Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
East Irondequoit Middle School Sciences 7.2 Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems Ecology
Transféré par
Muhammad IqbalCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
East Irondequoit Middle School Sciences 7.2 Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems Ecology
Transféré par
Muhammad IqbalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
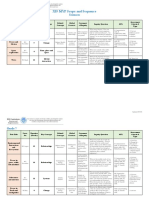
Teacher(s) Amy Gilbert, MaryEllen Felter, Victoria Romanchik Subject group and discipline Sciences: Sciences
Unit title Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems/Ecology (Unit 2) MYP Year Year 2 Unit duration 7 Weeks
Inquiry: Establishing the purpose of the unit Anticipated Board of Education approval September 2014
Key concept Related concept(s) Global context
Sciences
Form Energy
Change Environment
Scientific and technical
innovation
Organisms need to obtain
matter and energy from the
ecosystem to survive and grow.
Statement of inquiry
Humankind and the environment are affected by energy being transformed into different forms.
Inquiry questions
Factual What is the ultimate source of energy?
Conceptual How does energy flow through
ecosystems?
Debatable Ecosystems can be both fragile and
resilient. Should humans intervene to help restore an
ecosystem?
Objectives Summative assessment
A: Knowing and understanding Outline of summative assessment task(s) including assessment Relationship between summative assessment task(s) and
i. describe scientific knowledge criteria: statement of inquiry:
ii. apply scientific knowledge and understanding Task S Biome Research Poster (A, D) The Biome Research will allow the students to inquire
to solve problems set in familiar and unfamiliar about the different forms of energy and their
Students will select a Biome to research.
situations transformations.
Abiotic and biotic factors, food webs, food
iii. analyse information to make scientifically
supported judgments.
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 1 of 10
D: Reflecting on the impacts of science chains, and energy pyramids will be
i. describe the ways in which science is applied identified for that Biome. Students will
and used to address a specific problem or issue create a poster to present their Biome
ii. discuss and analyse the various implications Research to the class.
of the use of science and its application in solving a
specific problem or issue
iii. apply communication modes effectively
iv. document the work of others and sources of
information used.
Approaches to learning (ATL)
IB ATL CATEGORY MYP ATL CLUSTER SPECIFIC ATL SKILL LEARNING EXPERIENCES
Reading, writing and using language to
gather and communicate information
Read critically and for comprehension
Read a variety of sources for information and
for pleasure
Make inferences and draw conclusions
Use and interpret a range of discipline-
specific terms and symbols
Write for different purposes
Understand and use mathematical notation
Paraphrase accurately and concisely
Preview and skim texts to build
understanding
I. Communication skills
Take effective notes in class
Communication Make effective summary notes for studying
Use a variety of organizers for academic
writing tasks
Find information for disciplinary and
interdisciplinary inquiries, using a variety of
media
Organize and depict information logically
Structure information in summaries, essays
and reports
Exchanging thoughts, messages and
information effectively through interaction
Give and receive meaningful feedback
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 2 of 10
Use intercultural understanding to interpret
communication
Use a variety of speaking techniques to
communicate with a variety of audiences
Use appropriate forms of writing for different
purposes and audiences
Use a variety of media to communicate with
a range of audiences
Interpret and use effectively modes of non-
verbal communication
Negotiate ideas and knowledge with peers
and teachers
Participate in, and contribute to, digital social
media networks
Collaborate with peers and experts using a
variety of digital environments and media
Share ideas with multiple audiences using a
variety of digital environments and media
Working effectively with others
Use social media networks appropriately to
build and develop relationships
Practise empathy
Delegate and share responsibility for
decision-making
Help others to succeed
Take responsibility for ones own actions
Manage and resolve conflict and work
collaboratively in teams
II. Collaboration skills
Build consensus
Social Make fair and equitable decisions
Listen actively to other perspectives and
ideas
Negotiate effectively
Encourage others to contribute
Exercise leadership and take on a variety of
roles within groups
Give and receive meaningful feedback
Advocate for ones own rights and needs
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 3 of 10
Managing time and tasks effectively
Plan short- and long-term assignments;
meet deadlines
Create plans to prepare for summative
assessments (examinations and
performances)
Keep and use a weekly planner for
assignments
Set goals that are challenging and realistic
Plan strategies and take action to achieve
III. Organization skills personal and academic goals
Bring necessary equipment and supplies to
class
Keep an organized and logical system of
information files/notebooks
Use appropriate strategies for organizing
complex information
Understand and use sensory learning
preferences (learning styles)
Select and use technology effectively and
productively
Self-
(Re-)considering the process of learning;
management
choosing and using ATL skills
Develop new skills, techniques and
strategies for effective learning
Identify strengths and weaknesses of
personal learning strategies (self-assessment)
Demonstrate flexibility in the selection and
use of learning strategies
Try new ATL skills and evaluate their
effectiveness
V. Reflection skills
Consider content
- What did I learn about today?
