Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Power Quality
Transféré par
Rowell Javier Sentin0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues1 pagePower quality refers to maintaining electrical parameters within tolerances to allow equipment to function properly without damage or reduced lifespan. Poor power quality can cause equipment operating issues or component damage through problems like voltage sags, surges, interruptions, harmonics or frequency deviations. These issues are typically addressed through power conditioning equipment like surge suppressors, motor-generator sets or UPS systems, or methods like adding capacitors, isolating sensitive equipment or adjusting transformer taps.
Description originale:
Terms & definition used in power quality for better understanding.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPower quality refers to maintaining electrical parameters within tolerances to allow equipment to function properly without damage or reduced lifespan. Poor power quality can cause equipment operating issues or component damage through problems like voltage sags, surges, interruptions, harmonics or frequency deviations. These issues are typically addressed through power conditioning equipment like surge suppressors, motor-generator sets or UPS systems, or methods like adding capacitors, isolating sensitive equipment or adjusting transformer taps.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues1 pagePower Quality
Transféré par
Rowell Javier SentinPower quality refers to maintaining electrical parameters within tolerances to allow equipment to function properly without damage or reduced lifespan. Poor power quality can cause equipment operating issues or component damage through problems like voltage sags, surges, interruptions, harmonics or frequency deviations. These issues are typically addressed through power conditioning equipment like surge suppressors, motor-generator sets or UPS systems, or methods like adding capacitors, isolating sensitive equipment or adjusting transformer taps.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
POWER QUALITY
Power quality is a set of electrical boundaries that allows a piece of equipment to function in its intended manner
without significant loss of performance or life expectancy.
Effects of Power Quality on Equipment
There are two major categories of how power quality problems affect equipment:
1. Equipment Operating Problems
2. Component Damage
Types of Power Quality Problems
There are generally two basic types of power quality problems: (1) those created by the switching of electrical loads
or entire circuits and (2) those caused by the interaction of electrical equipment and the electrical supply system.
Extended Outages. Extended outages are the most recognizable type of disturbance. They are usually the result of
permanent electrical faults.
Momentary Interruptions. Momentary interruptions are temporary total loss of voltage and are often caused by the
operation of automatic overcurrent protective devices.
Sags. Sags are voltage levels lower than nominal for periods of 2s or less. Voltage sags may be the result of (1) large
loads such as motors or electric welders on the same circuit, (2) bus voltage collapse on the electric supply
distribution circuit from motor starting, or (3) electrical faults on circuits supplied from the source.
Surges. Surges are temporary voltage increases with duration similar to sags. Surges may be caused by lightning or
the switching of large loads.
System Disturbances. Surges and disturbances occur in a transmission circuit when circuit conditions are in any
way altered. Disturbances may be produced by causes within system itself, such as switching, grounds, or charges of
load, or they may be produced by external causes, such as lightning.
Impulses and Noise. Impulses are overvoltage conditions lasting for less than one-half cycle. Because of the
waveform impulses are sometimes called spikes or transients. Lighting or switching may cause impulses or
transients.
Noise is a repetitive impulse superimposed on the power sine wave. Radio transmitters, fluorescent lights,
battery charges, computers, and loose electrical connections may cause electrical noise.
Harmonics. Harmonic distortion is a form of electrical noise. It is the superposition of signals at multiples of the
fundamental power frequency on the power sine wave.
Frequency Deviations. Frequency deviation is rarely a problem, especially where multiple electric supply generating
systems join to form a utility grid system.
