Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Marrow
Transféré par
Josephine Armanne Aluyen0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
75 vues3 pagesbone marrow
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentbone marrow
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
75 vues3 pagesBone Marrow
Transféré par
Josephine Armanne Aluyenbone marrow
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
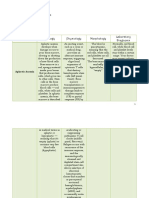
Hematology: Bone Marrow Leukemoid Leukemia Asses Iron Storage: 2.
Clotting factor deficiency
Iron Deficiency Anemia Hemophilia A this is the clotting factor 8-
WBC High High
common among women and bone marrow deficiency
Two types of Bones: LAP Hemophilia B this is the clotting factor 9-
transplantation is not required
Compact Bone (Leukocyte deficiency.
High Low or Zero Heteroplastic Anemia
Haversian System principal unit Astatine Hemophilia C this is the clotting factor 11-
abnormal Iron kinetics deficiency.
Osteocyte matrix of the bone Phosphatase)
full of Iron
Canalliculi interconnects osteocytes Blast Cell Iron not used accumulated in the body 3. Vitamin K Deficient
Haversian Canal lumen where blood vessels are Toxic granules -first 3 stages of It is contraindicated to get bone marrow to
located (pathopneumonic WBC (Myeloblast, Pearls/Prushian Blue Stain stain for Iron patients with Vitamin K deficiency because there
cell) Promyelocyte, are clotting factors.
Ferritin stored Iron
Spongy Bone Myelocyte) Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors: 2,7,9,10
Trabeculae principal unit Not cancer Cancer Rule out other hematological diseases:
- where red marrow is located 4. Serosis of the liver
Some Hematological Diseases wherein you it is considered as one of the contraindications
Indication: cannot diagnose it just using the Peripheral Blood Smear. because the Liver is the site of the clotting
Types of Bone Marrow: 1. Diagnose leukemia There are diseases we have to get at tissue sections like factors synthesis
Red Marrow 2. Infection bone marrow sections or biopsy. We cant get bone
- at birth 3. Monitoring of Infection marrow tissue in patients without knowing the
4. Neoplasia diagnosis & staging (leukemia) contraindications, because there are some patients that Before Bone Marrow collection:
- contains hematopoietic cells
5. Diagnosis of cytopenias might bleed or may have pupura. Purpura is a requires CBC 24 hours before the actual
- confined in all bones at birth
6. Assess Marrow function hemorrhage. procedure to determine if the patient is
- in late adolescence, only in flat bones:
7. Asses Iron Storage Lipidoses/Macrophage disorder qualified for the procedure
vertebrae, skull, ribs, sternum, shoulder and
8. Rule our other hematological diseases diseases of the macrophages Peripheral Blood Smear
pelvic girdle
9. Metabolic Disorders fats in the cytoplasm causing fat WBC mature cells should be seen
Niemann-Pick Disorder presence of WBC means leukemia or
Yellow Marrow
Gauchers Disease leukemoid
- fifth to seventh year of life
Asses Marrow Function should be in Fetal Procedure
- contains adipocytes or fats
- non-hematopoietic but may revert back into red Aplastic Anemia/Aplasia of the bone marrow
Metabolic disorders: o Trephination
marrow - Plasia growth and development
Gauchers - process wherein a bone is subjected to
- Bone marrow failure no blood production
Niemann Picks perforation using a trephine needle,
Acute Leukemia is more dangerous, because o Acquired
- due to toxic substances: Jamshidi needle, or Westerman-Jensen
acute means abrupt
Radioisotopes Contraindication: needle
Ex: SARS (Severe Acute Respiratrory
Leukemia uncontrolled development and Lead hamper cell development physicians must do first other tests or remedy to
maturation of abnormal cells (cancer cells Benzene perform the bone marrow biopsy or aspiration to Specimens:
invade tissues) clearing agent in histopathology prevent more problems. There are blood components Core Biopsy
Leukeoid reaction of body due to severe can lead to Hypoplastic Anemia which are given to patients with clotting factors - bone itself removed
infection Chloramphenicol (drug) deficiency Bone Marrow Aspirate