- What dont I yet understand?
- What questions do I have now?
Consider ATL skills development
- What can I already do?
- How can I share my skills to help peers
who need more practice?
- What will I work on next?
Consider personal learning strategies
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 4 of 10
- What can I do to become a more efficient
and effective learner?
- How can I become more flexible in my
choice of learning strategies?
- What factors are important for helping me
learn well?
Focus on the process of creating by imitating
the work of others
Consider ethical, cultural and environmental
implications
Keep a journal to record reflections
Action: Teaching and learning through inquiry
Content Learning process
Knowledge & Skills: Learning Experiences
How will students know what is expected of them? Will they see examples, rubrics, templates, etc.?
New York State Standards How will students aquire the knowledge and practice the skills required? How will they practice applying these?
5.1d The methods for obtaining nutrients vary among
Do the students have enough prior knowledge?
organisms. Producers, such as green plants, use light
energy to make their food. Consumers, such as animals,
take in energy-rich foods.
5.1e Herbivores obtain energy from plants. Carnivores
obtain energy from animals. Omnivores obtain energy
from both plants and animals. Decomposers, such as
bacteria and fungi, obtain energy by consuming wastes
and/or dead organisms. General Skills: Students
6.2a Photosynthesis is carried on by green plants and will follow safety procedures, use appropriate
other organisms containing chlorophyll. In this process, units for measured or
the Suns energy is converted into and stored as calculated values, recognize and analyze
chemical energy in the form of a sugar. The quantity of patterns/trends, classify objects
sugar molecules increases in green plants during according to and established scheme,
photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight. develop dichotomous key, sequence
6.2b The major source of atmospheric oxygen is events, identify cause-and-effect
photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is removed from the relationships, and interpret results.
atmosphere and oxygen is released during
photosynthesis.
6.2c Green plants are the producers of food which is
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 5 of 10
used directly or indirectly by consumers. General Skills: Safely and
5.1c All organisms require energy to survive. The accurately use the following measuring tools:
amount of energy needed and the method for obtaining metric ruler, balance,
this energy vary among cells. Some cells use oxygen to stopwatch, graduated cylinder, thermometer,
release the energy stored in food. spring scale, and voltmeter.
Next Generation Science Standards (NGS)
MS-LS1-6 Construct a scientific explanation based on
evidence for the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of -draw
matter and flow of energy into and out of organisms a flow chart explaining cellular respiration
MS-LS1-7 Develop a model to describe how food is
-construct
rearranged through chemical reactions forming new
a food web or food chain
molecules that support growth and/or release energy as
this matter moves through an organism
-diagram
MS-LS2-1 Analyze and interpret data to provide a model of the carbon/oxygen cycle
evidence for the effects of resource availability on
organisms and populations or organisms in an -brom-thymol
ecosystem blue experiment
MS-LS2-3 Develop a model to describe the cycling of -construct
matter and flow of energy among living and non-living food webs
parts of an ecosystem
-compare
MS-LS2-4 Construct an argument support by empirical and contrast consumers to producers to
evidence that changes to physical and biological decomposers
components of an ecosystem affect populations
-label
English Language Arts Standards Science & Technical and diagram the process of photosynthesis
Subjects
Key Ideas and Details: -experiment
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.1 to find what happens in a plant if
Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of photosynthesis does not occur
science and technical texts.
-produce
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.2 a model of the pond food chain
Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text;
provide an accurate summary of the text distinct from -manipulate
prior knowledge or opinions. a compound microscope to view microscopic
objects
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 6 of 10
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.3 -determine
Follow precisely a multistep procedure when carrying the size of a microscopic object, using a
out experiments, taking measurements, or performing compound microscope
technical tasks.
