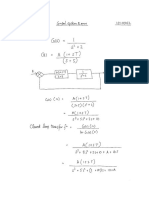
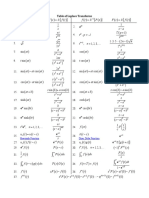
Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Nptel: Indian Society - Issues and Problems - Web Course
Transféré par
Muhammed MinhajDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Nptel: Indian Society - Issues and Problems - Web Course
Transféré par
Muhammed MinhajDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NPTEL Syllabus
Indian Society - Issues and
Problems - Web course
COURSE OUTLINE
This course proposes to problematise social problems in the Indian
economy, culture and polity.
NPTEL
The aim is to introduce the concepts, theories, and case studies that
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
seek to clarify social problems as social, cultural, political, economic
and historical phenomena which have the potential to unleash
larger implications for policy changes, social reforms, and even Humanities and Social
economic and political revolutions.
Sciences
1. Social Problems;
2. Illiteracy, Poverty, Unemployment and Population Growth;
3. Child Abuse, Child Labour and Violence against Women; Additional Reading:
4. Casteism, Communalism and Regionalism; 1. Bhattacharya, Rinki. Ed. 2004. Behind
Closed Doors: Domestic Violence in India.
5. Crime, Criminal and Juvenile Delinquency; New Delhi: Sage.
6. Alcoholism, Drug Abuse and Corruption. 2. Uberoi, Patricia. Ed. 1993. Family, Kinship
and Marriage in India. Delhi, Oxford
University Press.
COURSE DETAIL
3. Uberoi, Patricia. 2006. Freedom and Destiny:
Gender, Family, and Popular Culture in India.
Module Topics and Contents No. of Delhi: Oxford University Press.
Lectures
4. Beteille, Andre. Ed. 1969. Social Inequality:
Selected Readings. Harmondsworth:
Penguin.
1 Social Problems 5
5. Beteille, Andre. 1977. Inequality Among
1. Concept.
Men. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
2. Characteristics and Types.
6. Beteille, Andre. 1992. Society and Politics in
3. Causes and Reactions. India: Essays in a Comparative Perspective.
Delhi: Oxford University Press.
4. Theoretical and Methodological
Approaches. 7. Crompton, Rosemary. 1998. Class and
Stratification: An Introduction to Current
5. Rural and Urban Problems in India. Debates. Cambridge: Polity Press, 2nd
Edition.
6. Social Change in India.
8. Tumin, Melvin. 1999. Social Stratification.
7. Discussion. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall.
9. Gupta, Dipankar. Ed. 1992. Social
Stratification. Delhi: Oxford University Press.
2 Illiteracy, Poverty, Unemployment and 8
Population Growth 10. Desai, A. R. Ed. 1969. Rural Sociology in
India. New Delhi: Popular Prakashan.
1. Magnitude and Causes of Illiteracy.
11. Epstein, Scarlet. 1976. Economic
2. National Policy on Education. Development and Social Change. London:
ELTS.
3. Measurement of Poverty.
12. Srinivas, M.N. Ed. 1955. Indias Villages.
4. Causes of Poverty. Delhi: Oxford University Press.
5. Rural Poverty.
Hyperlinks:
Hyperlinks:
6. Poverty Alleviation Programmes.
1. http://docs.google.com/gview
7. Features, Types, Causes and
Consequences of 2. http://www.scribd.com/doc/2184672/Social-
Problems-of-India
8. Unemployment in India.
3. http://lifestyle.iloveindia.com/magazine/issues-
9. Rural and Urban Unemployment in
causes-10.html
India.
10. Youth Unrest. Coordinators:
11. National Rural Employment Dr. Liza Das
Guarantee Act. Department of Humanities and Social SciencesIIT
Guwahati
12. Causes and Effects of Population
Growth in India. Dr. Sambit Mallick
Department of Humanities and Social SciencesIIT
13. Population Policy. Guwahati
14. Family Planning.
15. Role of the Civil Society.
16. Discussion.
3 Child Abuse, Child Labour and 7
Violence against Women
1. Child Population and the Working
Children.
2. Types, Causes and Effects of Child
Abuse.