Ex: Sepsis / Septicemia bacteria in the blood abuse can lead to Hypoplastic bone - bone marrow fluid; 1-3 ml
Overreaction of the body produce a lot of marrow and can lead to aplasia 1. Platelet dysfunction
WBC Leukemoid Reaction o Congenital - platelet is essential for clotting
Fanconi Anemia - due to: Sites:
WBC: 5,000-10,000 cells/microLiter
Leukocytosis severe WBC count cytogenetic disorder that may lead to Quantitative Platelet Defect decreased platelets Pelvic
aplasia of the bone Qualitative Platelet Defect normal number of - adults
broken chromosome platelets but quality is the problem Posterior Superior Iliac Crest
- disease: - adults and children
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome - not prone to injury
platelet quality is defective - aspirate and core biopsy
patient may bleed rapidly if wounded Anterior Superior Iliac Crest
- patients who cant lie sideways
- most ideal
- Prone, Supine lying
Sternum IV. Staining Routine Stains: 1. Macroscopic
- ideal but replaced by Iliac Crest, because there are Stains examination Romanowsky ESR
major veins near the heart Hematoxylin Eosin/H&E H&E - Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
- heart injury - routine stain for tissues determination
Spinous process of Lumbar Vertebrae Pearls/Prussian Blue (Ferric Ferricyanide) - fluid from EDTA
Aspirate
- rarely used used for Iron - centrifuged: 2,000-3,000 gravitational force;
Tibia used along with Romanowsky stain - identification of types and proportion of 30 minutes
- children less than 2 years old Reticulin & Tricrome dyes hematologic cells and to look for morphologic - layers:
Acid-Fast stains variance a. fat 1-3%
Gram stain - has fat cells b. plasma variable; no reference value
Core Biopsy - immature WBC are normally seen
Immunohistochemical dyes c. myeloid erythroid/ME/buffy coat
- collected first Romanowsky: Wright or Wright-Giemsa EDTA - immature & nucleated cells
- for Histotechnique processing or tissue stains - routine coagulant - 3-5%; 5-8% (pelvic area)
processing - for bone marrow Macro/Microscopic cellularity d. RBC
demonstrates bone marrow studies - variable
architecture Cytochemical dyes/Special Stains Heparin - no reference value
first step: Fixtation identification - for special examination fat and buffy coat are the only ones checked
spatial relationships of hematologic - differentiate Myeloid Leukemia & Lymphoid - cytogenetic/chromosome studies
cells to fat, connective tissue and Leukemia fibrinogen causes blood to clot
Myeloperoxidase/Peroxidase (MPO) The microscopic and macroscopic examination of
bone marrow stroma Philadelphia Chromosome (Ph1)
- (+): Myeloid bone marrow fluid should be the same.
H&E stain is used - translocation between chromosome 9:22
- for cellularity studies - (-, colorless): Lymphoid - Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Normocellula Hypocellula Hypercellula
- for determining M:E ratio - detects Myelocytic cells by staining r r r
- for determining if theres any morphological cytoplasmic granular contents I. Fixative Fat
Sudan Black B (SBB) Increase in
abnormality of the bone marrow cells - Methanol Perivascula 1 to 3%
(+): Myeloid layer
cancer cells - r Layer
syncytial cells - (-, coloress): Lymphoid II. Anticoagulant Plasma
- detects Myelocytic cells by staining EDTA No reference value
- Layer
cytoplasmic granular contents
Myolepthisic Condition/Anemia
Leukocyte Astatine Phosphatase (LAP) III. Smear Preparation Buffy Coat 3 to 5% or 5 Increase in
- No bone cancer Pearls stain Direct Film / ME Layer to 8% only layer
- Space occupying tissue that is now Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) - smear specimen from syringe no
in the bone marrow - detects lymphocytic cells and certain anticoagulant
- Immature WBC due to tumor or abnormal erythrocytic cells by staining Packed RBC
Touch Preparation Film/Imprints No reference value
other cancer cell (Metastasis of cytoplasmic glycogen Layer
Particle Preparation/Crushed preparation
Cancer) Tartrate-Resistance Acid Phosphatase stain
Metastasis Cancer cancer cells (TRAP) IV. Routine Stain
detach from original site and - diagnose Hairy Cell Leukemia Pearls Stain
