Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
U14MCT701 Industrial Automation Ii L T P C 3 0 0 3
Transféré par
Ramkumar ATitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
U14MCT701 Industrial Automation Ii L T P C 3 0 0 3
Transféré par
Ramkumar ADroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
L T P C
U14MCT701 INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION II
3 0 0 3
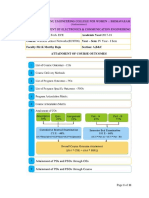
Course Outcomes
After successful completion of this course, the students should be able to
CO1: Classify the different types of communication protocols
CO2: Explain the importance of SCADA systems
CO3: Summarize the fundamentals of Distributed control systems
CO4: Design power supply, panel disk control for automation.
CO5: Describe various safety related parameters in designing automated system
Pre-requisite
Nil
CO/PO Mapping
(S/M/W indicates strength of correlation) S-Strong, M-Medium, W-Weak
Programme Outcomes(POs)
COs
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 P10
CO1 S S S
CO2 S
CO3 S S
CO4 S S
CO5 S S S
Course Assessment methods:
Direct Indirect
Internal test I
Internal test II
Internal test III Course end survey
End semester Examination
Assignment
INDUSTRIAL COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS 9 Hours
Definition of protocol, Introduction to Open System Interconnection (OSI) model,
Communication standard (RS232, RS485), Modbus (ASCII/RTU), Introduction to third party
interface, concept of OPC (Object linking and embedding for Process Control), HART Protocol:
Introduction, frame structure, programming, implementation examples, benefits, advantages and
limitation.
Foundation Fieldbus H1: Introduction, frame structure, programming, implementation examples,
benefits, advantages and limitation. Comparison of HART, Foundation Fieldbus, Devicenet,
Profibus, Controlnet, Industrial Ethernet.
SCADA SYSTEMS 9 Hours
SCADA Concept of SCADA systems, Programming techniques for : Creation of pages,
111
Signature of the chairman BOS /
Department of Mechatronics Engineering
Sequencing of pages, Creating graphics & animation, Dynamos programming with variables,
Trending, Historical data storage & Reporting, Alarm management, reporting of events and
parameters, Comparison of different SCADA packages, Interfacing PLC and SCADA using
communication link (RS232, RS485) , Protocols (Modbus ASCII/RTU) and OPC, Development
stages involved for PLC based automation systems, Application Development using SCADA
system.
DISTRIBUTED CONTROL SYSTEMS 9 Hours
DCS introduction, Various function Blocks, DCS components/block diagram, DCS Architecture
of different makes, comparison of these architectures with automation pyramid, DCS
specification, latest trend and developments, DCS support to Enterprise Resources Planning
(ERP), performance criteria for DCS and other automation tools.
DESIGN OF POWER SUPPLY, PANEL AND CONTROL DESK FOR 9 Hours
AUTOMATION
Power Supply: Power requirements calculation, Redundancy in Power supply schemes, Choice
of Circuit Breakers Inrush current, Interrogation Power Supply for Inputs / Outputs
Panels and Control Desks: Buffer Termination / Marshalling Cabinets, Power Supply,
Distribution in Panels, Control Desks / Panels, PLC/DCS Panels, Earthing Power, signal and
Panel Earthing, Network Cabinets and Racks - Preparation of Wiring Diagrams - Identification
and Tagging of cables & instruments - Common wiring practices - Cable schedule and choice of
cables.
PROCESS SAFETY AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS 9 Hours
Introduction to process safety, risk, risk terminologies, consequence and risk, risk measurement,
Process Hazard Analysis (PHA), Hazard and operability study ( HaZOp), Safety Integrity Level
(SIL), Introduction to IEC61511 standard for Functional safety , protection layers, Safety
Instrumented System: function, architecture, safety life cycle, Application of safety system.
Theory: 45Hr Total Hours: 45
REFERENCES
1.
2.
3. Frank D. Petruzella, -Hill Companies,
3rdEdition, March 2013.
4.
International, UK, 1992.
5.