-prepare
Craft and Structure: a wet mount slide
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.4
Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and -use
other domain-specific words and phrases as they are appropriate staining techniques
used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant
to grades 6-8 texts and topics. -design
and use a Punnett square or a pedigree chart
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.5 to predict the probability of
Analyze the structure an author uses to organize a text, certain traits
including how the major sections contribute to the
whole and to an understanding of the topic. -classify
living things according to a student-
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.6
generated scheme and an established
Analyze the author's purpose in providing an
scheme
explanation, describing a procedure, or discussing an
experiment in a text.
-interpret
Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity: and/or illustrate the energy flow in a food
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.6-8.10 chain, energy pyramid, or food
By the end of grade 8, read and comprehend science/ web
technical texts in the grades 6-8 text complexity band
independently and proficiently. -identify
pulse points and pulse rates
English Language Arts Standards Reading:
Informational Text -identify
Key Ideas and Details: structure and function relationships in
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RI.7.1 organisms
Cite several pieces of textual evidence to support
analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as
inferences drawn from the text.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RI.7.2
Determine two or more central ideas in a text and Teaching strategies
analyze their development over the course of the text; How will we use formative assessments to give students feedback during the unit?
provide an objective summary of the text. What different teaching methodologies will be employed?
How are we differentiating teaching and learning for all? Have we considered those learning in the language other
than their mother tongue? Have we considered those with special educational needs?
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 7 of 10
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RI.7.3
Analyze the interactions between individuals, events, -Quick writes
and ideas in a text (e.g., how ideas influence individuals - teacher created quizzes
or events, or how individuals influence ideas or events). - Labs: Cell Structure, Cell size, Uni-Cellular vs.
Multi-Cellular, Organization of Cells, Classification and Dichotomous Key
English Language Arts Standards Writing
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.7.2 -Use of graphic organizers
Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic -Short answer
and convey ideas, concepts, and information through responses
the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant -Cornell Notes
content. -Philosophical
Chairs
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.7.2.d -Socratic
Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary Seminars
to inform about or explain the topic. -WICOR Strategies
-Other AVID
Production and Distribution of Writing:
Science specific strategies
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.7.4
Produce clear and coherent writing in which the
-Pre-teaching
development, organization, and style are appropriate to
vocabulary
task, purpose, and audience. (Grade-specific
-Graphic
expectations for writing types are defined in standards
organizers
1-3 above.)
-Use of small
English Language Arts Standards Speaking & group read alouds
Listening -Guided notes
Comprehension and Collaboration: -Scaffolded
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.SL.7.1 questions
Engage effectively in a range of collaborative
discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led)
with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and
issues, building on others' ideas and expressing their
own clearly.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.SL.7.1.c
Pose questions that elicit elaboration and respond to
others' questions and comments with relevant
observations and ideas that bring the discussion back
on topic as needed.
Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas: Describe how you will differentiate teaching & learning for this unit?
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.SL.7.4
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 8 of 10
Present claims and findings, emphasizing salient points
in a focused, coherent manner with pertinent
descriptions, facts, details, and examples; use
appropriate eye contact, adequate volume, and clear
pronunciation.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.SL.7.5
Include multimedia components and visual displays in
presentations to clarify claims and findings and
emphasize salient points.
CCSS.ELA-Literacy.SL.7.6
Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and tasks,
demonstrating command of formal English when
indicated or appropriate. (See grade 7 Language
standards 1 and 3 here for specific expectations.)
Guided Questions
o How do different organisms get food? (Nutrition:
Photosynthesis/Consuming herbivore, carnivore,
omnivore, decomposers)
o How food energy is made available to organisms?
