Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Grammar Note (Verb Tenses)
Transféré par
psyhodrane0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues4 pagesUseful for english learners
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentUseful for english learners
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues4 pagesGrammar Note (Verb Tenses)
Transféré par
psyhodraneUseful for english learners
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
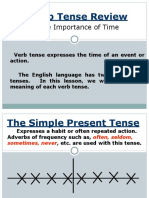
1) SIMPLE TENSES
Simple Present Tense
It snows in Alaska.
I watch television everyday.
I visit my cousin all the time.
In general, the simple present expresses events or
situations that exist always, usually, habitually; they
exist now, they have existed in the past, and will
probably exist in the future.
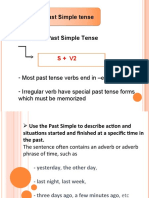
Simple Past Tense
It snowed yesterday.
I watched television last night.
I visited my cousin last year.
At one particular time in the past, this happened. It
began and ended in the past
Simple Future Tense
It will snow tomorrow.
I will watch television tonight.
I will visit my cousin later.
At one particular time in the future, this will happen.
2) PROGRESSIVE VERB TENSES
Present Progressive Tense
He is sleeping right now.
He is asleep at the moment. His sleep is in
progress at the present time, and will probably
continue.(at least for a while)
Past Progressive Tense
He was sleeping when I arrived.
He went to sleep at 10:00 last night. I arrived at
11:00. He was still asleep. His sleep began before
and was in progress at a particular time in the past.
It probably continued.(at least for a while)
Future Progressive Tense
He will be sleeping when we arrive.
He will go to sleep at 10:00 tomorrow night. We
will arrive around 11:00. The action of sleeping
will begin before we arrive, and it will be in
progress at a particular time in the future. His
sleep will probably continue.(at least for a while)
3) PERFECT VERB TENSES
Present Perfect Tense
I have already eaten.
I finished eating something before now. The exact time is
not important.
Past Perfect Tense
I had already eaten when they arrived.
First I finished eating. Later they arrived. My eating was
completely finished before another time in the past
Future Perfect Tense
I will have already eaten when they arrive.
First I will finish eating. Later they will arrive. My eating
will be completely finished before another time in the
future.
4) PERFECT PROGRESSIVE VERB TENSES
Present Perfect Progressive Tense
I have been studying for two hours.
Event in progress: studying
When? Before now, up to now
How long? For two hours
Past Perfect Progressive Tense
I had been studying for two hours before my friends
came.
Event in progress: studying
When? Before another event in the past
How long? For two hours
Future Perfect Progressive Tense
I will have been studying for two hours by the time
you arrive.
Event in progress: studying
When? Before another event in the future
How long? For two hours
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1) Simple Tenses Simple Present TenseDocument4 pages1) Simple Tenses Simple Present TenseArturo Jiménez MPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Chart Explaining Simple, Progressive, Perfect & Mixed FormsDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart Explaining Simple, Progressive, Perfect & Mixed FormsJuan Guillén FernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankLula Kotulova100% (1)
- D I S U S U N: Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesD I S U S U N: Bahasa InggrisEsri DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Activities and Verb Tenses TaskDocument4 pagesDaily Activities and Verb Tenses TaskEsri DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument3 pagesVerb TensesRhea CadungoPas encore d'évaluation
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimpleDocument5 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimplePrinces Aliesa Bulanadi0% (1)
- Unit 2. Verb TenseDocument15 pagesUnit 2. Verb TenseFahima tuzzahrohPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument1 pageVerb TensesJiang ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses - Simple Progresive TenseDocument21 pagesTenses - Simple Progresive TenseJuhadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankAlex PeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses ChartDocument4 pagesVerb Tenses Chartavid2chatPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Verb TensesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Verb Tensesakshatsahni425Pas encore d'évaluation
- English Grammar TensesDocument14 pagesEnglish Grammar TensesMaz Gedi60% (5)
- Mixed Tenses NT 2021Document23 pagesMixed Tenses NT 2021Ezra ManullangPas encore d'évaluation
- Cour MacDocument64 pagesCour MacMounir AakibPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankadityarizal0013Pas encore d'évaluation
- TensesDocument17 pagesTensesNaim Kharima SaraswatiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Verbal Tenses: Simple PresentDocument8 pagesThe Verbal Tenses: Simple PresentOriana PelagattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect Tense ExplainedDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect Tense ExplainedTaha GHPas encore d'évaluation
