Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Fundamentals 1. Answer The Following Questions From
Transféré par
Matias Caño Alvares0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
41 vues2 pageselectricalllll
Titre original
Electrical Fundamentals Questionnaire
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentelectricalllll
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
41 vues2 pagesElectrical Fundamentals 1. Answer The Following Questions From
Transféré par
Matias Caño Alvareselectricalllll
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Electrical Fundamentals
1. Answer the following questions from
www.autoshop101.com/trainmodules/electricity/elec101.html
2. What is matter?
R: Matter is anything that has mass (weight) and occupies space.
3. What is the difference between a compound and an element?
R:
4. What are the 4 states of matter?
R: Matter has three states: Solid, Liquid, and Vapor.
5. What are the names of the changes of states of matter?
R:
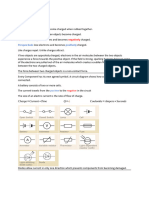
6. What are the components of the atoms?
R: A single atom consists of three basic components: a proton, a neutron, and
an electron.
7. What are the parts of the atoms?
R: Within the atom there is a Nucleus. The Nucleus contains the protons and
neutrons. Orbiting around the nucleus are the electrons.
8. Where are the electrons?
R: Electrons orbit around the nucleus of the atom
9. Whats electron flow?
R Since electrons are lighter than protons and are outside the nucleus, they
can be easily moved from atom to atom to form a flow of electrons.
10. Complete:
Opposite electrical charges _________, but like charges _________.
11. What is an ion?
R: The atom becomes either a positively or negatively charged particle called
an ION. These unbalanced charged ION particles are responsible for electron
flow (electricity).
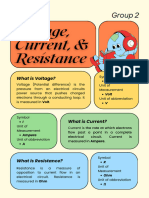
12. Complete the following table
MAGNITUDE DEFINITION MEASURE MEASURE MEASURE
UNIT UNIT DEVICE
SYMBOL
VOLTAGE Voltage is the Voltage is VOLTMETER
electrical force measured in units
that moves called VOLTS v
electrons through
a conductor
RESISTANCE Resistance is the Resistance is OHMMETER
force that reduces measured in units
or stops the flow called OHMS
of electrons. It
opposes voltage.
CURRENT CURRENT is the Current flow is GALVANOMETER
quantity or flow Measured in
rate of electrons Units called
moving past a Amperes or A
point within one AMPS.
second. Current
flow is also known
as amperage, or
amps for short.
INSULATION An electrical
insulation is a Megohmmeter refers
material with the to an instrument for
ability to conduct the measurement of
electrical insulation
electricity, used to
separate electrical
conductors
POWER
FREQUENCY
CONDUCTIVITY
13. What factors enhance resistance?
14. What types of electricity are there? Name them.
15. What do AC and DC stand for?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsD'EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Network Laws and TheoremsDocument2 pagesNetwork Laws and TheoremsPrenzi Balbuena EspirituPas encore d'évaluation
- The Basics of Electricity CompleteDocument9 pagesThe Basics of Electricity CompleteAlejandroDuranPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuit TheoryDocument6 pagesElectric Circuit TheoryPaula ZofioPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics Lec-1Document41 pagesBasic Electronics Lec-1world cup 2019Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics RevisionDocument5 pagesPhysics RevisionzPas encore d'évaluation
- Probing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Document9 pagesProbing Guide - Questions For Electrical Circuits 1 Lab 1Marydelle SubitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity 10thDocument45 pagesElectricity 10thSuryank sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo Guia InglishDocument10 pagesTrabajo Guia InglishAlejandroDuranPas encore d'évaluation
- Beeme Unit IDocument258 pagesBeeme Unit IGenga DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec - Basics of ElectronicsDocument40 pagesLec - Basics of Electronicszaheerduaa27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Document51 pagesElectrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Fiorella Amer CarrPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Physics PresentationDocument18 pagesMedical Physics Presentationsamavia sohailPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circuit SymbolsDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Symbolsanwar9602020Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3 ELECTRICAL TerminologyDocument10 pages3.3 ELECTRICAL TerminologyPalu AritPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Current ResistanceDocument54 pagesVoltage Current ResistanceAngilyn LumabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonDocument6 pagesHandout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonSRIREKHAPas encore d'évaluation