(Cellular Respiration) *energy transformations
chemical to chemical/heat/mechanical
Vocabulary
Oxygen Chemical energy
Carbon Dioxide Converted
Tissue Respiration
Organ Producers
Consumers Decomposers
Learner Profile
Inquirers:
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 9 of 10
Knowledgeable:
Caring:
Resources
Journal:
-AVID Write Path
Science Guide
-Science Insights Exploring Living Things
Textbook
Reflection: Considering the planning, process and impact of the inquiry
Prior to teaching the unit During teaching After teaching the unit
Middle Years Programme Unit planner Page 10 of 10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Changes Unit PlanDocument6 pagesChanges Unit PlanAnchal ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Relationship Interaction Models Scientific and Technical Innovation (Systems, Models and Methods)Document6 pagesRelationship Interaction Models Scientific and Technical Innovation (Systems, Models and Methods)Anchal Chadha100% (1)
- Unit Plan G10 Speed of Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesUnit Plan G10 Speed of Chemical ReactionsoscarbecPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordinator Job Desc 1 eDocument3 pagesCoordinator Job Desc 1 eRITA CHANDRANPas encore d'évaluation
- Seyoung An CV LatestDocument2 pagesSeyoung An CV Latestapi-313149236Pas encore d'évaluation
- MYP Sciences - Related ConceptsDocument2 pagesMYP Sciences - Related ConceptsLennoxMeldrum100% (1)
- Project Base LearningDocument5 pagesProject Base LearningBARISHA MANNAPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP 5 Biology Syllabus Breakdown 1Document2 pagesMYP 5 Biology Syllabus Breakdown 1Ayush GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP Unit PlannerDocument16 pagesMYP Unit Plannerzarna nirmal rawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Physical Quantities & Units 1.2 Scalars and Vectors: (1 Hour) (2 Hours)Document56 pages1.1 Physical Quantities & Units 1.2 Scalars and Vectors: (1 Hour) (2 Hours)elty TanPas encore d'évaluation
- DP Chem Unit 11 Measurement, Data Processing and AnalysisDocument4 pagesDP Chem Unit 11 Measurement, Data Processing and AnalysisPatrick AbidraPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Planner Chapter 2 Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesUnit Planner Chapter 2 Atomic StructureZrinka TopličanPas encore d'évaluation
- How Would You Describe Yourself?Document40 pagesHow Would You Describe Yourself?Bhawana SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication ProjectDocument4 pagesDNA Replication Projectrudra pratap0% (1)
- CH 10 PhotosynthesisDocument67 pagesCH 10 PhotosynthesisDVRaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Evaluation - Diversity of Life Year 1 Unit 2Document10 pagesUnit Evaluation - Diversity of Life Year 1 Unit 2api-405047057Pas encore d'évaluation
- Criterion B Task Specific ClarificationDocument4 pagesCriterion B Task Specific Clarificationapi-361230982Pas encore d'évaluation
- California State Science Fair 2007 Project SummaryDocument18 pagesCalifornia State Science Fair 2007 Project Summarysome_set18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and SoilDocument5 pagesRocks and SoilvijthorPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas Biology Genetics Evolution s1Document11 pagesAtlas Biology Genetics Evolution s1Tan Jha100% (1)
- Summative Periodic Table Unit TestDocument4 pagesSummative Periodic Table Unit Testapi-393175493Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingCharles GibbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Project First Draft Supervisor Feedback (Escuela Greenfield)Document5 pagesPersonal Project First Draft Supervisor Feedback (Escuela Greenfield)Edw Vergara100% (1)
- Plans IB HL AA Unit 08 VectorsDocument6 pagesPlans IB HL AA Unit 08 VectorsHui ZhengPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Unit 2 Assignment - Photosynthesis Factors.Document5 pagesGrade 10 Unit 2 Assignment - Photosynthesis Factors.MohdFahdelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Overview For Years 3 To 5Document9 pagesChemistry Overview For Years 3 To 5Ragin Benny (Teacher in Biology)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Create An Element Trading Card ProjectDocument2 pagesCreate An Element Trading Card Projectjkwong1331Pas encore d'évaluation
- AssessmentDocument4 pagesAssessmentapi-283316597100% (1)
- DP Chem Unit 3 PerodicityDocument5 pagesDP Chem Unit 3 PerodicityPatrick AbidraPas encore d'évaluation
- Myp Pedigree Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesMyp Pedigree Lesson Planapi-257190713Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topics 11 and 21 HL Measurement and Data ProcessingDocument23 pagesTopics 11 and 21 HL Measurement and Data ProcessingDuddlie YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Investigation MY3 Investigating RustingDocument5 pagesScience Investigation MY3 Investigating RustingPogo251Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical Plan - Myp ScienceDocument5 pagesVertical Plan - Myp Scienceapi-484776271100% (1)