- Konu Anlatımı - TENSESDocument5 pagesKonu Anlatımı - TENSESGülnihal IşıkPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument31 pagesVerb TensesLuisa Fernanda Arias80% (5)
- Simple Past Simple Present Simple Future: V2 Vs Will / To Be Going To V1Document1 pageSimple Past Simple Present Simple Future: V2 Vs Will / To Be Going To V1mutlu pythonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses in English: Past, Present and FutureDocument8 pagesTenses in English: Past, Present and FutureBenedictus PrabandanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeDocument34 pagesVerb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeISSAM AFSAHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses 1. The Simple Tenses: Before, Is in Progress During, and Continuous After Another Time orDocument3 pagesTenses 1. The Simple Tenses: Before, Is in Progress During, and Continuous After Another Time orlalafadillaftrPas encore d'évaluation
- TEAM 1 - ContinuousDocument21 pagesTEAM 1 - ContinuousЕкатерина ТарановаPas encore d'évaluation
- Tense: The Concept of Time Can Be Split IntoDocument9 pagesTense: The Concept of Time Can Be Split IntoS.m. ChandrashekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Tenses in English Grammar Verb TensesDocument8 pages12 Tenses in English Grammar Verb TensesJoely Lontiong50% (2)
- Perfect TensesDocument22 pagesPerfect TensesGuisel Barría VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- 40past TensesDocument27 pages40past TensesGiorgino WatersPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Verb Tenses: EXERCISE 1. Introductions and InterviewsDocument10 pagesOverview of Verb Tenses: EXERCISE 1. Introductions and InterviewsSarah AnnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousSorana PaleuPas encore d'évaluation
- Past TenseDocument5 pagesPast TenseSimona Diana MicuPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do We Use The Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesHow Do We Use The Present Perfect TenseAndrea Michelle LydzinskiPas encore d'évaluation
- English GrammarDocument3 pagesEnglish GrammarFredhung7Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Verb TensesDocument38 pages12 Verb Tensesvaidikdubey57739Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rules - Past Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesRules - Past Perfect Simple and ContinuousLengyel-Marosi RenátaPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Tenses and Forms: Simple Past, Present Perfect, Past PerfectDocument4 pagesPast Tenses and Forms: Simple Past, Present Perfect, Past PerfectGheorghe RatiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses: Forms and Kinds: Simple Present TenseDocument3 pagesTenses: Forms and Kinds: Simple Present TenseAminTuhamePas encore d'évaluation
- Past Simple TenseDocument36 pagesPast Simple TenseRosary QuilingPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Verb TensesDocument36 pages12 Verb Tensesモーラーリー いたちPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Perfect 6toDocument17 pagesPast Perfect 6toHazel Villalobos RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Tenses Perfect Tenses: It Snows in Alaska. I Watch Television Everyday. I Visit My Cousin All The TimeDocument1 pageSimple Tenses Perfect Tenses: It Snows in Alaska. I Watch Television Everyday. I Visit My Cousin All The TimeJuan Pablo JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Perfect Simple &continuous BooksDocument9 pagesPast Perfect Simple &continuous BooksMotaz AbdelhamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankLucas SeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- TensesDocument2 pagesTensesNurulhusna MohdPuatPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tense & ConsistencyDocument6 pagesVerb Tense & ConsistencyAml AmlPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do We Make The Present Perfect Tense?Document5 pagesHow Do We Make The Present Perfect Tense?mu'ammal ash-shiddiqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Meeting 3 Perfect Aspect: Presented By: Rafelia Elsa Davistasya (31160008) Diah Anggraeni (31160148)Document13 pagesMeeting 3 Perfect Aspect: Presented By: Rafelia Elsa Davistasya (31160008) Diah Anggraeni (31160148)rafeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses - LectureDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses - LectureAnne PatocPas encore d'évaluation
- Usage of TensesDocument4 pagesUsage of TensesstacyPas encore d'évaluation
- TENSESDocument7 pagesTENSESYash JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Book SMTR 5 TK 3Document32 pagesHand Book SMTR 5 TK 3kha irunPas encore d'évaluation
- Engleski CasoviDocument13 pagesEngleski CasoviSonjaStojanovićPas encore d'évaluation
- SIMPLE FUTURE TENSESDocument30 pagesSIMPLE FUTURE TENSESElvis Aguilar JulcaPas encore d'évaluation
