument2 pagesHaematinicsGerardLum100% (2)
- RBC DisordersDocument70 pagesRBC DisordersNdor Baribolo100% (1)
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyIvy Jan OcatePas encore d'évaluation
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDocument3 pagesRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaDocument61 pagesAnemia Pada Anak - DR AuliaSamuel ManurungPas encore d'évaluation
- MED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaFlora XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuliah AnemiaDocument185 pagesKuliah AnemiaAchmad Nur AffendickPas encore d'évaluation
- Ton Miles Calculation 1Document17 pagesTon Miles Calculation 1Alexander Armando Clemente Andrade100% (1)
- Dadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalDocument24 pagesDadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalAkshatPas encore d'évaluation
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- 2014 Curs Hematologie - FinalDocument333 pages2014 Curs Hematologie - FinalRamona Andreea ConstantinPas encore d'évaluation
- Microcytic Type Aeitology Clinical Features Investigations ManagementDocument7 pagesMicrocytic Type Aeitology Clinical Features Investigations ManagementJason AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of AnemiaDocument6 pagesTypes of AnemiaSittiePas encore d'évaluation
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument3 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiaMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia OutlineDocument3 pagesAnemia Outlinekaylakmills_10135868Pas encore d'évaluation
- 112 Lecture MidtermsDocument8 pages112 Lecture MidtermsRose Ann CammagayPas encore d'évaluation
- 112 Lecture MidtermsDocument18 pages112 Lecture MidtermsRose Ann CammagayPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument25 pagesAnaemiaIshali NuwanjiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Ai Lup YuhDocument5 pagesAnemia Ai Lup YuhcindysakiladandaPas encore d'évaluation
- PediatricDocument192 pagesPediatricbolt boltPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematology: MAP 6.1 AnaemiaDocument12 pagesHaematology: MAP 6.1 AnaemiaGrecia BocuPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument36 pagesAnemiaAshria Sonali PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia 2024Document50 pagesAnemia 2024b9p6vmfnc4Pas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument7 pagesAnemiaoktavianprPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument83 pagesAnaemiadoc19019696Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia, Ida 1Document131 pagesAnemia, Ida 1zaha shamseerPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9anemia Due To Increased Destruction of ErythrocytesDocument43 pages9anemia Due To Increased Destruction of ErythrocytesanonacadsPas encore d'évaluation
- Medico Study: General Overview of AnemiaDocument8 pagesMedico Study: General Overview of AnemiaKirubel DeribPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevDocument500 pagesSuper Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevMohd SaquibPas encore d'évaluation
- Pernicious Anemia - ECEDocument46 pagesPernicious Anemia - ECEaparna reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia 2 and Malaria 1Document30 pagesAnemia 2 and Malaria 1Aishwarya JeePas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Def BesiDocument5 pagesAnemia Def BesiM. PurnomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation of ErythropoiesisDocument3 pagesRegulation of ErythropoiesisFlowerPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC ANOMALIES AND INCLUSIONS With Their Associated DiseasesDocument2 pagesRBC ANOMALIES AND INCLUSIONS With Their Associated DiseasesCamella Beatrice Lujan VallePas encore d'évaluation
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument23 pagesMegaloblastic Anemiamameekasim75Pas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument33 pagesAnaemiaNurliyana RamliPas encore d'évaluation
- (PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)Document78 pages(PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)ricaannpanugalinogPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaDocument43 pages1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaAlex KamougerosPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC Anomalies: I. Variation in Hemoglobin ContentDocument6 pagesRBC Anomalies: I. Variation in Hemoglobin ContentMARIE NELLIE MOSTRADOPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia 1Document41 pagesAnemia 1julie kiskuPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC Micro-Macro MeasurementsDocument11 pagesRBC Micro-Macro MeasurementsDingdongLopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediateric Group 6 AnemiaDocument69 pagesPediateric Group 6 AnemiaAbdelruhman SobhyPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline: Anaemias I Microcytic, Iron Deficiency Microcytic, Iron Deficiency & Iron OverloadDocument11 pagesOutline: Anaemias I Microcytic, Iron Deficiency Microcytic, Iron Deficiency & Iron Overloaddorsa koraeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematological Disorders ErythropoiesisDocument4 pagesHematological Disorders Erythropoiesis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jashore University of Science and Technology: Presented by Presented ToDocument10 pagesJashore University of Science and Technology: Presented by Presented ToMohona Rahman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia DX TXDocument2 pagesAnemia DX TXProsanjit MajumderPas encore d'évaluation
- MSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaDocument44 pagesMSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaHariniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionDocument5 pagesAnemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionJette Charmae OlboPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Deficiency: Laboratory DiagnosisDocument5 pagesIron Deficiency: Laboratory DiagnosisKohii KekiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- Hematologic Disorders AnemiaDocument30 pagesHematologic Disorders AnemiaYjah Cheimira ASEBOPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Irma - AnemiaDocument23 pagesDR Irma - AnemiaWa JulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument38 pagesAnemiaMustafa Salam M.NooriPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument5 pagesAnemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDIANA CAMILLE CARITATIVOPas encore d'évaluation
- Khaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticDocument12 pagesKhaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticrupPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoD'EverandFast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laminar Premixed Flames 6Document78 pagesLaminar Premixed Flames 6rcarpiooPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDocument15 pagesFaculty of Engineering & TechnologyGangu VirinchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDocument3 pagesMaintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDavid OmoniyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Saeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Document11 pagesSaeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Mohammad Hassan100% (1)
- Prevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCDocument6 pagesPrevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCMuhammad FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive BreachingDocument25 pagesARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive Breachingrsreeth100% (1)
- KKS Equipment Matrik No PM Description PM StartDocument3 pagesKKS Equipment Matrik No PM Description PM StartGHAZY TUBePas encore d'évaluation
- HP 6940 Manual CompleteDocument150 pagesHP 6940 Manual CompletepaglafouPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Document75 pagesIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDocument20 pagesThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On PRT in IndiaDocument21 pagesA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFDocument38 pagesMge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFRafa TejedaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Path Vol 9 - William JudgeDocument472 pagesThe Path Vol 9 - William JudgeMark R. JaquaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi GuruDocument6 pagesPelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi Guruhenry jakatariPas encore d'évaluation
- Baumer Tdp02 Tdpz02 Ds enDocument4 pagesBaumer Tdp02 Tdpz02 Ds enQamar ZiaPas encore d'évaluation
- MICRF230Document20 pagesMICRF230Amador Garcia IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- GNT 52 60HZ enDocument4 pagesGNT 52 60HZ enEduardo VicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Section ADocument7 pagesSection AZeeshan HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Permeability PropertiesDocument12 pagesPermeability Propertieskiwi27_87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange 2010 UnderstandDocument493 pagesExchange 2010 UnderstandSeKoFiePas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodTHEVINESHPas encore d'évaluation
- The Politics of GenreDocument21 pagesThe Politics of GenreArunabha ChaudhuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Poster PresentationDocument3 pagesPoster PresentationNipun RavalPas encore d'évaluation
- R917007195 Comando 8RDocument50 pagesR917007195 Comando 8RRodrigues de OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Epson EcoTank ITS Printer L4150 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson EcoTank ITS Printer L4150 DatasheetWebAntics.com Online Shopping StorePas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Report 2022 2Document48 pagesAnnual Report 2022 2Dejan ReljinPas encore d'évaluation