transfers to other site cancer of Lymphocyte/B cell 2. Microscopic
Romanowsky
Nitro-Blue Tetrazolium stain (NBT) - stain with Sudan Black B for lipid emphasis
- can't penetrate fat cells
I. Touch Preparation/Imprints - diagnose Chronic Granulomatus - normal 1:1 or 2:1
*Sudan Black B
- touch the cell adhere in the glass slide Disease (CGD) - stains the fat cells
- fixative: 80-100% Methanol Esterase LPO
- may be stained with Routine or Special Stains - differentiate Granulositic Leukemia (- - assess peripheral blood dilution
V. Cellular Morphological studies
phils) from Non-Granulositic Leukemia - find bony spicules and areas of clear cell
- distribution of cells against fat cells
II. Fixation (most likely Monocyte abnormal cell morphology
- you cannot use bone marrow aspirate fluid to
- to preserve predominating in the blood) - observe fat-to-marrow ratio, estimate
identify cellularity studies because if the
- to undergo histotechnique procedure a. Specific cellularity
specimen is coming from the EDTA, theres a
5-10% buffered Formalin - Granulocytic - search for tumor cells in clusters
possibility of having dilutional or the bone
B5 - Alphanatochloroacetate Esterate - examine and estimate megakaryocytes
marrow fluid can be diluted which results in
Zenkers b. Non-specific Hypocellular bone marrow
III. Histotechnique - Non-granulocytic
- demonstrates bone marrow architecture - Alphanaptilacetate Esterate
HPO VI. Bone Marrow Film Myeloid-Erythroid Ratio Hematological cells mistaken as non-hematological cells
- observe myelocytic and erythrocytic - detecting abnormal cells - determines cell number between Myeloid & 1. Plasma Cells
maturation - could be from biopsy or aspirate Erythroid cells in the marrow - mistaken as Osteoblasts
- distinguish abnormal distribution of cells or - following are used to determine cell - count 800-1000 cells in the film then get the bone resorption
cell maturation stages morphology: percentage comet-shaped/water bag
- perform differential count on 300 to 1000 Imprints/Touch Preparation - 1.5:1 until 5:1 (reference value) appearance
cells Buffy Coat Preparation increased M:E ratio - nucleus: centrally located
- M:E ratio Direct Film Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia - Wright Stain: Perinuclear Halo / Zone of Hof
from the syringe, put the excess Leukemoid Reaction unstained portion of the cytoplasm of
Fat Cell and Bone Marrow Distribution aspirate fluid directly in the slide, and reverse M:E ratio plasma cells
the do a Wedge Smear Preparation - abnormal basis of the differentiation of plasma cells
Normocellular
Crush Preparation - overproduction of RBC precursors from osteoblasts
- 1:1/2:1
1. Put the excess bone marrow fluid from Polycytemia Vera - synthesize immunoglobulins
- within reference interval EDTA in a petri dish. AML-M6 or Erythroleukemia
2. In the petri dish, you will see white
- associated with Di Guglielmo 2. Megakaryocyte
Hypocellular elements microscopically. Get that white
elements and put it in a slide. disease/syndrome - mistaken as Osteoclasts
- increased ration of fat to cells
3. With the use of another slide, crash the abnormality of RBC entering leukemic multiple nuclei
- seen in Dry Tap caused by:
white elements in that slide. And do the phase separated nuclei
Aplastic Anemia
crush preparation. - mononucleated and is interconnected with
- Fanconi Anemia
Myeloid cell lineage threadlike material
- Acquired Anemia
All the Smears, mentioned, are examined under Low - granulocyte & its precursor cells - predominated in bone marrow in case of M7 or
Myelofibrosis
Power Objective, High Power Objective, and Oil Neutrophil (Band cells) Megakaryocytic Leukemia
- bone marrow full of fibrous tissue
Immersion Objective Lens. Basophil
Myelofibrosis with Myeloid Metaplasia (MMM)
Metamegakaryocyte Eosinophil 3. Mast Cells - seen in hypersensitivity reactions
- bone marrow replaced by fibrous tissue
4. Tumor Cells
- Dry Tap usually occurs it is a platelet-producing cell Erythroid cell lineage
one of the cells being determined in LPO, HPO, OIO - Includes nucleated RBC precursors
Hypercellucar Normal: It is approximately 2 to 10 per Low Power - Pronomoblasts
- decreased ratio of fat to cells Objective.