3. The Problem of Child Labour.
4. Nature, Extent and Characteristics
of Violence against Women.
5. Women's Harassment.
6. Violence against Widows.
7. Victims and Perpetrators of
Violence.
8. Motivations in Violence.
9. Self-image, Self-esteem and
Adjustment of Victims.
10. Discussion.
4 Casteism, Communalism and 8
Regionalism
1. Characteristics, Types, Causes and
Consequences of Casteism.
2. Remedial Measures to Tackle
Casteism.
3. Characteristics, Types, Causes and
Consequences of Communalism.
4. Communal Holocausts in India.
5. Remedial Measures to Tackle
Communalism.
6. Characteristics, Types, Causes and
Consequences of Regionalism.
7. Remedial Measures to Tackle
Regionalism.
8. Discussion.
5 Crime, Criminal and Juvenile 7
Delinquency
1. Crime, Criminal and Criminology.
2. Characteristics of Crime in India.
3. Sociological Explanations of Crime.
4. Nature, Characteristics, Types and
Factors of Juvenile Delinquency.
5. Methods of Treating Delinquents.
6. Preventive Programmes.
7. Discussion.
6 Alcoholism, Drug Abuse and 7
Corruption
1. Extent, Causes and Problems of
Alcoholism.
2. Anti Liquor Movements.
3. Control on Alcoholism.
4. Extent and Nature of Drug Abuse.
5. Role of Family and Peer Group in
Drug Abuse.
6. Measures to Combat Drug
Trafficking.
7. Causes and Impact of Corruption.
8. The Legislation.
9. Combating Corruption.
10. Discussion.
Total 42
References:
1. Das, Veena. Ed. 2003. The Oxford India Companion to
Sociology and Social Anthropology, Vol. II. Delhi: Oxford
University Press (Sect.9).
2. Giddens, Anthony. 2000. Introduction to Sociology, New
York: Norton.
3. Goodwin, Jeff and Jasper, James M. Ed. 2003. The Social
Movements Reader: Cases and Concepts, Oxford: Blackwell.
4. Kumar, Radha. 2001. From Chipko to Sati: The Contemporary
Indian Women's Movement in Nivedita Menon, ed., Gender
Indian Women's Movement in Nivedita Menon, ed., Gender
and Politics in India, Delhi: Oxford University Press.
A joint venture by IISc and IITs, funded by MHRD, Govt of India http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Community Organisation NotesDocument95 pagesCommunity Organisation NotesArull Msw100% (2)
- Al Hizbul Azam in 30 Parts - Original TranslationDocument181 pagesAl Hizbul Azam in 30 Parts - Original TranslationMuhammed Minhaj100% (1)
- Question Bank Gender Society PDFDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Gender Society PDFKanika Jain100% (1)
- Radical FeminismDocument6 pagesRadical FeminismAlisha GobinsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politicsjaypee raguroPas encore d'évaluation
- Grandin Blood of GuatemalaDocument365 pagesGrandin Blood of Guatemalamarku7272100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Aspects of Culture and SocietyDocument38 pagesLesson 2 - Aspects of Culture and SocietyJoshua Corpuz100% (1)
- The Marxist Theory of The StateDocument12 pagesThe Marxist Theory of The Stateshaani_pratapPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Contract TheoryDocument29 pagesSocial Contract TheoryFaiz Syed MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- 21st CENTURY LITERATURE - Q2 SUMMATIVE 1Document4 pages21st CENTURY LITERATURE - Q2 SUMMATIVE 1Dave Sulam0% (1)
- Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences TestDocument5 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences TestVergel Torrizo100% (3)
- State Level Syllabus of Sociology For Undergraduate LevelDocument10 pagesState Level Syllabus of Sociology For Undergraduate LevelKrishna AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- BA SociologyDocument10 pagesBA Sociologyankit boxerPas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology GeneralDocument66 pagesSociology GeneralHazelPas encore d'évaluation
- MA SocioDocument25 pagesMA Sociokomalkatre11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Sociology Course OutlineDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Sociology Course OutlineAhmad JamPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Principles of Sociology and Indian Culture Subject Code: HbbaDocument2 pagesSubject: Principles of Sociology and Indian Culture Subject Code: HbbaShantanu AgnihotriPas encore d'évaluation
- Sosio SyllabusDocument30 pagesSosio SyllabusAvisha Singh xïï ÇPas encore d'évaluation
