Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan For Broncho
Transféré par
Pal_in100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
196 vues9 pagesAfter 8 hours of nursing intervention, she will be able to: General: Maintain patent airway. -temperature is above normal value because of increase in pyrogens37.90c -Pulse is rapid, weak90 bpm -RR- 29cpm -BP- may be elevated.
Description originale:
Titre original
Nursing Care Plan for Broncho
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAfter 8 hours of nursing intervention, she will be able to: General: Maintain patent airway. -temperature is above normal value because of increase in pyrogens37.90c -Pulse is rapid, weak90 bpm -RR- 29cpm -BP- may be elevated.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
196 vues9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Broncho
Transféré par
Pal_inAfter 8 hours of nursing intervention, she will be able to: General: Maintain patent airway. -temperature is above normal value because of increase in pyrogens37.90c -Pulse is rapid, weak90 bpm -RR- 29cpm -BP- may be elevated.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 9
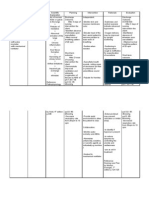
NURSING CARE PLAN
Diagnosis Need Desired Interventions Rationale Evaluation Intervention Rationale
Outcome Statement Modification
1. Ineffective airway After 8 hours
clearance related to of nursing
plueric chest pain, P intervention,
positioning, fatigue, H she will be
and thick secretions Y able to:
as manifested by S
cough, tenacious I General:
sputum, crackles/ O Maintain
wheezes and L patent airway.
dyspnea. O Independent
G Specific: 1. Establish 1. This would Goal met. Continue Bronchop
S/O cues: I Expectorat rapport with the help in building The patient nursing neumonia
-with pleuritic pain C e secretions patient and trust of the was able to intervention cannot be
-with headache readily. significant patient to the maintain s. treated for
-dyspnea N others. student nurse. patent 8 hours. It
-tachypnea E Rapport will help airway by needs a
-chills E Establish the student expectoratin longer
-low grade fever D clear breath obtain accurate g time so
-rapid shallow sounds. data from the secretions. the
breathing patient and the The patient interventio
-Cough with significant other. also ns should
greenish or yellow Provides manifest be
mucu-appears therapeutic and continued
anxious communication established to
-with sputum between the clear breath promote
production student nurse sounds comfort.
-Weakness noted and the patient upon For
-flushed cheeks as well as the auscultation continuity
-use of accessory significant other. . of care
muscles and
2. This will serve
-crackles/ wheezing facilitate
as the baseline
-consolidation 2. Monitor and patient in
data for the shift.
-bronchial breath record vital recovery.
It would help in
sounds signs.
determining the
-chest expansion
current status of
may be diminished /
the patient and
unequal on
determine
inspiration
response to the
VS:
-Temperature is . therapy.
above normal value
because of increase
in pyrogens- 37.9⁰C 3. IVF 3. To provide
-Pulse is rapid, regulation and accurate amount
weak- 90 bpm monitoring of IVF to the
-RR- 29cpm patient
-BP- may be . preventing fluid
hypotensive – volume deficit/
80/60mmHg overload.
Background: 4. Evaluate 4. To determine
Inability to clear cough reflex the ability in
secretions or and swallowing protecting
obstructions from ability. airway.
the respiratory tract
to maintain a clear 5. Promote 5. To reduce
airway. rest. oxygen demands
Pneumonia is of tissues and
caused by a prevent fatigue..
bacterial/ viral
infection that results 6. Monitor 6. This would
in an inflammatory respiration and help in
process in the lungs. breath sounds. determining
It is an infectious respiratory
process that is distress and
spread by droplets accumulation of
or by contact. secretions.
Bronchopneumonia
is a term used to 7. Provide an 7. To promote an
describe pneumonia allergen free environment
that is distributed in environment. conducive to the
a patchy fashion, condition of the
having originated in patient and
one or more reduce the risk of
localized areas worsening of the
within the bronchi condition.
extending to the 8. Assist
8.To take
adjacent patient in semi-
advantage of the
surrounding lung fowler’s
gravity
parenchyma. position.
decreasing
pressure on the
diaphragm and
enhancing
drainage of
secretions. To
maximize lung
expansion.
9. Provide
adequate fluids
9. Hydration can
and encourage
help liquefy
use of warm
viscous
liquids.
secretions and
improve
secretion
clearance. Warm
liquids aids to
lessen viscosity
of secretions.
10. Encourage
to expel 10. To remove
secretions the secretions
and decrease
secretions from
the respiratory
11. Encourage tract.
to splint chest
11. To minimize
when
chest pain when
coughing.
coughing.
and deep
breathing
exercise.
12. Provide
12. To determine
information
the color of
about the
secretions thus
necessity of
aid in
expectorating
determining the
secretions
type infection.
versus
swallowing it.