112
Signature of the chairman BOS /
Department of Mechatronics Engineering
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- U17MCI5202 - Programmable Logic ControllersDocument2 pagesU17MCI5202 - Programmable Logic ControllersNIRMAL PRASAATH T 17BMC053Pas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument17 pagesSyllabusShanmuk ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus CST 476 MCDocument9 pagesSyllabus CST 476 MCSoubhagya V NPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Data Sheet - CNDocument4 pagesCourse Data Sheet - CNS RPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus OrganizedDocument9 pagesSyllabus OrganizedDatta RajendraPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS SyllabusDocument5 pagesCNS Syllabussaru priyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Document107 pages20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Ms. Meenakshi G M MCA. Associate ProfessorPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0017Document2 pagesWa0017Rohit VetrivelPas encore d'évaluation
- CN LAB MANUAL IIIrd YEARDocument54 pagesCN LAB MANUAL IIIrd YEARGUKKAN KPas encore d'évaluation
- r14r WSN Fcar Final With Po Attainment 7oct 2018 KMR FelDocument11 pagesr14r WSN Fcar Final With Po Attainment 7oct 2018 KMR FelKommisetty MurthyrajuPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 3-2 SyllabusDocument14 pagesECE 3-2 SyllabusRamcharan KadamPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC SyllabusDocument15 pagesPLC SyllabussivaeinfoPas encore d'évaluation
- B.tech Cse VTR Uge2021 de SyllabusDocument4 pagesB.tech Cse VTR Uge2021 de SyllabusBOLLIGARLA MOHAN SAI AKASH,CSE2021 Vel Tech, ChennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuk 6 ThsemesterDocument17 pagesKuk 6 ThsemesterAakash SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comm Networks LabDocument74 pagesComm Networks Labjaba123jaba100% (1)
- CSE2006 Syllabus PDFDocument9 pagesCSE2006 Syllabus PDFMohit SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- 116AL01Document3 pages116AL01Danidhariya NiravPas encore d'évaluation
- EC8691-Microprocessor and Microcontroller Department of IT 2021-2022Document24 pagesEC8691-Microprocessor and Microcontroller Department of IT 2021-2022ManjariPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Plan Control Engg 2020-2021Document7 pagesCourse Plan Control Engg 2020-2021Satheeswaran VPas encore d'évaluation
- Ug-r20-Eee & Ece MPMC SyllabusDocument3 pagesUg-r20-Eee & Ece MPMC SyllabusSanoxPas encore d'évaluation
- 1151CS104 Digitalelectronics SyllabusDocument2 pages1151CS104 Digitalelectronics Syllabusdogece8707Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vlsi, VHDL and PCB Design: in Electronics and Communication Engineering byDocument45 pagesVlsi, VHDL and PCB Design: in Electronics and Communication Engineering byAbhishek DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- CO Architecture and OrganizationDocument2 pagesCO Architecture and OrganizationArun Kumar DashPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc Updated Practical ListDocument2 pagesSoc Updated Practical Listpankaj chandankhedePas encore d'évaluation
- Idc & DCSDocument4 pagesIdc & DCSAniket SafariPas encore d'évaluation
- Sreenivasa Institute Question Bank on CAD/CAM/CIMDocument8 pagesSreenivasa Institute Question Bank on CAD/CAM/CIMAbdalmalek ShamsanPas encore d'évaluation
- 191cs42b - Os RecordDocument142 pages191cs42b - Os RecordanithatPas encore d'évaluation
- AB PLCDocument3 pagesAB PLCdasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Lab ManualDocument8 pagesEmbedded Lab ManualAlazmi Faleh50% (2)
- 1153ec105 Analog and Digital Communication SystemDocument3 pages1153ec105 Analog and Digital Communication Systemdogece8707Pas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusSHAIK MOHAMMED YASEEN,Cse2020 Vel Tech, ChennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Curriculum - SEM4Document13 pagesIT Curriculum - SEM4vidihac283Pas encore d'évaluation
- IDE-1 Courses SyllabusDocument8 pagesIDE-1 Courses SyllabusPulluru Sreenivas Sai LokeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Co1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Co6Document2 pagesCo1 Co2 Co3 Co4 Co5 Co6Mathavaraja JeyaramanPas encore d'évaluation
- IT131P-Networking Basics SyllabusDocument5 pagesIT131P-Networking Basics SyllabusJess Doria100% (1)
- Electronics Technology and DesignDocument4 pagesElectronics Technology and DesignVenkatasamy EEEPas encore d'évaluation
- BTech ECE VLSI Design Course InfoDocument3 pagesBTech ECE VLSI Design Course InfoKameshSontiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mca Lab-Ece-3014-Manual - Ay 2022-23Document49 pagesMca Lab-Ece-3014-Manual - Ay 2022-23bushraarhaan02Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Document107 pages20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Ms. Meenakshi G M MCA. Associate ProfessorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pias 2020-18earc302Document23 pagesPias 2020-18earc302Deepak KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular 20230722105129 Cho CN 22cs008 Batch2022Document9 pagesCircular 20230722105129 Cho CN 22cs008 Batch2022parth2029.be22Pas encore d'évaluation
- EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN Course Code 1153EC103Document3 pagesEMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN Course Code 1153EC103divya EswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Networks and SecurityDocument14 pagesPresentation On Networks and SecurityheraldPas encore d'évaluation
- CS Lab Manual FinalDocument40 pagesCS Lab Manual FinalYashwin.v YashuPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus BCADocument243 pagesSyllabus BCAAkshay mukundPas encore d'évaluation
- Eszg656 Course HandoutDocument8 pagesEszg656 Course HandoutfenytepePas encore d'évaluation
- Course Design Template Name of The Course: 21UEC959 Principles of CommunicationDocument6 pagesCourse Design Template Name of The Course: 21UEC959 Principles of CommunicationDevika R ECEPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Plan Comm Engg 2020-2021Document8 pagesCourse Plan Comm Engg 2020-2021Satheeswaran VPas encore d'évaluation
- EI 6702-Logic and Distributed Control SystemDocument2 pagesEI 6702-Logic and Distributed Control SystemMnskSaro50% (2)
- Model QP Os Set 3 UpdatedDocument3 pagesModel QP Os Set 3 Updatednarenmadhavan5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Me Eee Es R13Document42 pagesMe Eee Es R13Revathy VijayanPas encore d'évaluation
- ME VLSI & EmdDocument58 pagesME VLSI & EmdAnil V. WalkePas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor PSO-CO-PO 2017Document3 pagesMicroprocessor PSO-CO-PO 2017Eshwar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Automation - 3rd Year - SyllabusDocument2 pagesIndustrial Automation - 3rd Year - SyllabusvivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller FundamentalsDocument6 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller Fundamentalsgoons7777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation (Aecb32) (ECE) B.TECH V-Semester (IARE-R18) By, Dr. B. Surekha Reddy, Assistant Professor, ECEDocument493 pagesElectronic Measurement and Instrumentation (Aecb32) (ECE) B.TECH V-Semester (IARE-R18) By, Dr. B. Surekha Reddy, Assistant Professor, ECEsanjuPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB-Digitizing Copper - Defining Key Elements To Ensure Succesful Integration From Concepts To MaintenanceDocument8 pagesABB-Digitizing Copper - Defining Key Elements To Ensure Succesful Integration From Concepts To MaintenanceGustavo AguayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Coding: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications: Academic Press Library in Mobile and Wireless CommunicationsD'EverandChannel Coding: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications: Academic Press Library in Mobile and Wireless CommunicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiential LearningDocument12 pagesExperiential LearningRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Automation IIDocument33 pagesIndustrial Automation IIRamkumar A100% (1)
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Blooms PDFDocument1 pageBlooms PDFVianne ArcenioPas encore d'évaluation
- ER Soft Fieldbus Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesER Soft Fieldbus Comparison Chartaugur886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Delta SMPS TechguideDocument152 pagesDelta SMPS TechguideBharat DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- SensorsDocument30 pagesSensorsapi-3720161100% (1)
- Graded Lab ExperimentsDocument7 pagesGraded Lab ExperimentsRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Robot Mechanical Issues PDFDocument32 pagesRobot Mechanical Issues PDFRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of HartDocument59 pagesBasics of Hartjmathew_984887Pas encore d'évaluation
- Line FollowerDocument7 pagesLine FollowerRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of HartDocument59 pagesBasics of Hartjmathew_984887Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's Learning ModelDocument18 pagesBloom's Learning ModelRamkumar A100% (1)
- Baby First Food RecipesDocument54 pagesBaby First Food RecipesRamkumar A100% (1)
- PLC or DCS PDFDocument12 pagesPLC or DCS PDFsafvanshaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Rubrics For Presentation Skills Technical ContentDocument2 pagesEngineering Rubrics For Presentation Skills Technical ContentRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- DeviceNet Understand The TopologyDocument4 pagesDeviceNet Understand The TopologyRamkumar A100% (1)