- MA Sociology Syllabus Sem I 2020-21Document15 pagesMA Sociology Syllabus Sem I 2020-21Prajot AsolkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidayatullah National Law University Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh) Syllabus: SociologyDocument2 pagesHidayatullah National Law University Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh) Syllabus: SociologyNISHTHA SHRIVASTAVAPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidayatullah National Law University Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh) Syllabus: Sociology (2016)Document2 pagesHidayatullah National Law University Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh) Syllabus: Sociology (2016)AnantHimanshuEkkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Sociology Course OutlineDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Sociology Course Outlineiam scavengerPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Outline of Soc HECDocument3 pagesCourse Outline of Soc HECRehana Shahid PmlnPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus Sociology: Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Document15 pagesSyllabus Sociology: Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Marumamula Santosh Kumar100% (1)
- BA SOCIOLOGY OPTIONAL V & VI Sem 2021-22 & ONWORDS PDFDocument19 pagesBA SOCIOLOGY OPTIONAL V & VI Sem 2021-22 & ONWORDS PDFSumit TirakannavarPas encore d'évaluation
- MA Sociology New 2012Document63 pagesMA Sociology New 2012Indianhoshi HoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- 304 Gender & Society MA Sociology - III304 2019Document275 pages304 Gender & Society MA Sociology - III304 2019Jitendra PanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 SociologyDocument13 pages11 SociologyMalsawmkima Maski-a100% (5)
- Sociology of India SyllabusDocument5 pagesSociology of India SyllabusRoonah KayPas encore d'évaluation
- MSW I & III (1) Under CbcsDocument8 pagesMSW I & III (1) Under Cbcsपं रामकृष्ण गौड़Pas encore d'évaluation
- Block 5Document52 pagesBlock 5richaPas encore d'évaluation
- Block-1 Status of Women in IndiaDocument62 pagesBlock-1 Status of Women in IndiaJona JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- History & Philosophy NotesDocument406 pagesHistory & Philosophy Notesandroos achayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbcs Syllabus (Nep) : Ug - Sociology (I & Ii Semester)Document26 pagesCbcs Syllabus (Nep) : Ug - Sociology (I & Ii Semester)Unknown 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soc Major&MinorDocument7 pagesSoc Major&MinorYash TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- MA Sociology SyllabusDocument26 pagesMA Sociology SyllabusJitendra PanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- G.S Ghurye-1Document3 pagesG.S Ghurye-1Hemochandra YumnamPas encore d'évaluation
- General Principles of SociologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Sociologygkm8127Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Readings in Indian Sociology - Volume I) Paramjit S Judge (Editor) - Readings in Indian Sociology - Volume I - Towards Sociology of Dalits-Sage Publications Pvt. LTD (2013)Document3 549 pages(Readings in Indian Sociology - Volume I) Paramjit S Judge (Editor) - Readings in Indian Sociology - Volume I - Towards Sociology of Dalits-Sage Publications Pvt. LTD (2013)Milton BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- 48 Sociology: B.A./B.Sc.: Elective and OptionalDocument4 pages48 Sociology: B.A./B.Sc.: Elective and OptionalMPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus: Social Work Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Document20 pagesSyllabus: Social Work Admitted Batch 2008 - 2009Marumamula Santosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- New Sociology SyllabusDocument2 pagesNew Sociology SyllabusSanjith SibiPas encore d'évaluation
- SocioDocument12 pagesSociokhushi chouhanPas encore d'évaluation
- SOCIOLOGYDocument7 pagesSOCIOLOGYjnvyaariyanPas encore d'évaluation
- TriumphIAS - Sociology SyllabusDocument6 pagesTriumphIAS - Sociology Syllabusankit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Skmu Ug SociologyDocument9 pagesSkmu Ug Sociologyneha827110Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSW2Document58 pagesMSW2Achuna Gangmei0% (1)