Power Conditioning Equipment
1. Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors
2. Motor-Generator Sets
3. UPS and Standby Power Supplies
Other Methods for Addressing Power Quality Problems
1. Adding Capacitors to DC Supplies
2. Isolating Sensitive Equipment Sections
3. Changing Transformer Taps
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Leroy SomerDocument86 pagesLeroy SomerSimón Klein100% (1)
- Service Manual PerkinsDocument130 pagesService Manual Perkinsgelu2003home100% (12)
- Identification of Sags and Swells Using Pic MicrocontrollerDocument6 pagesIdentification of Sags and Swells Using Pic MicrocontrollerijsretPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Origins of Power Quality ProblemDocument12 pages1 Origins of Power Quality ProblemJagannathWijekoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report On Power Quality MonitoringDocument23 pagesSeminar Report On Power Quality MonitoringBhaargava Rama kodumuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality ProblemsDocument19 pagesPower Quality Problemsdinesh005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review:: Electric Power Quality Is The Degree To Which The Voltage, Frequency, andDocument7 pagesLiterature Review:: Electric Power Quality Is The Degree To Which The Voltage, Frequency, andfiraol temesgenPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage FluctuationsDocument2 pagesVoltage FluctuationsM e l o nPas encore d'évaluation
- Power QualityDocument69 pagesPower Qualityparamak958Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supply ProblemDocument6 pagesSupply ProblemMadiha QayumPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Book Document in WordDocument52 pagesProject Book Document in WordDëçèñt BøyPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentors: Reniva, John Simon Remot, Mark Angelo Santiago, Mark Anthony Sentin, Rowell J. Tejeresas, Mark ChesterDocument7 pagesPresentors: Reniva, John Simon Remot, Mark Angelo Santiago, Mark Anthony Sentin, Rowell J. Tejeresas, Mark ChesterRowell Javier SentinPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Overvoltages in Power System PDFDocument5 pagesTransient Overvoltages in Power System PDFanandPas encore d'évaluation
- Power QualityDocument7 pagesPower QualityJatin KansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality: More Papers and Presentations Available On Above SiteDocument10 pagesPower Quality: More Papers and Presentations Available On Above SiteBharadwaj SanthoshPas encore d'évaluation
- PQ 2Document16 pagesPQ 2AKASH CSDPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Problems and Solutions: An: Mehebub Alam, Mandela GainDocument7 pagesPower Quality Problems and Solutions: An: Mehebub Alam, Mandela GainRafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Answers PQDocument15 pagesAssignment Answers PQManikantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality: Prepared by - Jitendra Choudhary 6 SEM. (EE)Document8 pagesPower Quality: Prepared by - Jitendra Choudhary 6 SEM. (EE)Jitendra choudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Power Quality: TopicDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Power Quality: TopicArpit SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document70 pagesUnit 1Dilip Kumar100% (1)
- Unit-1 Class-1Document29 pagesUnit-1 Class-1sai krishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 - Introduction To POWER QUALITYDocument36 pagesLec 1 - Introduction To POWER QUALITYÙdayà Nirrmàl FernàñdòPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Determines The Fitness Of: Electrical Power Consumer Devices Electrical SystemsDocument5 pagesPower Quality Determines The Fitness Of: Electrical Power Consumer Devices Electrical SystemsAparnaHaridevPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of FaultsDocument13 pagesTypes of FaultsRahul SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3 - VOLTAGE SWELLDocument35 pagesLec 3 - VOLTAGE SWELLÙdayà Nirrmàl FernàñdòPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesEe 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and Answersscientistabbas100% (4)