- MYP 1. Criterion C. Sentence Starters and Rubric PDFDocument3 pagesMYP 1. Criterion C. Sentence Starters and Rubric PDFAadhya AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- XIS Scope and Sequence MYP SCIENCEDocument5 pagesXIS Scope and Sequence MYP SCIENCEDwight StephensonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Plan Stichiometry.Document8 pagesUnit Plan Stichiometry.Muntha AnilPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibmyp Approaches To Learning Atl Continuum Documnet - May 2013Document10 pagesIbmyp Approaches To Learning Atl Continuum Documnet - May 2013api-283502298Pas encore d'évaluation
- Year 8 Science Unit Outline For EnergyDocument3 pagesYear 8 Science Unit Outline For Energyapi-297560946Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleotides and Ribonucleic Acid Worksheet: 12.what Is This Reaction?Document2 pagesNucleotides and Ribonucleic Acid Worksheet: 12.what Is This Reaction?nurnisa janybekPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Plan Yr 12 2017Document15 pagesWeekly Plan Yr 12 2017api-246410374Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why Sugar Is Bad For You - Limit Sugar For Healthier Life: ExcessDocument2 pagesWhy Sugar Is Bad For You - Limit Sugar For Healthier Life: ExcessMikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Command Terms For ChemistryDocument2 pagesIb Command Terms For ChemistryMichaelAnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Heat Unit PlanDocument23 pagesFull Heat Unit Planapi-231734004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Myp Biology Egg Cell LabDocument3 pagesMyp Biology Egg Cell Labapi-367957505Pas encore d'évaluation
- G-7 Amount of Detergent Criterion-B C.finalDocument23 pagesG-7 Amount of Detergent Criterion-B C.finalLuvya KothariPas encore d'évaluation
- Criterion B Grade 8 - (Aim-Method) Energy PracticalDocument7 pagesCriterion B Grade 8 - (Aim-Method) Energy PracticalNatashaPas encore d'évaluation
- JASON Velocity LabDocument4 pagesJASON Velocity LabklblackPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 Chemistry Unit PlanDocument24 pagesScience 10 Chemistry Unit Planapi-477617112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Plan Dna 2Document7 pagesUnit Plan Dna 2api-513750879Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3 Particle ModelDocument23 pages6.3 Particle ModelFloPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Service ReflectionDocument1 pageCommunity Service Reflectionapi-479453127Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Specialised CellsDocument19 pages5 Specialised CellsKassyKasPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP 4 Chemistry Last WeekDocument2 pagesMYP 4 Chemistry Last Weekwama ojhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Updated Topic Coverage For Physics For The IB MYP 45Document2 pagesUpdated Topic Coverage For Physics For The IB MYP 45Rajat Arora100% (1)
- MYP 8th Grade Science SyllabusDocument3 pagesMYP 8th Grade Science SyllabusJerry DPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Research Myp Nov09Document55 pagesWater Research Myp Nov09Nazakat Ali KhosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report TemplateDocument9 pagesLab Report TemplateValeria MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- Inquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The Unit: Curious Scientist 1Document5 pagesInquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The Unit: Curious Scientist 1tsygcjihcgxfcdndznPas encore d'évaluation
- IBMYP-4 Chemistry Unit Plan - Nature of MatterDocument9 pagesIBMYP-4 Chemistry Unit Plan - Nature of Matteraaryana.ganesh09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Exam-Sample Paper 1Document19 pagesCambridge Exam-Sample Paper 1Pon KrithikhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scince X Solved PaperDocument149 pagesScince X Solved PaperTarique WaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Central 2010Document1 481 pagesExperiment Central 2010D BASU100% (1)
- Secondary Progression Test Stage 9 Science Paper 1Document25 pagesSecondary Progression Test Stage 9 Science Paper 1Stephen OnkwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 October/November 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 October/November 2019Seth JacobsPas encore d'évaluation
- 5090 w12 QP 12Document20 pages5090 w12 QP 12mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 2 Q4 Module 1 Week 1 FINALE EDITEDDocument27 pagesScience 2 Q4 Module 1 Week 1 FINALE EDITEDJenet Estrada100% (4)
- Effect of Pollution On Growth and Development of PlantsDocument56 pagesEffect of Pollution On Growth and Development of PlantsJessica OkekePas encore d'évaluation
- Transport in Cells 2 QP - PAPER 2 GOOD QUESTION PDFDocument14 pagesTransport in Cells 2 QP - PAPER 2 GOOD QUESTION PDFAlexia Micallef GattPas encore d'évaluation
- 428 2322 1 PB PDFDocument10 pages428 2322 1 PB PDFDaryl BermejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Ed Science PDFDocument8 pagesGen Ed Science PDFMaricel NogaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Non Cyclic PhotophosphorylationDocument3 pagesReview Non Cyclic PhotophosphorylationMarc Ian YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFDocument346 pagesComplete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFHusein Dharas95% (19)
