Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension
Transféré par
DareRaymondCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension
Transféré par
DareRaymondDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
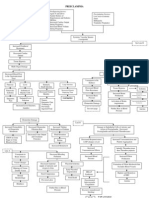
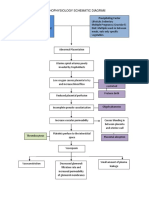
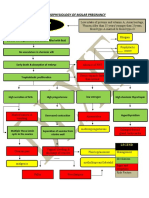
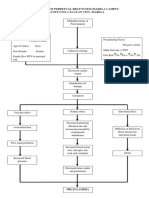
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PRENANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION
Precipitating Factors:
Predisposing Factors:
- Primigravida
- Age (31 years old)
- Lifestyle
- 180/100 mmHg
-
Decrease Responsiveness,
Endothelial Damage Effects of Prostaglandin
Decrease Blood pressure,
Virchows Triad
Vasospasm
NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
-Ineffective tissue perfusion r/t
Vasoconstriction of blood vessels
Vascular effect Kidney Effects
-Risk for fetal injury r/t reduced placental
Perfusion secondary to vasospasm
-Social Isolation r/t to prescribed bed rest Decreased Glomeruli filtration
-Risk for Injury Vasoconstriction
rate and increased permeability
-Risk for Bleeding of glomeruli membranes
-Risk for decreased cardiac output
Poor organ
Perfusion
- Pancreas Increased serum blood urea
- Liver nitrogen (BUN), Uric Acid and
- Brain Increased Blood Creatinine
- Retina Pressure
- Placenta
Decreased urine output
Increased pressure in the and Proteinuria
blood vessel
Diffusion of fluid from
Increased pressure in the placenta bloodstream into
interstitial tissue
Decreased oxygen in the Edema
placenta
Decreased oxygen of the fetus
Hypoxia
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pathophysiology of PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of PreeclampsiaKristine Alejandro100% (14)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDocument1 pageGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Incomplete AbortionDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Incomplete AbortionClaire Nimor Ventulan50% (4)
- Preeclampsia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPreeclampsia PathophysiologyIrene Zuñiga100% (4)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (2)
- Iii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesIii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsVianne Arcenio100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorCarrie A100% (2)
- PaThoPhysiology of EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPaThoPhysiology of Eclampsiahailleyann100% (2)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraPas encore d'évaluation
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocument7 pagesPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- NCP (GDM)Document16 pagesNCP (GDM)Jay Jay Jayyi100% (1)
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument23 pagesHydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of VSDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of VSDMarlon CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesPathophysiologyeunams_1195% (20)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument21 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageNidhi SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Stroke Scalp AcupunctureDocument64 pagesPost Stroke Scalp AcupunctureJosé Mário91% (11)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorCarrie APas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of PIHDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PIHCarren_Louise__8090Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaPearl IbisatePas encore d'évaluation
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 pagePreeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Pathophysiology PP FinalDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PP FinalLouie Kem Anthony Babaran0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (1)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDocument1 pageGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyAntonette CedroPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology PreeclampsiaPATHOSHOPPEPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DMDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational DMAnonymous GtR96jCPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis: Republic of The Philippines Bicol UniversityDocument7 pagesCase Analysis: Republic of The Philippines Bicol UniversityTrixia AlmendralPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP On Ectopic PregnancyDocument5 pagesNCP On Ectopic PregnancyDaisy Lui100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument35 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscotePas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (1)
- Gestational Diabetes NCP-3Document2 pagesGestational Diabetes NCP-3Jeffrey RasonabePas encore d'évaluation
- Diagram Myoma IDocument1 pageDiagram Myoma IJoann100% (12)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Large For Gestational Age (LGA)Document4 pagesLarge For Gestational Age (LGA)Aira AlaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DiabetesDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Gestational DiabetesKM Onda100% (5)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomaDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY MyomareapRaven0856% (9)
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyDocument1 pagePartial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPatho PhysiologyKeith MadarangPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageEctopic Pregnancy - PathophysiologyMarimiel PagulayanPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE STUDY Cesarean DeliveryDocument15 pagesCASE STUDY Cesarean Deliverydirkdarren100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Severe PreeclampsiaDocument84 pagesSevere PreeclampsiaJm Bernardo50% (2)
- Gestational HypertensionDocument6 pagesGestational HypertensionDimitrisSoulisPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaChristine Karen Ang SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- BSN 4D-2D Ectopic PregnancyDocument50 pagesBSN 4D-2D Ectopic PregnancyMac Cristian A. CaraganPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems of The PassengerDocument9 pagesProblems of The PassengerDanah Grace SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- RLEhospLUMC PATHOPHYSIOLOGYcasepresDocument3 pagesRLEhospLUMC PATHOPHYSIOLOGYcasepresSandy DuranPas encore d'évaluation
- THE PATIENT'S ILLNESS - Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : Non Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesTHE PATIENT'S ILLNESS - Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : Non Modifiable Risk FactorsWei Navarro CanlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Pathophysiology: University of Perpetual Help Sytem-Isabela Campus Minante Uno, Cauayan City, IsabelaDocument1 pageB. Pathophysiology: University of Perpetual Help Sytem-Isabela Campus Minante Uno, Cauayan City, IsabelaAnton RossiniPas encore d'évaluation