- Lecture 11 - Power QualityDocument9 pagesLecture 11 - Power Quality12onn1ePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1 INTRODUCTION TO POWER QUALITYDocument117 pagesUnit-1 INTRODUCTION TO POWER QUALITYsujithPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Problem1Document15 pagesPower Quality Problem1Suvra PattanayakPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentmidunPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Power Quality and HarmonicsDocument6 pagesI. Power Quality and Harmonicshodeegits9526Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality DisturbancesDocument24 pagesPower Quality DisturbancesSunil SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of Transients in Power Systems: Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesAn Overview of Transients in Power Systems: Executive SummaryariphinePas encore d'évaluation
- Ana College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power QualityDocument59 pagesAna College of Engineering and Management Studies: Power Qualityprabhu kirpaPas encore d'évaluation
- PQ Unit-1Document25 pagesPQ Unit-1HariNarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- PSH 1 HarmonicsDocument44 pagesPSH 1 HarmonicsArnel Pascual Laquindanum0% (1)
- To Presentation of Seminar On: "Power Quality Disturbances andDocument26 pagesTo Presentation of Seminar On: "Power Quality Disturbances andSreerag VazhayilPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Management in Smart Grids: Issues and ImprovementsDocument5 pagesPower Quality Management in Smart Grids: Issues and ImprovementsJeff DalePas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Seminar Paper PDFDocument5 pagesTechnical Seminar Paper PDFJeff DalePas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Faults A Review IJERTCONV4IS02020Document2 pagesPower System Faults A Review IJERTCONV4IS02020Mohamed Daw HamoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Engineering: Causes of Over Voltage in Power SystemDocument8 pagesHigh Voltage Engineering: Causes of Over Voltage in Power SystemMohammed Sabeel KinggPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality 2 MARKSDocument12 pagesPower Quality 2 MARKSBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- ModuleDocument20 pagesModuleAbdalla ElsayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of ProtectionDocument18 pagesElements of ProtectionChetan TawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Deteksi Transformasi WaveletDocument10 pagesDeteksi Transformasi WaveletAank Anggun PurnomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Protection Week-01: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA UniversityDocument93 pagesPower System Protection Week-01: Shoaib Ahmed Shaikh Lecturer (EE) Sukkur IBA UniversitySagar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Ishwar KPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality: Presented by - Kaustubh Nande and Group Guided by - Prof. P.M.M. (YCCE)Document54 pagesPower Quality: Presented by - Kaustubh Nande and Group Guided by - Prof. P.M.M. (YCCE)Sundhar SivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Power Quality - WikipediaDocument6 pagesElectric Power Quality - WikipediakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of Power QualityDocument2 pagesDefinition of Power QualityEngr. AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture, Transients in Power Systems, March 2024Document64 pagesLecture, Transients in Power Systems, March 2024Amongin JulietPas encore d'évaluation
- Lightning Protection SeminarDocument54 pagesLightning Protection SeminarMurali Krishnan100% (1)
- Subject Code: Ee 1005 Subject Name: Power Quality: What Are The Causes Due To Short Circuit in TheDocument22 pagesSubject Code: Ee 1005 Subject Name: Power Quality: What Are The Causes Due To Short Circuit in TheChetan KotwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Power Quality UG-UNIT-1Document72 pagesElectric Power Quality UG-UNIT-1Praveen kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument65 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Power System Protectionjaved kazim100% (1)
- Unit Iii OvervoltagesDocument16 pagesUnit Iii Overvoltageslvb123Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Unit 4 Power Quality Problems in Distribution System StuDocument38 pagesA Unit 4 Power Quality Problems in Distribution System Stumayurshurkar20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Protection (PSP) : Week-01 Introductory Concepts Instructor: Dr. Wahab AliDocument49 pagesPower System Protection (PSP) : Week-01 Introductory Concepts Instructor: Dr. Wahab Alisafiking100% (1)