- Genral Science Notes For Grade SeventhDocument52 pagesGenral Science Notes For Grade SeventhZohaib AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Capstone Paper Brassica JunceaDocument34 pagesCapstone Paper Brassica JunceaTito Tirol IIPas encore d'évaluation
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of Hydrogen Production From Biomass: Meng Ni, Dennis Y.C. Leung, Michael K.H. Leung, K. SumathyDocument12 pagesAn Overview of Hydrogen Production From Biomass: Meng Ni, Dennis Y.C. Leung, Michael K.H. Leung, K. SumathyNancy Eloisa RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology WorksheetDocument12 pagesEcology WorksheetHamidan Z WijasenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Form 5 ScienceDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Form 5 ScienceSensei J-dai91% (35)
- Boardworks PhotosynthesisDocument48 pagesBoardworks Photosynthesiskian shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Reviewer QuestionsDocument10 pagesBiology Reviewer QuestionsMICHELLE DE GUZMAN SOTTOPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF - Marine Bio Semester One Review SheetDocument2 pagesPDF - Marine Bio Semester One Review Sheetapi-205313794Pas encore d'évaluation
- Refrences: Mays L.) Hybrids Sown On Various Dates During Kharif in Peshawar-Pakistan. JDocument27 pagesRefrences: Mays L.) Hybrids Sown On Various Dates During Kharif in Peshawar-Pakistan. JqadriranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelsadsPas encore d'évaluation
- K/10 U/16 A/17 S/2 Tot/40: Ap018 Jgs/exam/if-02/r00Document5 pagesK/10 U/16 A/17 S/2 Tot/40: Ap018 Jgs/exam/if-02/r00SashankPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Photosynthesis-NotesDocument6 pages13 Photosynthesis-NotesDe DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Processes TutionDocument37 pagesLife Processes Tutionmanpreet kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Dulwich College Year 9 Science Specimen Exam Test PaperDocument12 pagesDulwich College Year 9 Science Specimen Exam Test PaperlusavkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review - Bioethanol Production From Microalgae PolysaccharidesDocument18 pagesReview - Bioethanol Production From Microalgae PolysaccharidesRElinePas encore d'évaluation
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationD'EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (37)
- Chesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandD'EverandChesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (38)
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”D'EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- On Fire: The Case for the Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The Case for the Green New DealÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (109)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutD'EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (142)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeD'EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- 438 Days: An Extraordinary True Story of Survival at SeaD'Everand438 Days: An Extraordinary True Story of Survival at SeaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (188)
- The Exploration of the Colorado river and its CanyonsD'EverandThe Exploration of the Colorado river and its CanyonsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastD'EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (31)
- How to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldD'EverandHow to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- The Great Displacement: Climate Change and the Next American MigrationD'EverandThe Great Displacement: Climate Change and the Next American MigrationÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (32)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateD'EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1003)
- Under a White Sky: The Nature of the FutureD'EverandUnder a White Sky: The Nature of the FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (159)
- The Worst Hard Time: The Untold Story of Those Who Survived the Great American Dust BowlD'EverandThe Worst Hard Time: The Untold Story of Those Who Survived the Great American Dust BowlÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (26)
- Soil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenD'EverandSoil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (16)
- Herbology At Home: Making Herbal RemediesD'EverandHerbology At Home: Making Herbal RemediesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (4)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsD'EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1424)
- Gaia Alchemy: The Reuniting of Science, Psyche, and SoulD'EverandGaia Alchemy: The Reuniting of Science, Psyche, and SoulPas encore d'évaluation
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsD'EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (177)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeD'EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Nature's Best Hope: A New Approach to Conservation that Starts in Your YardD'EverandNature's Best Hope: A New Approach to Conservation that Starts in Your YardÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (43)