- Normoblasts
- cells predominate doctors examine metamegakaryocyte under OIO
- possible Dry Tap one septae of the bone marrow is used to
determine it differential counting
Leukemia
Polycytemia Vera (PV)
- true cells (platelet, WBC, RBC) Differential counting of BM (differentiation of the cell)
- genes are affected: JAK2V617F - use buffy coat
- Pancytosis (when blood examined) - used to determine M:E ratio
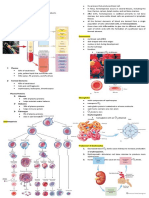
Cells in the Bone Marrow (that we can see):
Myeloblast they are the immature forms
of granulocytes
o Myeloblast (immature)
Granulocyte Neutrophil,
Basophil, Eosinophil.
Rubriblast
Mature WBC
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- HEMA 2 - Midterm Topic 3 - Anemia of Bone Marrow DisorderDocument10 pagesHEMA 2 - Midterm Topic 3 - Anemia of Bone Marrow DisorderLowenstein JenzenPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMA2 GroupNo.1 AnemiaofBoneMarrowDisordersDocument13 pagesHEMA2 GroupNo.1 AnemiaofBoneMarrowDisordersLowenstein JenzenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology 1 L1 Introduction To Hematology 1 LectureDocument2 pagesHematology 1 L1 Introduction To Hematology 1 LectureChelze Faith DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMA Lec 03 Bone Marrow Collection Lymphoid Organs 1Document9 pagesHEMA Lec 03 Bone Marrow Collection Lymphoid Organs 1Patrick AbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- vt59.2708-21242375124 394146998891967 4683953301704066077 n.pdfHEMA-HANDOUTS-1.pdf NC Cat 106&ccb 1-7&Document15 pagesvt59.2708-21242375124 394146998891967 4683953301704066077 n.pdfHEMA-HANDOUTS-1.pdf NC Cat 106&ccb 1-7&jasminemuammilPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument4 pagesAnaemiaRichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans OS216 Hema 15Document6 pagesTrans OS216 Hema 15api-3799593Pas encore d'évaluation
- I. Nursing Care Management of Problems On Oxygenation (Transport)Document6 pagesI. Nursing Care Management of Problems On Oxygenation (Transport)AltrOi Agtang100% (1)
- Hematopoiesis: 6 - Blood andDocument38 pagesHematopoiesis: 6 - Blood andRuth MSPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematologic System and DisordersDocument68 pagesHematologic System and DisordersRellie Castro100% (1)
- PathologyDocument30 pagesPathologyPRAJWAL PES HDPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of AnemiaDocument6 pagesTypes of AnemiaSittiePas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- HO Notecards 1Document12 pagesHO Notecards 1MrSomnambululPas encore d'évaluation
- Ninja Nerd AnemiaDocument13 pagesNinja Nerd AnemiaAndra Bauer100% (3)
- Clinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesDocument55 pagesClinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesShiv Sookun100% (1)
- RBC Abnormalities in Morphology: HematologyDocument6 pagesRBC Abnormalities in Morphology: HematologyCarlo SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerPaul AgcaoiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Blood Vessels in Hemostasis: Villa, M.D. MLS 4CDocument10 pagesRole of Blood Vessels in Hemostasis: Villa, M.D. MLS 4CMarianne Dennesse100% (1)
- Mtap 2 HematologyDocument15 pagesMtap 2 HematologyNaomi NicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology Complete (1 and 2) - 1Document103 pagesHematology Complete (1 and 2) - 1NUEVO SUSANNA N.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and Lymph (Autosaved)Document46 pagesBlood and Lymph (Autosaved)Shaikh SaqibPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematologic System, Oncologic Disorders & Anemias: DR Ibrahreem Bashayreh, RN, PHDDocument68 pagesHematologic System, Oncologic Disorders & Anemias: DR Ibrahreem Bashayreh, RN, PHDYA HOPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Cell AnomaliesDocument4 pagesBlood Cell AnomaliesCiullaePas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia DM-1 - REV.Document44 pagesAnemia DM-1 - REV.abdulrahmanbelewa96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Histology & Cell BiologyDocument33 pagesHistology & Cell BiologyMohSen100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Blood ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Blood ReviewerPhilline ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Haemolytic Anaemia: HyperspleenismDocument21 pagesHaemolytic Anaemia: HyperspleenismZabihullahPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 2 Microcytic Anemias PDFDocument3 pages5 2 Microcytic Anemias PDFPrabhat GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument8 pagesAnemiasibanah menor100% (1)