- Power System and Faults: A ReviewDocument4 pagesPower System and Faults: A ReviewANIL reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture01 - Introductory ConceptsDocument30 pagesLecture01 - Introductory ConceptsCarl PPas encore d'évaluation
- Parker Pneumatic Sensors PDFDocument25 pagesParker Pneumatic Sensors PDFyouri59490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ci Ride Leader - Guide To Cycling On The Road PDFDocument10 pagesCi Ride Leader - Guide To Cycling On The Road PDFΑυτός είμαι εγώPas encore d'évaluation
- SNJB's Late Sau. Kantabai Bhavarlalji Jain College of Engineering, ChandwadDocument10 pagesSNJB's Late Sau. Kantabai Bhavarlalji Jain College of Engineering, ChandwadAkash JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Building MassingDocument6 pagesBuilding MassingJohn AmirPas encore d'évaluation
- EPRI Advances in Life AssessmentDocument1 285 pagesEPRI Advances in Life AssessmentPenjual AirPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Dispatch Centre: By-Siddharth KumarDocument16 pagesLoad Dispatch Centre: By-Siddharth KumarSIDDHARTHPas encore d'évaluation
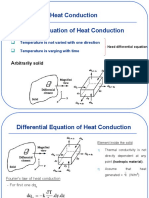
- Heat Conduction Differential Equation of Heat Conduction: Rbitrarily SolidDocument31 pagesHeat Conduction Differential Equation of Heat Conduction: Rbitrarily SolidJoshua StrykrPas encore d'évaluation
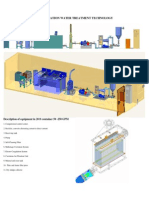
- Cavigulation Water Treatment Technology 20 FT 2Document3 pagesCavigulation Water Treatment Technology 20 FT 2firmansyachPas encore d'évaluation
- Abb RmuDocument88 pagesAbb RmumarkfoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding ElectrodesDocument13 pagesWelding ElectrodesArimoro Cyril ObusePas encore d'évaluation
- Dd311 Specification Sheet EnglishDocument4 pagesDd311 Specification Sheet EnglishJose Antonio Sanchez SegoviaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO-50001-JK-WhiteDocument24 pagesISO-50001-JK-WhiteAgustinusDwiSusantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tunisia - Nawara Southern Tunisian Gas Pipeline - ESIA Executive SummaryDocument28 pagesTunisia - Nawara Southern Tunisian Gas Pipeline - ESIA Executive SummaryodeinatusPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 503 DomDocument9 pagesME 503 Domsuneel kumar rathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Foot MouswitchDocument11 pagesFoot MouswitchnewbeatleePas encore d'évaluation
- 103 - Chemical House M&E R-2Document7 pages103 - Chemical House M&E R-2Gayan IndunilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lnk584-586 Linkzero-Ax: Zero Standby Consumption Integrated Off-Line SwitcherDocument16 pagesLnk584-586 Linkzero-Ax: Zero Standby Consumption Integrated Off-Line Switchershiva1luPas encore d'évaluation
- Epocoat 111 PDFDocument3 pagesEpocoat 111 PDFjunaid112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ramakant Sir Physics Tutorials: (Magnetism) DURATION: 45mins MARKS: 50Document5 pagesRamakant Sir Physics Tutorials: (Magnetism) DURATION: 45mins MARKS: 50Kshitij BichavePas encore d'évaluation
- Mohammad Shadab Khan - Field OperatorDocument6 pagesMohammad Shadab Khan - Field OperatorDonPas encore d'évaluation
- 59529-Especificaciones para Preservacion EquiposDocument65 pages59529-Especificaciones para Preservacion EquiposrodolfostiPas encore d'évaluation
- NFPA 25 Form AES 5.4 ITM Electric Fire Pump Annual 2013 - 4 of 7Document1 pageNFPA 25 Form AES 5.4 ITM Electric Fire Pump Annual 2013 - 4 of 7Mark Louie GuintoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument8 pages10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsMokshPas encore d'évaluation
- Booster Basics PresentationDocument49 pagesBooster Basics PresentationbinhjukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 Properties and Handling of Particulate SolidsDocument95 pagesLec 1 Properties and Handling of Particulate SolidsAli HasSsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Application of A Spreadsheet-Based ModelDocument7 pagesDesign and Application of A Spreadsheet-Based ModelPassmore DubePas encore d'évaluation
- 6.1 Mastering IELTS Writing Task 1 (PDFeBook) PDFDocument228 pages6.1 Mastering IELTS Writing Task 1 (PDFeBook) PDFHarsh Patel100% (6)