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preeclampsia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPreeclampsia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsAnton RossiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Document13 pagesCase Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Ivan Laurentine AceretPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocument6 pagesHypertensive Disorders in PregnancyLuiciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- TCP Med Ward Mayo Copy 2Document6 pagesTCP Med Ward Mayo Copy 2DareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Nop 0054Document7 pagesNop 0054DareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Ob - 1.02 Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesOb - 1.02 Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- MedsDocument2 pagesMedsDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology AntibioticsDocument91 pagesPharmacology AntibioticsDareRaymond100% (1)
- Ob - 1.02 Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesOb - 1.02 Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1 Water IntoxicationDocument20 pages10.1 Water IntoxicationDareRaymond100% (2)
- VREDocument30 pagesVREDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDocument120 pagesPharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDareRaymond100% (1)
- Analysis ProperDocument4 pagesAnalysis ProperDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesCase Study - Urinary Tract InfectionJiffy198867% (3)
- Content ServerDocument9 pagesContent ServerDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastric Cancer: Calag, Prescilla Tavas, Charme FayeDocument20 pagesGastric Cancer: Calag, Prescilla Tavas, Charme FayeDareRaymond0% (1)
- Respiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaDocument16 pagesRespiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaDareRaymond100% (2)
- Philippines EconDocument16 pagesPhilippines EconDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- FeverDocument2 pagesFeverDareRaymond0% (1)
- Hypo Kale MiaDocument14 pagesHypo Kale MiaDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Birthing PositionDocument10 pagesOB Birthing PositionDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: DR Waseem ChistiDocument21 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: DR Waseem ChistiDarryl AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- BCG VaccinatonDocument11 pagesBCG VaccinatonDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Junk Food PDFDocument5 pagesCommunity Junk Food PDFDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureDocument20 pagesRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- Ah 1 N 1Document9 pagesAh 1 N 1DareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Systematic ABG AnalysisDocument31 pages2 Systematic ABG AnalysisDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- DiabetesDocument11 pagesDiabetesDareRaymondPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Placenta - Libre PathologyDocument26 pages2 Placenta - Libre PathologyfadoPas encore d'évaluation
- TrishaDocument5 pagesTrishatata totoPas encore d'évaluation
- Embase OnlyDocument138 pagesEmbase OnlyAnastasiaKurtiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emergence Profile en PeriodontallyDocument13 pagesThe Emergence Profile en PeriodontallySebastián BernalPas encore d'évaluation
- Subcutaneous Injection: Patient InformationDocument4 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Patient InformationDiane MPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Marijuana BrochureDocument2 pagesMedical Marijuana BrochureMPP100% (1)
- Evaluasi Penatalaksanaan Prolanis Di Puskesmas Kota BengkuluDocument11 pagesEvaluasi Penatalaksanaan Prolanis Di Puskesmas Kota Bengkulunanasila02Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 SUA Dental Public Health-Educational - ModuleDocument14 pages2012 SUA Dental Public Health-Educational - ModuleDiana DrutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteomyelitis Oral SurgeryDocument17 pagesOsteomyelitis Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Upload - PDs - 35717-KPI Guide For StaffDocument5 pagesUpload - PDs - 35717-KPI Guide For StaffBilal Salameh100% (1)
- Fractures (Causes, Symptoms, Types and Treatments) : What Is A Fracture?Document2 pagesFractures (Causes, Symptoms, Types and Treatments) : What Is A Fracture?Adanxitto Perez GalarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cme (Tdhi)Document64 pagesCme (Tdhi)OB-Gyne TDHIPas encore d'évaluation
- A - Replication - Study - of - Fall - TIDocument8 pagesA - Replication - Study - of - Fall - TIfebbywahyunitaa kasimPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts CD Prof. RojasDocument6 pagesHandouts CD Prof. RojasChallen CulturaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Form No 86 Health ExaminationDocument1 pageGeneral Form No 86 Health ExaminationArminda Annabelle Bangks86% (22)
- Resumen - Act 14 - Ley de Incentivos para La Retención y Retorno de Profesionales MédicosDocument1 pageResumen - Act 14 - Ley de Incentivos para La Retención y Retorno de Profesionales MédicosEdgardo VázquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Gambaran Kebutuhan Keluarga Pasien Diruang Intensif: Literature Review Nurhidayatul Nadya Gamya Tri Utami, Riri NovayelindaDocument10 pagesGambaran Kebutuhan Keluarga Pasien Diruang Intensif: Literature Review Nurhidayatul Nadya Gamya Tri Utami, Riri Novayelindagamma kurnia mahananiPas encore d'évaluation
- NP1 Nursing Board Exam June 2008 Answer KeyDocument15 pagesNP1 Nursing Board Exam June 2008 Answer KeyBettina SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- EbolaDocument15 pagesEbolaIbama MirillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Icra FormDocument34 pagesIcra FormFitria RismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Incident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrenceDocument3 pagesIncident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrenceRenzo FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Transitional Care Management Services Article From AAFP JournalDocument6 pagesTransitional Care Management Services Article From AAFP Journalkisria100% (1)
- Mackenzie TortorichDocument2 pagesMackenzie Tortorichapi-509402148Pas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Emergency Medicine - 2022 - Jessen - Restrictive Fluids Versus Standard Care in Adults With Sepsis in TheDocument32 pagesAcademic Emergency Medicine - 2022 - Jessen - Restrictive Fluids Versus Standard Care in Adults With Sepsis in TheLenin BlancasPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of EyelidsDocument48 pagesDisorders of EyelidsUdaif BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Behavior Towards Ayurvedic ProductsDocument5 pagesConsumer Behavior Towards Ayurvedic ProductsVikrant AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- TB Screening Form For TAMUDocument1 pageTB Screening Form For TAMUmandar0072100% (1)