- English Verb Tenses GuideDocument5 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses GuideNabil El makoudyPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses Guide: Past, Present and FutureDocument31 pagesVerb Tenses Guide: Past, Present and FutureJesiah PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack and Jill Were Unable To Play Because of Their Injuries. Amy or Miya Will Be at Her Computer TomorrowDocument1 pageJack and Jill Were Unable To Play Because of Their Injuries. Amy or Miya Will Be at Her Computer TomorrowpsyhodranePas encore d'évaluation
- All Tenses Form CheatsheetDocument1 pageAll Tenses Form Cheatsheetapi-271296545Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blade Sizing Chart: Spinner BladesDocument7 pagesBlade Sizing Chart: Spinner BladespsyhodranePas encore d'évaluation
- E-Solat - Sistem Panduan Solat Harian Anda Pulau PinangDocument1 pageE-Solat - Sistem Panduan Solat Harian Anda Pulau PinangQamarina AzizanPas encore d'évaluation
- All Claims Documentation PDFDocument2 pagesAll Claims Documentation PDFpsyhodranePas encore d'évaluation
- Relieve Stress Brochure QuestionsDocument6 pagesRelieve Stress Brochure QuestionspsyhodranePas encore d'évaluation
- Plural Nouns Exercises AnswersDocument2 pagesPlural Nouns Exercises AnswersRosa Karen PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Case of Unaccusatives - Adriana BellettiDocument35 pagesThe Case of Unaccusatives - Adriana BellettiRonaldo NogueiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring the Building Blocks of Language: A Look at Affixes and Their Role in Word FormationDocument33 pagesExploring the Building Blocks of Language: A Look at Affixes and Their Role in Word FormationRenjie OliverosPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia de Comparativos y DescriptivosDocument2 pagesGuia de Comparativos y Descriptivoscarolina mundacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Grammar Practice: Modal Verbs Modal PerfectsDocument1 pageUnit 3 Grammar Practice: Modal Verbs Modal PerfectsCristina EstévezPas encore d'évaluation
- Active PassiveDocument1 pageActive PassiveArt Marcelo DuantePas encore d'évaluation
- Anh 8, HK1Document7 pagesAnh 8, HK1honghuydanghoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Most Important Rules for Forming Superlative AdjectivesDocument12 pagesThe Most Important Rules for Forming Superlative AdjectivesJuan Arréstegui GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs ListTays Vilches VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Middle EnglishDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Middle EnglishDewi Sartika UmulPas encore d'évaluation
- Going To VS WillDocument9 pagesGoing To VS WillLas creaciones de albanyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Quando É Usado o Present Perfect StudentDocument2 pages1 Quando É Usado o Present Perfect StudentamapecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Causative Verbs (Passive Voice) PDFDocument7 pagesCausative Verbs (Passive Voice) PDFBrinnely MarcanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nacionalidades Ejercicios InglesDocument2 pagesNacionalidades Ejercicios InglesHELENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Track Grammar Review For EFL TeachersDocument66 pagesFast Track Grammar Review For EFL TeachersquedolorquedolorquepenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of Speech & Sentence StructureDocument41 pagesPart of Speech & Sentence StructureAniezeEchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study English S1 Ep10: Connect IdeasDocument4 pagesStudy English S1 Ep10: Connect IdeasThuý SmilerPas encore d'évaluation
- ADJECTIVESDocument2 pagesADJECTIVESbrown jaramilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Universidad Abierta para Adultos (UAPA) : Psicología GeneralDocument3 pagesUniversidad Abierta para Adultos (UAPA) : Psicología GeneralErick JavielPas encore d'évaluation
- Amazing classroom resourcesDocument57 pagesAmazing classroom resourcesEvelyn100% (7)
- Perfect Past Tense Piscoya LDocument18 pagesPerfect Past Tense Piscoya LLucy Piscoya InoñanPas encore d'évaluation
- (Chapter 1) Answer SheetDocument2 pages(Chapter 1) Answer SheetMochammed AlamsyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Communications PPT SlidesDocument35 pagesBusiness Communications PPT SlidesAhmed SeifelnasrPas encore d'évaluation
- GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY For CAMBRIDGE ADVANCED AND PROFICIENCYDocument274 pagesGRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY For CAMBRIDGE ADVANCED AND PROFICIENCYAliona Solomon100% (3)
- Putri KartikaDocument11 pagesPutri KartikaAbhijata Kartika SilanandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Free German LessonsDocument2 pagesFree German LessonsSteven MartensenPas encore d'évaluation
- PeoplescharacterDocument7 pagesPeoplescharacterapi-242719344100% (1)
- Paul Noble ItalianDocument80 pagesPaul Noble ItalianScribdAddict100% (2)
- 5697 Past Simple of Regular VerbsDocument2 pages5697 Past Simple of Regular VerbsAhmed FaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Feel - Robbie WilliamsDocument2 pagesFeel - Robbie WilliamsRosana HundtPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT GrammarDocument6 pagesSAT GrammarHuy Nguyen100% (1)