- P4 Electric CircuitsDocument2 pagesP4 Electric CircuitsArun DontePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesModule 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToMustapha IsaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 12: ElectricityDocument22 pagesChapter - 12: ElectricityAgrasen SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electricity ParametersDocument90 pagesBasic Electricity Parameterssubbaiah54100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document61 pagesLecture 1jackdrejePas encore d'évaluation
- My First Physics Lab 01Document2 pagesMy First Physics Lab 01juttu6348Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yellow Blue Retro Take A Break Reminder Portrait PosterDocument3 pagesYellow Blue Retro Take A Break Reminder Portrait PosterHiccaPas encore d'évaluation
- CurrentDocument10 pagesCurrentShanto NiceschoolPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 15: Electrical Circuits and Their Applications: LO1:Know Principal Electrical Terms, Quantities and RelationshipsDocument39 pagesUNIT 15: Electrical Circuits and Their Applications: LO1:Know Principal Electrical Terms, Quantities and RelationshipsePas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document51 pagesPresentation 1Workineh AsefaPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument9 pagesStudent Lab Manual: Fundamentals of ElectricityAbdisalam A. MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 Basic Electronics - 00 V2.0Document64 pagesTopic 1 Basic Electronics - 00 V2.0JENNIFER SERVOPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectricityDocument18 pagesElectricityRishi GovindaHarryPas encore d'évaluation
- G8 Week5 6 WorksheetDocument5 pagesG8 Week5 6 WorksheetArvin RescatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectthaswikaamaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Recap: VOLTAGE Is The Amount of Energy Given To Electrons AsDocument31 pagesRecap: VOLTAGE Is The Amount of Energy Given To Electrons AsengrroyPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectricityDocument85 pagesElectricityapi-2851792610% (1)
- Basic ElectricityDocument19 pagesBasic ElectricityTerfaia NadjatPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 1Document32 pagesClass 1Bhargav LahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Principal Mwalusi Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument216 pagesPrincipal Mwalusi Basic Electrical EngineeringVictor mulotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circuits & QuantitiesDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuits & QuantitiesDejaunae Lawson50% (2)
- Wa0002Document164 pagesWa0002wilson simfukwePas encore d'évaluation
- 3544 FdocDocument8 pages3544 FdocDean SeepanePas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Current and Electric ChargeDocument10 pagesElectric Current and Electric ChargesuhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation of ElectricityDocument26 pagesFoundation of ElectricityRaven TarroquinPas encore d'évaluation
- Natsci2 Under Mr. Pili: ElectricityDocument27 pagesNatsci2 Under Mr. Pili: Electricityhhnflaws29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsDocument39 pagesPresentation - Basic Aircraft Familiarization Course - AvionicsFlorencioPautangPas encore d'évaluation
- Hm's Law EquationDocument4 pagesHm's Law EquationRavi KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIDAD9 CircuitsDocument6 pagesUNIDAD9 CircuitsPedro MIRANDA FERNANDEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Electrical Magnitudes: Ii. T FDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Electrical Magnitudes: Ii. T FIsrael De La TorrePas encore d'évaluation
- E CH Erence Energydiff Ifference Potentiald: Allan RiddickDocument7 pagesE CH Erence Energydiff Ifference Potentiald: Allan RiddickAngel LaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument6 pagesChapter 12 ElectricityShiv Prakash SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SSS 1 3RD TermDocument21 pagesSSS 1 3RD TermabiodunokoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Electricity FinalsDocument33 pages12 Electricity FinalsKelly FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio in TleDocument16 pagesPortfolio in TleAileen Javines50% (2)