13. Assist and
facilitate oral 13. To remove
hygiene unpalatable taste
measures. of mucous
secretions from
mouth.
14. Provide
humidification 14. To prevent
of inhaled air. dryness of
mucous
membranes.
15. Facilitate in
suctioning 15.To maintain
mucous patent airway
and facilitate
removal of
sputum and
mucous plugs.
Collaboration/
Dependent
1. Monitor
sputum, chest 1. To determine
x-ray. changes and
improvement of
the condition and
determine
progression of
the disease
process.
2. Administer
medications 2. To follow the
ordered by the therapeutic
physician. regimen and aid
patient in
recovery. To
promote
expectoration.
3. Administer
oxygen therapy 3. To maintain
as ordered. optimal oxygen
level and
increase comfort.
4. Monitor
arterial blood 4. To assess
gasses as oxygenation
ordered. status.
5. Consult
respiratory 5. To aid in
therapist for improving the
chest patient’s
physiotherapy condition and to
and nebulizer provide comfort.
treatments.
6. Assist with
bronchoscopy 6. To assist
and patient in
thoracentesis recovery and
as needed. promote comfort.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nursing Care Plan: JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acids: Complete Protein Multi-Purposed DIGESTIVE ENZYMESDocument8 pagesAmino Acids: Complete Protein Multi-Purposed DIGESTIVE ENZYMESPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- A Family Case StudyDocument2 pagesA Family Case StudyPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- RetractingDocument1 pageRetractingPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- Prioritization of Health ProblemsDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Health ProblemsPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubal LigationDocument3 pagesTubal LigationPal_inPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Dangers of SmokingDocument4 pagesDangers of SmokingNhiyar Indah HasniarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument3 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 7 - RespirationGerard Selvaraj100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Hypoxemic Respiratory FailureDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Hypoxemic Respiratory FailurevidagurlPas encore d'évaluation
- Caring For Mechanical Ventilated PatientDocument10 pagesCaring For Mechanical Ventilated Patientems100% (1)
- acutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2Document236 pagesacutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2nompanemPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Care of Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument63 pages3 Care of Respiratory and Circulatoryfrancoise b.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology of Oral CancerDocument62 pagesEtiology of Oral CancerShabnaLekhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Science 8Document340 pagesCambridge Science 8Matthew MetcalfePas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Biology 12 PDFDocument69 pagesComplete Biology 12 PDFAbdul Baseer50% (2)
- Voltage, The Key To Rebuilding You LifeDocument33 pagesVoltage, The Key To Rebuilding You LifeLodan Ranue100% (3)
- Pediatric Test DrillDocument5 pagesPediatric Test DrillDwayne GriffenPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 notes-ME..Document23 pagesUnit 2 notes-ME..Kowsi MathiPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC ChestDocument4 pagesABC ChestSintounPas encore d'évaluation
- "Transforming The Jing Into Qi" WLPDocument11 pages"Transforming The Jing Into Qi" WLPValentina D'OnofrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument7 pagesGas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsMarvin MelisPas encore d'évaluation
- Breathe In: Write Your Answer On These Activity SheetDocument4 pagesBreathe In: Write Your Answer On These Activity Sheetirah jane valentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Respiratory SystemDocument15 pages01 Respiratory Systemnaseer alfahdPas encore d'évaluation
- "Dyspnea: Mechanisms, Assessment & Management": Seminar OnDocument31 pages"Dyspnea: Mechanisms, Assessment & Management": Seminar OnPriya KuberanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pure Bio ANSWERDocument17 pagesPure Bio ANSWERlohbernard168Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basset and Howley 2000Document15 pagesBasset and Howley 2000Susan KPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts and Myths About EpilepsyDocument10 pagesFacts and Myths About EpilepsyAarkayChandruPas encore d'évaluation
- 153 PreExerEval ECG PFTDocument15 pages153 PreExerEval ECG PFTlylePas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchangeiloveanne87% (30)
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument38 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyAbdirazak AliPas encore d'évaluation
- RESPIRATIONDocument5 pagesRESPIRATIONShatviga VisvalingamPas encore d'évaluation
- Kadar Nilai NormalDocument11 pagesKadar Nilai NormalM Riski KurniardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oswaal ICSE Board Solved Paper 2020 Biology Class - 9Document6 pagesOswaal ICSE Board Solved Paper 2020 Biology Class - 9chinnubnair73Pas encore d'évaluation
- EdemaDocument5 pagesEdemaaldwinngPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Test (Grade 8) First QuarterDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test (Grade 8) First QuarterZara RejusoPas encore d'évaluation
- EC2021-Medical Electronics Notes For All Five UnitsDocument147 pagesEC2021-Medical Electronics Notes For All Five UnitsJason Jackson100% (1)