- Accurate GuanacoDocument3 pagesAccurate Guanacorehan786bokhiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Socio Anthro Course Outline 1st Sem 2014 To 15Document3 pagesSocio Anthro Course Outline 1st Sem 2014 To 15Anonymous MkxqW5wHMPas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology (Optional)Document7 pagesSociology (Optional)praveenakg0% (1)
- 2020 C.V. - Pranta Pratik PatnaikDocument15 pages2020 C.V. - Pranta Pratik PatnaikPranta Pratik PatnaikPas encore d'évaluation
- True or FalseDocument1 pageTrue or FalseRonalyn Cajudo25% (8)
- 11sociology Hindi 2021 22Document192 pages11sociology Hindi 2021 22rk3138549Pas encore d'évaluation
- TQ 3RD QTR DissDocument3 pagesTQ 3RD QTR DissdwacindyfjPas encore d'évaluation
- B.SC., (N) Sociology .UNIT I: Two Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesB.SC., (N) Sociology .UNIT I: Two Mark QuestionsBasit RamzanPas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadDocument16 pagesDownloadSwathy s LaijuPas encore d'évaluation
- CCF Women StudiesDocument9 pagesCCF Women Studiesf20220612Pas encore d'évaluation
- B.A. III Sociology 12Document36 pagesB.A. III Sociology 12Abinash BorahPas encore d'évaluation
- 504 - M - A - Sociology-2Document2 pages504 - M - A - Sociology-2rajravi203542Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology - Sem-IDocument2 pagesSociology - Sem-ISaumya RaizadaPas encore d'évaluation
- F.4 - Gender School and SocietyDocument2 pagesF.4 - Gender School and SocietyNikhil Vivek 'A'Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding GandhiDocument122 pagesUnderstanding Gandhihimaniyadav7393Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology: Themes and PerspectivesDocument4 pagesSociology: Themes and PerspectivesH SPas encore d'évaluation
- GE 01 Indian Society-Images and RealitiesDocument5 pagesGE 01 Indian Society-Images and RealitiesDeepansh TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllab Abus and Regulations NS: P Post Basic B.Sc. NursingDocument4 pagesSyllab Abus and Regulations NS: P Post Basic B.Sc. NursingmuthukumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sociology Course OutlineDocument3 pagesSociology Course OutlineWARDA ARIF M.Sc. Applied PsychologyPas encore d'évaluation
- TelkensosDocument1 pageTelkensosMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- StasDocument1 pageStasMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 WDDocument6 pages4 WDMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Wheel Tractor ScrapersDocument30 pagesWheel Tractor ScrapersMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- ItineraryDocument4 pagesItineraryMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- MetroligyDocument1 pageMetroligyMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- CentigrodeDocument1 pageCentigrodeMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Inwards Travel Restrictions Operation Directive: SituationDocument4 pagesInwards Travel Restrictions Operation Directive: SituationMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- AdmitCard 230310582216Document4 pagesAdmitCard 230310582216Muhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Form - Junior Executive Assistant - Direct RecruitmentDocument3 pagesApplication Form - Junior Executive Assistant - Direct RecruitmentMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Shortest / Rigorous Path: QualifierDocument3 pagesShortest / Rigorous Path: QualifierMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Qualifier Solution: Computational ThinkingDocument13 pagesMock Qualifier Solution: Computational ThinkingMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2020-01-03 at 4.34.27 AmDocument1 pageScreenshot 2020-01-03 at 4.34.27 AmMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Forty Hadith On Good Character - Faith in Allah PDFDocument19 pagesForty Hadith On Good Character - Faith in Allah PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Refining Processes Slides PDFDocument18 pagesAdditional Refining Processes Slides PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Forty Hadiths On The Merit of Saying La Ilaha IllallahDocument7 pagesForty Hadiths On The Merit of Saying La Ilaha IllallahMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- ELEN90055 Control Systems Workshop 2: Open-Loop and Closed-Loop ControlDocument11 pagesELEN90055 Control Systems Workshop 2: Open-Loop and Closed-Loop ControlMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- RoadDocument1 pageRoadMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Processing