- (Hema) 1.1 Intro To Hema (Perez) - PANDADocument6 pages(Hema) 1.1 Intro To Hema (Perez) - PANDATony DawaPas encore d'évaluation
- HO Notecards2Document12 pagesHO Notecards2MrSomnambululPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hematology SectionDocument4 pagesThe Hematology SectionVENUS LIRIA PANTIPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of AnemiaDocument14 pagesDiagnosis of AnemiaAnggie AnggriyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC anomalies-ANEMIADocument19 pagesRBC anomalies-ANEMIAJeremiahPas encore d'évaluation
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument35 pagesAnemiaagengbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Meningitis DifferentialsDocument20 pagesMeningitis DifferentialsJoherPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of The Child With A Hematologic Disorder TermsDocument8 pagesNursing Care of The Child With A Hematologic Disorder TermsJœnríčk AzueloPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood FilmDocument2 pagesBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- M6 Decreased RBC ProdnDocument3 pagesM6 Decreased RBC ProdnJan TrishaPas encore d'évaluation
- BLOOD TransesDocument7 pagesBLOOD TransesBianca Paulyn CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Anemia Etiology Physiology Morphology Laboratory DiagnosisDocument19 pagesTypes of Anemia Etiology Physiology Morphology Laboratory DiagnosisEG OngtecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11: BLOOD: Functions of Blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Composition of Blood ErythrocytesDocument4 pagesChapter 11: BLOOD: Functions of Blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Composition of Blood ErythrocytesPrecious Faith RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Microcytic Type Aeitology Clinical Features Investigations ManagementDocument7 pagesMicrocytic Type Aeitology Clinical Features Investigations ManagementJason AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematologic System LectureDocument15 pagesHematologic System LecturedumonilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Assistant 09.08.2014Document43 pagesTeaching Assistant 09.08.2014Rival VirgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Your Knowledge. True or FalseDocument11 pagesTest Your Knowledge. True or Falsejelly beanPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 Plasma Cell Neoplasms - Libre Pathology PDFDocument5 pages17 Plasma Cell Neoplasms - Libre Pathology PDFfadoPas encore d'évaluation
- MED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaFlora XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Determinando EtiologiaDocument9 pagesAnemia Determinando EtiologiaNayara CamattaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology ReviewerDocument4 pagesHematology ReviewerAbigail Puno100% (1)
- Chapter 13Document2 pagesChapter 13Nona PeriarcePas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysDocument6 pagesBlood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysHanamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aplastic Anemia (Dr. Kadek)Document41 pagesAplastic Anemia (Dr. Kadek)galuh dharmapatniPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMOSTASISDocument12 pagesHEMOSTASISRyan PedregosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lecture 1Document25 pagesPathology Lecture 1Abdo HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Blood SmearDocument3 pagesPeripheral Blood SmearJosephine Armanne AluyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pituitary Hormone SummaryDocument2 pagesPituitary Hormone SummaryJosephine Armanne AluyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Board of Certification Study Guide For Clinical Laboratory Certification Examinations PDFDocument496 pagesBoard of Certification Study Guide For Clinical Laboratory Certification Examinations PDFKathleenDawal67% (3)
- Passion Planner ClassicDocument2 pagesPassion Planner ClassicKyle Walker80% (5)
- Contraceptive Use Among Filipino WomenDocument6 pagesContraceptive Use Among Filipino WomenJosephine Armanne AluyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Treasure - Burno MarsDocument1 pageTreasure - Burno MarsJosephine Armanne AluyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Maksim Mrvica Croatian RhapsodyDocument5 pagesMaksim Mrvica Croatian RhapsodyCage_nPas encore d'évaluation