- Intro-Duction To Electricity: Force Field Which Is Neither Gravitational Nor Nuclear. To Understand What ThisDocument9 pagesIntro-Duction To Electricity: Force Field Which Is Neither Gravitational Nor Nuclear. To Understand What ThisAbdisalam A. MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical+thermal PhysicsDocument20 pagesElectrical+thermal PhysicsTaha YousafPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad 5 InglesDocument10 pagesActividad 5 InglesVictoria FlorezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsDocument23 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsHassan Al MamunPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuits: AP Physics BDocument24 pagesElectric Circuits: AP Physics BFaIz Rizq ÅrdPas encore d'évaluation
- Null 22Document254 pagesNull 22mohamed ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- 1SDA071192R1 E4 2n 4000 Ekip Dip Lsi 3p F HRDocument3 pages1SDA071192R1 E4 2n 4000 Ekip Dip Lsi 3p F HRjunior_jazzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground ImprovementDocument17 pagesGround Improvementpatelahmad77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Using Different Perforated Lids On The MAS-100 Family Air SamplersDocument6 pagesUsing Different Perforated Lids On The MAS-100 Family Air SamplersJuan Salvador MaestrePas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting Technology Y2Document202 pagesDrafting Technology Y2Anderson MarantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Usb 3.0Document21 pagesPresentation On Usb 3.0Anuj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidebook 184Document1 pageGuidebook 184Anonymous 7GOnu0xeuCPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Owners of Handy House - Smith and TrippDocument17 pagesHistory of Owners of Handy House - Smith and TrippwestporthistoricalPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Quality Intro PDFDocument32 pagesPower Quality Intro PDFsheila hariPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Vibration Chapter03Document130 pagesAdvanced Vibration Chapter03Alooy MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Report of Apollo 201 Review BoardDocument2 540 pagesReport of Apollo 201 Review BoardBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Ring Smart Lighting Transformer Manual ENDocument11 pagesRing Smart Lighting Transformer Manual ENjust let me download assholePas encore d'évaluation
- GLR EstimateDocument2 pagesGLR EstimateanbujePas encore d'évaluation
- VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) 5.0 Step by Step Setup GuideDocument110 pagesVMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) 5.0 Step by Step Setup Guidehj192837Pas encore d'évaluation
- PowerLogic ION 8600 Product Part Number Guide 052006Document2 pagesPowerLogic ION 8600 Product Part Number Guide 052006Magistra AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- STA505Document10 pagesSTA505kizonzPas encore d'évaluation
- New Build Snagging List TemplateDocument13 pagesNew Build Snagging List TemplatekekerodePas encore d'évaluation
- Ground Water Recharge Techniques 2Document141 pagesGround Water Recharge Techniques 2Ravi Bhushan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation Engineering Shot NotesDocument21 pagesFoundation Engineering Shot NotesSejal VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Database - Chap 5Document84 pagesAdvanced Database - Chap 5Anhtho LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Refuelling HoseDocument4 pagesAircraft Refuelling HoseBimo IndroPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine - Activity - Lab - Sheet Rev.ADocument5 pagesEngine - Activity - Lab - Sheet Rev.AAvery KarevPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction ManualDocument462 pagesInstruction ManualCaraluaPas encore d'évaluation
- 132-LogSat JRC JLN-720 Instruct Manual 1-10-2019Document134 pages132-LogSat JRC JLN-720 Instruct Manual 1-10-2019Sunil S I ShippingPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Consumer Perception Mahindra ThesisDocument95 pagesMarket Consumer Perception Mahindra ThesisHarmeet singh100% (1)
- Skim Mik Powder MSDSDocument6 pagesSkim Mik Powder MSDSVampireSuicidePas encore d'évaluation
- Charpy Impact Test - STP 1072Document219 pagesCharpy Impact Test - STP 1072biancogallazzi100% (3)
- ASCOM Users GuideDocument21 pagesASCOM Users GuideleloalmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intel® System Identification UtilityDocument2 pagesIntel® System Identification UtilityPatel NikhilPas encore d'évaluation
- FIDIC Red Book Construction Contract 1st Edition 1 9Document9 pagesFIDIC Red Book Construction Contract 1st Edition 1 9raviPas encore d'évaluation
- Charpy Impact TestDocument3 pagesCharpy Impact TestRamana IkkurthiPas encore d'évaluation