Natural Gas Slides PDFDocument13 pagesProcessing Natural Gas Slides PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- (QR Code Paper1)Document6 pages(QR Code Paper1)Muhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- QWSD PDFDocument1 pageQWSD PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Sinky: Size If 5Document8 pagesSinky: Size If 5Muhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- CP12 RSH 191 PDFDocument61 pagesCP12 RSH 191 PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemDocument30 pagesControl SystemMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- II - Es: SkiffsDocument13 pagesII - Es: SkiffsMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGM90011 2020 Final Exam PDFDocument3 pagesENGM90011 2020 Final Exam PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- CP12 RSH 192 PDFDocument88 pagesCP12 RSH 192 PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Toansfvfn - GG: Gcs S2Document9 pagesToansfvfn - GG: Gcs S2Muhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFMuhammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Stratification in Pakistan, Social Difference, Social ClassDocument22 pagesSocial Stratification in Pakistan, Social Difference, Social ClassMuti ullah100% (1)
- Distributive JustceDocument6 pagesDistributive JustcepriyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Who Are The Objects of Positive and Negative Gossip at WorkDocument13 pagesWho Are The Objects of Positive and Negative Gossip at WorkCornelPas encore d'évaluation
- Anarchism AintDocument8 pagesAnarchism AintDante IrreraPas encore d'évaluation
- OP 1 Analysis Paper On Rhys' MannequinDocument4 pagesOP 1 Analysis Paper On Rhys' MannequinNica LelisPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc Sociological Perspectives Writing AssignmentDocument3 pagesSoc Sociological Perspectives Writing Assignmentapi-366708920100% (1)
- The Question of Capitalist Desire: Deleuze and Guattari With MarxDocument16 pagesThe Question of Capitalist Desire: Deleuze and Guattari With MarxavidadollarsPas encore d'évaluation
- Language Under ErasureDocument9 pagesLanguage Under Erasureashanl20Pas encore d'évaluation
- PolSci 14 NotesDocument5 pagesPolSci 14 NotesIan Ignacio AgngarayngayPas encore d'évaluation
- TheoDocument3 pagesTheoAshley LapusPas encore d'évaluation
- Article CritiqueDocument2 pagesArticle CritiqueLj QuiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Kritik: Kritik: Noun - in The Philosophical Context, Kritik (Or Critique) Refers To TheDocument4 pagesThe Kritik: Kritik: Noun - in The Philosophical Context, Kritik (Or Critique) Refers To TheNathan JohnstonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics, Integrity and AptitudeDocument6 pagesEthics, Integrity and Aptitudevarunkkaushal5967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Confederalism, Cetralism, Federalism TableDocument3 pagesConfederalism, Cetralism, Federalism TableAlejandra SigüenzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts and Problems of Comparative PoliticsDocument24 pagesConcepts and Problems of Comparative PoliticsPriya MathurPas encore d'évaluation
- Modernisation Pros and ConsDocument3 pagesModernisation Pros and Consshahanavas10% (1)
- Democracy - An Ideal Form of GovernmentDocument9 pagesDemocracy - An Ideal Form of GovernmentasfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversation With György Lukács - Franco Ferrarotti S InterviewDocument5 pagesConversation With György Lukács - Franco Ferrarotti S Interviewapi-3796837Pas encore d'évaluation
- Post, or Distribute: Advocacy in Social WorkDocument20 pagesPost, or Distribute: Advocacy in Social WorkFlorentina LucanPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Theory Roots and Branches 5Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesSocial Theory Roots and Branches 5Th Edition Full Chapterjason.schermann510100% (31)
- Bureaucracy (Weber)Document5 pagesBureaucracy (Weber)Jamilah EdwardPas encore d'évaluation
- Habitus and Field WrittenDocument2 pagesHabitus and Field WrittenBimby Ali LimpaoPas encore d'évaluation
- MGVRKG© Ckvi G J Eva I BXWZGVJV: BdwbuDocument20 pagesMGVRKG© Ckvi G J Eva I BXWZGVJV: BdwbuScientia Online CarePas encore d'évaluation
- International Business Chapter 4Document3 pagesInternational Business Chapter 4DhavalPas encore d'évaluation