- Game of ThronesDocument5 pagesGame of ThronesJosephine Armanne AluyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Chapter1 ManagementDocument7 pagesActivity Chapter1 ManagementTricia Amigo SacarePas encore d'évaluation
- "Shiksha Se Hi Suraksha": Literacy Campaign WeekDocument4 pages"Shiksha Se Hi Suraksha": Literacy Campaign WeekVaishali100% (1)
- Donna Claire B. Cañeza: Central Bicol State University of AgricultureDocument8 pagesDonna Claire B. Cañeza: Central Bicol State University of AgricultureDanavie AbergosPas encore d'évaluation
- JURDING (Corticosteroids Therapy in Combination With Antibiotics For Erysipelas)Document21 pagesJURDING (Corticosteroids Therapy in Combination With Antibiotics For Erysipelas)Alif Putri YustikaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO210 Lab Report 3Document6 pagesBIO210 Lab Report 3Isra MallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Education Pre-Licensure Examination For TeachersDocument12 pagesProfessional Education Pre-Licensure Examination For TeachersJudy Mae ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- GST 101 Exam Past QuestionsDocument6 pagesGST 101 Exam Past QuestionsBenjamin Favour100% (2)
- I Wonder Lonely As A Cloud by W. Words WorthDocument6 pagesI Wonder Lonely As A Cloud by W. Words WorthGreen Bergen100% (1)
- Oedogonium: Class: Chlorophyceae Order: Oedogoniales Family: OedogoniaceaeDocument28 pagesOedogonium: Class: Chlorophyceae Order: Oedogoniales Family: OedogoniaceaeA SASIKALAPas encore d'évaluation
- The Bible Does Not Condemn Premarital SexDocument16 pagesThe Bible Does Not Condemn Premarital SexKeith502100% (3)
- Marriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, EthiopiaDocument2 pagesMarriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, Ethiopiajoseph mathewPas encore d'évaluation
- RF Design MCQ-1Document16 pagesRF Design MCQ-1JeyavelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Financial System in DevelopmentDocument5 pagesThe Role of Financial System in DevelopmentCritical ThinkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Marijuana - PR 1Document11 pagesEffects of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Marijuana - PR 1Mark Andris GempisawPas encore d'évaluation
- Task Basis JurisprudenceDocument10 pagesTask Basis JurisprudenceKerwin LeonidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Angel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithDocument1 pageAngel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithKhally KatiePas encore d'évaluation
- NorthStar 5th Edition Reading-Writing SKILLS 3-4Document265 pagesNorthStar 5th Edition Reading-Writing SKILLS 3-4Hassan JENZYPas encore d'évaluation
- Tool Stack Template 2013Document15 pagesTool Stack Template 2013strganeshkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- COMM 103 Floyd Chapters Study GuideDocument4 pagesCOMM 103 Floyd Chapters Study GuideMad BasblaPas encore d'évaluation
- Polynomials Level 3Document17 pagesPolynomials Level 3greycouncilPas encore d'évaluation
- Sta. Lucia National High School: Republic of The Philippines Region III-Central LuzonDocument7 pagesSta. Lucia National High School: Republic of The Philippines Region III-Central LuzonLee Charm SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- ThermodynamicsDocument341 pagesThermodynamicsjonathan2788100% (4)
- Managing Ambiguity and ChangeDocument7 pagesManaging Ambiguity and ChangeTracey FeboPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset Management PlanDocument160 pagesAsset Management Planbkalatus1100% (1)
- Symbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP) 2004: InstructionsDocument21 pagesSymbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP) 2004: InstructionsHarsh JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Micro FinanceDocument61 pagesImpact of Micro FinancePerry Arcilla SerapioPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 5 Forces Acting On Structures and Mechanisms CirriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Forces Acting On Structures and Mechanisms Cirriculumapi-2072021750% (1)
- Million-Day Gregorian-Julian Calendar - NotesDocument10 pagesMillion-Day Gregorian-Julian Calendar - Notesraywood100% (1)
- 1sebastian Vs CalisDocument6 pages1sebastian Vs CalisRai-chan Junior ÜPas encore d'évaluation
- Who, Summary NotesDocument12 pagesWho, Summary NotesIvan Lohr100% (2)