- IfixDocument3 pagesIfixRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Lxm23d Manual v201 enDocument403 pagesLxm23d Manual v201 enRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- IfixDocument4 pagesIfixRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- IfixDocument4 pagesIfixRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- SoMachine Introduction - Compatibility and Migration - enDocument152 pagesSoMachine Introduction - Compatibility and Migration - enRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Bug AlgorithmDocument7 pagesBug AlgorithmRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Robot ProgrammingDocument12 pagesRobot ProgrammingRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Robot control part 1: Forward transform matricesDocument37 pagesRobot control part 1: Forward transform matricesRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- World Energy ResourcesDocument22 pagesWorld Energy ResourcesRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- TQMDocument9 pagesTQMRamkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics R15 23.6.16Document161 pagesMechatronics R15 23.6.16Ramkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Course Introduction: Collection and Presentation of Data The Frequency Distribution Graphical Presentation of DataDocument61 pagesCourse Introduction: Collection and Presentation of Data The Frequency Distribution Graphical Presentation of DataShekinah Vingno LingcongPas encore d'évaluation
- Cult of KUDocument31 pagesCult of KUEli GiudicePas encore d'évaluation
- Advancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesAdvancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsGuadalupe Abigail Rueda AguileraPas encore d'évaluation
- NotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationDocument20 pagesNotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationluzuPas encore d'évaluation
- HOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Document27 pagesHOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Hiếu KoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimating PSCC for Electrical InstallationsDocument2 pagesEstimating PSCC for Electrical InstallationsgmuitaPas encore d'évaluation
- MIL (Second Quarter)Document13 pagesMIL (Second Quarter)Menma ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Seasons of Life by Jim RohnDocument111 pagesThe Seasons of Life by Jim RohnChristine Mwaura97% (29)
- Food 8 - Part 2Document7 pagesFood 8 - Part 2Mónica MaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Garbage Gym GameDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Garbage Gym Gameapi-272479731Pas encore d'évaluation
- Upper Six 2013 STPM Physics 2 Trial ExamDocument11 pagesUpper Six 2013 STPM Physics 2 Trial ExamOw Yu Zen100% (2)
- Final Case Study 0506Document25 pagesFinal Case Study 0506Namit Nahar67% (3)
- ST Veronica Giuliani For OFS PresentationDocument7 pagesST Veronica Giuliani For OFS Presentationleo jPas encore d'évaluation
- Rustia V Cfi BatangasDocument2 pagesRustia V Cfi BatangasAllen GrajoPas encore d'évaluation
- Srimanta Shankardev: Early LifeDocument3 pagesSrimanta Shankardev: Early LifeAnusuya BaruahPas encore d'évaluation
- G10 - Math - Q1 - Module 7 Grade 10Document12 pagesG10 - Math - Q1 - Module 7 Grade 10Shua HongPas encore d'évaluation
- Release emotions with simple questionsDocument10 pagesRelease emotions with simple questionsDubravko ThorPas encore d'évaluation
- BCMEDocument9 pagesBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ti 1000 0200 - enDocument2 pagesTi 1000 0200 - enJamil AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentChristopher BellardPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiological Cutoff Values For Antifungal Susceptibility TestingDocument36 pagesEpidemiological Cutoff Values For Antifungal Susceptibility Testingdadrrui100% (1)
- Atlanta Pipes and FittingsDocument2 pagesAtlanta Pipes and Fittingsotadoyreychie31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 2 TaskDocument4 pagesDay 2 TaskYaathriganPas encore d'évaluation
- 4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishDocument6 pages4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishBernard GaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 7: "The Nearest Approximation To An Understanding of Life Is To Feel It and Realize It To The Fullest."Document16 pagesMath 7: "The Nearest Approximation To An Understanding of Life Is To Feel It and Realize It To The Fullest."benjamin ladesma0% (1)
- Zombie Exodus Safe Haven GuideDocument148 pagesZombie Exodus Safe Haven GuidejigglepopperPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity IA - CHEMDocument4 pagesViscosity IA - CHEMMatthew Cole50% (2)
- 68rfe IntroductionDocument71 pages68rfe IntroductionThePokeOne83% (6)
- Class 9 - Half Yearly Examination - 2023 - Portions and BlueprintDocument16 pagesClass 9 - Half Yearly Examination - 2023 - Portions and BlueprintSUBRAMANI MANOHARANPas encore d'évaluation
- Black BeautyDocument70 pagesBlack BeautyMeryem DevirgenPas encore d'évaluation